【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十五、Rust命令行参数解析库(clap)
系列文章目录
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】一、Rust 编程基础
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二、Rust 包管理工具使用
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】三、Rust 的基本程序概念
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】四、理解 Rust 的所有权概念
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】五、使用结构体关联结构化数据
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】六、枚举和模式匹配
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】七、使用包(Packages)、单元包(Crates)和模块(Module)来管理项目
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】八、常见的集合
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】九、错误处理(Error Handling)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十一、编写自动化测试
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十二、构建一个命令行程序
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十三、函数式语言特性:迭代器和闭包
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十四、关于 Cargo 和 Crates.io
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十五、智能指针(Smart Point)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十六、无畏并发(Fearless Concurrency)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十七、面向对象语言特性
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十八、模式匹配(Patterns and Matching)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】十九、高级特性
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十、进阶扩展
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十一、网络编程
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十三、Cargo 使用指南
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十四、内联汇编(inline assembly)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十五、Rust命令行参数解析库(clap)
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- @[TOC](文章目录)
- 前言
- 一、 Clap 使用方式一:build构建
- 1.1、引入 clap 库
- 1.2、快速启动
- 1.3、配置解析器(Configuring the Parser)
- 1.3.1、使用 Command 构建解析器
- 1.3.2、使用 command! 构建解析器
- 1.3.2、使用 Command::next_line_help 方法
- 1.4、添加命令行参数(Adding Arguments)
- 1.4、设置参数行为
- 1.5、参数选项
- 1.5.1、参数选项
- 1.5.2、开启/关闭标志
- 1.5.3、参数调用计数
- 1.5.4、默认值
- 1.5.5、参数校验
- 1.5.5.1、默认情况
- 1.5.5.2、枚举值(Enumerated values)
- 1.5.5.3、校验值(Validated values)
- 1.5.5.4、自定义解析器(Custom Parser)
- 1.5.5.5、参数关系(Argument Relations)
- 1.5.5.6、自定义校验(Custom Validation)
- 1.6、子命令(Subcommand)
- 1.7、测试
- 二、 Clap 使用方式二:derive feature
- 2.1、添加依赖
- 2.2、快速开始
- 2.3、配置解析器
- 2.3.1、配置解析器
- 2.3.2、默认值
- 2.3.3、Command::next_line_help 替代
- 2.4、添加参数
- 2.4.1、添加可选参数
- 2.4.2、添加多值参数
- 2.4.3、参数选项
- 2.4.3.1、短参数名称和长参数名称
- 2.4.3.2、开启和关闭
- 2.4.3.3、参数计数
- 2.4.3.4、参数默认值
- 2.4.3.5、参数枚举
- 2.4.3.6、参数校验
- 2.4.3.7、自定义解析
- 2.4.3.8、参数关系
- 2.4.3.9、自定义校验
- 2.5、子命令
- 三、如何选择
- 总结
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- @[TOC](文章目录)
- 前言
- 一、 Clap 使用方式一:build构建
- 1.1、引入 clap 库
- 1.2、快速启动
- 1.3、配置解析器(Configuring the Parser)
- 1.3.1、使用 Command 构建解析器
- 1.3.2、使用 command! 构建解析器
- 1.3.2、使用 Command::next_line_help 方法
- 1.4、添加命令行参数(Adding Arguments)
- 1.4、设置参数行为
- 1.5、参数选项
- 1.5.1、参数选项
- 1.5.2、开启/关闭标志
- 1.5.3、参数调用计数
- 1.5.4、默认值
- 1.5.5、参数校验
- 1.5.5.1、默认情况
- 1.5.5.2、枚举值(Enumerated values)
- 1.5.5.3、校验值(Validated values)
- 1.5.5.4、自定义解析器(Custom Parser)
- 1.5.5.5、参数关系(Argument Relations)
- 1.5.5.6、自定义校验(Custom Validation)
- 1.6、子命令(Subcommand)
- 1.7、测试
- 二、 Clap 使用方式二:derive feature
- 2.1、添加依赖
- 2.2、快速开始
- 2.3、配置解析器
- 2.3.1、配置解析器
- 2.3.2、默认值
- 2.3.3、Command::next_line_help 替代
- 2.4、添加参数
- 2.4.1、添加可选参数
- 2.4.2、添加多值参数
- 2.4.3、参数选项
- 2.4.3.1、短参数名称和长参数名称
- 2.4.3.2、开启和关闭
- 2.4.3.3、参数计数
- 2.4.3.4、参数默认值
- 2.4.3.5、参数枚举
- 2.4.3.6、参数校验
- 2.4.3.7、自定义解析
- 2.4.3.8、参数关系
- 2.4.3.9、自定义校验
- 2.5、子命令
- 三、如何选择
- 总结
前言
本章节内容讲解 Rust 的第三方库 Clap,这是一个命令行参数解析库。使用API创建解析的方式有两种:Derive 方式、Builder方式。
主要教材参考 《The Rust Programming Language》
主要教材参考 《Rust For Rustaceans》
主要教材参考 《The Rustonomicon》
主要教材参考 《Rust 高级编程》
主要教材参考 《Cargo 指南》
一、 Clap 使用方式一:build构建
1.1、引入 clap 库
cargo add clap -- features cargo
需要注意:如果不启用 cargo feature ,则会报如下错误。
requires `cargo` feature
1.2、快速启动
//main.rs
use std::path::PathBuf;use clap::{arg, command, value_parser, ArgAction, Command};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!([name] "Optional name to operate on")).arg(arg!(-c --config <FILE> "Sets a custom config file")// We don't have syntax yet for optional options, so manually calling `required`.required(false).value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)),).arg(arg!(-d --debug ... "Turn debugging information on")).subcommand(Command::new("test").about("does testing things").arg(arg!(-l --list "lists test values").action(ArgAction::SetTrue)),).get_matches();// You can check the value provided by positional arguments, or option argumentsif let Some(name) = matches.get_one::<String>("name") {println!("Value for name: {name}");}if let Some(config_path) = matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("config") {println!("Value for config: {}", config_path.display());}// You can see how many times a particular flag or argument occurred// Note, only flags can have multiple occurrencesmatch matches.get_one::<u8>("debug").expect("Count's are defaulted"){0 => println!("Debug mode is off"),1 => println!("Debug mode is kind of on"),2 => println!("Debug mode is on"),_ => println!("Don't be crazy"),}// You can check for the existence of subcommands, and if found use their// matches just as you would the top level cmdif let Some(matches) = matches.subcommand_matches("test") {// "$ myapp test" was runif matches.get_flag("list") {// "$ myapp test -l" was runprintln!("Printing testing lists...");} else {println!("Not printing testing lists...");}}// Continued program logic goes here...
}
1、默认执行情况
cargo run
Debug mode is off
2、参看帮助文档
cargo run --help
Run a binary or example of the local packageUsage: cargo run [OPTIONS] [args]...Arguments:[args]... Arguments for the binary or example to runOptions:-q, --quiet Do not print cargo log messages--bin [<NAME>] Name of the bin target to run--example [<NAME>] Name of the example target to run-p, --package [<SPEC>] Package with the target to run-j, --jobs <N> Number of parallel jobs, defaults to # of CPUs.--keep-going Do not abort the build as soon as there is an error (unstable)-r, --release Build artifacts in release mode, with optimizations--profile <PROFILE-NAME> Build artifacts with the specified profile-F, --features <FEATURES> Space or comma separated list of features to activate--all-features Activate all available features--no-default-features Do not activate the `default` feature--target <TRIPLE> Build for the target triple--target-dir <DIRECTORY> Directory for all generated artifacts--manifest-path <PATH> Path to Cargo.toml--message-format <FMT> Error format--unit-graph Output build graph in JSON (unstable)--ignore-rust-version Ignore `rust-version` specification in packages--timings[=<FMTS>] Timing output formats (unstable) (comma separated): html, json-h, --help Print help-v, --verbose... Use verbose output (-vv very verbose/build.rs output)--color <WHEN> Coloring: auto, always, never--frozen Require Cargo.lock and cache are up to date--locked Require Cargo.lock is up to date--offline Run without accessing the network--config <KEY=VALUE> Override a configuration value-Z <FLAG> Unstable (nightly-only) flags to Cargo, see 'cargo -Z help' for detailsRun `cargo help run` for more detailed information.
3、使用 -dd 参数
cargo run -- -dd test
Debug mode is on
Not printing testing lists...
1.3、配置解析器(Configuring the Parser)
1.3.1、使用 Command 构建解析器
你可以使用 Command 开始构建一个解析器。
use clap::{arg, Command};fn main() {let matches = Command::new("MyApp").version("1.0").author("Kevin K. <kbknapp@gmail.com>").about("Does awesome things").arg(arg!(--two <VALUE>).required(true)).arg(arg!(--one <VALUE>).required(true)).get_matches();println!("two: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("two").expect("required"));println!("one: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("one").expect("required"));
}
1、查看帮助文档
cargo run -- --helpDoes awesome thingsUsage: hello_world --two <VALUE> --one <VALUE>Options:--two <VALUE> --one <VALUE> -h, --help Print help-V, --version Print version
1.3.2、使用 command! 构建解析器
你也可以使用 command! 宏 构建解析器,不过要想使用 command! 宏,你需要开启 cargo feature。
use clap::{arg, command};fn main() {// requires `cargo` feature, reading name, version, author, and description from `Cargo.toml`let matches = command!().arg(arg!(--two <VALUE>).required(true)).arg(arg!(--one <VALUE>).required(true)).get_matches();println!("two: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("two").expect("required"));println!("one: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("one").expect("required"));
}
1、查看帮助文档
cargo run -- --helpUsage: hello_world --two <VALUE> --one <VALUE>Options:--two <VALUE> --one <VALUE> -h, --help Print help-V, --version Print version
1.3.2、使用 Command::next_line_help 方法
使用 Command::next_line_help 方法 可以修改参数打印行为
use clap::{arg, command, ArgAction};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.next_line_help(true).arg(arg!(--two <VALUE>).required(true).action(ArgAction::Set)).arg(arg!(--one <VALUE>).required(true).action(ArgAction::Set)).get_matches();println!("two: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("two").expect("required"));println!("one: {:?}",matches.get_one::<String>("one").expect("required"));
}
1、显示帮助文档
cargo run -- --helpUsage: hello_world --two <VALUE> --one <VALUE>Options:--two <VALUE>--one <VALUE>-h, --helpPrint help-V, --versionPrint version
效果就是:参数的描述和参数是分行的,描述信息在参数下一行。
1.4、添加命令行参数(Adding Arguments)
我们可以使用 Command::arg 方法来添加 Arg 对象来添加命令行参数
use clap::{command, Arg};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(Arg::new("name")).get_matches();println!("name: {:?}", matches.get_one::<String>("name"));
}
1、查看帮助文档
cargo run -- --helpUsage: hello_world [name]Arguments:[name] Options:-h, --help Print help-V, --version Print version
2、使用 name 参数:默认
cargo run
name: None
3、使用 name 参数:blob
cargo run bob
name: Some("bob")
1.4、设置参数行为
需要注意:参数默认值是一个 Set 类型
我们可以使用 Command::action 方法来设置 参数行为。如果可以添加多个只,我们可以使用 ArgAction::Append
use clap::{command, Arg, ArgAction};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(Arg::new("name").action(ArgAction::Append)).get_matches();let args = matches.get_many::<String>("name").unwrap_or_default().map(|v| v.as_str()).collect::<Vec<_>>();println!("names: {:?}", &args);
}
1.5、参数选项
1.5.1、参数选项
一个参数行为的标志:
- 顺序无关
- 可选参数
- 意图清晰
use clap::{command, Arg};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(Arg::new("name").short('n').long("name")).get_matches();println!("name: {:?}", matches.get_one::<String>("name"));
}
上述代码:我们定义了一个name参数,缩写是n,全拼是name,也就是如下形式
-n, --name <name>
我们使用方式就有如下几种
cargo run -- --name blo
cargo run -- --name=blob
cargo run -- -n blob
cargo run -- -n=blob
cargo run -- -nblob1.5.2、开启/关闭标志
我们可以是 ArgAction::SetTrue 开启参数
use clap::{command, Arg, ArgAction};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(Arg::new("verbose").short('v').long("verbose").action(ArgAction::SetTrue),).get_matches();println!("verbose: {:?}", matches.get_flag("verbose"));
}1.5.3、参数调用计数
我们可以使用 ArgAction::Count
use clap::{command, Arg, ArgAction};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(Arg::new("verbose").short('v').long("verbose").action(ArgAction::Count),).get_matches();println!("verbose: {:?}", matches.get_count("verbose"));
}
默认值是0,多次使用参数就会计数
1.5.4、默认值
我们前面设置的参数都是必选的,但是也可以使用可选的,如果是可选的,我们可以使用 Option 并且可以使用 unwrap_or 方法,也可以使用 Arg::default_value 方法设置默认值。
use clap::{arg, command, value_parser};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!([PORT]).value_parser(value_parser!(u16)).default_value("2023"),).get_matches();println!("port: {:?}",matches.get_one::<u16>("PORT").expect("default ensures there is always a value"));
}
1.5.5、参数校验
1.5.5.1、默认情况
默认情况下,参数被认为是 String,并且使用 UTF-8 校验。
1.5.5.2、枚举值(Enumerated values)
如果你的参数有多个特定的值,我们可以使用 PossibleValuesParser 解析器 或者使用 Arg::value_parser([“val1”, …]) 进行设置。
use clap::{arg, command};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!(<MODE>).help("What mode to run the program in").value_parser(["fast", "slow"]),).get_matches();// Note, it's safe to call unwrap() because the arg is requiredmatch matches.get_one::<String>("MODE").expect("'MODE' is required and parsing will fail if its missing").as_str(){"fast" => {println!("Hare");}"slow" => {println!("Tortoise");}_ => unreachable!(),}
}
如果我们开启了 derive feature, 则我们也可以实现 ValueEnum 特征实现相同的功能
use clap::{arg, builder::PossibleValue, command, value_parser, ValueEnum};#[derive(Copy, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord)]
enum Mode {Fast,Slow,
}// Can also be derived with feature flag `derive`
impl ValueEnum for Mode {fn value_variants<'a>() -> &'a [Self] {&[Mode::Fast, Mode::Slow]}fn to_possible_value<'a>(&self) -> Option<PossibleValue> {Some(match self {Mode::Fast => PossibleValue::new("fast").help("Run swiftly"),Mode::Slow => PossibleValue::new("slow").help("Crawl slowly but steadily"),})}
}impl std::fmt::Display for Mode {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {self.to_possible_value().expect("no values are skipped").get_name().fmt(f)}
}impl std::str::FromStr for Mode {type Err = String;fn from_str(s: &str) -> Result<Self, Self::Err> {for variant in Self::value_variants() {if variant.to_possible_value().unwrap().matches(s, false) {return Ok(*variant);}}Err(format!("invalid variant: {s}"))}
}fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!(<MODE>).help("What mode to run the program in").value_parser(value_parser!(Mode)),).get_matches();// Note, it's safe to call unwrap() because the arg is requiredmatch matches.get_one::<Mode>("MODE").expect("'MODE' is required and parsing will fail if its missing"){Mode::Fast => {println!("Hare");}Mode::Slow => {println!("Tortoise");}}
}
1.5.5.3、校验值(Validated values)
我们可以使用 Arg::value_parser 验证并解析成我们需要的任何类型。
use clap::{arg, command, value_parser};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!(<PORT>).help("Network port to use").value_parser(value_parser!(u16).range(1..)),).get_matches();// Note, it's safe to call unwrap() because the arg is requiredlet port: u16 = *matches.get_one::<u16>("PORT").expect("'PORT' is required and parsing will fail if its missing");println!("PORT = {port}");
}
1.5.5.4、自定义解析器(Custom Parser)
我们也可以使用自定义解析器用于改进错误信息提示和额外的验证。
use std::ops::RangeInclusive;use clap::{arg, command};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!(<PORT>).help("Network port to use").value_parser(port_in_range),).get_matches();// Note, it's safe to call unwrap() because the arg is requiredlet port: u16 = *matches.get_one::<u16>("PORT").expect("'PORT' is required and parsing will fail if its missing");println!("PORT = {port}");
}const PORT_RANGE: RangeInclusive<usize> = 1..=65535;fn port_in_range(s: &str) -> Result<u16, String> {let port: usize = s.parse().map_err(|_| format!("`{s}` isn't a port number"))?;if PORT_RANGE.contains(&port) {Ok(port as u16)} else {Err(format!("port not in range {}-{}",PORT_RANGE.start(),PORT_RANGE.end()))}
}1.5.5.5、参数关系(Argument Relations)
我们可以声明 Arg 和 ArgGroup。ArgGroup 用于声明参数关系。
use std::path::PathBuf;use clap::{arg, command, value_parser, ArgAction, ArgGroup};fn main() {// Create application like normallet matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature// Add the version arguments.arg(arg!(--"set-ver" <VER> "set version manually")).arg(arg!(--major "auto inc major").action(ArgAction::SetTrue)).arg(arg!(--minor "auto inc minor").action(ArgAction::SetTrue)).arg(arg!(--patch "auto inc patch").action(ArgAction::SetTrue))// Create a group, make it required, and add the above arguments.group(ArgGroup::new("vers").required(true).args(["set-ver", "major", "minor", "patch"]),)// Arguments can also be added to a group individually, these two arguments// are part of the "input" group which is not required.arg(arg!([INPUT_FILE] "some regular input").value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)).group("input"),).arg(arg!(--"spec-in" <SPEC_IN> "some special input argument").value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)).group("input"),)// Now let's assume we have a -c [config] argument which requires one of// (but **not** both) the "input" arguments.arg(arg!(config: -c <CONFIG>).value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)).requires("input"),).get_matches();// Let's assume the old version 1.2.3let mut major = 1;let mut minor = 2;let mut patch = 3;// See if --set-ver was used to set the version manuallylet version = if let Some(ver) = matches.get_one::<String>("set-ver") {ver.to_owned()} else {// Increment the one requested (in a real program, we'd reset the lower numbers)let (maj, min, pat) = (matches.get_flag("major"),matches.get_flag("minor"),matches.get_flag("patch"),);match (maj, min, pat) {(true, _, _) => major += 1,(_, true, _) => minor += 1,(_, _, true) => patch += 1,_ => unreachable!(),};format!("{major}.{minor}.{patch}")};println!("Version: {version}");// Check for usage of -cif matches.contains_id("config") {let input = matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("INPUT_FILE").unwrap_or_else(|| matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("spec-in").unwrap()).display();println!("Doing work using input {} and config {}",input,matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("config").unwrap().display());}
}
此时 --set-ver <VER>|--major|--minor|--patch 是一个组的参数。
1.5.5.6、自定义校验(Custom Validation)
我们可以创建自定义校验错误 Command::error 方法可以返回指定错误 Error和自定义错误信息
use std::path::PathBuf;use clap::error::ErrorKind;
use clap::{arg, command, value_parser, ArgAction};fn main() {// Create application like normallet mut cmd = command!() // requires `cargo` feature// Add the version arguments.arg(arg!(--"set-ver" <VER> "set version manually")).arg(arg!(--major "auto inc major").action(ArgAction::SetTrue)).arg(arg!(--minor "auto inc minor").action(ArgAction::SetTrue)).arg(arg!(--patch "auto inc patch").action(ArgAction::SetTrue))// Arguments can also be added to a group individually, these two arguments// are part of the "input" group which is not required.arg(arg!([INPUT_FILE] "some regular input").value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf))).arg(arg!(--"spec-in" <SPEC_IN> "some special input argument").value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)),)// Now let's assume we have a -c [config] argument which requires one of// (but **not** both) the "input" arguments.arg(arg!(config: -c <CONFIG>).value_parser(value_parser!(PathBuf)));let matches = cmd.get_matches_mut();// Let's assume the old version 1.2.3let mut major = 1;let mut minor = 2;let mut patch = 3;// See if --set-ver was used to set the version manuallylet version = if let Some(ver) = matches.get_one::<String>("set-ver") {if matches.get_flag("major") || matches.get_flag("minor") || matches.get_flag("patch") {cmd.error(ErrorKind::ArgumentConflict,"Can't do relative and absolute version change",).exit();}ver.to_string()} else {// Increment the one requested (in a real program, we'd reset the lower numbers)let (maj, min, pat) = (matches.get_flag("major"),matches.get_flag("minor"),matches.get_flag("patch"),);match (maj, min, pat) {(true, false, false) => major += 1,(false, true, false) => minor += 1,(false, false, true) => patch += 1,_ => {cmd.error(ErrorKind::ArgumentConflict,"Can only modify one version field",).exit();}};format!("{major}.{minor}.{patch}")};println!("Version: {version}");// Check for usage of -cif matches.contains_id("config") {let input = matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("INPUT_FILE").or_else(|| matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("spec-in")).unwrap_or_else(|| {cmd.error(ErrorKind::MissingRequiredArgument,"INPUT_FILE or --spec-in is required when using --config",).exit()}).display();println!("Doing work using input {} and config {}",input,matches.get_one::<PathBuf>("config").unwrap().display());}
}
1.6、子命令(Subcommand)
我们可以使用 Command::subcommand 方法添加子命令。每一个子命令都自己的版本、作者、参数和它的子命令。
use clap::{arg, command, Command};fn main() {let matches = command!() // requires `cargo` feature.propagate_version(true).subcommand_required(true).arg_required_else_help(true).subcommand(Command::new("add").about("Adds files to myapp").arg(arg!([NAME])),).get_matches();match matches.subcommand() {Some(("add", sub_matches)) => println!("'myapp add' was used, name is: {:?}",sub_matches.get_one::<String>("NAME")),_ => unreachable!("Exhausted list of subcommands and subcommand_required prevents `None`"),}
}
- 我们使用 Command::arg_required_else_help 如果参数不存在,优雅的退出。
- 使用 Command::propagate_version 可以打印命令的版本号
1.7、测试
我们可以使用 debug_assert! 宏 或者 使用 Command::debug_assert 方法。
use clap::{arg, command, value_parser};fn main() {let matches = cmd().get_matches();// Note, it's safe to call unwrap() because the arg is requiredlet port: usize = *matches.get_one::<usize>("PORT").expect("'PORT' is required and parsing will fail if its missing");println!("PORT = {port}");
}fn cmd() -> clap::Command {command!() // requires `cargo` feature.arg(arg!(<PORT>).help("Network port to use").value_parser(value_parser!(usize)),)
}#[test]
fn verify_cmd() {cmd().debug_assert();
}
二、 Clap 使用方式二:derive feature
2.1、添加依赖
cargo add clap --features derive
使用这种方式,更加符合我们面向对象的设计方案。
2.2、快速开始
use std::path::PathBuf;use clap::{Parser, Subcommand};#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {/// Optional name to operate onname: Option<String>,/// Sets a custom config file#[arg(short, long, value_name = "FILE")]config: Option<PathBuf>,/// Turn debugging information on#[arg(short, long, action = clap::ArgAction::Count)]debug: u8,#[command(subcommand)]command: Option<Commands>,
}#[derive(Subcommand)]
enum Commands {/// does testing thingsTest {/// lists test values#[arg(short, long)]list: bool,},
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();// You can check the value provided by positional arguments, or option argumentsif let Some(name) = cli.name.as_deref() {println!("Value for name: {name}");}if let Some(config_path) = cli.config.as_deref() {println!("Value for config: {}", config_path.display());}// You can see how many times a particular flag or argument occurred// Note, only flags can have multiple occurrencesmatch cli.debug {0 => println!("Debug mode is off"),1 => println!("Debug mode is kind of on"),2 => println!("Debug mode is on"),_ => println!("Don't be crazy"),}// You can check for the existence of subcommands, and if found use their// matches just as you would the top level cmdmatch &cli.command {Some(Commands::Test { list }) => {if *list {println!("Printing testing lists...");} else {println!("Not printing testing lists...");}}None => {}}// Continued program logic goes here...
}
2.3、配置解析器
2.3.1、配置解析器
我们可以是 Parse 属性开启构建解析器
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(name = "MyApp")]
#[command(author = "xiaojia")]
#[command(version = "1.0")]
#[command(about = "完成一些事情", long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[arg(long)]two: String,#[arg(long)]one: String,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("two: {:?}", cli.two);println!("one: {:?}", cli.one);
}
2.3.2、默认值
我们也可使用使用 #[command(author, version, about)] 形式从 Cargo.toml 读取配置消息
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)] // Read from `Cargo.toml`
struct Cli {#[arg(long)]two: String,#[arg(long)]one: String,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("two: {:?}", cli.two);println!("one: {:?}", cli.one);
}
2.3.3、Command::next_line_help 替代
我们可以使用 #[command(next_line_help = true)] 方法替代 Command::next_line_help
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
#[command(next_line_help = true)]
struct Cli {#[arg(long)]two: String,#[arg(long)]one: String,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("two: {:?}", cli.two);println!("one: {:?}", cli.one);
}
2.4、添加参数
2.4.1、添加可选参数
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {name: Option<String>,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("name: {:?}", cli.name.as_deref());
}
2.4.2、添加多值参数
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {name: Vec<String>,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("name: {:?}", cli.name);
}
2.4.3、参数选项
2.4.3.1、短参数名称和长参数名称
我们可以使用 #[arg(short = ‘n’)] 和 #[arg(long = “name”)] 属性设置参数的短名称和长名称
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[arg(short, long)]name: Option<String>,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("name: {:?}", cli.name.as_deref());
}
2.4.3.2、开启和关闭
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[arg(short, long)]verbose: bool,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("verbose: {:?}", cli.verbose);
}
需要注意我们默认调用的是clap::ArgAction::SetTrue
2.4.3.3、参数计数
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[arg(short, long, action = clap::ArgAction::Count)]verbose: u8,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("verbose: {:?}", cli.verbose);
}
2.4.3.4、参数默认值
我们使用 #[arg(default_value_t)] 属性来给参数设置默认值
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[arg(default_value_t = 2020)]port: u16,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("port: {:?}", cli.port);
}
2.4.3.5、参数枚举
我们使用 #[arg(value_enum)] 设置参数枚举 结合枚举类
use clap::{Parser, ValueEnum};#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {/// What mode to run the program in#[arg(value_enum)]mode: Mode,
}#[derive(Copy, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord, ValueEnum)]
enum Mode {/// Run swiftlyFast,/// Crawl slowly but steadily////// This paragraph is ignored because there is no long help text for possible values.Slow,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();match cli.mode {Mode::Fast => {println!("Hare");}Mode::Slow => {println!("Tortoise");}}
}
2.4.3.6、参数校验
use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {/// Network port to use#[arg(value_parser = clap::value_parser!(u16).range(1..))]port: u16,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("PORT = {}", cli.port);
}
2.4.3.7、自定义解析
use std::ops::RangeInclusive;use clap::Parser;#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {/// Network port to use#[arg(value_parser = port_in_range)]port: u16,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();println!("PORT = {}", cli.port);
}const PORT_RANGE: RangeInclusive<usize> = 1..=65535;fn port_in_range(s: &str) -> Result<u16, String> {let port: usize = s.parse().map_err(|_| format!("`{s}` isn't a port number"))?;if PORT_RANGE.contains(&port) {Ok(port as u16)} else {Err(format!("port not in range {}-{}",PORT_RANGE.start(),PORT_RANGE.end()))}
}
2.4.3.8、参数关系
use clap::{Args, Parser};#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {#[command(flatten)]vers: Vers,/// some regular input#[arg(group = "input")]input_file: Option<String>,/// some special input argument#[arg(long, group = "input")]spec_in: Option<String>,#[arg(short, requires = "input")]config: Option<String>,
}#[derive(Args)]
#[group(required = true, multiple = false)]
struct Vers {/// set version manually#[arg(long, value_name = "VER")]set_ver: Option<String>,/// auto inc major#[arg(long)]major: bool,/// auto inc minor#[arg(long)]minor: bool,/// auto inc patch#[arg(long)]patch: bool,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();// Let's assume the old version 1.2.3let mut major = 1;let mut minor = 2;let mut patch = 3;// See if --set_ver was used to set the version manuallylet vers = &cli.vers;let version = if let Some(ver) = vers.set_ver.as_deref() {ver.to_string()} else {// Increment the one requested (in a real program, we'd reset the lower numbers)let (maj, min, pat) = (vers.major, vers.minor, vers.patch);match (maj, min, pat) {(true, _, _) => major += 1,(_, true, _) => minor += 1,(_, _, true) => patch += 1,_ => unreachable!(),};format!("{major}.{minor}.{patch}")};println!("Version: {version}");// Check for usage of -cif let Some(config) = cli.config.as_deref() {let input = cli.input_file.as_deref().unwrap_or_else(|| cli.spec_in.as_deref().unwrap());println!("Doing work using input {input} and config {config}");}
}
2.4.3.9、自定义校验
use clap::error::ErrorKind;
use clap::{CommandFactory, Parser};#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
struct Cli {/// set version manually#[arg(long, value_name = "VER")]set_ver: Option<String>,/// auto inc major#[arg(long)]major: bool,/// auto inc minor#[arg(long)]minor: bool,/// auto inc patch#[arg(long)]patch: bool,/// some regular inputinput_file: Option<String>,/// some special input argument#[arg(long)]spec_in: Option<String>,#[arg(short)]config: Option<String>,
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();// Let's assume the old version 1.2.3let mut major = 1;let mut minor = 2;let mut patch = 3;// See if --set-ver was used to set the version manuallylet version = if let Some(ver) = cli.set_ver.as_deref() {if cli.major || cli.minor || cli.patch {let mut cmd = Cli::command();cmd.error(ErrorKind::ArgumentConflict,"Can't do relative and absolute version change",).exit();}ver.to_string()} else {// Increment the one requested (in a real program, we'd reset the lower numbers)let (maj, min, pat) = (cli.major, cli.minor, cli.patch);match (maj, min, pat) {(true, false, false) => major += 1,(false, true, false) => minor += 1,(false, false, true) => patch += 1,_ => {let mut cmd = Cli::command();cmd.error(ErrorKind::ArgumentConflict,"Can only modify one version field",).exit();}};format!("{major}.{minor}.{patch}")};println!("Version: {version}");// Check for usage of -cif let Some(config) = cli.config.as_deref() {let input = cli.input_file.as_deref()// 'or' is preferred to 'or_else' here since `Option::as_deref` is 'const'.or(cli.spec_in.as_deref()).unwrap_or_else(|| {let mut cmd = Cli::command();cmd.error(ErrorKind::MissingRequiredArgument,"INPUT_FILE or --spec-in is required when using --config",).exit()});println!("Doing work using input {input} and config {config}");}
}
2.5、子命令
我们使用 #[command(subcommand)] 属性和#[derive(Subcommand)] 联合起来使用声明子命令。
use clap::{Parser, Subcommand};#[derive(Parser)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
#[command(propagate_version = true)]
struct Cli {#[command(subcommand)]command: Commands,
}#[derive(Subcommand)]
enum Commands {/// Adds files to myappAdd { name: Option<String> },
}fn main() {let cli = Cli::parse();// You can check for the existence of subcommands, and if found use their// matches just as you would the top level cmdmatch &cli.command {Commands::Add { name } => {println!("'myapp add' was used, name is: {name:?}")}}
}
三、如何选择
我们需要注意 clap 的yaml 支持在新版本之中转移到了 clap_serde 库了。 我们建议使用 derive APi,因为此种方式跟容易阅读、修改;更加保持参数声明和参数读取同步;更容易复用,符合面向对象设计。
我们也可以使用 fncmd 库来实现命令行接口像函数一样使用。
总结
相关文章:
)
【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二十五、Rust命令行参数解析库(clap)
系列文章目录 【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】一、Rust 编程基础 【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】二、Rust 包管理工具使用 【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】三、Rust 的基本程序概念 【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】四、理解 Rust 的所有权概念 【跟小嘉学 Rust 编程】五、使用结构体关联结构化数据 【跟小嘉学…...
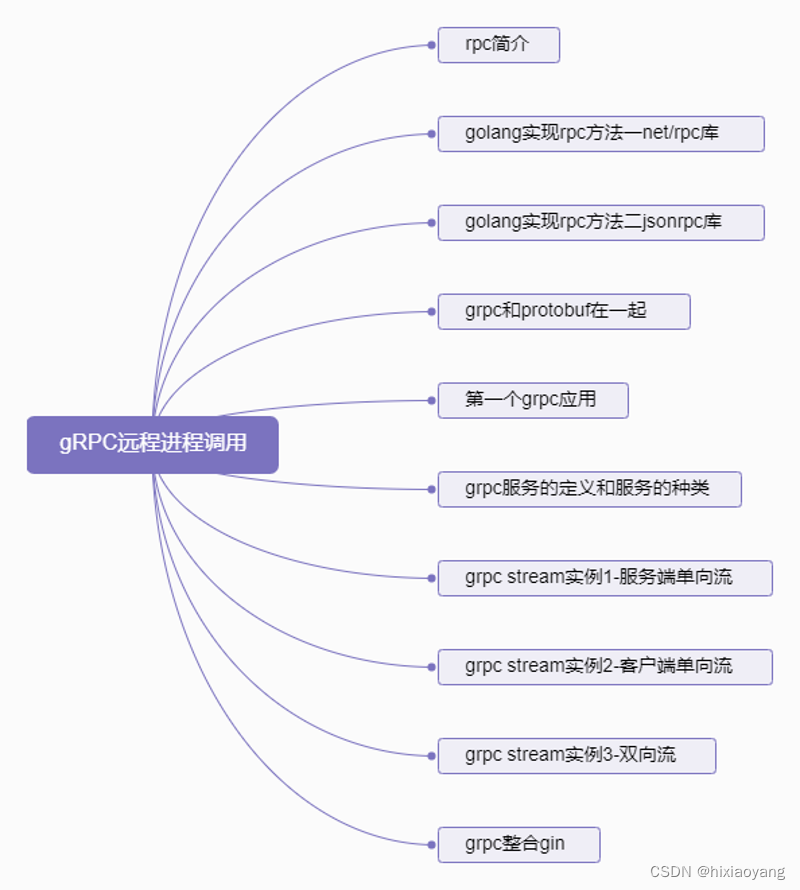
gRPC远程进程调用
gRPC远程进程调用 rpc简介golang实现rpc方法一net/rpc库golang实现rpc方法二jsonrpc库grpc和protobuf在一起第一个grpc应用grpc服务的定义和服务的种类grpc stream实例1-服务端单向流grpc stream实例2-客户端单向流grpc stream实例3-双向流grpc整合gin...
什么是继承
提示:继承基础概念 文章目录 一、继承1.1 基础概念1.2 继承作用与继承方式1.2 继承中的隐藏1.3 类中构造、析构在继承方面知识1.4 继承知识拓展 一、继承 1.1 基础概念 继承机制是面向对象程序设计使代码可以复用的最重要的手段,它允许在保持原有类特性…...
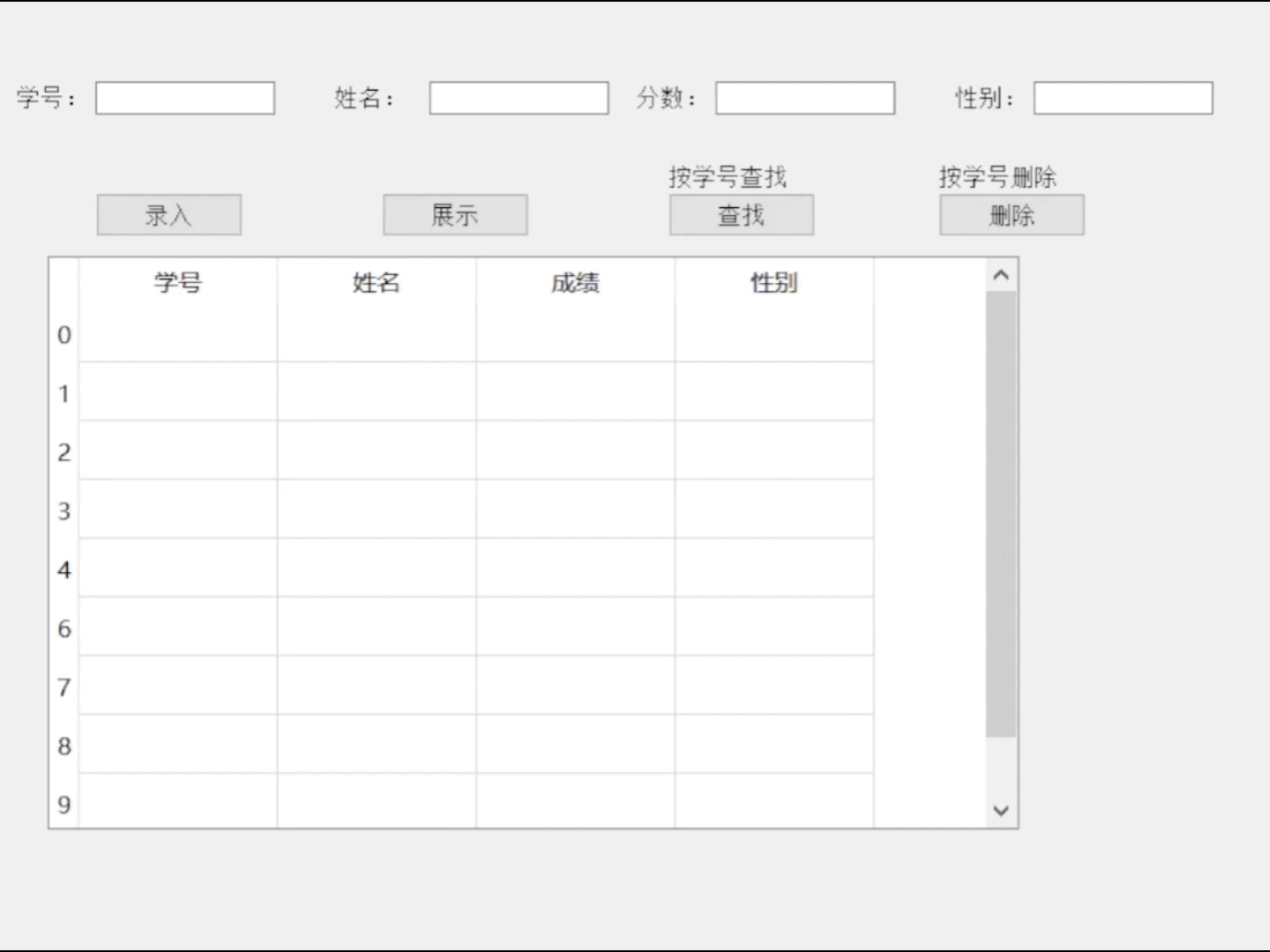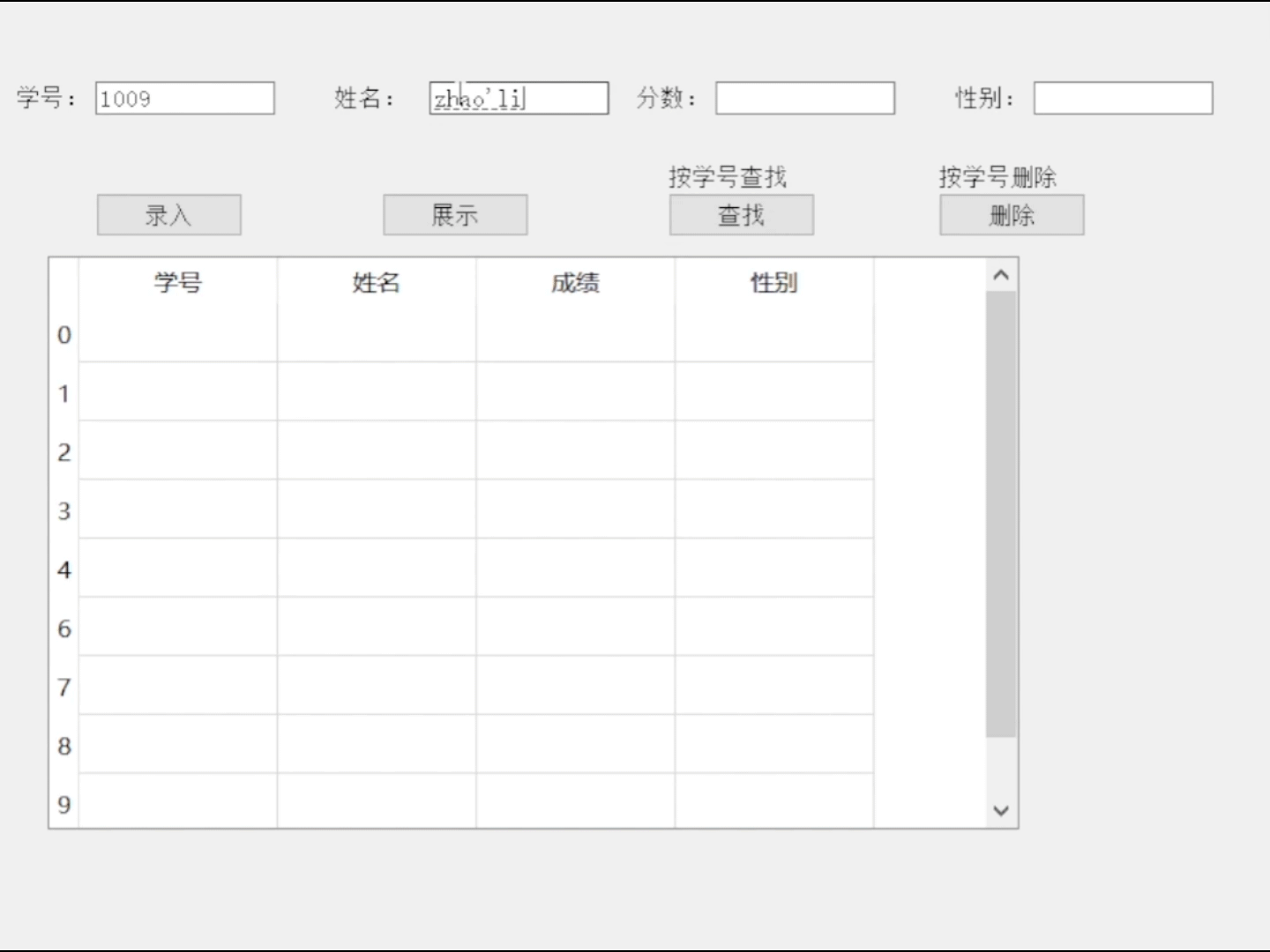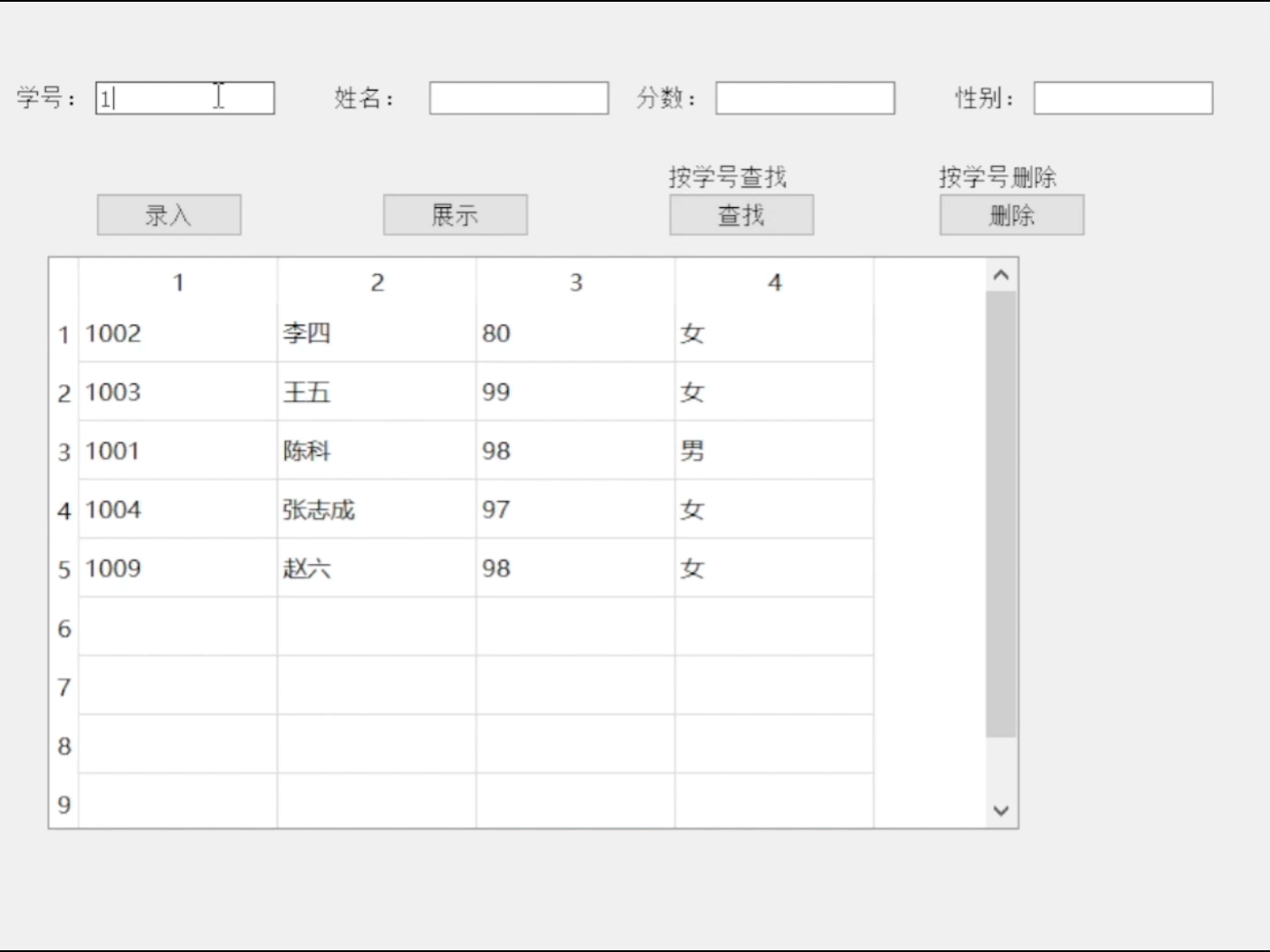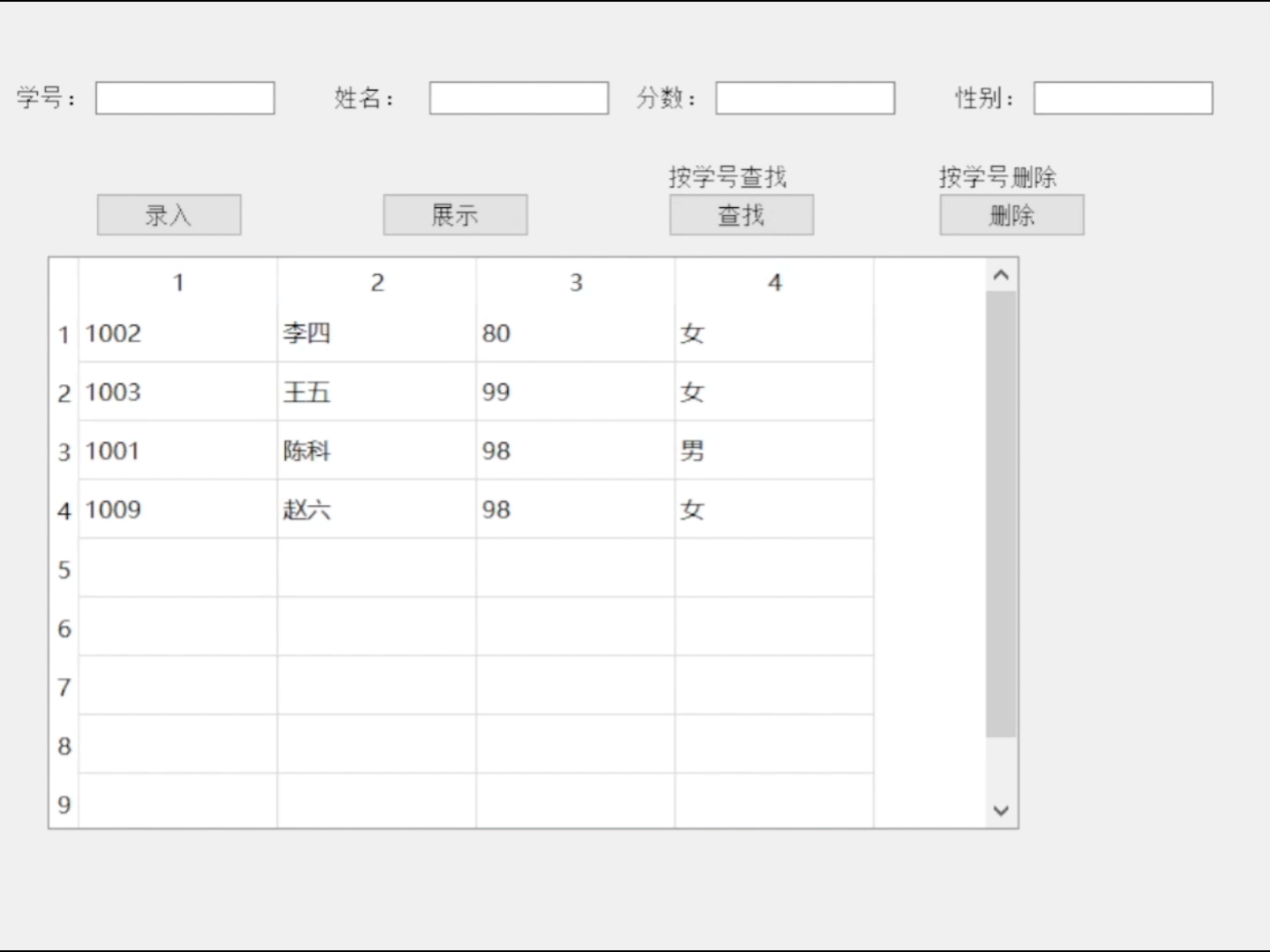
QT连接数据库
目录 数据库 数据库基本概念 常用的数据库 SQLite3基础 SQLite特性: QT连接数据库 1.1 QT将数据库分为三个层次 1.2 实现数据库操作的相关方法 sql语句(常用) 1)创建表格 2)删除表格 3)插入记录 …...
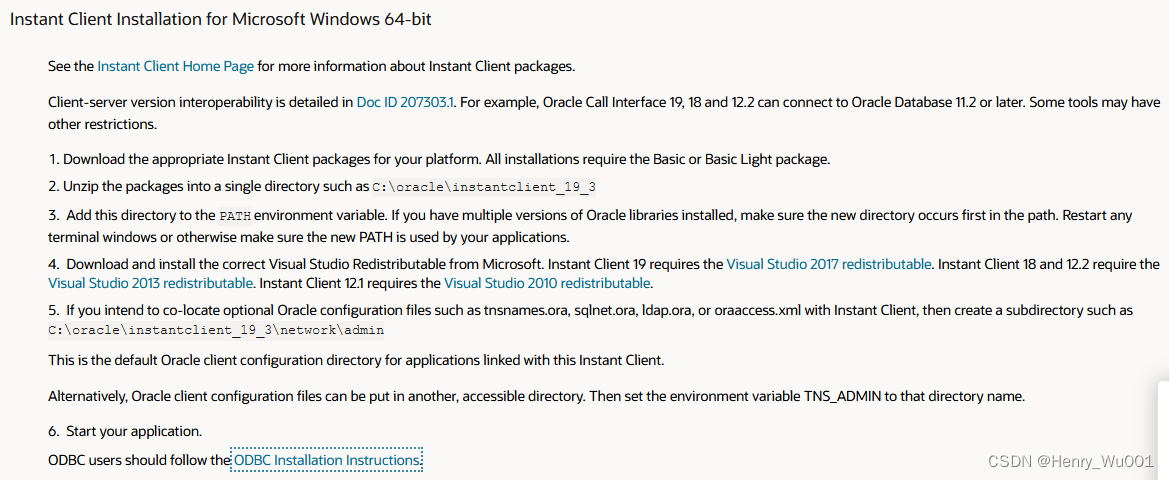
navicat访问orcal数据库
1)因为不能直接访问服务器,所以通过中介进行了端口转发; 2)依然不能访问,提示netadmin权限什么错误; 3)下载了一个 PLSQL Developer 13.0.0.1883 版本,自带的instantclient 好像不…...

Linux中查找某路径下,包含某个字符串的所有文件
path表示需要查找的路径,string表示需要包含的字符\字符串 grep -rnw path -e "string"只查找包含特定string的所有.c和.h文件 grep --include\*.{c,h} -rnw -rnw path -e "string" 除去所有.o文件,查找其他文件是否包含特定strin…...
的原理解析与C语言实现)
常见信号滤波方法(卡尔曼滤波、滑动平均、异常值剔除)的原理解析与C语言实现
常见信号滤波方法(卡尔曼滤波、滑动平均、异常值剔除)的原理解析与C语言实现 日期作者版本备注2023.09.04Dog TaoV1.0完成文档的初始版本。 文章目录 常见信号滤波方法(卡尔曼滤波、滑动平均、异常值剔除)的原理解析与C语言实现前…...
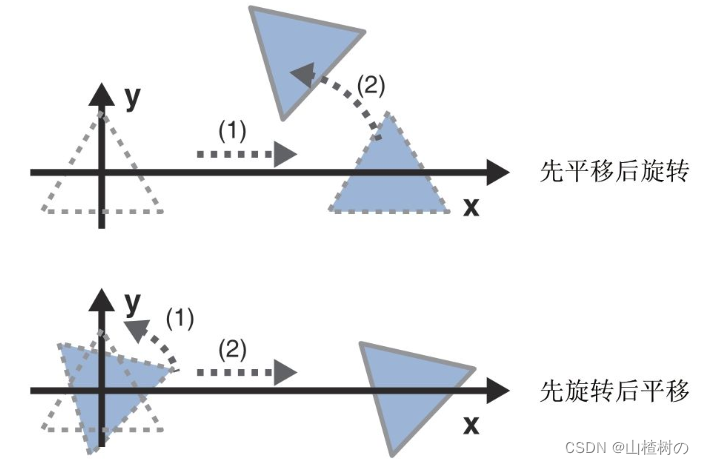
WebGL模型矩阵
前言:依赖矩阵库 WebGL矩阵变换库_山楂树の的博客-CSDN博客 先平移,后旋转的模型变换: 1.将三角形沿着X轴平移一段距离。 2.在此基础上,旋转三角形。 先写下第1条(平移操作)中的坐标方程式。 等式1&am…...

Flutter:WebSocket封装-实现心跳、重连机制
前言Permalink Flutter简介 Flutter 是 Google推出并开源的移动应用开发框架,主打跨平台、高保真、高性能。开发者可以通过 Dart语言开发 App,一套代码同时运行在 iOS 和 Android平台。 Flutter提供了丰富的组件、接口,开发者可以很快地为 F…...

c语言中:struct timespec
在C语言中,struct timespec 是一个结构体,通常用于处理时间和时间间隔。这个结构体通常包含以下两个成员: tv_sec:这是一个长整型(long),用于存储秒数。它表示时间的整数部分,即秒数…...
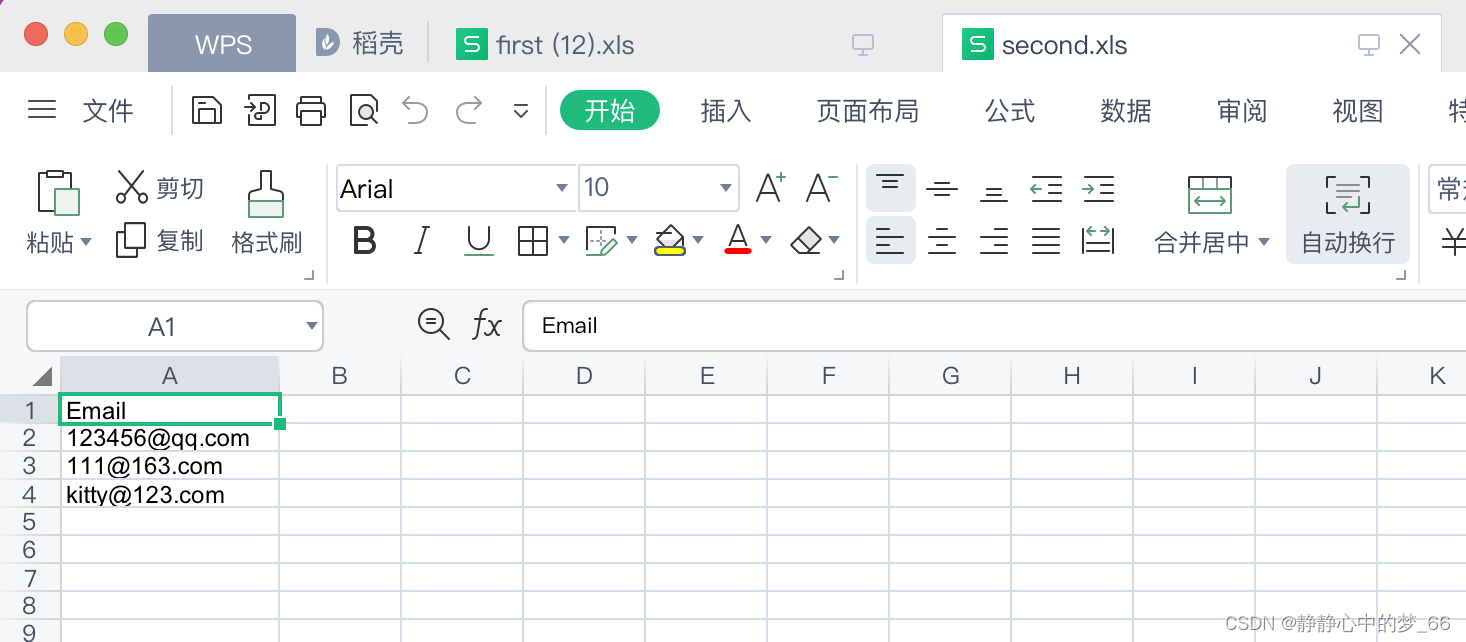
Mendix如何实现导出文件
刚刚接触Mendix低代码两周,花了一周在b站看初级视频然后考完初级,第二周开始做个列表查询感觉照葫芦画瓢没啥难度。但最近要求写个导出列表数据,在mendix社区翻了翻,这个功能算是常见的。找了mendix官方提供的Docs磕磕盼盼才实现了…...

在IIS服务器上安装SSL证书(2023配置启用HTTPS部署教程)内容来源SSL市场网
https://www.sslmarket.com.cn/146.html...

如何处理ChatGPT与用户之间的互动和反馈?
处理ChatGPT与用户之间的互动和反馈是关于改进和优化用户体验的关键方面。这涉及到在聊天、对话和交互中建立积极的用户关系,同时利用用户的反馈来不断改进ChatGPT的性能和功能。本文将探讨如何有效地处理ChatGPT与用户之间的互动和反馈,以提供更好的用户…...
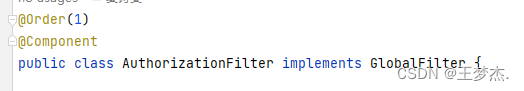
微服务-gateway鉴权
文章目录 一、前言二、gateway鉴权1、依赖配置2、编写代码3、GlobalFilter详解3.1、GlobalFilter简介3.2、GlobalFilter自定义执行顺序3.2.1、实现Order接口实现自定义执行顺序 一、前言 网关是介于客户端和服务器端之间的中间层,所有的外部请求都会先经过 网关这一…...
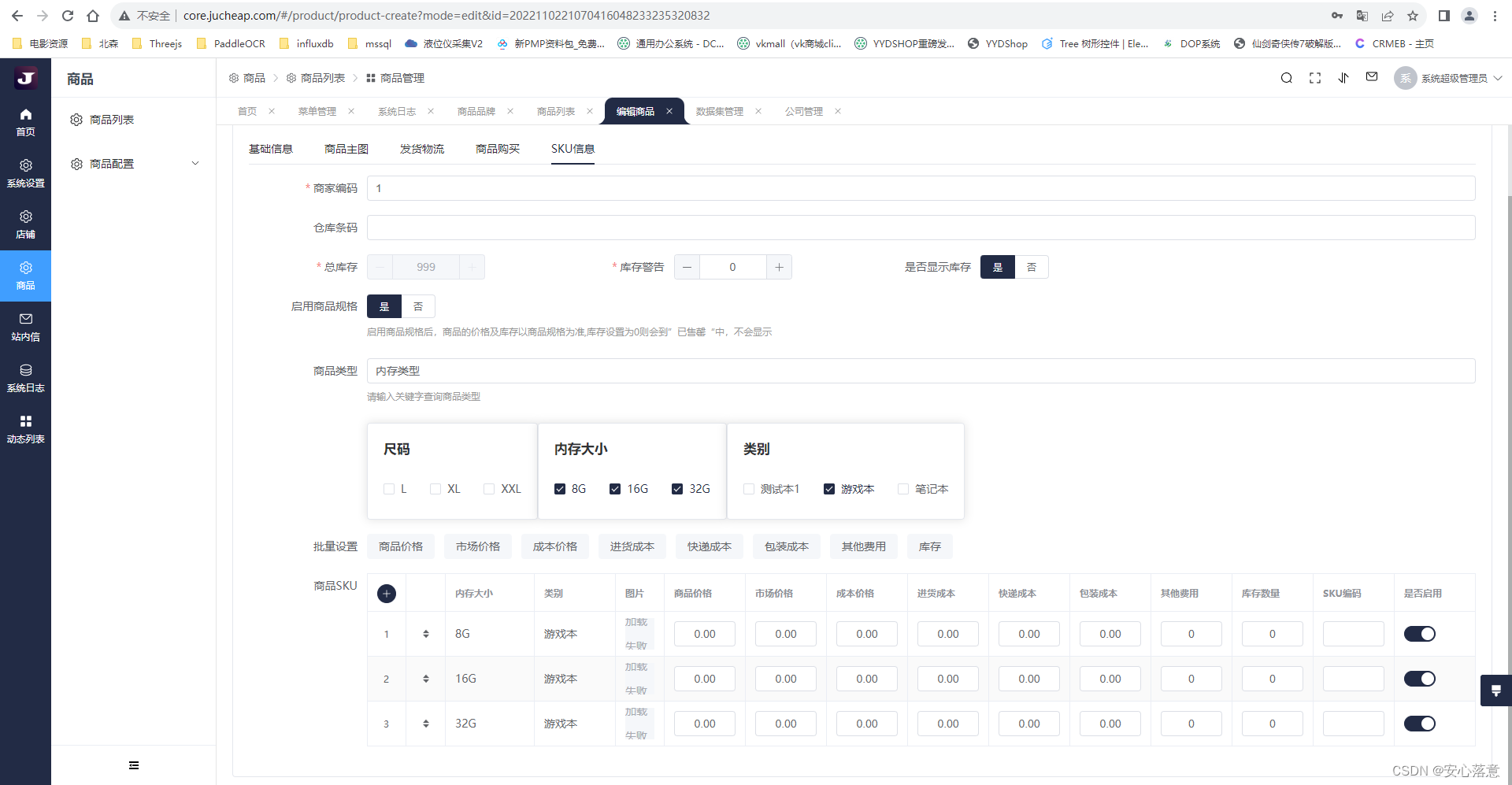
NET7快速开发一个商品管理模块-商品列表开发(一)
商品管理模块,一般包含以下几个模块: 商品列表:这里可以看到所有已发布的商品信息列表。 商品管理:添加商品、编辑商品以及删除商品。 具体功能如下图: 1.商品列表 2.添加商品 3.商品SKU编辑...
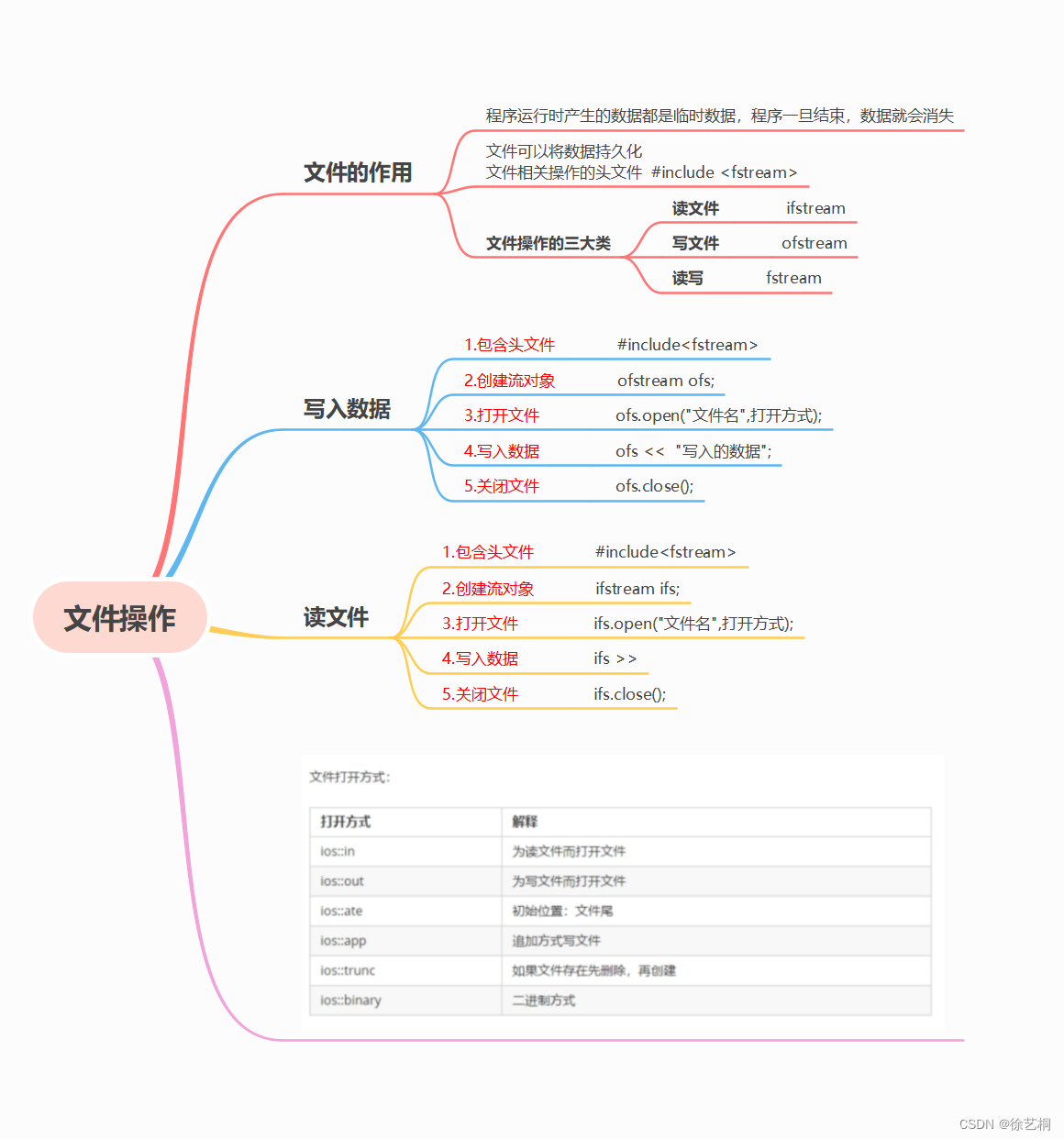
0829|C++day7 auto、lambda、C++数据类型转换、C++标准模板库(STL)、list、文件操作
一、思维导图 二、【试编程】将实例化类对象写入容器后,写入.txt文本中,再重新定义一个类容器,将.txt中的内容读取出来,输出到终端 封装一个学生的类,定义一个学生这样类的vector容器, 里面存放学生对象(至…...

SpringBoot连接MySQL数据库实例【tk.mybatis连接mysql数据库】
文章目录 一、数据库表二、引入依赖三、修改配置文件四、公共组件1、BaseController2、BaseService3、IService4、BaseMapper 五、代码1、Application2、Student实体类3、Controller4、Service5、ServiceImpl6、Mapper7、Mapper.xml 一、数据库表 CREATE TABLE student (id i…...

node基础之三:http 模块
// 1. 导入模块 const http require("http"); // 2. 创建服务 const server http.createServer((request, response) > {// 获取请求方法request.method;// 获取请求 url(只包含url中的路径和查询字符串)request.url;// 获取 HTTP 协议版…...

【高阶数据结构】AVL树 {概念及实现;节点的定义;插入并调整平衡因子;旋转操作:左单旋,右单旋,左右双旋,右左双旋;AVL树的验证及性能分析}
AVL树 一、AVL树的概念 二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,两位俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii和E.M.Landis在1962年发明…...
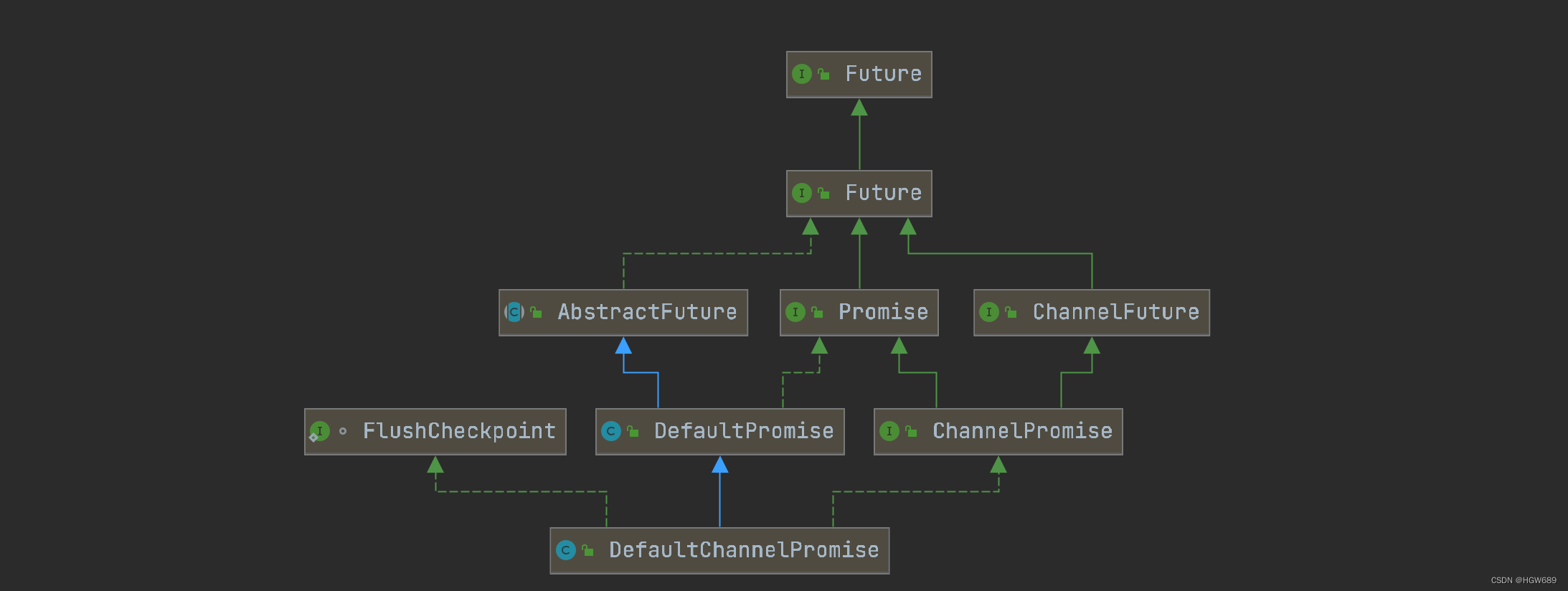
Netty—FuturePromise
Netty—Future&Promise 一、JDK原生 Future二、Netty包下的 Future三、Promise1、使用Promise同步获取结果2、使用Promise异步获取结果.3、使用Promise同步获取异常 - sync & get4、使用Promise同步获取异常 - await5、使用Promise异步获取异常 在异步处理时࿰…...

Linux链表操作全解析
Linux C语言链表深度解析与实战技巧 一、链表基础概念与内核链表优势1.1 为什么使用链表?1.2 Linux 内核链表与用户态链表的区别 二、内核链表结构与宏解析常用宏/函数 三、内核链表的优点四、用户态链表示例五、双向循环链表在内核中的实现优势5.1 插入效率5.2 安全…...
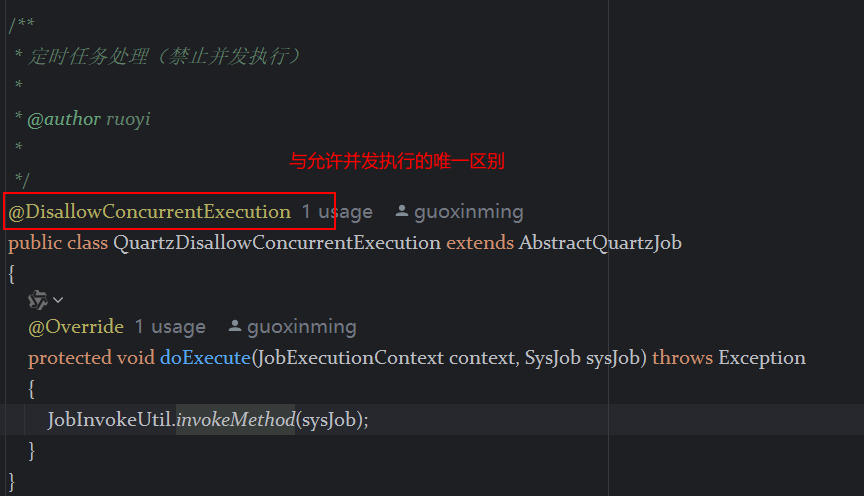
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...

Nuxt.js 中的路由配置详解
Nuxt.js 通过其内置的路由系统简化了应用的路由配置,使得开发者可以轻松地管理页面导航和 URL 结构。路由配置主要涉及页面组件的组织、动态路由的设置以及路由元信息的配置。 自动路由生成 Nuxt.js 会根据 pages 目录下的文件结构自动生成路由配置。每个文件都会对…...

Java毕业设计:WML信息查询与后端信息发布系统开发
JAVAWML信息查询与后端信息发布系统实现 一、系统概述 本系统基于Java和WML(无线标记语言)技术开发,实现了移动设备上的信息查询与后端信息发布功能。系统采用B/S架构,服务器端使用Java Servlet处理请求,数据库采用MySQL存储信息࿰…...
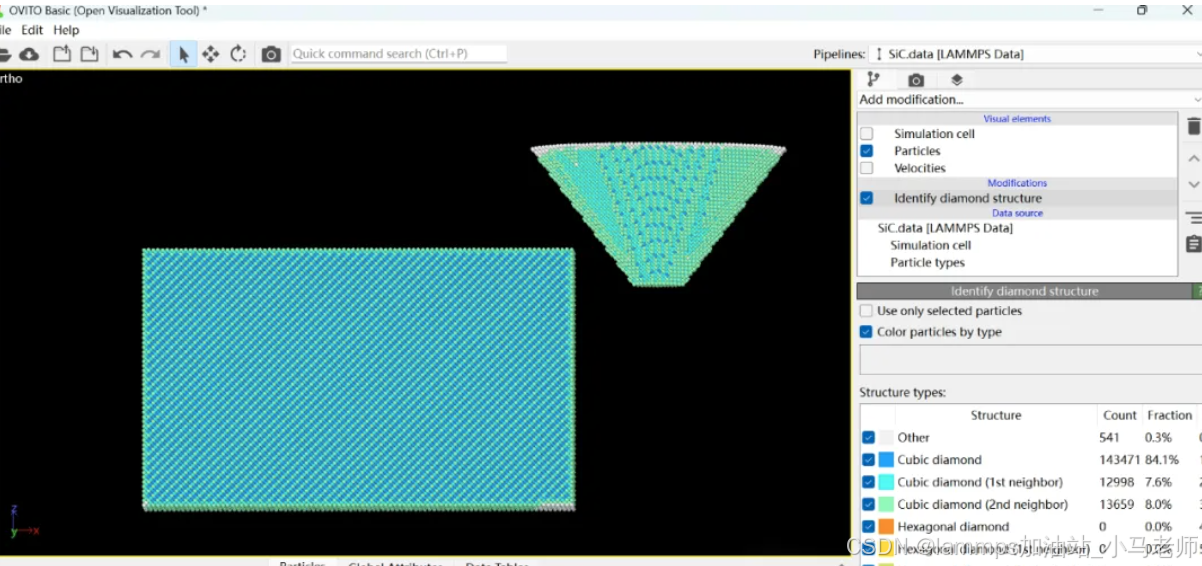
Python Ovito统计金刚石结构数量
大家好,我是小马老师。 本文介绍python ovito方法统计金刚石结构的方法。 Ovito Identify diamond structure命令可以识别和统计金刚石结构,但是无法直接输出结构的变化情况。 本文使用python调用ovito包的方法,可以持续统计各步的金刚石结构,具体代码如下: from ovito…...
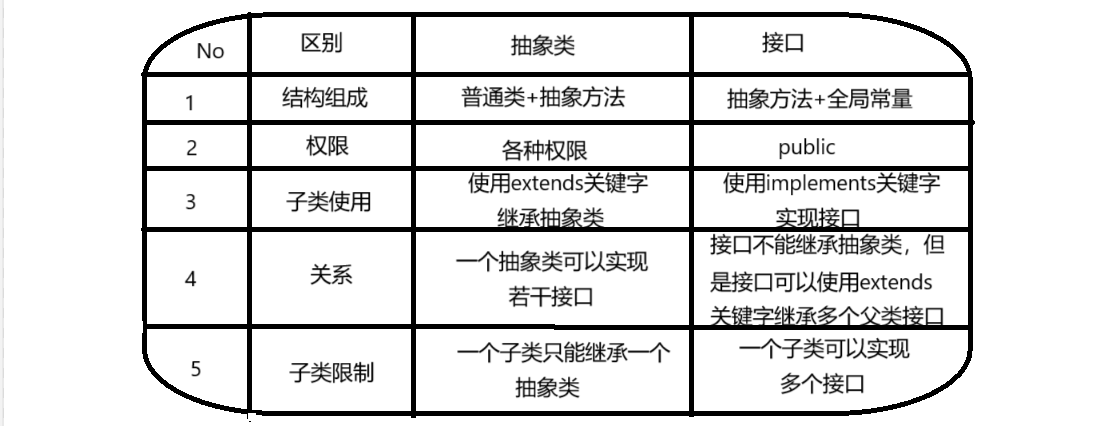
抽象类和接口(全)
一、抽象类 1.概念:如果⼀个类中没有包含⾜够的信息来描绘⼀个具体的对象,这样的类就是抽象类。 像是没有实际⼯作的⽅法,我们可以把它设计成⼀个抽象⽅法,包含抽象⽅法的类我们称为抽象类。 2.语法 在Java中,⼀个类如果被 abs…...

SQL Server 触发器调用存储过程实现发送 HTTP 请求
文章目录 需求分析解决第 1 步:前置条件,启用 OLE 自动化方式 1:使用 SQL 实现启用 OLE 自动化方式 2:Sql Server 2005启动OLE自动化方式 3:Sql Server 2008启动OLE自动化第 2 步:创建存储过程第 3 步:创建触发器扩展 - 如何调试?第 1 步:登录 SQL Server 2008第 2 步…...

绕过 Xcode?使用 Appuploader和主流工具实现 iOS 上架自动化
iOS 应用的发布流程一直是开发链路中最“苹果味”的环节:强依赖 Xcode、必须使用 macOS、各种证书和描述文件配置……对很多跨平台开发者来说,这一套流程并不友好。 特别是当你的项目主要在 Windows 或 Linux 下开发(例如 Flutter、React Na…...

前端高频面试题2:浏览器/计算机网络
本专栏相关链接 前端高频面试题1:HTML/CSS 前端高频面试题2:浏览器/计算机网络 前端高频面试题3:JavaScript 1.什么是强缓存、协商缓存? 强缓存: 当浏览器请求资源时,首先检查本地缓存是否命中。如果命…...

算术操作符与类型转换:从基础到精通
目录 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 算术操作符超级详解 算术操作符:、-、*、/、% 赋值操作符:和复合赋值 单⽬操作符:、--、、- 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 在先前的文…...
