Python “贪吃蛇”游戏,在不断改进中学习pygame编程
目录
前言
改进过程一
增加提示信息
原版帮助摘要
pygame.draw
pygame.font
class Rect
class Surface
改进过程二
增加显示得分
改进过程三
增加背景景乐
增加提示音效
音乐切换
静音切换
mixer.music.play 注意事项
原版帮助摘要
pygame.mixer
pygame.mixer.Sound
小结
pygame编程框架
前言
在上一篇博文里,从讯飞星火中获取到游戏“贪吃蛇”的代码,运行效果如上图。代码并不完整,当蛇死了就退出游戏,不能多次玩这个游戏。
前文链接:
讯飞星火、文心一言和通义千问同时编“贪吃蛇”游戏,谁会胜出?
代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREY = (211, 211, 211) # 淡灰色def init():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamepygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:game_quit()'''此处可增加与用户的交互,如:if askyesno('title','again?'):init() # Yes to Play againelse:game_quit() # No to Exit'''# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程一
增加提示信息
之前没有仔细学过pygame的编程,刚好拿这例程练练手,在不断改进中学习pygame编程。
原代码一执行,蛇就开始游动了,就从这里入手。开始前,增加显示“按任意键开始...”的提示。
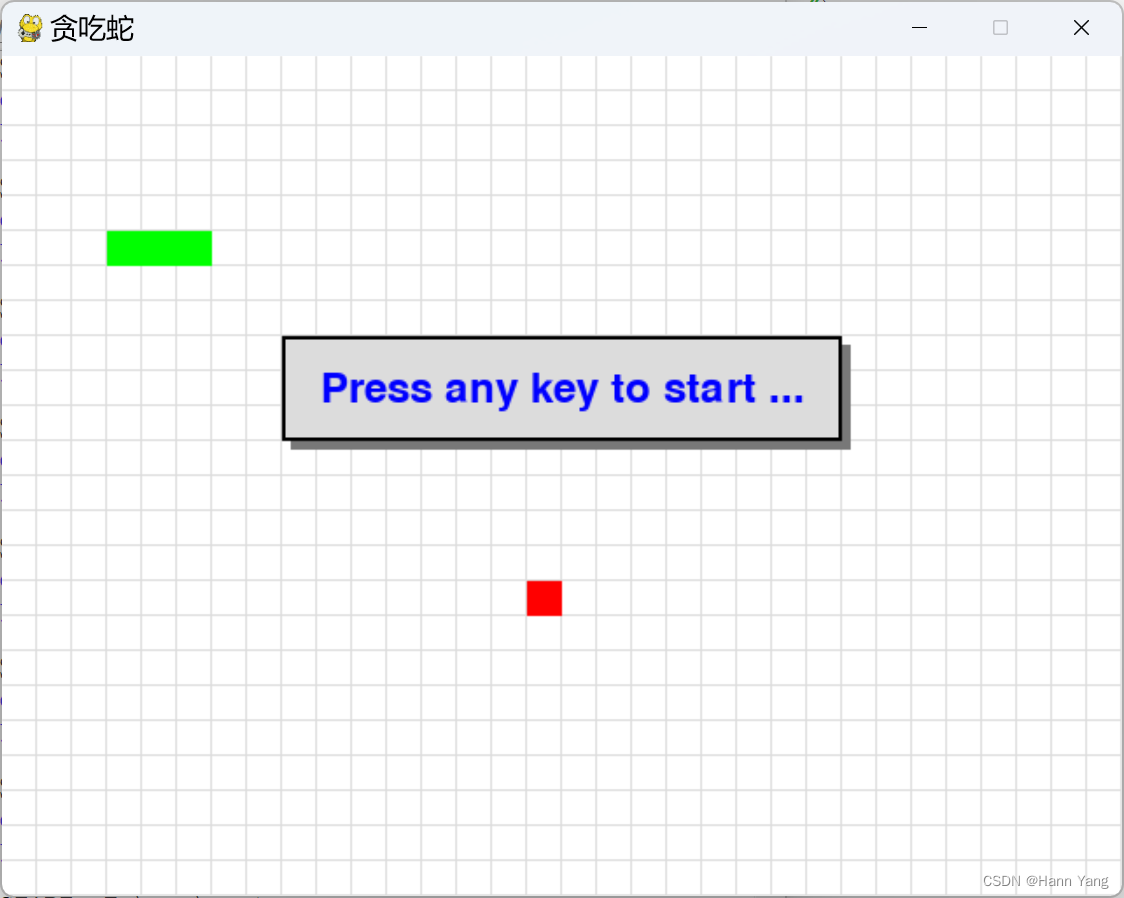
蛇死后,提醒是否重来?Yes to play again, No to quit game.

同时,在游戏中允许按ESC键暂停游戏,再按一次继续。
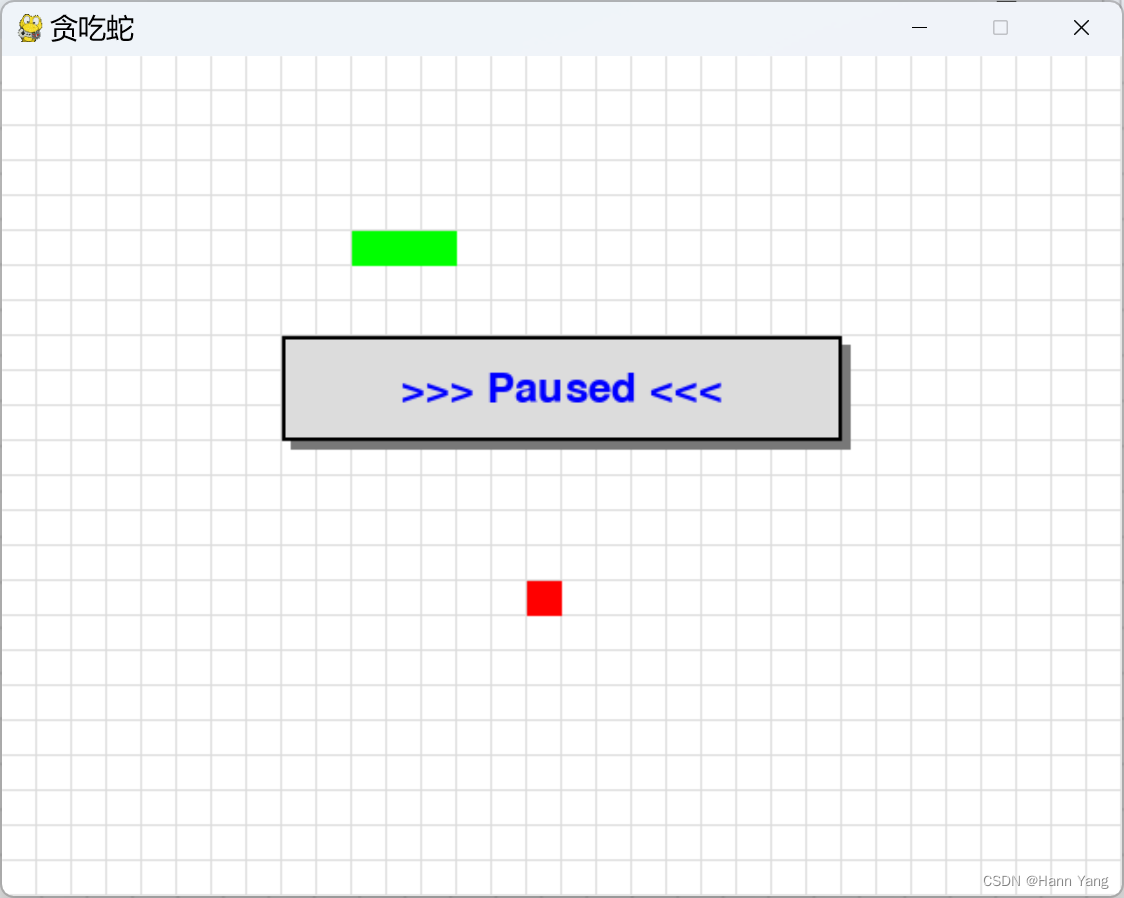
由于没查到 pygame 有弹出信息窗口的方法(函数),于是用了DOS时代显示信息窗口的办法,画多个矩形窗口来模拟窗口,最后在矩形框上写上提示文字。代码如下:
def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):
x = screen.get_rect().centerx
y = screen.get_rect().centery - 50
font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)
text = font.render(msg, True, color)
text_rect = text.get_rect()
text_rect.centerx = x
text_rect.centery = y
rectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)
rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2
screen.blit(text, text_rect)
pygame.display.flip()
原版帮助摘要
pygame.draw
NAME
pygame.draw - pygame module for drawing shapes
FUNCTIONS
aaline(...)
aaline(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos) -> Rect
aaline(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos, blend=1) -> Rect
draw a straight antialiased line
aalines(...)
aalines(surface, color, closed, points) -> Rect
aalines(surface, color, closed, points, blend=1) -> Rect
draw multiple contiguous straight antialiased line segments
arc(...)
arc(surface, color, rect, start_angle, stop_angle) -> Rect
arc(surface, color, rect, start_angle, stop_angle, width=1) -> Rect
draw an elliptical arc
circle(...)
circle(surface, color, center, radius) -> Rect
circle(surface, color, center, radius, width=0, draw_top_right=None, draw_top_left=None, draw_bottom_left=None, draw_bottom_right=None) -> Rect
draw a circle
ellipse(...)
ellipse(surface, color, rect) -> Rect
ellipse(surface, color, rect, width=0) -> Rect
draw an ellipse
line(...)
line(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos) -> Rect
line(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos, width=1) -> Rect
draw a straight line
lines(...)
lines(surface, color, closed, points) -> Rect
lines(surface, color, closed, points, width=1) -> Rect
draw multiple contiguous straight line segments
polygon(...)
polygon(surface, color, points) -> Rect
polygon(surface, color, points, width=0) -> Rect
draw a polygon
rect(...)
rect(surface, color, rect) -> Rect
rect(surface, color, rect, width=0, border_radius=0, border_top_left_radius=-1, border_top_right_radius=-1, border_bottom_left_radius=-1, border_bottom_right_radius=-1) -> Rect
draw a rectangle
pygame.font
NAME
pygame.font - pygame module for loading and rendering fonts
CLASSES
builtins.object
Font
class Font(builtins.object)
| Font(file_path=None, size=12) -> Font
| Font(file_path, size) -> Font
| Font(pathlib.Path, size) -> Font
| Font(object, size) -> Font
| create a new Font object from a file
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| get_ascent(...)
| get_ascent() -> int
| get the ascent of the font
|
| get_bold(...)
| get_bold() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered bold
|
| get_descent(...)
| get_descent() -> int
| get the descent of the font
|
| get_height(...)
| get_height() -> int
| get the height of the font
|
| get_italic(...)
| get_italic() -> bool
| check if the text will be rendered italic
|
| get_linesize(...)
| get_linesize() -> int
| get the line space of the font text
|
| get_strikethrough(...)
| get_strikethrough() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered with a strikethrough
|
| get_underline(...)
| get_underline() -> bool
| check if text will be rendered with an underline
|
| metrics(...)
| metrics(text) -> list
| gets the metrics for each character in the passed string
|
| render(...)
| render(text, antialias, color, background=None) -> Surface
| draw text on a new Surface
|
| set_bold(...)
| set_bold(bool) -> None
| enable fake rendering of bold text
|
| set_italic(...)
| set_italic(bool) -> None
| enable fake rendering of italic text
|
| set_script(...)
| set_script(str) -> None
| set the script code for text shaping
|
| set_strikethrough(...)
| set_strikethrough(bool) -> None
| control if text is rendered with a strikethrough
|
| set_underline(...)
| set_underline(bool) -> None
| control if text is rendered with an underline
|
| size(...)
| size(text) -> (width, height)
| determine the amount of space needed to render text
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| bold
| bold -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered in (faked) bold.
|
| italic
| italic -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered in (faked) italics.
|
| strikethrough
| strikethrough -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered with a strikethrough.
|
| underline
| underline -> bool
| Gets or sets whether the font should be rendered with an underline.
class Rect
Help on class Rect in module pygame.rect:
class Rect(builtins.object)
| Rect(left, top, width, height) -> Rect
| Rect((left, top), (width, height)) -> Rect
| Rect(object) -> Rect
| pygame object for storing rectangular coordinates
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| clamp(...)
| clamp(Rect) -> Rect
| moves the rectangle inside another
|
| clamp_ip(...)
| clamp_ip(Rect) -> None
| moves the rectangle inside another, in place
|
| clip(...)
| clip(Rect) -> Rect
| crops a rectangle inside another
|
| clipline(...)
| clipline(x1, y1, x2, y2) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline(x1, y1, x2, y2) -> ()
| clipline((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline((x1, y1), (x2, y2)) -> ()
| clipline((x1, y1, x2, y2)) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline((x1, y1, x2, y2)) -> ()
| clipline(((x1, y1), (x2, y2))) -> ((cx1, cy1), (cx2, cy2))
| clipline(((x1, y1), (x2, y2))) -> ()
| crops a line inside a rectangle
|
| collidedict(...)
| collidedict(dict) -> (key, value)
| collidedict(dict) -> None
| collidedict(dict, use_values=0) -> (key, value)
| collidedict(dict, use_values=0) -> None
| test if one rectangle in a dictionary intersects
|
| collidedictall(...)
| collidedictall(dict) -> [(key, value), ...]
| collidedictall(dict, use_values=0) -> [(key, value), ...]
| test if all rectangles in a dictionary intersect
|
| collidelist(...)
| collidelist(list) -> index
| test if one rectangle in a list intersects
|
| collidelistall(...)
| collidelistall(list) -> indices
| test if all rectangles in a list intersect
|
| collideobjects(...)
| collideobjects(rect_list) -> object
| collideobjects(obj_list, key=func) -> object
| test if any object in a list intersects
|
| collideobjectsall(...)
| collideobjectsall(rect_list) -> objects
| collideobjectsall(obj_list, key=func) -> objects
| test if all objects in a list intersect
|
| collidepoint(...)
| collidepoint(x, y) -> bool
| collidepoint((x,y)) -> bool
| test if a point is inside a rectangle
|
| colliderect(...)
| colliderect(Rect) -> bool
| test if two rectangles overlap
|
| contains(...)
| contains(Rect) -> bool
| test if one rectangle is inside another
|
| copy(...)
| copy() -> Rect
| copy the rectangle
|
| fit(...)
| fit(Rect) -> Rect
| resize and move a rectangle with aspect ratio
|
| inflate(...)
| inflate(x, y) -> Rect
| grow or shrink the rectangle size
|
| inflate_ip(...)
| inflate_ip(x, y) -> None
| grow or shrink the rectangle size, in place
|
| move(...)
| move(x, y) -> Rect
| moves the rectangle
|
| move_ip(...)
| move_ip(x, y) -> None
| moves the rectangle, in place
|
| normalize(...)
| normalize() -> None
| correct negative sizes
|
| scale_by(...)
| scale_by(scalar) -> Rect
| scale_by(scalex, scaley) -> Rect
| scale the rectangle by given a multiplier
|
| scale_by_ip(...)
| scale_by_ip(scalar) -> None
| scale_by_ip(scalex, scaley) -> None
| grow or shrink the rectangle size, in place
|
| union(...)
| union(Rect) -> Rect
| joins two rectangles into one
|
| union_ip(...)
| union_ip(Rect) -> None
| joins two rectangles into one, in place
|
| unionall(...)
| unionall(Rect_sequence) -> Rect
| the union of many rectangles
|
| unionall_ip(...)
| unionall_ip(Rect_sequence) -> None
| the union of many rectangles, in place
|
| update(...)
| update(left, top, width, height) -> None
| update((left, top), (width, height)) -> None
| update(object) -> None
| sets the position and size of the rectangle
class Surface
class Surface(builtins.object)
| Surface((width, height), flags=0, depth=0, masks=None) -> Surface
| Surface((width, height), flags=0, Surface) -> Surface
| pygame object for representing images
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| blit(...)
| blit(source, dest, area=None, special_flags=0) -> Rect
| draw one image onto another
|
| blits(...)
| blits(blit_sequence=((source, dest), ...), doreturn=1) -> [Rect, ...] or None
| blits(((source, dest, area), ...)) -> [Rect, ...]
| blits(((source, dest, area, special_flags), ...)) -> [Rect, ...]
| draw many images onto another
|
| convert(...)
| convert(Surface=None) -> Surface
| convert(depth, flags=0) -> Surface
| convert(masks, flags=0) -> Surface
| change the pixel format of an image
|
| convert_alpha(...)
| convert_alpha(Surface) -> Surface
| convert_alpha() -> Surface
| change the pixel format of an image including per pixel alphas
|
| copy(...)
| copy() -> Surface
| create a new copy of a Surface
|
| fill(...)
| fill(color, rect=None, special_flags=0) -> Rect
| fill Surface with a solid color
|
| get_abs_offset(...)
| get_abs_offset() -> (x, y)
| find the absolute position of a child subsurface inside its top level parent
|
| get_abs_parent(...)
| get_abs_parent() -> Surface
| find the top level parent of a subsurface
|
| get_alpha(...)
| get_alpha() -> int_value
| get the current Surface transparency value
|
| get_at(...)
| get_at((x, y)) -> Color
| get the color value at a single pixel
|
| get_at_mapped(...)
| get_at_mapped((x, y)) -> Color
| get the mapped color value at a single pixel
|
| get_bitsize(...)
| get_bitsize() -> int
| get the bit depth of the Surface pixel format
|
| get_blendmode(...)
| Return the surface's SDL 2 blend mode
|
| get_bounding_rect(...)
| get_bounding_rect(min_alpha = 1) -> Rect
| find the smallest rect containing data
|
| get_buffer(...)
| get_buffer() -> BufferProxy
| acquires a buffer object for the pixels of the Surface.
|
| get_bytesize(...)
| get_bytesize() -> int
| get the bytes used per Surface pixel
|
| get_clip(...)
| get_clip() -> Rect
| get the current clipping area of the Surface
|
| get_colorkey(...)
| get_colorkey() -> RGB or None
| Get the current transparent colorkey
|
| get_flags(...)
| get_flags() -> int
| get the additional flags used for the Surface
|
| get_height(...)
| get_height() -> height
| get the height of the Surface
|
| get_locked(...)
| get_locked() -> bool
| test if the Surface is current locked
|
| get_locks(...)
| get_locks() -> tuple
| Gets the locks for the Surface
|
| get_losses(...)
| get_losses() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the significant bits used to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_masks(...)
| get_masks() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the bitmasks needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_offset(...)
| get_offset() -> (x, y)
| find the position of a child subsurface inside a parent
|
| get_palette(...)
| get_palette() -> [RGB, RGB, RGB, ...]
| get the color index palette for an 8-bit Surface
|
| get_palette_at(...)
| get_palette_at(index) -> RGB
| get the color for a single entry in a palette
|
| get_parent(...)
| get_parent() -> Surface
| find the parent of a subsurface
|
| get_pitch(...)
| get_pitch() -> int
| get the number of bytes used per Surface row
|
| get_rect(...)
| get_rect(**kwargs) -> Rect
| get the rectangular area of the Surface
|
| get_shifts(...)
| get_shifts() -> (R, G, B, A)
| the bit shifts needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| get_size(...)
| get_size() -> (width, height)
| get the dimensions of the Surface
|
| get_view(...)
| get_view(<kind>='2') -> BufferProxy
| return a buffer view of the Surface's pixels.
|
| get_width(...)
| get_width() -> width
| get the width of the Surface
|
| lock(...)
| lock() -> None
| lock the Surface memory for pixel access
|
| map_rgb(...)
| map_rgb(Color) -> mapped_int
| convert a color into a mapped color value
|
| mustlock(...)
| mustlock() -> bool
| test if the Surface requires locking
|
| premul_alpha(...)
| premul_alpha() -> Surface
| returns a copy of the surface with the RGB channels pre-multiplied by the alpha channel.
|
| scroll(...)
| scroll(dx=0, dy=0) -> None
| Shift the surface image in place
|
| set_alpha(...)
| set_alpha(value, flags=0) -> None
| set_alpha(None) -> None
| set the alpha value for the full Surface image
|
| set_at(...)
| set_at((x, y), Color) -> None
| set the color value for a single pixel
|
| set_clip(...)
| set_clip(rect) -> None
| set_clip(None) -> None
| set the current clipping area of the Surface
|
| set_colorkey(...)
| set_colorkey(Color, flags=0) -> None
| set_colorkey(None) -> None
| Set the transparent colorkey
|
| set_masks(...)
| set_masks((r,g,b,a)) -> None
| set the bitmasks needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| set_palette(...)
| set_palette([RGB, RGB, RGB, ...]) -> None
| set the color palette for an 8-bit Surface
|
| set_palette_at(...)
| set_palette_at(index, RGB) -> None
| set the color for a single index in an 8-bit Surface palette
|
| set_shifts(...)
| set_shifts((r,g,b,a)) -> None
| sets the bit shifts needed to convert between a color and a mapped integer
|
| subsurface(...)
| subsurface(Rect) -> Surface
| create a new surface that references its parent
|
| unlock(...)
| unlock() -> None
| unlock the Surface memory from pixel access
|
| unmap_rgb(...)
| unmap_rgb(mapped_int) -> Color
| convert a mapped integer color value into a Color
另外增加了3个状态变量,初始状态为:
is_running = False
is_paused = False
is_dead = False
增加了4个按键判别:
is_dead时,判断重新开始还是退出游戏
pygame.K_y: 字母Y/y
pygame.K_n: 字母N/n
暂停和恢复
pygame.K_ESCAPE: Esc键
pygame.K_SPACE: 空格键
完整代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamepygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_sizeglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedelse: # 任意键进入开始状态is_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Truecontinue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程二
增加显示得分
每吃到一个食物+10分,蛇长和食物靠近边界会有额外加分;顺带显示出蛇的坐标位置。
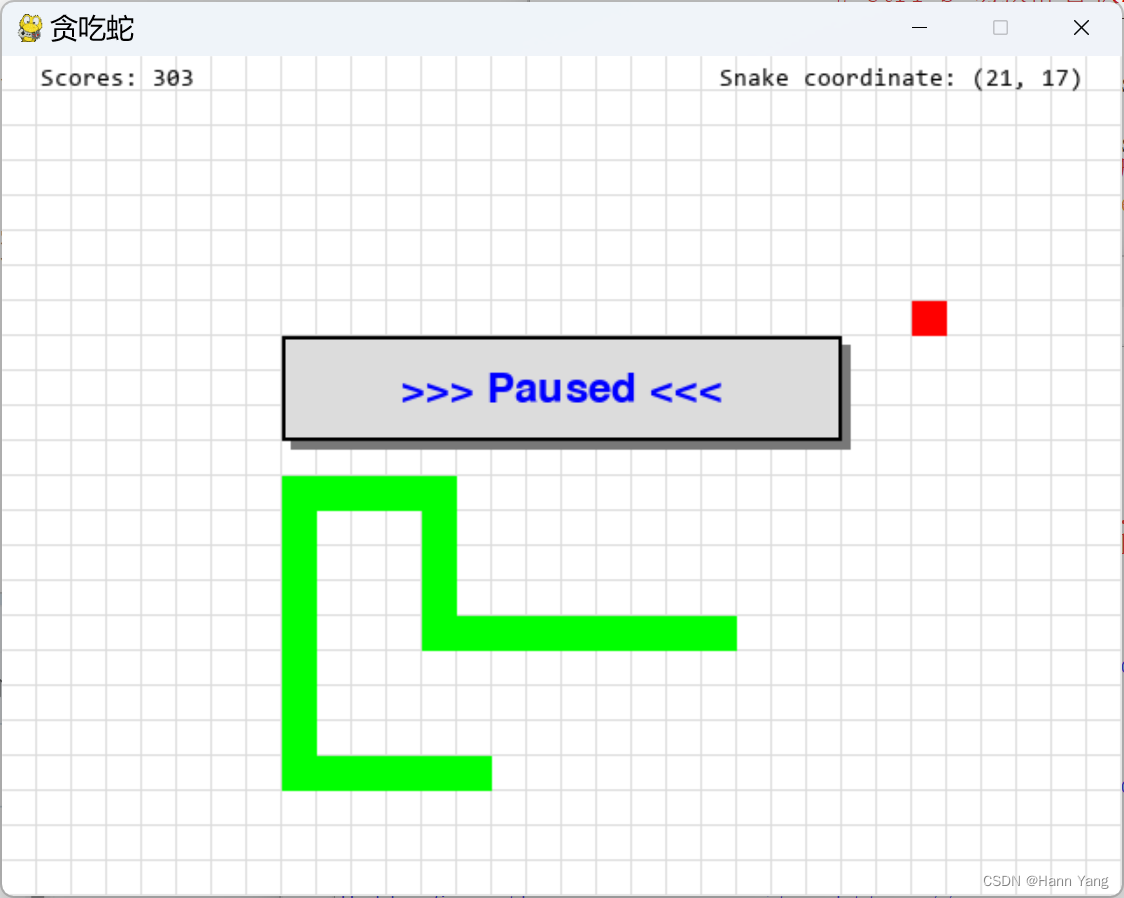
函数show_msg_at(),比show_msg增加x,y坐标,把信息显示到指定的位置:
def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):
font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14) # 使用系统字库
text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)
text_rect = text.get_rect()
text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, y
screen.blit(text, text_rect)
pygame.display.flip()
另外新增一个全局变量 scores,当碰到食物时加10分,蛇长超过5以及食物靠近边界的距离小3会有额外加分,规则可以自己定,例如:
if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:
scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5
if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:
scores += 5
完整代码如下:
import pygame
import sys
import random# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamescores = 0pygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()show_msg_at(22, 6, f'Scores: {scores}')show_msg_at(410, 6, f'Snake coordinate: ({1+snake_pos[0][0]//20:2}, {1+snake_pos[0][1]//20:2})')def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14)text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, yscreen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:if is_dead: continueif is_paused: is_paused = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedelse: # 任意键进入开始状态if is_dead: continueis_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:scores += 5 food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Truecontinue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()改进过程三
增加背景景乐
def play_music(mp3, volume = 1, loops = -1):
# 初始化pygame的mixer模块
pygame.mixer.init()
# 加载音乐文件
pygame.mixer.music.load(mp3)
# 控制音量 volume = 0~1,1为最高音量
pygame.mixer.music.set_volume(volume)
# 播放音乐 loops = -1 为循环播放
pygame.mixer.music.play(loops)
增加提示音效
def play_sound(wav_no):
sound_fn = f'sound{wav_no}.wav'
if os.path.exists(sound_fn):
alert_sound = pygame.mixer.Sound(sound_fn)
alert_sound.play()
音乐切换
快捷键 Ctrl+M
elif event.key == pygame.K_m and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:
# Ctrl+M 切换背景音乐
is_mute = False
music_no = 1 if music_no == 3 else music_no + 1
music_fn = f"voice{music_no}.mp3"
if os.path.exists(music_fn):
t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))
t.start()
静音切换
快捷键 Ctrl+S
elif event.key == pygame.K_s and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:
# Ctrl+S 切换静音状态
is_mute = not is_mute
if is_mute:
pygame.mixer.music.pause()
else:
pygame.mixer.music.unpause()
mixer.music.play 注意事项
1. pygame.mixer.music.play() 只能播放pygame支持的音频格式,包括WAV, MP3等。
2. 如果音频文件未找到或无法读取,pygame.mixer.music.play( ) 会抛出一个异常。使用需要确保音频文件的路径正确,且文件存在。导入os库,用os.path.exists(music_file) 判断文件是否存在。
3. pygame.mixer.music.play() 是一个阻塞函数,在音频播放期间程序将不会执行其他操作。如果需要在播放同时执行其他操作,需要在一个单独的线程中调用pygame.mixer.music.play()。
4. 多线程需要导入threading库,例如:
t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))
t.start()
原版帮助摘要
pygame.mixer
NAME
pygame.mixer_music - pygame module for controlling streamed audio
FUNCTIONS
fadeout(...)
fadeout(time) -> None
stop music playback after fading out
get_busy(...)
get_busy() -> bool
check if the music stream is playing
get_endevent(...)
get_endevent() -> type
get the event a channel sends when playback stops
get_pos(...)
get_pos() -> time
get the music play time
get_volume(...)
get_volume() -> value
get the music volume
load(...)
load(filename) -> None
load(fileobj, namehint=) -> None
Load a music file for playback
pause(...)
pause() -> None
temporarily stop music playback
play(...)
play(loops=0, start=0.0, fade_ms=0) -> None
Start the playback of the music stream
queue(...)
queue(filename) -> None
queue(fileobj, namehint=, loops=0) -> None
queue a sound file to follow the current
rewind(...)
rewind() -> None
restart music
set_endevent(...)
set_endevent() -> None
set_endevent(type) -> None
have the music send an event when playback stops
set_pos(...)
set_pos(pos) -> None
set position to play from
set_volume(...)
set_volume(volume) -> None
set the music volume
stop(...)
stop() -> None
stop the music playback
unload(...)
unload() -> None
Unload the currently loaded music to free up resources
unpause(...)
unpause() -> None
resume paused music
pygame.mixer.Sound
class Sound(builtins.object)
| Sound(filename) -> Sound
| Sound(file=filename) -> Sound
| Sound(file=pathlib_path) -> Sound
| Sound(buffer) -> Sound
| Sound(buffer=buffer) -> Sound
| Sound(object) -> Sound
| Sound(file=object) -> Sound
| Sound(array=object) -> Sound
| Create a new Sound object from a file or buffer object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| fadeout(...)
| fadeout(time) -> None
| stop sound playback after fading out
|
| get_length(...)
| get_length() -> seconds
| get the length of the Sound
|
| get_num_channels(...)
| get_num_channels() -> count
| count how many times this Sound is playing
|
| get_raw(...)
| get_raw() -> bytes
| return a bytestring copy of the Sound samples.
|
| get_volume(...)
| get_volume() -> value
| get the playback volume
|
| play(...)
| play(loops=0, maxtime=0, fade_ms=0) -> Channel
| begin sound playback
|
| set_volume(...)
| set_volume(value) -> None
| set the playback volume for this Sound
|
| stop(...)
| stop() -> None
| stop sound playback
完整代码:
import pygame
import sys, os
import random
import threading# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
BLUE = (0, 0, 255)
GREY = (220, 220, 220) # 淡灰色
DARK = (120, 120, 120) # 深灰色def init():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speed# 初始化pygamescores = 0pygame.init()# 设置屏幕大小screen_size = (640, 480)screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置游戏标题pygame.display.set_caption("贪吃蛇")# 蛇的初始位置snake_pos = [[100, 100], [80, 100], [60, 100]]# 食物的初始位置food_pos = [300, 300]# 蛇的初始速度snake_speed = [20, 0]def play_music(mp3, volume = 1, loops = -1):# 初始化pygame的mixer模块pygame.mixer.init()# 加载音乐文件pygame.mixer.music.load(mp3)# 控制音量pygame.mixer.music.set_volume(volume)# 播放音乐pygame.mixer.music.play(loops)def play_sound(wav_no):sound_fn = f'sound{wav_no}.wav'if os.path.exists(sound_fn):alert_sound = pygame.mixer.Sound(sound_fn)alert_sound.play()def show_msg(msg, color = BLUE):x = screen.get_rect().centerxy = screen.get_rect().centery - 50font = pygame.font.Font(None, 36)text = font.render(msg, True, color)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.centerx = xtext_rect.centery = yrectangle1 = pygame.Rect(x-155, y-25, 320, 60)rectangle2 = pygame.Rect(x-160, y-30, 320, 60)pygame.draw.rect(screen, DARK, rectangle1)pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREY, rectangle2)pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK, rectangle2, 2) # 边框宽为2screen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def repaint():# 绘制游戏界面screen.fill(WHITE)# 定义线段的端点坐标x,y = (-1,640,640,-1)*16, []for i in range(36):for _ in range(2):y.append(19+i*20)# 使用pygame.draw.lines()函数绘制线段points = list(zip(x,y))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 线宽为1points = list(zip(y,x))pygame.draw.lines(screen, GREY, False, points, 1) # 重画蛇和食物for pos in snake_pos:pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, pygame.Rect(pos[0], pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.draw.rect(screen, RED, pygame.Rect(food_pos[0], food_pos[1], 20, 20))pygame.display.flip()show_msg_at(22, 6, f'Scores: {scores}')show_msg_at(410, 6, f'Snake coordinate: ({1+snake_pos[0][0]//20:2}, {1+snake_pos[0][1]//20:2})')def show_msg_at(x, y, msg):font = pygame.font.SysFont('Consolas', 14)text = font.render(msg, True, BLACK)text_rect = text.get_rect()text_rect.x, text_rect.y = x, yscreen.blit(text, text_rect)pygame.display.flip()def game_quit():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def main():global screen, screen_size, scoresglobal snake_pos, food_pos, snake_speedis_running = Falseis_paused = Falseis_dead = Falseis_mute = Falserepaint()show_msg("Press any key to start ...")# 创建一个线程来播放音乐music_no = 1music_fn = "voice1.mp3"if os.path.exists(music_fn):t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))t.start()# 主循环while True:# 处理游戏事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:game_quit()elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_UP:snake_speed = [0, -20]elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:snake_speed = [0, 20]elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:snake_speed = [-20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:snake_speed = [20, 0]elif event.key == pygame.K_y:if is_dead:init()is_dead = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_n:if is_dead: game_quit()else: is_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:if is_dead: continueif is_paused: is_paused = Falseis_running = Trueelif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:if is_running:show_msg(">>> Paused <<<")is_paused = not is_pausedif not is_mute and is_paused: play_sound(1)elif event.key == pygame.K_m and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:# Ctrl+M 切换背景音乐is_mute = Falsemusic_no = 1 if music_no == 3 else music_no + 1music_fn = f"voice{music_no}.mp3"if os.path.exists(music_fn):t = threading.Thread(target=play_music, args=(music_fn,0.8,))t.start()elif event.key == pygame.K_s and event.mod & pygame.KMOD_CTRL:# Ctrl+S 切换静音状态is_mute = not is_muteif is_mute:pygame.mixer.music.pause()else:pygame.mixer.music.unpause()is_running = Trueelse: # 任意键进入开始状态if is_dead: continueis_running = Trueif not is_running: continueif is_paused and is_running: continue# 更新蛇的位置snake_pos.insert(0, [snake_pos[0][0] + snake_speed[0], snake_pos[0][1] + snake_speed[1]])# 检查蛇头是否碰到食物if snake_pos[0] == food_pos:scores += 10 + len(snake_pos) // 5if not 1 < snake_pos[0][0]//20 < 30 or not 1 < snake_pos[0][1]//20 < 22:scores += 5if not is_mute: play_sound(2)food_pos = [random.randrange(1, screen_size[0] // 20) * 20, random.randrange(1, screen_size[1] // 20) * 20]else:snake_pos.pop()# 检查蛇头是否碰到墙壁或者蛇身if snake_pos[0][0] < 0 or snake_pos[0][0] >= screen_size[0] or snake_pos[0][1] < 0 or snake_pos[0][1] >= screen_size[1] or snake_pos[0] in snake_pos[1:]:show_msg("Dead! Again? (Y or N)")is_running = Falseis_dead = Trueif not is_mute: play_sound(3)continue# 重画界面及蛇和食物repaint()# 控制游戏速度pygame.time.Clock().tick(10)if __name__ == "__main__":init()main()小结
本文以贪吃蛇游戏为例,对pygame编程的一个简单框架进行了深入的学习,包括对画图、字体、音乐等各个方面操作的各种方法和函数,学习后在pygame这方面的编程能力有所长进提高。
pygame编程框架
import pygame
import sys# 初始化Pygame
pygame.init()# 设置窗口大小
screen_size = (800, 600)# 创建窗口
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screen_size)# 设置窗口标题
pygame.display.set_caption("Pygame Example")# 主循环
while True:# 处理事件for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.QUIT:pygame.quit()sys.exit()elif event.type == ...... // 处理按键事件# 填充背景色screen.fill((255, 255, 255))# 绘制矩形pygame.draw.rect(screen, (0, 0, 255), (400, 300, 100, 50))# 更新显示pygame.display.flip()最终版的源代码及音乐文件列表如下:
下载地址:
https://download.csdn.net/download/boysoft2002/88231961
相关文章:

Python “贪吃蛇”游戏,在不断改进中学习pygame编程
目录 前言 改进过程一 增加提示信息 原版帮助摘要 pygame.draw pygame.font class Rect class Surface 改进过程二 增加显示得分 改进过程三 增加背景景乐 增加提示音效 音乐切换 静音切换 mixer.music.play 注意事项 原版帮助摘要 pygame.mixer pygame.mix…...

Linux网络编程_Ubuntu环境配置安装
文章目录: 一:基于vmware虚拟机安装Ubuntu系统(虚拟机) 1.vmware下载 2.Ubuntu系统下载 3.配置 3.1 无法连网:这里很容易出现问题 3.2 更换国内源 3.3 无法屏幕适配全屏 3.4 汉化 二:直接安装Ubun…...

gradle java插件
gradle java插件 1. 由来 Gradle是一种现代化的构建工具,Java插件是Gradle官方提供的插件,用于支持和管理Java项目的构建过程。 2. 常见五种示例和说明 示例1:配置源代码目录和编译选项 plugins {id java }sourceSets {main {java {srcD…...

神经网络基础-神经网络补充概念-48-rmsprop
概念## 标题 RMSProp(Root Mean Square Propagation)是一种优化算法,用于在训练神经网络等机器学习模型时自适应地调整学习率,以加速收敛并提高性能。RMSProp可以有效地处理不同特征尺度和梯度变化,对于处理稀疏数据和…...
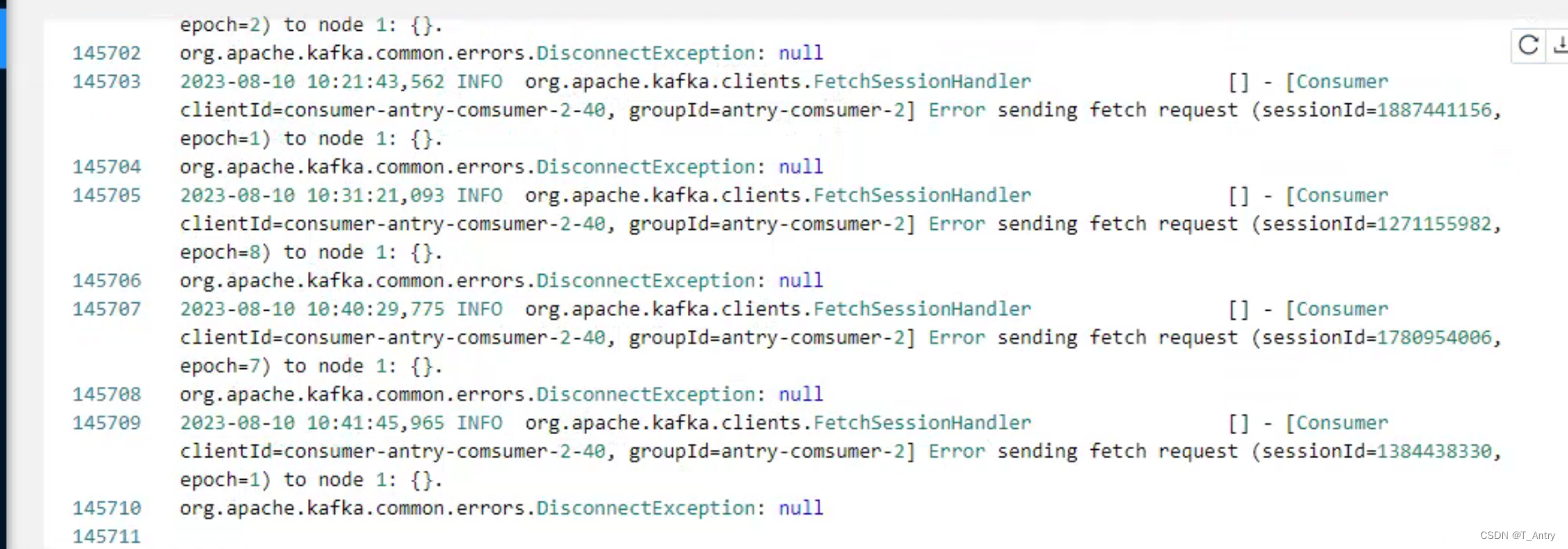
分析Flink,源和算子并行度不一致时,运行一段时间后,看似不再继续消费的问题,提供解决思路。
文章目录 背景分析 问题来了比较一开始的情况解决方式 背景 之前有分析过一次类似问题,最终结论是在keyby之后,其中有一个key数量特别庞大,导致对应的subtask压力过大,进而使得整个job不再继续运作。在这个问题解决之后ÿ…...
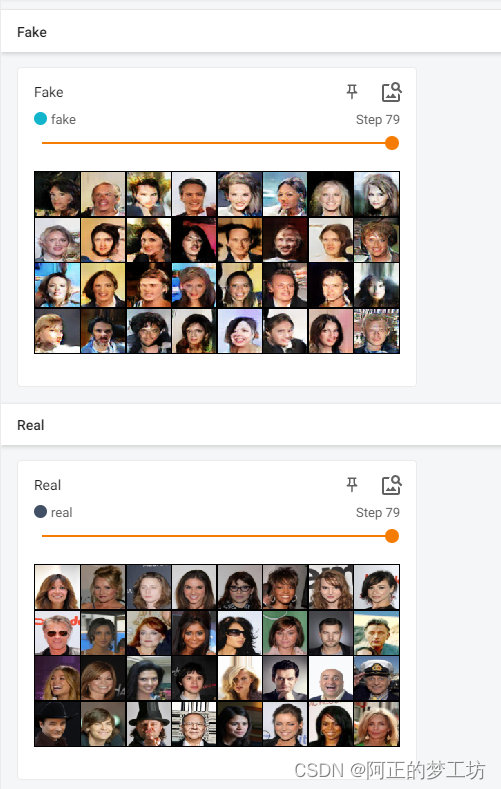
PyTorch训练深度卷积生成对抗网络DCGAN
文章目录 DCGAN介绍代码结果参考 DCGAN介绍 将CNN和GAN结合起来,把监督学习和无监督学习结合起来。具体解释可以参见 深度卷积对抗生成网络(DCGAN) DCGAN的生成器结构: 图片来源:https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.06434 代码 model.py impor…...

Spring-4-掌握Spring事务传播机制
今日目标 能够掌握Spring事务配置 Spring事务管理 1 Spring事务简介【重点】 1.1 Spring事务作用 事务作用:在数据层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败 Spring事务作用:在数据层或业务层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败 1.2 案例分析Spring…...
[PyTorch][chapter 49][创建自己的数据集 1]
前言: 后面几章主要利用DataSet 创建自己的数据集,实现建模, 训练,迁移等功能。 目录: pokemon 数据集深度学习工程步骤 一 pokemon 数据集介绍 1.1 pokemon: 数据集地址: 百度网盘路径: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1…...
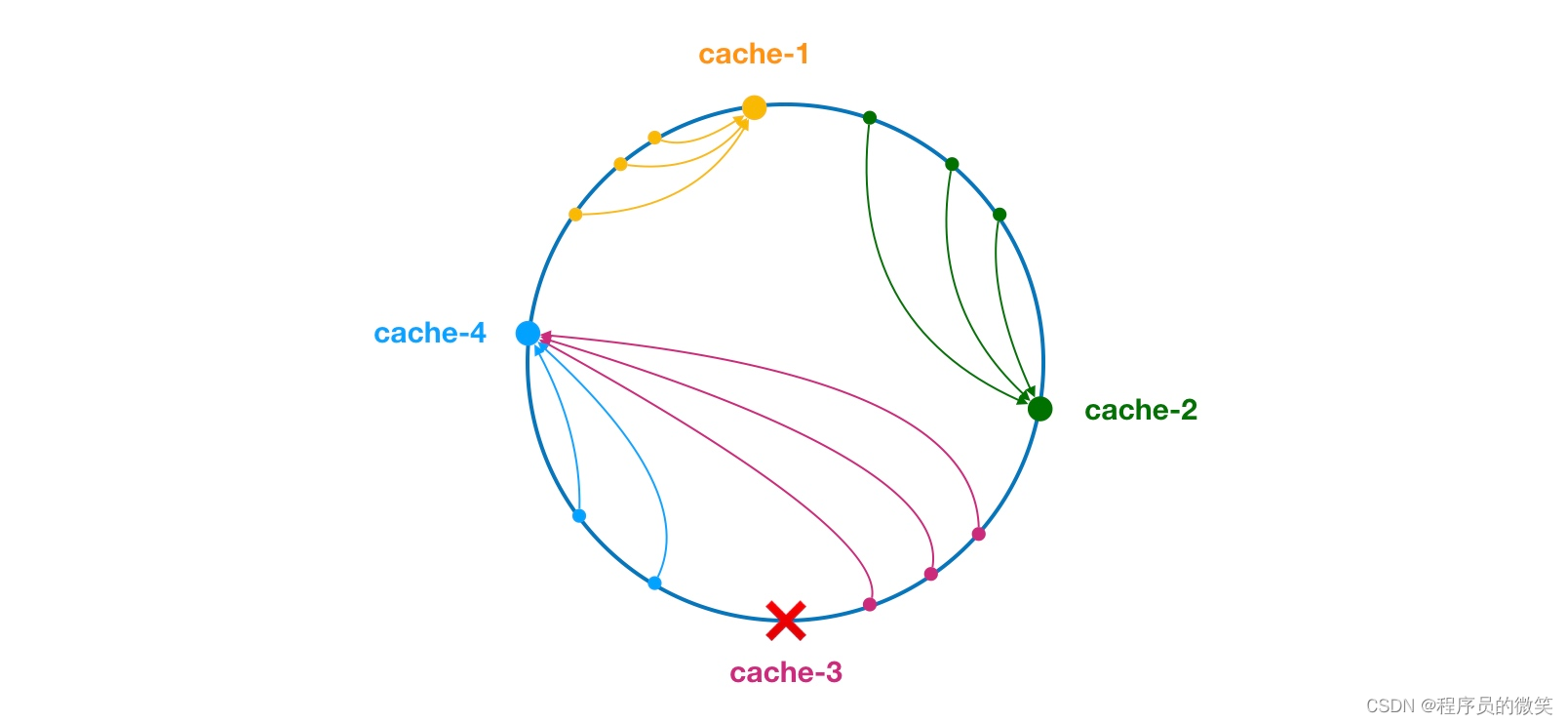
中间件(二)dubbo负载均衡介绍
一、负载均衡概述 支持轮询、随机、一致性hash和最小活跃数等。 1、轮询 ① sequences:内部的序列计数器 ② 服务器接口方法权重一样:(sequences1)%服务器的数量(决定调用)哪个服务器的服务。 ③ 服务器…...
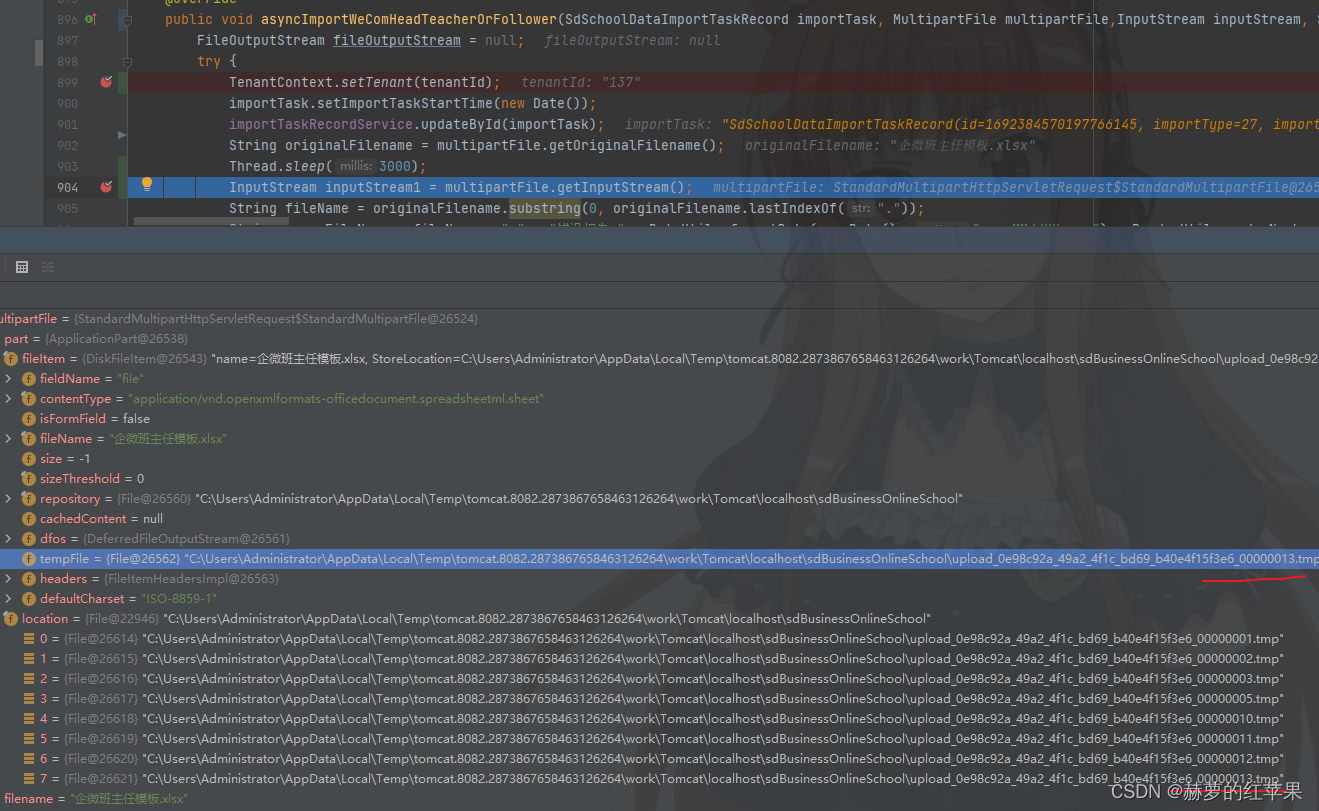
springboot异步文件上传获取输入流提示找不到文件java.io.FileNotFoundException
springboot上传文件,使用异步操作处理上传的文件数据,出现异常如下: 这个是在异步之后使用传过来的MultipartFile对象尝试调用getInputStream方法发生的异常。 java.io.FileNotFoundException: C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\to…...

安装jenkins-cli
1、要在 Linux 操作系统上安装 jcli curl -L https://github.com/jenkins-zh/jenkins-cli/releases/latest/download/jcli-linux-amd64.tar.gz|tar xzv sudo mv jcli /usr/local/bin/ 在用户根目录下,增加 jcli 的配置文件: jcli config gen -ifalse …...

linux通过NC工具启动临时端口监听
1.安装nc工具 yum install nc -y2. 启动监听指定端口 #例如监听8080端口 nc -lk 8080#后台监听 nc -lk 8080 &3. 验证 #通过另外一台网络能通的机器,telnet 该机器ip 监听端口能通,并且能接手数据 telnet 192.xxx.xxx.xx 8080...

开源语音聊天软件Mumble
网友 大气 告诉我,Openblocks在国内还有个版本叫 码匠,更贴合国内软件开发的需求,如接入了国内常用的身份认证,接入了国内的数据库和云服务,也对小程序、企微 sdk 等场景做了适配。 在 https://majiang.co/docs/docke…...

JDK 1.6与JDK 1.8的区别
ArrayList使用默认的构造方式实例 jdk1.6默认初始值为10jdk1.8为0,第一次放入值才初始化,属于懒加载 Hashmap底层 jdk1.6与jdk1.8都是数组链表 jdk1.8是链表超过8时,自动转为红黑树 静态方式不同 jdk1.6是先初始化static后执行main方法。 jdk1.8是懒加…...

单片机实训报告
这周我们进行了单片机实训,一周中我们通过七个项目1:P1 口输入/输出 2:继电器控制 3 音频控制 4:子程序设计 5:字符碰头程序设计 6:外部中断 7: 急救车与交通信号灯,练习编写了子程…...

【编织时空四:探究顺序表与链表的数据之旅】
本章重点 链表的分类 带头双向循环链表接口实现 顺序表和链表的区别 缓存利用率参考存储体系结构 以及 局部原理性。 一、链表的分类 实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构: 1. 单向或者双向 2. 带头或者不带头 3. 循环或者非…...

PHP8的字符串操作1-PHP8知识详解
字符串是php中最重要的数据之一,字符串的操作在PHP编程占有重要的地位。在使用PHP语言开发web项目的过程中,为了实现某些功能,经常需要对某些字符串进行特殊的处理,比如字符串的格式化、字符串的连接与分割、字符串的比较、查找等…...
电脑提示msvcp140.dll丢失的解决方法,dll组件怎么处理
Windows系统有时在打开游戏或者软件时, 系统会弹窗提示缺少“msvcp140.dll.dll”文件 或者类似错误提示怎么办? 错误背景: msvcp140.dll是Microsoft Visual C Redistributable Package中的一个动态链接库文件,它在运行软件时提…...

stable diffusion基础
整合包下载:秋叶大佬 【AI绘画8月最新】Stable Diffusion整合包v4.2发布! 参照:基础04】目前全网最贴心的Lora基础知识教程! VAE 作用:滤镜微调 VAE下载地址:C站(https://civitai.com/models…...

Greiner–Hormann裁剪算法深度探索:C++实现与应用案例
介绍 在计算几何中,裁剪是一个核心的主题。特别是,多边形裁剪已经被广泛地应用于计算机图形学,地理信息系统和许多其他领域。Greiner-Hormann裁剪算法是其中之一,提供了一个高效的方式来计算两个多边形的交集、并集等。在本文中&…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
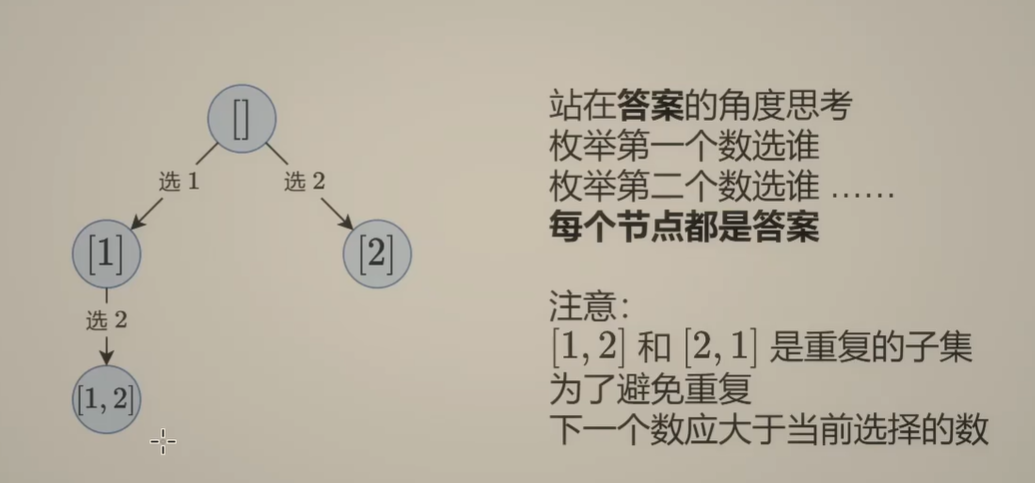
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

前端导出带有合并单元格的列表
// 导出async function exportExcel(fileName "共识调整.xlsx") {// 所有数据const exportData await getAllMainData();// 表头内容let fitstTitleList [];const secondTitleList [];allColumns.value.forEach(column > {if (!column.children) {fitstTitleL…...

基于Uniapp开发HarmonyOS 5.0旅游应用技术实践
一、技术选型背景 1.跨平台优势 Uniapp采用Vue.js框架,支持"一次开发,多端部署",可同步生成HarmonyOS、iOS、Android等多平台应用。 2.鸿蒙特性融合 HarmonyOS 5.0的分布式能力与原子化服务,为旅游应用带来…...
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...

如何在最短时间内提升打ctf(web)的水平?
刚刚刷完2遍 bugku 的 web 题,前来答题。 每个人对刷题理解是不同,有的人是看了writeup就等于刷了,有的人是收藏了writeup就等于刷了,有的人是跟着writeup做了一遍就等于刷了,还有的人是独立思考做了一遍就等于刷了。…...
Mobile ALOHA全身模仿学习
一、题目 Mobile ALOHA:通过低成本全身远程操作学习双手移动操作 传统模仿学习(Imitation Learning)缺点:聚焦与桌面操作,缺乏通用任务所需的移动性和灵活性 本论文优点:(1)在ALOHA…...
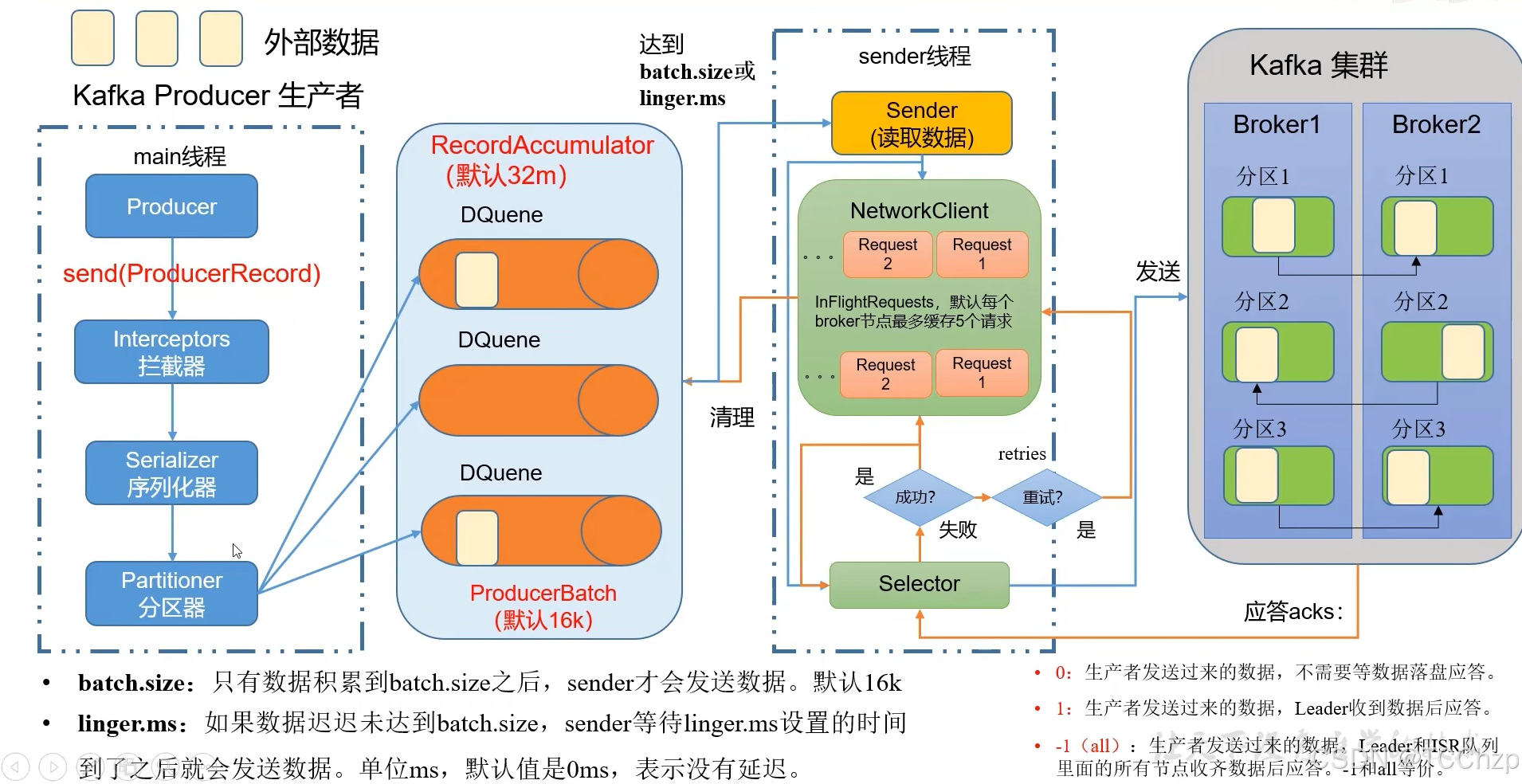
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...
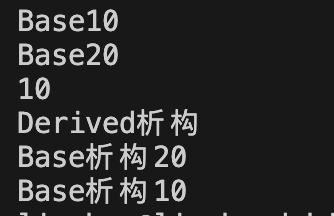
c++第七天 继承与派生2
这一篇文章主要内容是 派生类构造函数与析构函数 在派生类中重写基类成员 以及多继承 第一部分:派生类构造函数与析构函数 当创建一个派生类对象时,基类成员是如何初始化的? 1.当派生类对象创建的时候,基类成员的初始化顺序 …...
