MySQL 高级语句 Part1(进阶查询语句+MySQL数据库函数+连接查询)
高级语句 第一部分
- 一、MySQL进阶查询语句
- 1.1 select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
- 1.2 distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录
- 1.3 where ----有条件查询
- 1.4 and or ----且 或
- 1.5 in----显示已知的值的数据记录
- 1.6 between----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
- 1.7 通配符
- 1.8 like ----模糊匹配
- 1.9 order by
- 1.10 group by ----汇总分组
- 1.11 having
- 1.12 别名 ----字段別名 表格別名
- 1.13 子查询语句
- 1.14 exists
- 1.15 练习
- 二、MySQL数据库函数
- 2.1 数学函数
- 2.2 聚合函数
- 2.3 字符串函数
- 1)trim
- 2)concat
- 3)substr
- 4)length
- 5)replace
- 三、连接查询
- 3.1 表连接
- 3.2 union语句
- 3.3 多表查询之求交集值
- 3.4 多表查询之求无交集值
- 四、SQL语句执行顺序
- 小结
一、MySQL进阶查询语句
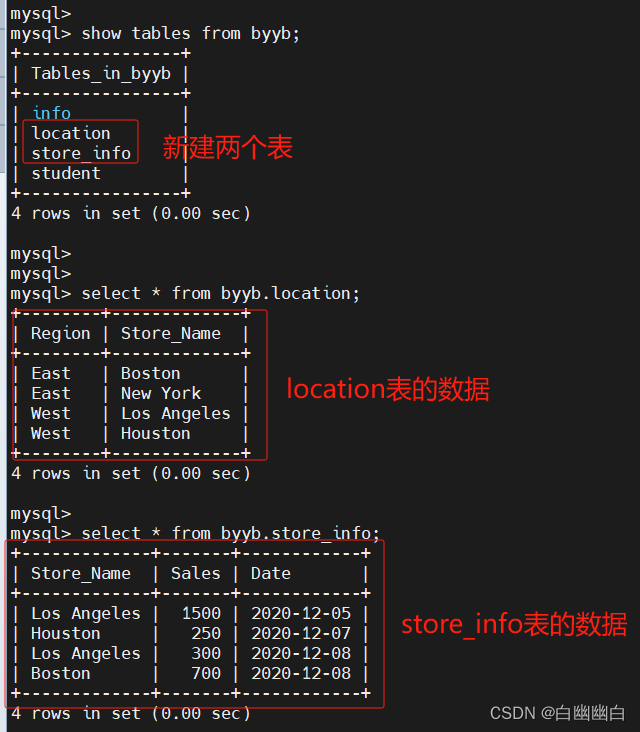
先建立byyb数据库,再建立location 表和Store_Info 表,用于测试和演示。
create database byyb;use byyb;
create table location (Region char(20),Store_Name char(20));
insert into location values('East','Boston');
insert into location values('East','New York');
insert into location values('West','Los Angeles');
insert into location values('West','Houston');create table store_info (Store_Name char(20),Sales int(10),Date char(10));
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','1500','2020-12-05');
insert into store_info values('Houston','250','2020-12-07');
insert into store_info values('Los Angeles','300','2020-12-08');
insert into store_info values('Boston','700','2020-12-08');
1.1 select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录
语法
select "字段" from "表名";
举个例子
select * from store_info;
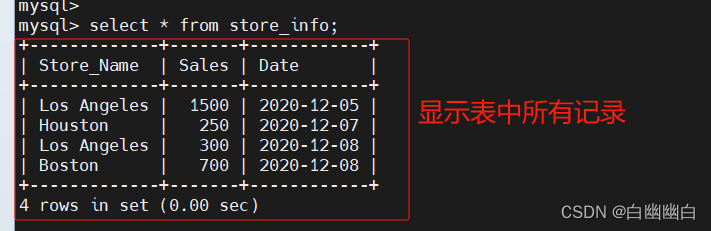
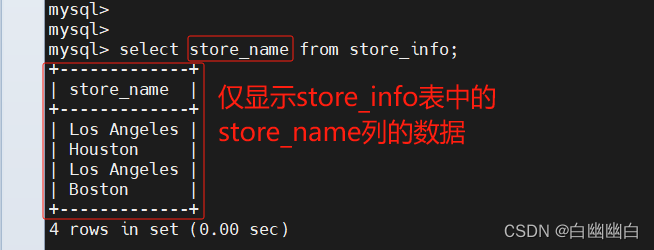
select store_name from store_info;
1.2 distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录
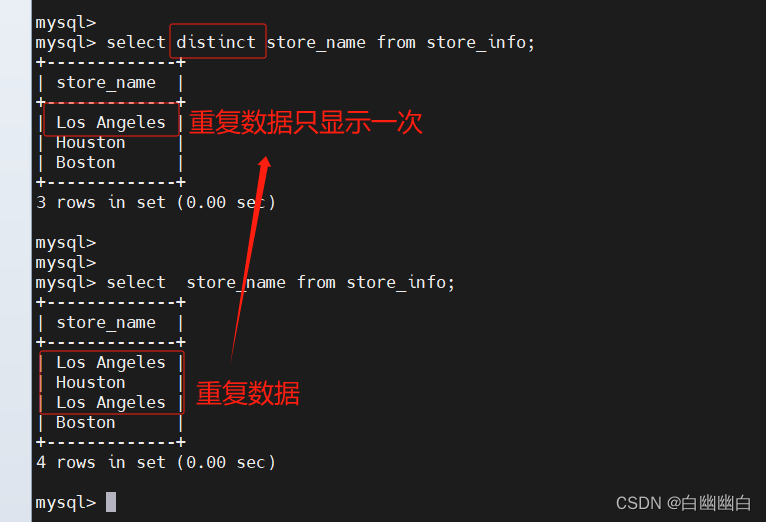
语法
select distinct "字段" from "表名"
#举个例子
select distinct store_name from store_info;
1.3 where ----有条件查询
where是对源语句进行条件查询。
语法
select "字段" from "表名" where "条件";
#举个例子
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000;
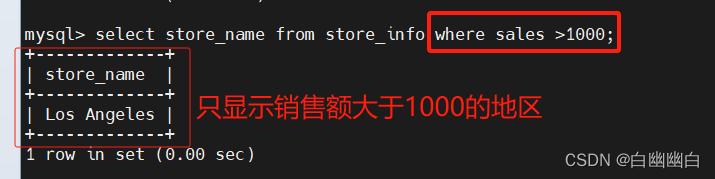
1.4 and or ----且 或
语法
select "字段" from "表名" where "条件1" {[and|or] "条件2"}+ ;
#举个例子
select store_name from store_info where sales > 1000 or (sales < 500 and sales > 200);
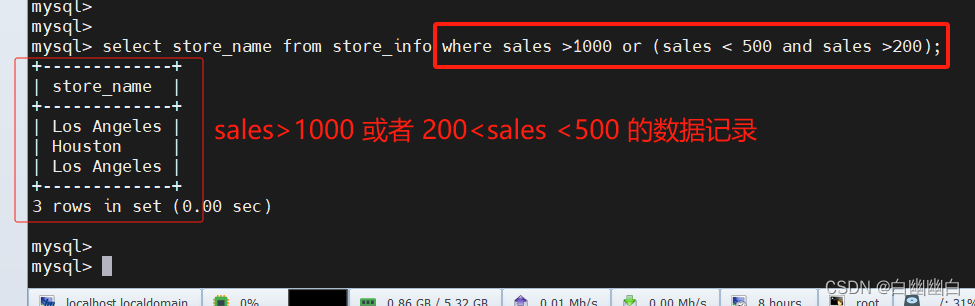
1.5 in----显示已知的值的数据记录
语法
select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" in ('值1', '值2', ...);
#举个例子
select * from store_info where store_name in ('los angeles', 'houston');
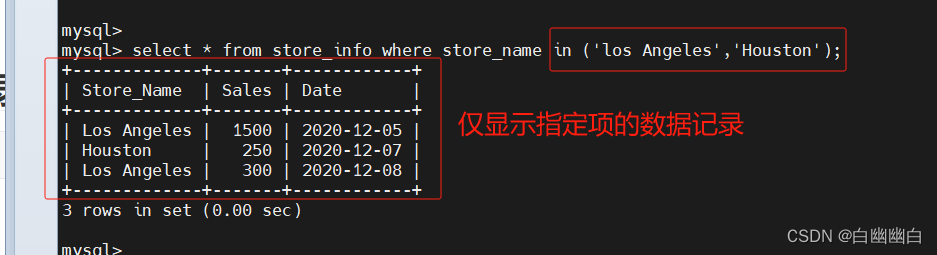
1.6 between----显示两个值范围内的数据记录
语法:select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" between '值1' and '值2';
#举个例子
select * from store_info where date between '2020-12-06' and '2020-12-10';
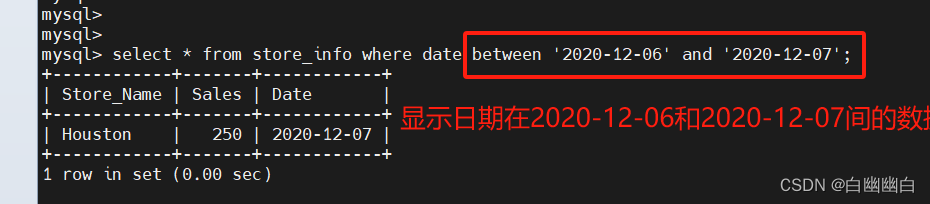
1.7 通配符
% :百分号表示零个、一个或多个字符
_ :下划线表示单个字符'A_Z':所有以 'A' 起头,另一个任何值的字符,且以 'Z' 为结尾的字符串。例如,'ABZ' 和 'A2Z' 都符合这一个模式,而 'AKKZ' 并不符合 (因为在 A 和 Z 之间有两个字符,而不是一个字符)。
'ABC%': 所有以 'ABC' 起头的字符串。例如,'ABCD' 和 'ABCABC' 都符合这个模式。
'%XYZ': 所有以 'XYZ' 结尾的字符串。例如,'WXYZ' 和 'ZZXYZ' 都符合这个模式。
'%AN%': 所有含有 'AN'这个模式的字符串。例如,'LOS ANGELES' 和 'SAN FRANCISCO' 都符合这个模式。
'_AN%':所有第二个字母为 'A' 和第三个字母为 'N' 的字符串。例如,'SAN FRANCISCO' 符合这个模式,而 'LOS ANGELES' 则不符合这个模式。
1.8 like ----模糊匹配
一般和通配符配合使用。
模糊匹配默认会扫描全表,索引不生效。
语法
select "字段" from "表名" where "字段" like {模式};
#举个例子
select * from store_info where store_name like '%os%';

1.9 order by
按关键字排序
语法
select "字段" from "表名" [where "条件"] order by "字段" [asc, desc];
#asc 是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式。
#desc 是按降序方式进行排序。
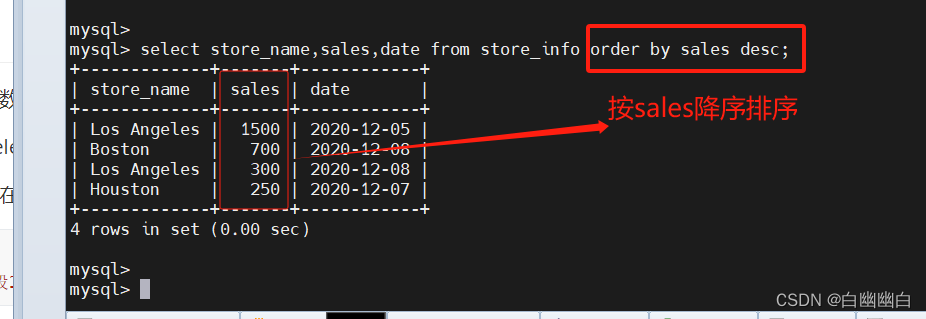
#举个例子
select store_name,sales,date from store_info order by sales desc;
1.10 group by ----汇总分组
对group by后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的。
group by 有一个原则,凡是在 group by 后面出现的字段,必须在 select 后面出现;
凡是在 select 后面出现的、且未在聚合函数中出现的字段,必须出现在 group by 后面。
语法
select "字段1", sum("字段2") from "表名" group by "字段1";
举个例子
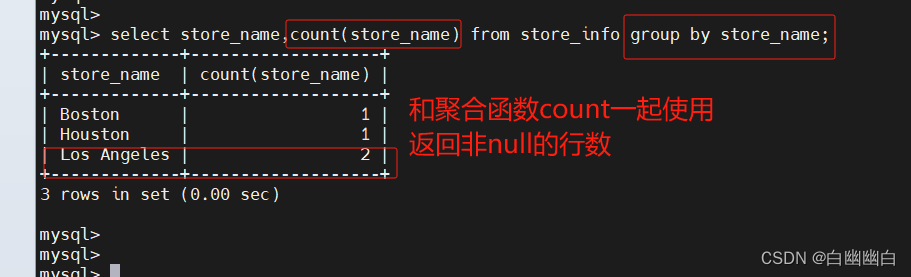
select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name order by sales desc;

select store_name,count(store_name) from store_info group by store_name;
1.11 having
对group by语句的结果,进行条件筛选。
用来过滤由 group by 语句返回的记录集,通常与 group by 语句联合使用.
having 语句的存在弥补了 where 关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
语法
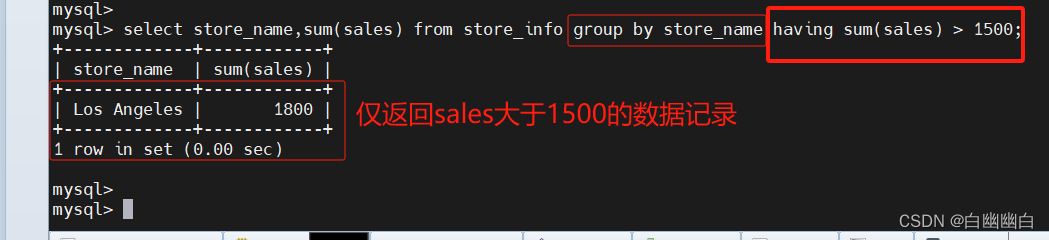
select "字段1", sum("字段2") from "表格名" group by "字段1" having (函数条件);
#举个例子
select store_name, sum(sales) from store_info group by store_name having sum(sales) > 1500;
1.12 别名 ----字段別名 表格別名
as可省略,仅在当前SQL语句生效。
语法
select "表格別名"."字段1" [as] "字段別名" from "表格名" [as] "表格別名";
#举个例子
select a.store_name store, sum(a.sales) as "total sales" from store_info as a group by a.store_name;

1.13 子查询语句
连接表格,在where 子句或 having 子句中插入另一个 sql 语句。
语法
select "字段1" from "表格1" where "字段2" [比较运算符] (select "字段1" from "表格2" where "条件");
#外查询 (#内查询)
#内查询的结果,作为外查询的参数[比较运算符]
#可以是符号的运算符,例如 =、>、<、>=、<=
#也可以是文字的运算符,例如 like、in、between
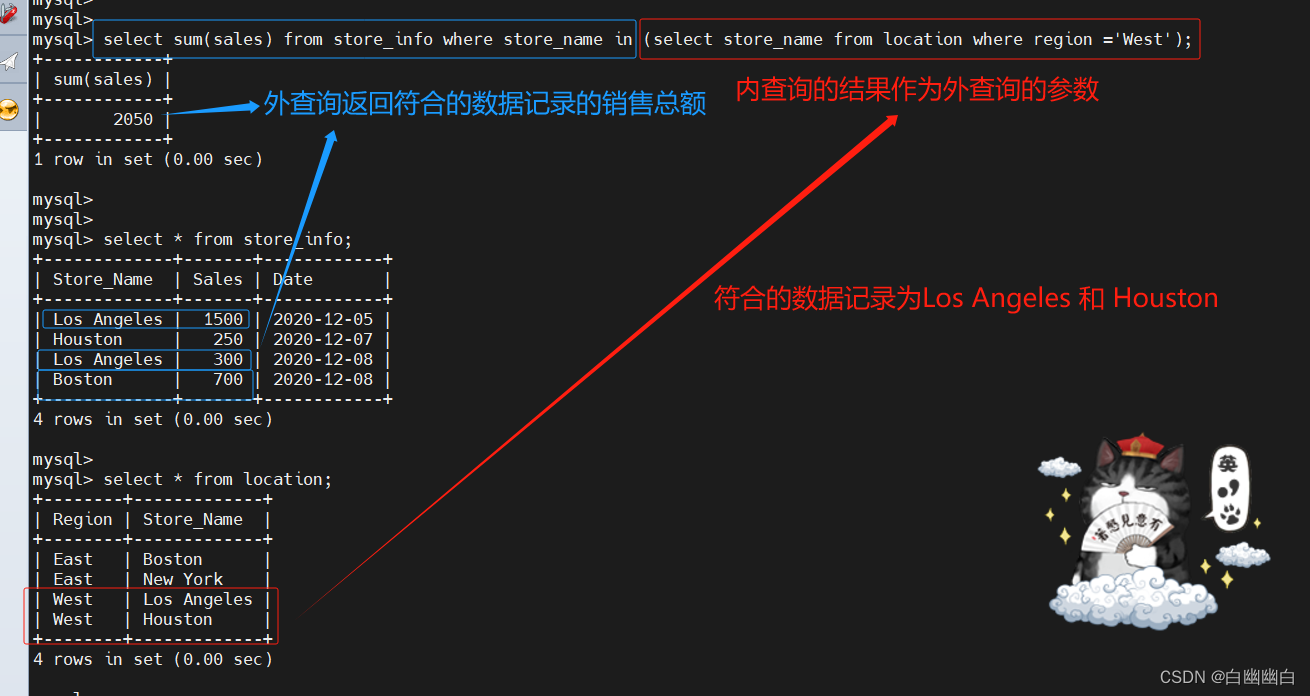
#举个例子
select sum(sales) from store_info where store_name in (select store_name from location where region = 'West');
#举个例子2
select sum(A.sales) from store_info as A where A.store_name in (select store_name from location as B where B.store_name = A.store_name);
#store_info表 别名为A表,在当前语句中,可以直接用a代替store_info使用
#location表 别名为B表

1.14 exists
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果。
如果有,系统就会执行外查询中的sql语句;
如果没有,那整个 SQL语句就不会产生任何结果。
语法
select "字段1" from "表格1" where exists (select * from "表格2" where "条件";
#举个例子
select sum(sales) from store_info where exists (select * from location where region = 'West');select sum(sales) from store_info where exists (select store_name from location where region ='Westt');

1.15 练习
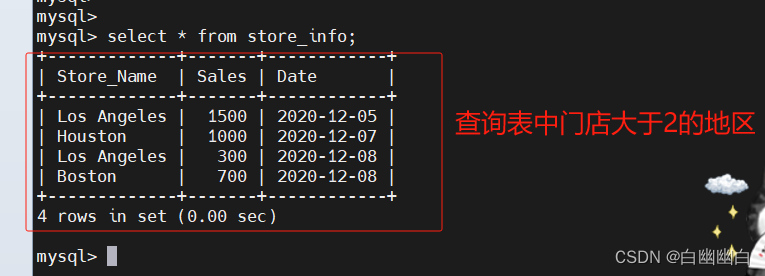
通过SQL语句,查找到门店数大于等于2的地区
group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2;select store_name from store_info group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2;select store_name,count(store_name) from store_info group by store_name having count(store_name) >=2;

二、MySQL数据库函数
2.1 数学函数
| 数学函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | 返回 x 的绝对值 |
| rand() | 返回 0 到 1 的随机数 |
| mod(x,y) | 返回 x 除以 y 以后的余数 |
| power(x,y) | 返回 x 的 y 次方 |
| round(x) | 返回离 x 最近的整数 |
| round(x,y) | 保留 x 的 y 位小数四舍五入后的值 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回 x 的平方根 |
| truncate(x,y) | 返回数字 x 截断为 y 位小数的值 |
| ceil(x) | 返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数 |
| floor(x) | 返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数 |
| greatest(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最大的值,也可以返回多个字段的最大的值 |
| least(x1,x2…) | 返回集合中最小的值,也可以返回多个字段的最小的值 |
select abs(-1), rand(), mod(5,3), power(2,3), round(1.89);
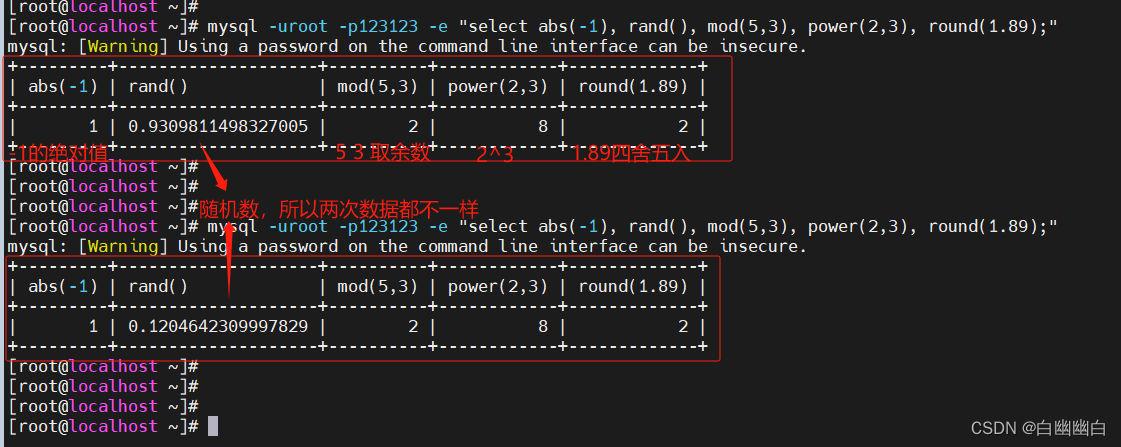
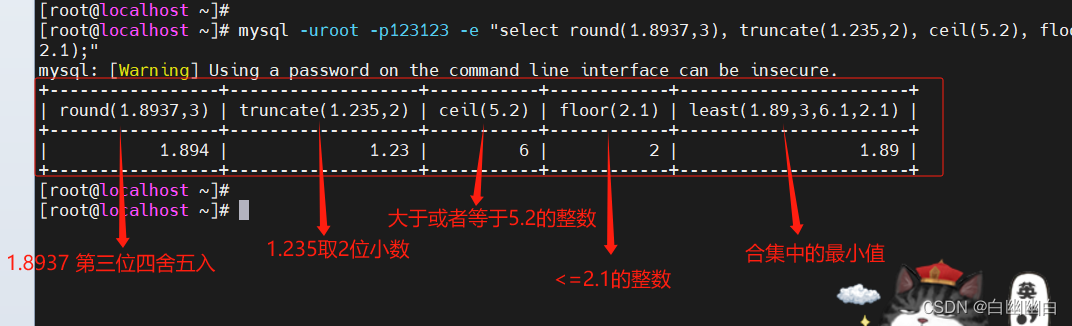
select round(1.8937,3), truncate(1.235,2), ceil(5.2), floor(2.1), least(1.89,3,6.1,2.1);
2.2 聚合函数
| 聚合函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| avg() | 返回指定列的平均值 |
| count( 字段 ) | 返回指定列中非 NULL 值的个数(行数) |
| count(*) | 返回指定列中所有行数,不忽略NULL值 |
| min( ) | 返回指定列的最小值 |
| max( ) | 返回指定列的最大值 |
| sum(x) | 返回指定列的所有值之和 |
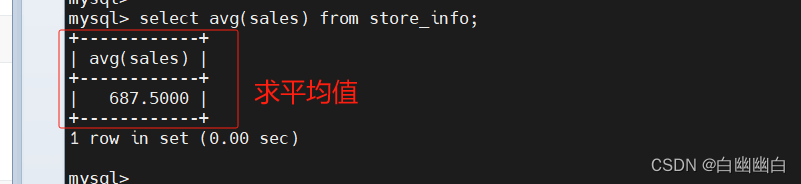
avg
select avg(sales) from store_info;
count
select count(store_name) from store_info;
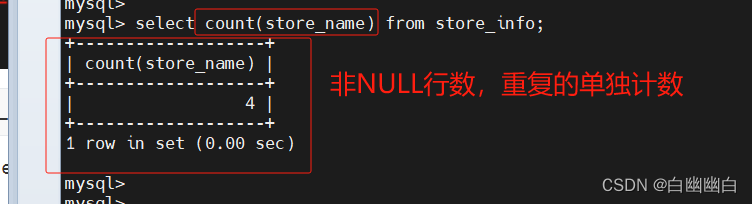
select count(distinct store_name) from store_info;
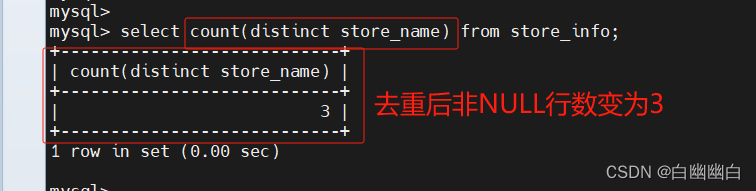
max 和 min
select max(sales) from store_info;
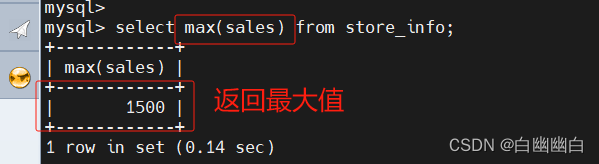
select min(sales) from store_info;
sum
select sum(sales) from store_info;
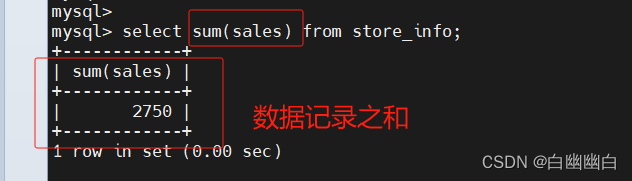
2.3 字符串函数
| 字符串函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| trim() | 返回去除指定格式的值 |
| concat(x,y) | 将提供的参数 x 和 y 拼接成一个字符串 |
| substr(x,y) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始的字符串,跟substring()函数作用相同 |
| substr(x,y,z) | 获取从字符串 x 中的第 y 个位置开始长度为 z 的字符串 |
| length(x) | 返回字符串 x 的长度 |
| replace(x,y,z) | 替换,将字符串 z 替代字符串 x 中的字符串 y |
| upper(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成大写字母 |
| lower(x) | 将字符串 x 的所有字母变成小写字母 |
| left(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的前 y 个字符 |
| right(x,y) | 返回字符串 x 的后 y 个字符 |
| repeat(x,y) | 将字符串 x 重复 y 次 |
| space(x) | 返回 x 个空格 |
| strcmp(x,y) | 比较 x 和 y,返回的值可以为-1,0,1 |
| reverse(x) | 将字符串 x 反转 |
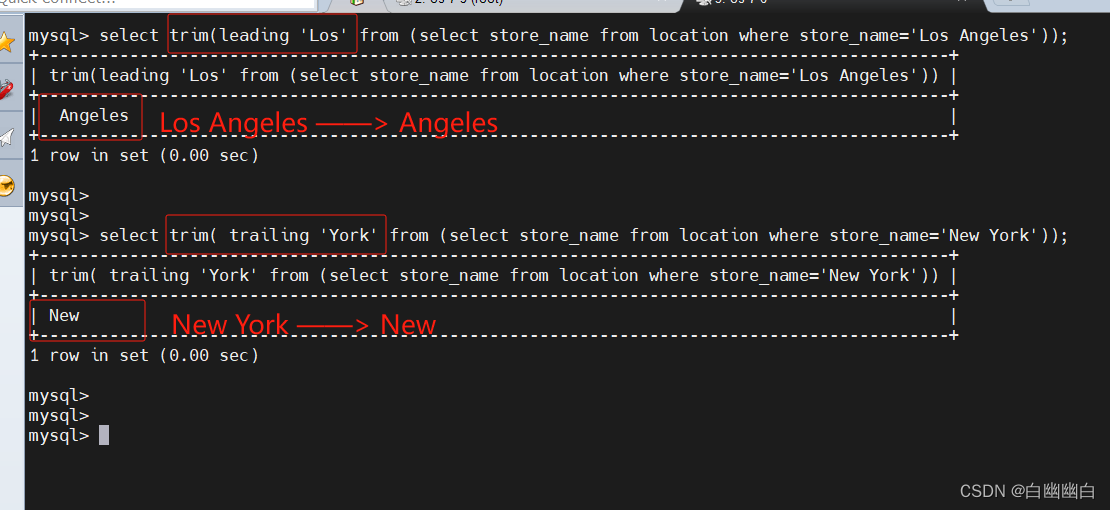
1)trim
#示例1:从名字开头的开始,移除Sun Dasheng中的Sun显示
select trim(leading ‘Sun’ from ‘Sun Dasheng’);
select trim([ [位置] [要移除的字符串] from ] 字符串);
#[位置]:的值可以为 leading (起头), trailing (结尾), both (起头及结尾)。
#[要移除的字符串]:从字串的起头、结尾,或起头及结尾移除的字符串。缺省时为空格。
#子查询语句,select 嵌套selectselect trim(leading 'Los' from (select store_name from location where store_name='Los Angeles'));select trim( trailing 'York' from (select store_name from location where store_name='New York'));
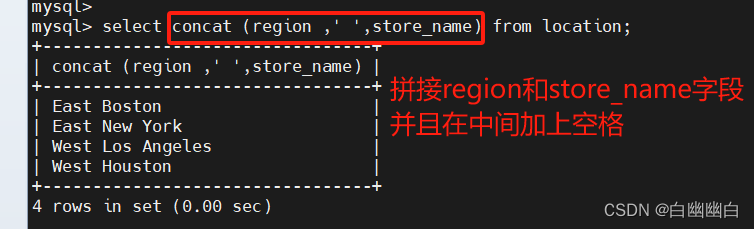
2)concat
字段名 不要加 ' '
字符串 要加' '
select concat (region ,' ',store_name) from location;
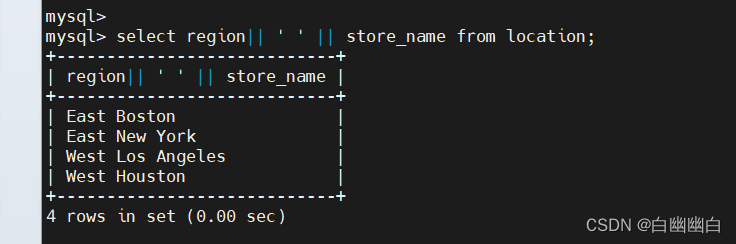
select region|| ' ' || store_name from location;
3)substr
select substr(store_name,5) from location where store_name ='Los Angeles';select substr(store_name,5,6) from location where store_name ='Los Angeles';
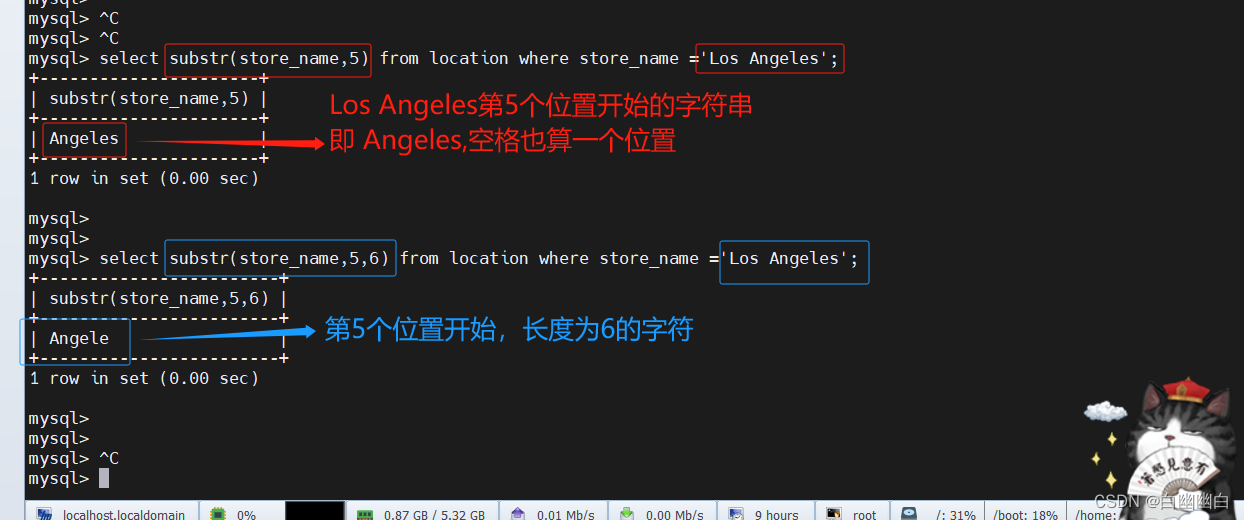
4)length
select replace(region,'stern','st'),store_name,length(store_name) from location;

5)replace
select replace (region,'st','stern') from location;

三、连接查询
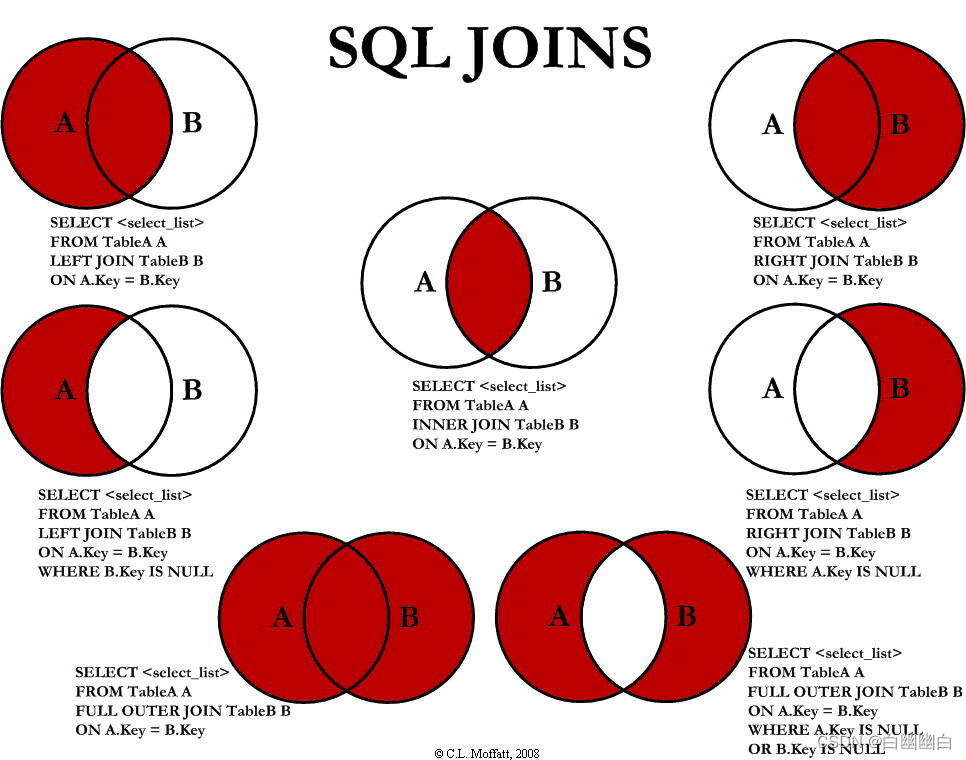
3.1 表连接
| 表连接 | 概述 | |
|---|---|---|
| inner join | 内连接 | 只返回两个表中联结字段相等的行记录 |
| left join | 左连接 | 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录,不相等的部分返回NULL |
| right join | 右连接 | 返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联结字段相等的记录,不相等的部分返回NULL |
| union | 联集 | 将两个select查询语句的结果合并,并去重 |
| union all | 联集 | 将两个select查询语句的结果合并,不去重 |
3.2 union语句
联集,将两个sql语句的结果合并起来,两个sql语句所产生的字段需要是同样的数据记录种类。
union :生成结果的数据记录值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序。
语法
[select 语句 1] union [select 语句 2];
select store_name from location union select store_name from store_info;

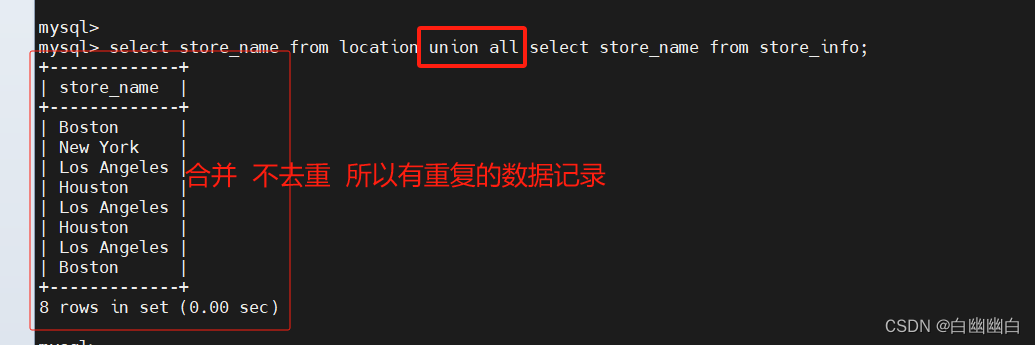
union all :将生成结果的数据记录值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法
[select 语句 1] union all [select 语句 2];
select store_name from location union all select store_name from store_info;
3.3 多表查询之求交集值
取两个SQL语句结果的交集。
基本语法
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段;
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B using(同名字段);select A.字段 from 左表 A, 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段;select A.字段 from 左表 A where A.字段 in (select B.字段 from 右表 B);select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is not null;
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is not null;
举个例子
#求交集
#方式一
select A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;

#方式二
select A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B using (store_name);

#取两个SQL语句结果的交集,且没有重复
select distinct A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B on A.store_name = B.store_name;select distinct A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B using (store_name);
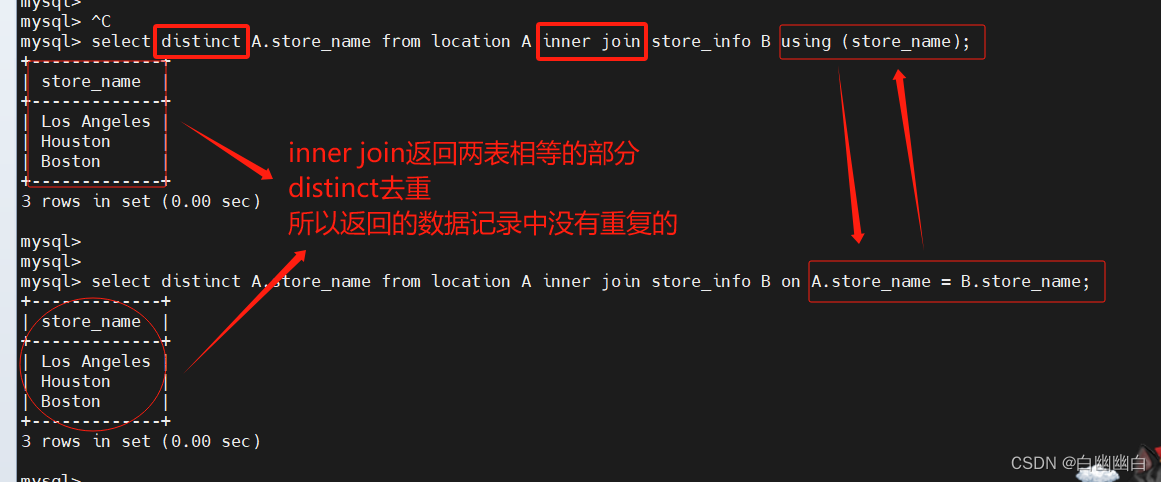
select distinct A.store_name from location A inner join store_info B using (store_name) where B.store_name is not NULL;
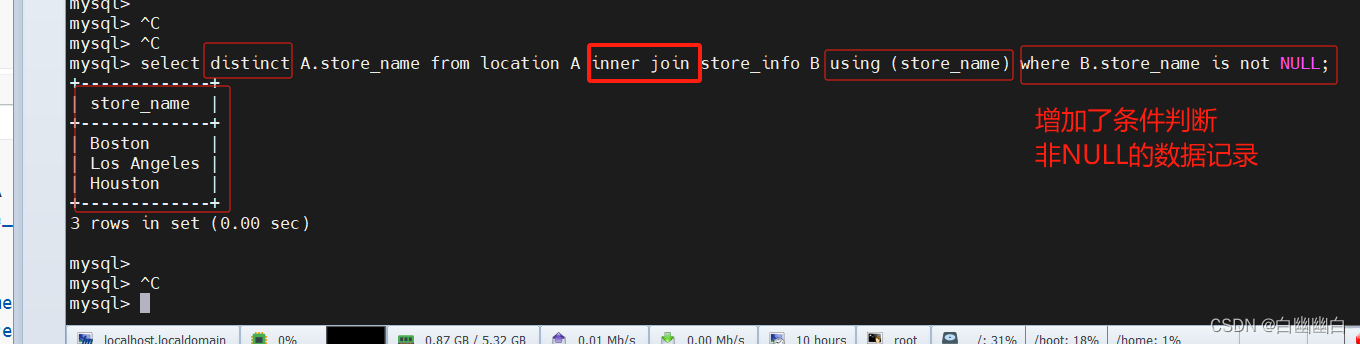
select A.store_name from (select B.store_name from location B inner join store_info C on B.store_name = C.store_name) A group by A.store_name;

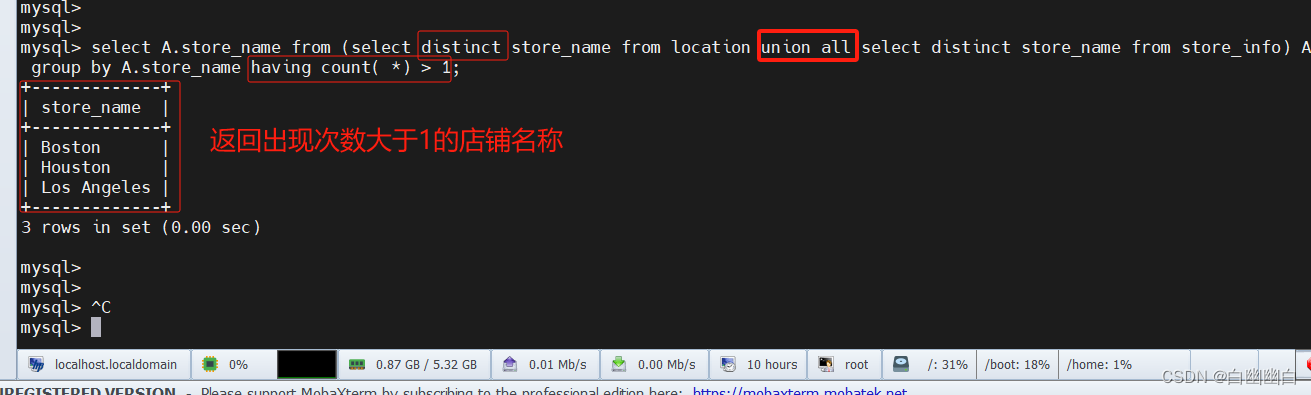
select A.store_name from (select distinct store_name from location union all select distinct store_name from store_info) A group by A.store_name having count( *) > 1;。#首先,子查询`select distinct store_name from location`从“location”表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。
#然后,子查询`select distinct store_name from store_info`从“store_info”表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。
#使用`union all`将两个子查询的结果合并,并作为临时表A。
#最后,对临时表A按照店铺名称进行分组,使用`having count(*) > 1`筛选出出现次数大于1的店铺名称。
3.4 多表查询之求无交集值
显示第一个SQL语句的结果,且与第二个SQL语句没有交集的结果,且没有重复。
求左表无交集
select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is null;select 字段 from 左表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 右表);求右表无交集
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is null;select 字段 from 右表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 左表);求多表的无交集
select A.字段 from (select distinct 字段 from 左表 union all select distinct 字段 from 右表) A group by A.字段 having count(A.字段)=1;
举个例子
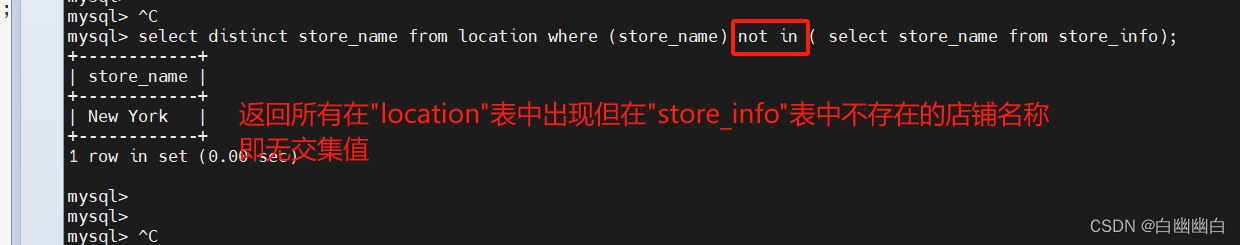
select distinct store_name from location where (store_name) not in ( select store_name from store_info);#子查询`select store_name from store_info`从"store_info"表中选择所有的店铺名称。
#主查询`select distinct store_name from location`从"location"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。
#使用`where (store_name) not in`条件将主查询中的店铺名称过滤掉那些在子查询结果中出现的店铺名称。
select distinct A.store_name from location A left join store_info B using (store_name) where B.store_name is NULL;#使用`left join`将"location"表(作为左表,记为A)和"store_info"表(作为右表,记为B)按照店铺名称进行连接。
#使用`using (store_name)`条件指定以店铺名称为连接的字段。
#使用`where B.store_name is NULL`条件过滤掉在连接结果中,店铺名称在"location"表中出现但在"store_info"表中没有匹配的记录。
#最后,使用`distinct`关键字来返回不重复的店铺名称。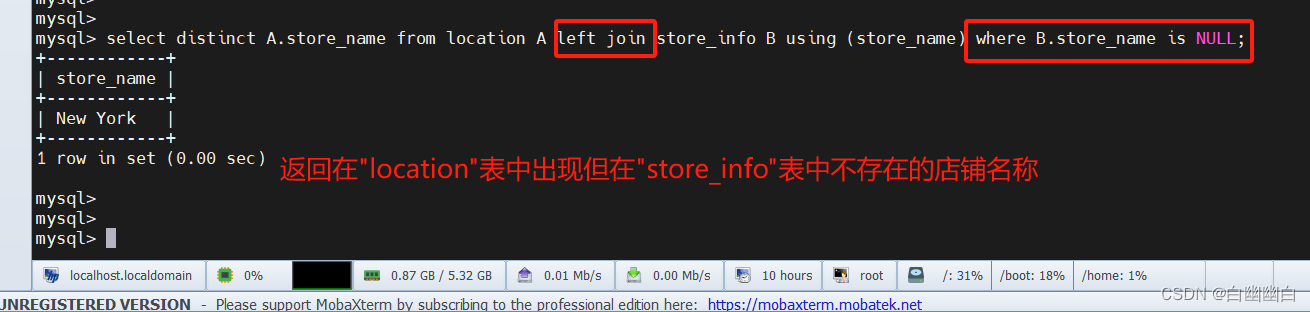
select A.store_name from (select distinct store_name from location union all select distinct store_name from store_info) as A group by A.store_name having count(*)=1;#子查询`select distinct store_name from location`从"location"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。
#子查询`select distinct store_name from store_info`从"store_info"表中选择所有不重复的店铺名称。
#使用`union all`将两个子查询的结果合并。
#将合并结果作为临时表A,并使用`as A`来给临时表起一个别名。
#在临时表A的基础上,使用`group by A.store_name`对店铺名称进行分组。
#使用`having count(*) = 1`筛选出出现次数为1的店铺名称。
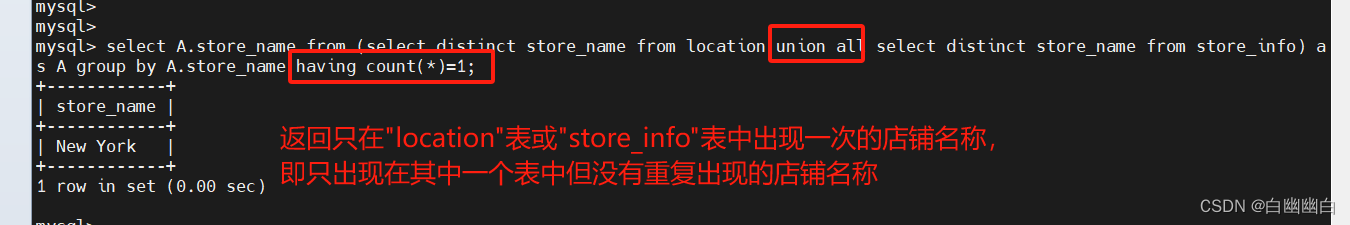
四、SQL语句执行顺序
FROM
<left table>ON
<join_condition>
<join_type>JOIN
<right_table>WHERE
<where condition>GROUP BY
<group_by_list>HAVING
<having_condition>SELECTDISTINCT
<select list>ORDER BY
<order_by_condition>LIMIT
<limit number>########################################################################################################
在SQL中,一般而言,SQL查询语句的执行顺序如下:1. FROM:指定要查询的数据表或视图。
2. JOIN:根据指定的条件连接多个表。
3. WHERE:基于指定的条件筛选出符合要求的行。
4. GROUP BY:按照指定的列进行分组。
5. HAVING:对分组后的结果进行条件筛选。
6. SELECT:选择要返回的列。
7. DISTINCT:去除重复的行。
8. ORDER BY:按照指定的列进行排序。
9. LIMIT/OFFSET:限制返回的结果数量和起始位置。
小结
order by 字段 ASC|DESC #排序
group by 字段 #分组
group by 字段 having 条件表达式 #根据group by分组后的结果再进行条件过滤表连接
inner join 内连接,只返回两个表的字段相等的行记录
left join 左连接,返回左表所有的行记录和右表字段相等的行记录,不相等的行返回NULL
right join 右连接,返回右表所有的行记录和左表字段相等的行记录,不相等的行返回NULL
union 联集,将两个select查询语句的结果合并,并去重
union all 联集,将两个select查询语句的结果合并,不去重求交集
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段;
select A.字段 from 左表 A inner join 右表 B using(同名字段);select A.字段 from 左表 A, 右表 B where A.字段 = B.字段;select A.字段 from 左表 A where A.字段 in (select B.字段 from 右表 B);select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is not null;
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is not null;求左表无交集
select A.字段 from 左表 A left join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where B.字段 is null;select 字段 from 左表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 右表);求右表无交集
select B.字段 from 左表 A right join 右表 B on A.字段 = B.字段 where A.字段 is null;select 字段 from 右表 where 字段 not in (select 字段 from 左表);求多表的无交集
select A.字段 from (select distinct 字段 from 左表 union all select distinct 字段 from 右表) A group by A.字段 having count(A.字段)=1;
相关文章:

MySQL 高级语句 Part1(进阶查询语句+MySQL数据库函数+连接查询)
高级语句 第一部分 一、MySQL进阶查询语句1.1 select ----显示表格中一个或数个字段的所有数据记录1.2 distinct ----不显示重复的数据记录1.3 where ----有条件查询1.4 and or ----且 或1.5 in----显示已知的值的数据记录1.6 between----显示两个值范围内的数据记录1.7 通配符…...

Rust免杀 Shellcode加载与混淆2
前言 这是半年前我学习Rust和免杀时的一些记录,最近打开知识库看到了这篇半年前的笔记,并且发现我常逛的安全社区都比较少有人分享Rust以及Rust免杀的帖子,于是想着将这篇笔记分享出来供大家参考和指正。由于我写这篇文章时也刚刚开始接触Ru…...

牛客java训练题 day1
9.24 day1 Q 1. this 指针是用来干什么的? 2.基类和派生类分别是指什么? 3.为什么方法中不能写静态变量 4. 解释一下ASCII码和ANSI码和两者的区别 5.简述j ava.io java.sql java.awt java.rmi 分别是什么类型的包 6. 看下面一段代码:…...
接口测试练习步骤
在接触接口测试过程中补了很多课, 终于有点领悟接口测试的根本; 偶是个实用派~,那么现实中没有用的东西,基本上我都不会有很大的概念; 下面给的是接口测试的统一大步骤,其实就是让我们对接口…...

Qt/C++音视频开发56-udp推流和拉流/组播和单播推流
一、前言 之前已经实现了rtsp/rtmp推流,rtsp/rtmp/hls/flv/ws-flv/webrtc等拉流,这种一般都需要依赖一个独立的流媒体服务程序,有没有一种更便捷的方式不需要这种依赖,然后又能实现推拉流呢,当然有的那就是udpp推流&a…...

人工智能轨道交通行业周刊-第61期(2023.9.18-9.24)
本期关键词:焊线机器人、智能综合运维管理系统、信号平面图、铁路部门架构、书生浦语大模型 1 整理涉及公众号名单 1.1 行业类 RT轨道交通人民铁道世界轨道交通资讯网铁路信号技术交流北京铁路轨道交通网上榜铁路视点ITS World轨道交通联盟VSTR铁路与城市轨道交通…...

for...in 和 for...of 的区别
for...in 和 for...of 都是 JavaScript 中的循环语句,但它们的作用和使用方式略有不同。 1、for..in 循环 for..in 循环用于遍历对象的可枚举属性,它会将对象的每个属性名称(或键名)作为迭代变量来遍历。 以下是 for...in 的基本语法 for (variable …...

高并发系统 - 接口幂等技术方案,高可用系统架构与技术选型
幂等概念来自于数学,在计算机科学中,幂等表示一次后、或多次请求某一资源,应该有同样的影响效果。 在业务表现上一般是同样的数据效果,下面就常用的业务场景,来聊聊幂等的技术方案。 ----------------- 数据层 ----------------- 索引与事务 根据业务需要,给表添加唯一索…...
简单的手机电脑无线传输方案@固定android生成ftp的IP地址(android@windows)
文章目录 abstractwindows浏览android文件环境准备客户端软件无线网络链接步骤其他方法 手机浏览电脑文件公网局域网everythingpython http.server 高级:固定android设备IP准备检查模块是否生效 windows 访问ftp服务器快捷方式命令行方式双击启动方式普通快捷方式映射新的网络位…...
Unity3D 检测鼠标位置的Sprite像素颜色
思路 获取鼠标所在屏幕坐标(Vector2)通过相机ScreenToWorldPoint(Vector3)转为世界坐标 (注意Vector3的z是距离相机的距离,相机需要正交)通过SpriteRenderer访问边界Bounds通过Bounds.Contain检测世界坐标是否在SpriteBounds内通过比例计算来确定在Sprite内的UV坐标…...

layui input 监听事件
//监听表单单选框复选框选择 form.on(radio, function (data) { console.log(data.value); //得到被选中的值 }); //监听表单下拉菜单选择 form.on(select, function (data) { console.log(data.value); //得到被选中的值 }); //监听表单复选框选择 …...
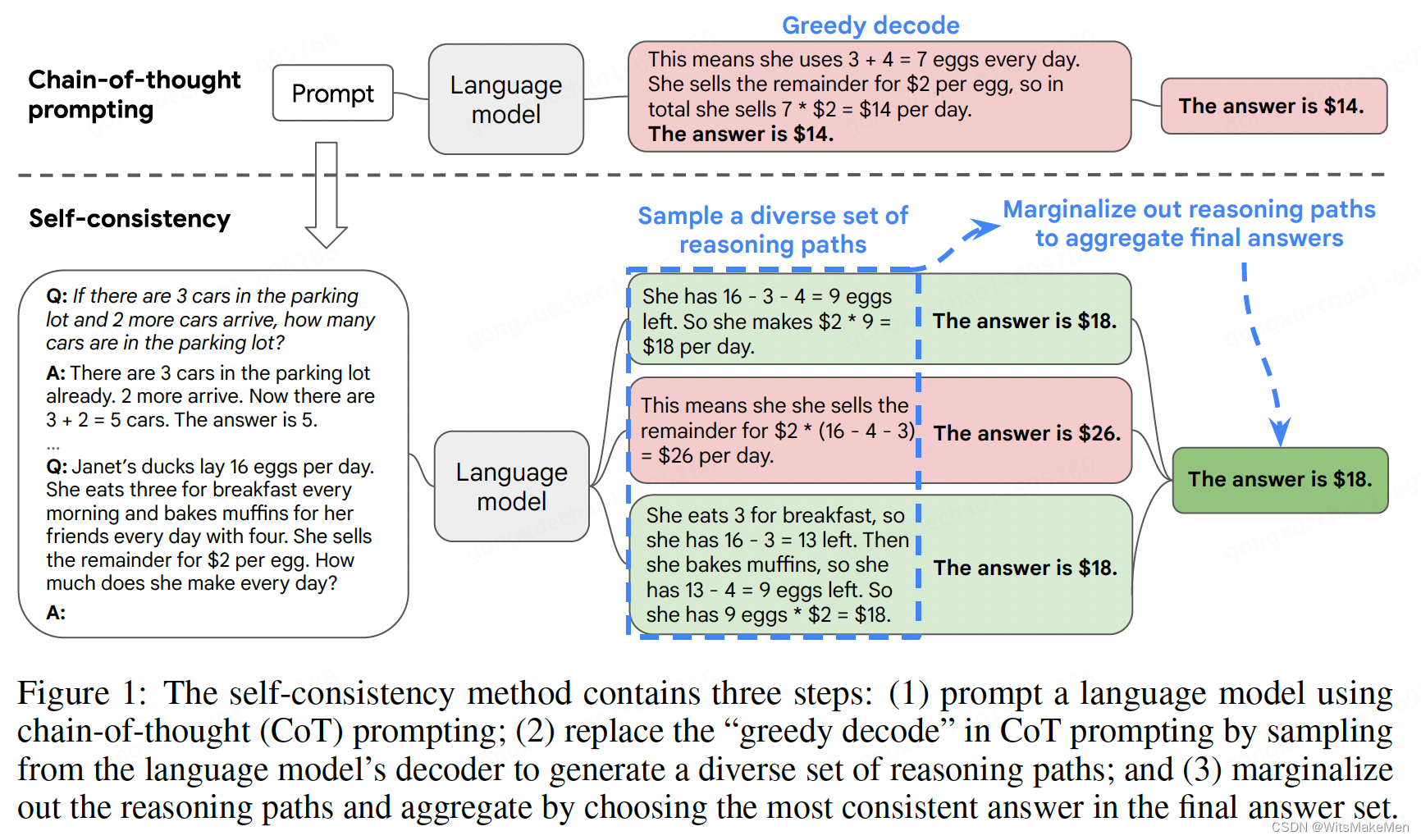
一致性思维链(SELF-CONSISTENCY IMPROVES CHAIN OF THOUGHT REASONING IN LANGUAGE MODELS)
概要 思维链已经在很多任务上取得了非常显著的效果,这篇论文中提出了一种 self-consistency 的算法,来代替 贪婪解码 算法。本方法通过 采样多个思维链集合,然后LLM模型生成后,选择一个最一致的答案作为最后的结果。一致性思维链…...
腾讯云16核服务器配置大全_16核CPU型号性能测评
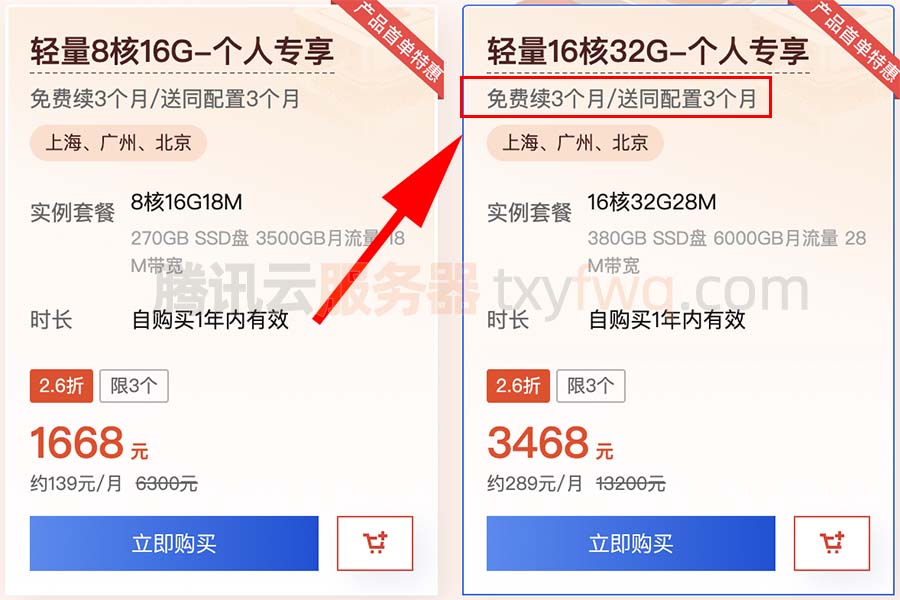
腾讯云16核CPU服务器有哪些配置可以选择?可以选择标准型S6、标准型SA3、计算型C6或标准型S5等,目前标准型S5云服务器有优惠活动,性价比高,计算型C6云服务器16核性能更高,轻量16核32G28M带宽优惠价3468元15个月…...

HTML中Input elements should have autocomplete attributes的解决方案
kwfwservice.php:1 [DOM] Input elements should have autocomplete attributes (suggested: “current-password”): (More info: https://goo.gl/9p2vKq) <input name"password" id"password" lay-verify"required" placeholder"密码&…...
2808. 使循环数组所有元素相等的最少秒数;1015. 可被 K 整除的最小整数;1001. 网格照明
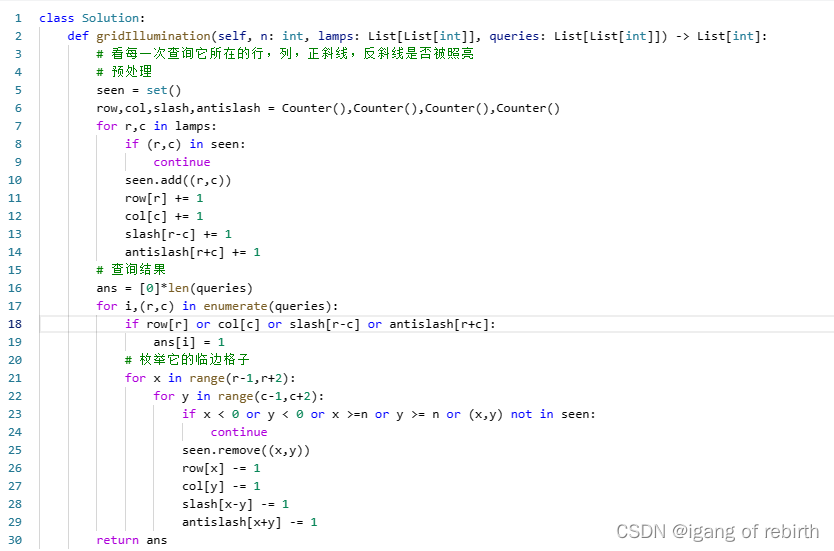
2808. 使循环数组所有元素相等的最少秒数 核心思想:枚举每个元素作为相等元素最多需要多少秒,然后维护它的最小值。最多需要多少秒是怎么计算的,我们可以把相等值的下标拿出来,然后你会发现两个相邻下标(相邻下标只的…...

Python爬虫在Web应用自动化测试中的应用
在Web应用开发过程中,自动化测试是确保应用质量和稳定性的重要环节。本文将介绍如何使用Python爬虫与自动化测试技术相结合,实现对Web应用进行自动化测试的方法和步骤。通过这种结合,我们可以提高测试效率、减少人力成本,并确保应…...
苹果手机短信删除了怎么恢复?3种有效方法介绍
手机短信是一种即时通信方式,人们可以使用短信来达到快速传递信息的目的。在没有网络或者网络不稳定的时候,短信仍然可以做到发送和接收,这弥补了其他网络通信软件的缺点。 所以说,手机短信仍然是我们生活中不可缺少的一部分。当…...

前端JavaScript中的 == 和 ===区别,以及他们的应用场景,快来看看吧,积累一点知识。
🎬 江城开朗的豌豆:个人主页 🔥 个人专栏 :《 VUE 》 《 javaScript 》 ⛺️ 生活的理想,就是为了理想的生活 ! 目录 一、等于操作符 二、全等操作符 三、区别 小结 一、等于操作符 等于操作符用两个等于号( &am…...

文献阅读:LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment
文献阅读:LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment 1. 内容简介2. 实验设计 1. 整体实验设计2. 数据准备3. 模型准备4. metrics设计 3. 实验结果 1. 基础实验2. 消解实验3. 多轮对话 4. 结论 & 思考 文献链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.11206 1. 内容简…...
机器学习第十四课--神经网络
总结起来,对于深度学习的发展跟以下几点是离不开的: 大量的数据(大数据)计算资源(如GPU)训练方法(如预训练) 很多时候,我们也可以认为真正让深度学习爆发起来的是数据和算力,这并不是没道理的。 由于神经网络是深度学习的基础,学…...

Android Wi-Fi 连接失败日志分析
1. Android wifi 关键日志总结 (1) Wi-Fi 断开 (CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED reason3) 日志相关部分: 06-05 10:48:40.987 943 943 I wpa_supplicant: wlan0: CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED bssid44:9b:c1:57:a8:90 reason3 locally_generated1解析: CTR…...

Ubuntu系统下交叉编译openssl
一、参考资料 OpenSSL&&libcurl库的交叉编译 - hesetone - 博客园 二、准备工作 1. 编译环境 宿主机:Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTSHost:ARM32位交叉编译器:arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-11.1.0 2. 设置交叉编译工具链 在交叉编译之前&#x…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...

DeepSeek 赋能智慧能源:微电网优化调度的智能革新路径
目录 一、智慧能源微电网优化调度概述1.1 智慧能源微电网概念1.2 优化调度的重要性1.3 目前面临的挑战 二、DeepSeek 技术探秘2.1 DeepSeek 技术原理2.2 DeepSeek 独特优势2.3 DeepSeek 在 AI 领域地位 三、DeepSeek 在微电网优化调度中的应用剖析3.1 数据处理与分析3.2 预测与…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
基于uniapp+WebSocket实现聊天对话、消息监听、消息推送、聊天室等功能,多端兼容
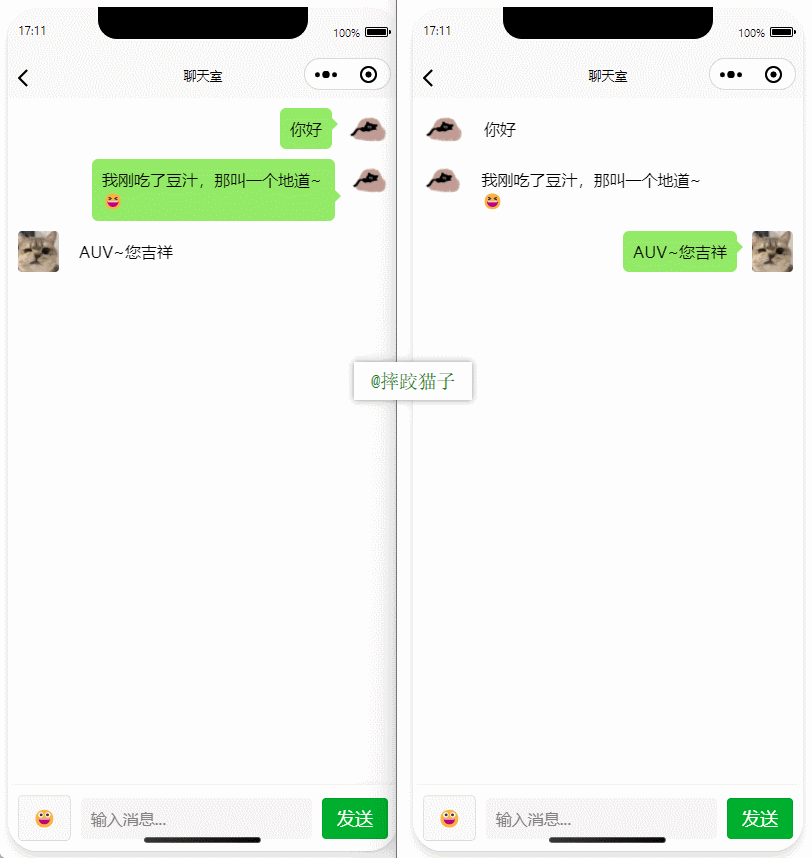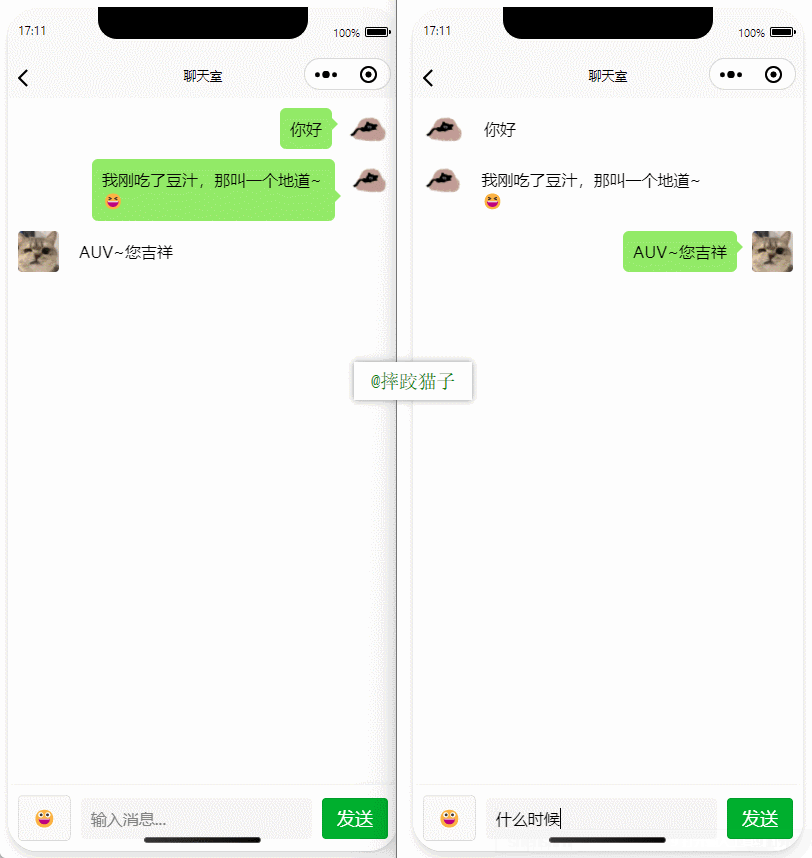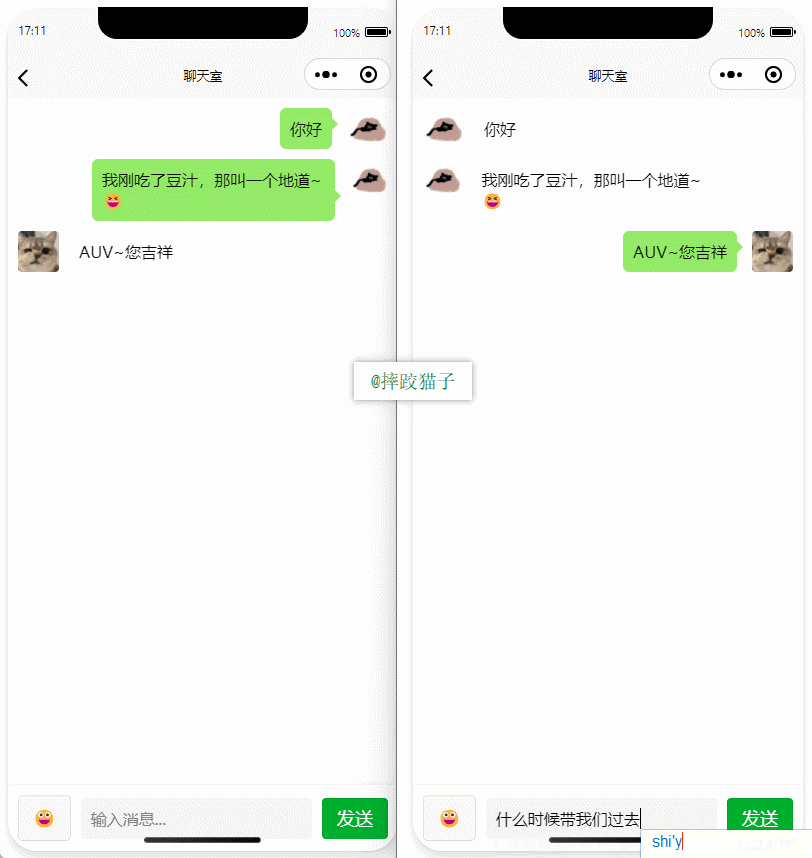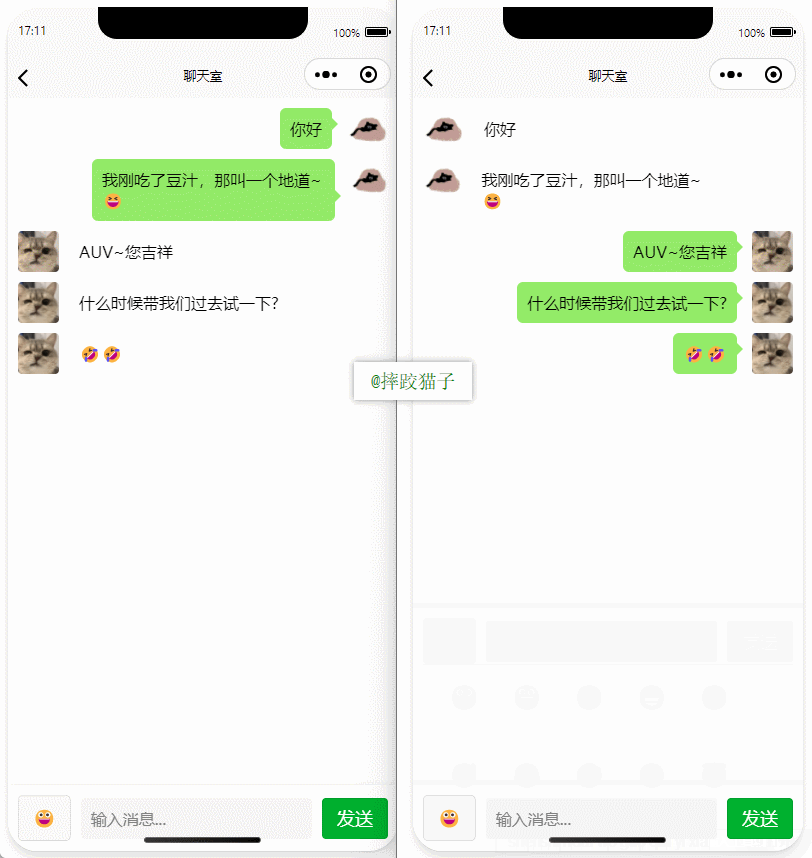
基于 UniApp + WebSocket实现多端兼容的实时通讯系统,涵盖WebSocket连接建立、消息收发机制、多端兼容性配置、消息实时监听等功能,适配微信小程序、H5、Android、iOS等终端 目录 技术选型分析WebSocket协议优势UniApp跨平台特性WebSocket 基础实现连接管理消息收发连接…...
最新SpringBoot+SpringCloud+Nacos微服务框架分享
文章目录 前言一、服务规划二、架构核心1.cloud的pom2.gateway的异常handler3.gateway的filter4、admin的pom5、admin的登录核心 三、code-helper分享总结 前言 最近有个活蛮赶的,根据Excel列的需求预估的工时直接打骨折,不要问我为什么,主要…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...

数据链路层的主要功能是什么
数据链路层(OSI模型第2层)的核心功能是在相邻网络节点(如交换机、主机)间提供可靠的数据帧传输服务,主要职责包括: 🔑 核心功能详解: 帧封装与解封装 封装: 将网络层下发…...

涂鸦T5AI手搓语音、emoji、otto机器人从入门到实战
“🤖手搓TuyaAI语音指令 😍秒变表情包大师,让萌系Otto机器人🔥玩出智能新花样!开整!” 🤖 Otto机器人 → 直接点明主体 手搓TuyaAI语音 → 强调 自主编程/自定义 语音控制(TuyaAI…...
