内存管理框架---页(一)
文章目录
- 物理内存的模型
- 非一致内存访问--NUMA
- 一致内存访问模型--UMA
- 内存管理架构
- 页
- 页框管理
- 页描述符
- 页描述符字段
- flags字段详解
- gfp_mask 标志
- 获得页
- alloc_pages
- __get_free_pages
- 获得填充为0的页
- 释放页
- kmalloc
- vmalloc
- 参考资料
你用心写的每一篇文章,可能会带别人和自己,走进另一个充满玄妙且多姿多彩的世界。
物理内存的模型
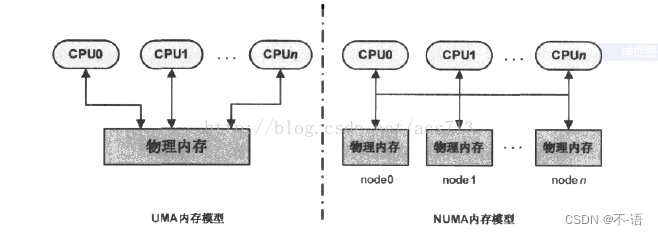
非一致内存访问–NUMA
NUMA (Non Uniform Memory Access) 即非一致内存访问。
非一致内存访问的特点如下:
- 在多CPU系统中,有可能出现给定CPU对不同内存单元访问的时间不同。为了让指定CPU总能最先使用访问时间最短的内存,Linux把物理内存分成几块并以节点(node)标识。
- 这样一来,每个CPU都有最快访问内存的节点,但并不等于只能访问这个节点。
- 内核中用struct pglist_data结构体来存放节点信息,多个内存节点通过链表串接起来;
- node_zonelists 将其他节点的各管理区也链了进来,但均排在本节点管理区之后,以示其它节点优先级低于本节点。
一致内存访问模型–UMA
与UMA不同,NUMA模型下处理器访问本地内存的速度要快于其他内存访问本地内存的速度。
UMA模型只有一个内存节点
内存管理架构
为了合理快速的获取内存,Linux分多层管理结构以适应不同架构及不同的使用方式。
注: 一个系统中并不一定是2个node,一般情况下UMA只使用1个node,而NUMA最多使用8个或16个

| 层次 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 存储节点(Node) | 系统物理内存被划分为多个节点,每个节点内cpu访问页面的时间是相同的,对应的数据结构:节点描述符 |
| 管理区(Zone) | 每个节点又分为多个管理区,用于表示不同范围的内存, 内核可以使用不同的映射方式映射物理内存 |
| 页描述符 | 描述每一个页框的状态信息,所有的也描述符都保存在mem_map[]数组中,每个描述符32个字节。mem_map是一个struct page的数组,管理着系统中所有的物理内存页面。在系统启动的过程中,创建和分配mem_map的内存区域 |
注: 物理内存的描述,必须牢牢记住,页框就是物理内存。
页

- MMU是Memory Management Unit的缩写,中文名是内存管理单元。是中央处理器(CPU)中用来管理虚拟存储器、物理存储器的控制线路,同时也负责提供硬件机制的内存访问授权,以及虚拟地址映射为物理地址。在本文MMU就是把虚拟地址转换为物理地址的硬件,通常以页为单位管理系统中的页表。
- 从虚拟内存的角度来看,页就是最小单位;
- 32位体系结构支持4KB的页,64位体系结构支持8KB的页;
- 内核用 struct page结构体来表示系统的每个页。不同的体系支持的页大小不同
1.什么叫动态内存?
RAM部分空间被永久地分配给内核,用来存放内核代码和静态内核数据结构。而RAM的其他部分成为动态内存。
2.如何有效的管理动态内存?
多任务操作系统都在尽力优化对动态内存的使用,即用时分配,不用时及时释放。另外,整个系统的性能取决于如何有效地管理动态内存。
3.内核给自己分配动态内存的三种方法:
“页框管理”和“内存区管理”介绍了对连续物理内存区处理的两种不同技术,而“非连续内存区管理”介绍了对处理非连续内存区的第三种技术。
页框管理
Intel的奔腾处理器采用两种不同的页框大小:4KB和4MB。Linux采用4KB页框大小作为标准的内存分配单元。
1.内核必须记录每个页框当前的状态,当前的状态包括什么?
- 内核必须能区分那些页框包含的是属于进程的页,而那些页框包含的是内核代码或内核数据。
- 内核还必须能够确定动态内存中的页框是否空闲。
2.什么样的页框是空闲页框?
如果内存中的页框不包含有用的数据,那么这个页框就是空闲的。
3.什么是有用的数据?
用户态进程的数据,某个软件高速缓存的数据,动态分配的内核数据结构,设备驱动程序的缓冲,内核模块的代码等等。
4.页框的状态信息保存在一个类型为page的页描述符中,即struct page页描述符中, 使用联合体union来优化其结构大小。所有的页描述符存放在mem_map数组中。每个描述符长度为32字节,所以mem_map所需要的空间不足整个RAM的百分之一。
页描述符
struct page结构体内容如下,定义在include/linux/mm_types.h文件中
struct page {unsigned long flags; /* Atomic flags, some possibly* updated asynchronously *//** Five words (20/40 bytes) are available in this union.* WARNING: bit 0 of the first word is used for PageTail(). That* means the other users of this union MUST NOT use the bit to* avoid collision and false-positive PageTail().*/union {struct { /* Page cache and anonymous pages *//*** @lru: Pageout list, eg. active_list protected by* lruvec->lru_lock. Sometimes used as a generic list* by the page owner.*/union {struct list_head lru;/* Or, for the Unevictable "LRU list" slot */struct {/* Always even, to negate PageTail */void *__filler;/* Count page's or folio's mlocks */unsigned int mlock_count;};/* Or, free page */struct list_head buddy_list;struct list_head pcp_list;};/* See page-flags.h for PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS */struct address_space *mapping; pgoff_t index; /* Our offset within mapping. *//*** @private: Mapping-private opaque data.* Usually used for buffer_heads if PagePrivate.* Used for swp_entry_t if PageSwapCache.* Indicates order in the buddy system if PageBuddy.*/unsigned long private;};struct { /* page_pool used by netstack *//*** @pp_magic: magic value to avoid recycling non* page_pool allocated pages.*/unsigned long pp_magic;struct page_pool *pp;unsigned long _pp_mapping_pad;unsigned long dma_addr;union {/*** dma_addr_upper: might require a 64-bit* value on 32-bit architectures.*/unsigned long dma_addr_upper;/*** For frag page support, not supported in* 32-bit architectures with 64-bit DMA.*/atomic_long_t pp_frag_count;};};struct { /* Tail pages of compound page */unsigned long compound_head; /* Bit zero is set *//* First tail page only */unsigned char compound_dtor;unsigned char compound_order;atomic_t compound_mapcount;atomic_t compound_pincount;
#ifdef CONFIG_64BITunsigned int compound_nr; /* 1 << compound_order */
#endif};struct { /* Second tail page of compound page */unsigned long _compound_pad_1; /* compound_head */unsigned long _compound_pad_2;/* For both global and memcg */struct list_head deferred_list;};struct { /* Page table pages */unsigned long _pt_pad_1; /* compound_head */pgtable_t pmd_huge_pte; /* protected by page->ptl */unsigned long _pt_pad_2; /* mapping */union {struct mm_struct *pt_mm; /* x86 pgds only */atomic_t pt_frag_refcount; /* powerpc */};
#if ALLOC_SPLIT_PTLOCKSspinlock_t *ptl;
#elsespinlock_t ptl;
#endif};struct { /* ZONE_DEVICE pages *//** @pgmap: Points to the hosting device page map. */struct dev_pagemap *pgmap;void *zone_device_data;/** ZONE_DEVICE private pages are counted as being* mapped so the next 3 words hold the mapping, index,* and private fields from the source anonymous or* page cache page while the page is migrated to device* private memory.* ZONE_DEVICE MEMORY_DEVICE_FS_DAX pages also* use the mapping, index, and private fields when* pmem backed DAX files are mapped.*/};/** @rcu_head: You can use this to free a page by RCU. */struct rcu_head rcu_head;};union { /* This union is 4 bytes in size. *//** If the page can be mapped to userspace, encodes the * number of times this page is referenced by a page table.*/atomic_t _mapcount; /** If the page is neither PageSlab nor mappable to userspace,* the value stored here may help determine what this page* is used for. See page-flags.h for a list of page types* which are currently stored here.*/unsigned int page_type;};/* Usage count. *DO NOT USE DIRECTLY*. See page_ref.h */atomic_t _refcount;#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCGunsigned long memcg_data;
#endif/** On machines where all RAM is mapped into kernel address space,* we can simply calculate the virtual address. On machines with* highmem some memory is mapped into kernel virtual memory* dynamically, so we need a place to store that address.* Note that this field could be 16 bits on x86 ... ;)** Architectures with slow multiplication can define* WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL in asm/page.h*/
#if defined(WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL)void *virtual; /* Kernel virtual address (NULL ifnot kmapped, ie. highmem) */
#endif /* WANT_PAGE_VIRTUAL */#ifdef CONFIG_KMSAN/** KMSAN metadata for this page:* - shadow page: every bit indicates whether the corresponding* bit of the original page is initialized (0) or not (1);* - origin page: every 4 bytes contain an id of the stack trace* where the uninitialized value was created.*/struct page *kmsan_shadow;struct page *kmsan_origin;
#endif#ifdef LAST_CPUPID_NOT_IN_PAGE_FLAGSint _last_cpupid;
#endif
} _struct_page_alignment;
可以看到主要由两个union组成,第一个union联合体占用40个字节(32位系统下为20个字节),第二个联合体占4个字节。page结构与物理页相关,而并非与虚拟页相关。因此,该结构对页的描述只是短暂的。
页描述符字段
| 字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| flag | 用来存放页的状态,每一位代表一种状态,所以至少可以同时表示出32中不同的状态,这些状态定义在linux/page-flags.h中 |
| _refcount | _refcount表示该物理页的引用次数,即内核中引用该page的次数。当该值为0时, 表示没有引用该page的位置,所以该page可以被解除映射,在内存回收时是有用的。定义在 linux-4.19/include/linux/page_ref.h |
| virtual | 通常情况下,它就是页在虚拟内存中的地址。有些内存(即所谓的高端内存)并不永久地映射到内核地址空间上。在这种情况下,这个域的值为NULL,需要的时候,必须动态地映射这些页 |
| _mapcount | 被页表映射的次数,也就是说该page同时被多少个进程共享。初始值为-1,如果只被一个进程的页表映射了,该值为0. 如果该page处于伙伴系统中,该值为PAGE_BUDDY_MAPCOUNT_VALUE(-128),内核通过判断该值是否为PAGE_BUDDY_MAPCOUNT_VALUE来确定该page是否属于伙伴系统 |
flags字段详解
/include/linux/page-flags.h
enum pageflags {PG_locked, /* Page is locked. Don't touch. */ /*page已经上锁,不要访问*/PG_referenced, /* 控制系统使用该页面的活跃程度,在kswapd页面回收中使用。*/PG_uptodate, /* 表示页面的数据已经从块设备成功读取 */PG_dirty, /* 表示页面内容发生改变,页面为脏,页面内容被改写后还没有和外部存储器进行同步操作。*/ PG_lru, /* 表示页面加入了LRU链表,内核使用LRU链表管理活跃和不活跃页面。*/PG_active, /* 控制页面活跃程度,在kswapd页面回收中使用。*/PG_workingset, PG_waiters, /* Page has waiters, check its waitqueue. Must be bit #7 and in the same byte as "PG_locked" */ /* */PG_error, /* 页面操作过程中发生错误会设置该位。*/PG_slab, /* 用于slab分配器 */PG_owner_priv_1, /* Owner use. If pagecache, fs may use*/ /* 页面的所有者使用,如果是page cache页面,文件系统可能在使用 */PG_arch_1, /* 与体系结构相关的页面状态位 */PG_reserved, /* 页留给内核代码或者没有使用,这种页是不受内存管理系统用于分配的,所以不能被回收算法回收。*/PG_private, /* If pagecache, has fs-private data */ /* 表示该页是有效的。如果页面是page cache,那么包含一些文件系统相关的数据信息。 */PG_private_2, /* If pagecache, has fs aux data */PG_writeback, /* Page is under writeback */PG_head, /* A head page */PG_mappedtodisk, /* Has blocks allocated on-disk */PG_reclaim, /* To be reclaimed asap */ /* */PG_swapbacked, /* Page is backed by RAM/swap */PG_unevictable, /* Page is "unevictable" */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMUPG_mlocked, /* Page is vma mlocked */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_USES_PG_UNCACHEDPG_uncached, /* Page has been mapped as uncached */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_FAILUREPG_hwpoison, /* hardware poisoned page. Don't touch */
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PAGE_IDLE_FLAG) && defined(CONFIG_64BIT)PG_young,PG_idle,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_64BITPG_arch_2,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_KASAN_HW_TAGSPG_skip_kasan_poison,
#endif__NR_PAGEFLAGS,PG_readahead = PG_reclaim,/** Depending on the way an anonymous folio can be mapped into a page* table (e.g., single PMD/PUD/CONT of the head page vs. PTE-mapped* THP), PG_anon_exclusive may be set only for the head page or for* tail pages of an anonymous folio. For now, we only expect it to be* set on tail pages for PTE-mapped THP.*/PG_anon_exclusive = PG_mappedtodisk,/* Filesystems */PG_checked = PG_owner_priv_1,/* SwapBacked */PG_swapcache = PG_owner_priv_1, /* Swap page: swp_entry_t in private *//* Two page bits are conscripted by FS-Cache to maintain local caching* state. These bits are set on pages belonging to the netfs's inodes* when those inodes are being locally cached.*/PG_fscache = PG_private_2, /* page backed by cache *//* XEN *//* Pinned in Xen as a read-only pagetable page. */PG_pinned = PG_owner_priv_1,/* Pinned as part of domain save (see xen_mm_pin_all()). */PG_savepinned = PG_dirty,/* Has a grant mapping of another (foreign) domain's page. */PG_foreign = PG_owner_priv_1,/* Remapped by swiotlb-xen. */PG_xen_remapped = PG_owner_priv_1,/* SLOB */PG_slob_free = PG_private,/* Compound pages. Stored in first tail page's flags */PG_double_map = PG_workingset,#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_FAILURE/** Compound pages. Stored in first tail page's flags.* Indicates that at least one subpage is hwpoisoned in the* THP.*/PG_has_hwpoisoned = PG_error,
#endif/* non-lru isolated movable page */PG_isolated = PG_reclaim,/* Only valid for buddy pages. Used to track pages that are reported */PG_reported = PG_uptodate,#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG/* For self-hosted memmap pages */PG_vmemmap_self_hosted = PG_owner_priv_1,
#endif
};
1) 该结构体成员与体系架构无关,主要用来存放页的属性;
2) 页的各种不同属性通过一系列标志描述,存储在flags成员的各个bit中,比如该页是否被锁定中(如果该bit置位,表示内核的其他部分不允许访问该页,防止内存管理出现竞态条件)、该页是否能够被回收、该页最近是否被访问过、该页数据是否是脏的,该页是否用于slab分配器等等。
3) 通过一系列宏用来操作该flags的各个标志位。SetPageXXX用来设置XXXbit; ClearPageXXX用来清除XXXbit; PageXXX用来查询是否置位。
gfp_mask 标志
在低级页分配函数和kmalloc中都用到了分配器标志。标志可分为3类:
- 行为修饰符:在某些特定情况下,只能使用某些特定的方法分配内存,比如在中断处理程序要求内核在分配内存的过程中不能睡眠(因为中断处理程序不能被重新调度)。
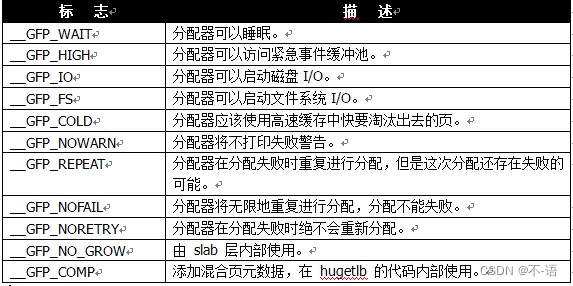
- 区修饰符:表示从那一区分配内存
| 标志 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| __GFP_DMA | 从ZONE_DMA分配 |
| __GFP_HIGHMEM | 从ZONE_HIGHMEM或ZONE_NORMAL分配 |
指定以上标志中的一个就可以改变内核试图进行分配的区。如果没有指定任何标志,则内核从ZONE_DMA或ZONE_NORMAL进行分配,优先从ZONE_NORMAL进行分配。不能给 _get_free_pages 或 kmalloc 指定 __GFP_HIGHMAM,因为这两个函数返回的都是逻辑地址,而不是 page 结构,这两个函数分配的内存,当前有可能还没有映射到内核的虚拟地址空间。因此,也可能根本就没有逻辑地址。只有 alloc_pages 才能分配高端内存。
- 类型:组合了行为修饰符和区修饰符,组合在一起,简化了修饰符的使用。一般使用类型修饰符就够了。
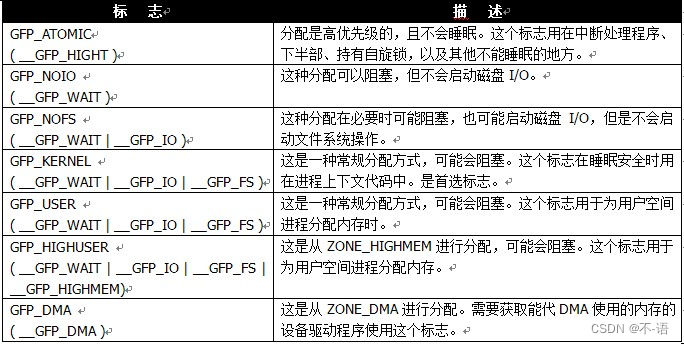
-
GFP_KERNEL参数是gfp_mask标志的一个例子。调用_get_free_pages()之后要注意进行错误检查。内核分配可能失败,因此代码必须进行检查并做相应的处理。这意味在此之前,你所做的所有工作可能前功尽弃,甚至还需要回归到原来的状态。正因为如此,在程序开始时就先进行内存分配时很有意义的,这能让错误处理得到容易一点。如果你不这么做,那么在你想要分配内存的时候如果失败了,局面可能很难以控制了。当需要以页为单位的一族连续物理页时,尤其是在你只需要一两页时,这些低级页函数很有用。对于常用的以字节为单位的分配来说,内核提供的函数是kmalloc()。
-
内核中最常用的标志是 GFP_KERNEL。这种分配可能会引起睡眠,它使用的是普通优先级,因此这个标志只用在可以重新安全调度的进程上下文中(也就是没有锁被持有的情况)。另一个全然相反的标志是 GFP_ATOMIC。因为这个标志表示不能睡眠的内存分配,因此想要满足调用者获取内存的请求将会受到很严格的限制。GFP_USER用在为用户空间分配内存的场景中。
获得页
alloc_pages
通过使用标志、内存域修饰符和各个分配函数,内核提供了一种非常灵活的内存分配体系。尽管如此, 所有接口函数都可以追溯到一个简单的基本函数(alloc_pages_node)。

在内核中分配和释放内存, 都是以页为单位分配内存。alloc_pages函数调用流程如下:

<linux/gfp.h>
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
static inline struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{return alloc_pages_current(gfp_mask, order);
}
#else
#define alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order) \alloc_pages_node(numa_node_id(), gfp_mask, order)
#endif
alloc_pages是通过alloc_pages_node函数实现的。该函数执行了一个简单的检查, 如果指定负的结点ID(不存在, 即NUMA_NO_NODE = -1), 内核自动地使用当前执行CPU对应的结点nid = numa_mem_id();, 然后调用__alloc_pages_node函数进行了内存分配。
<linux/gfp.h>
/** Allocate pages, preferring the node given as nid. When nid == NUMA_NO_NODE,* prefer the current CPU's closest node. Otherwise node must be valid and* online.*/
static inline struct page *alloc_pages_node(int nid, gfp_t gfp_mask,unsigned int order)
{if (nid == NUMA_NO_NODE)nid = numa_mem_id();return __alloc_pages_node(nid, gfp_mask, order);
}static inline struct page *__alloc_pages_node(int nid, gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{VM_BUG_ON(nid < 0 || nid >= MAX_NUMNODES);VM_WARN_ON((gfp_mask & __GFP_THISNODE) && !node_online(nid));return __alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order, nid);
}
__alloc_pages函数直接将自己的所有信息传递给__alloc_pages_nodemask来完成内存的分配
<linux/gfp.h>
static inline struct page *
__alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,struct zonelist *zonelist)
{return __alloc_pages_nodemask(gfp_mask, order, zonelist, NULL);
}
到__alloc_pages_nodemask就进入了比较正式的流程了,主要包含两步:
- 直接分配
- 分配失败选择另一种方式即slowpath继续处理.
首次尝试分配是调用了
static struct page
*get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, nodemask_t *nodemask, unsigned int order,struct zonelist *zonelist, int high_zoneidx, int alloc_flags,struct zone *preferred_zone, int migratetype)
核心机制就是遍历zonelist上的zone,找到一个page。该函数主要实现功能:
- 在zonelist中找到一个合适的zone
- 从zone中分配页面。
在选定zone的阶段,在正常情况下需要进行一系列的验证,保证当前zone有足够的可用页面供分配。须携带ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS标识的,所以这里就分为两种情况。这里涉及到一个分配水位watermark,关于zone_watermark的知识可参考Arnold Lu@南京和LoyenWang的文章。水位有三种:
kernel-4.19/include/linux/mmzone.h
enum zone_watermarks {WMARK_MIN,WMARK_LOW,WMARK_HIGH,NR_WMARK
};#define min_wmark_pages(z) (z->watermark[WMARK_MIN])
#define low_wmark_pages(z) (z->watermark[WMARK_LOW])
#define high_wmark_pages(z) (z->watermark[WMARK_HIGH])
在分配之前一般会指定满足那个水位才允许分配,或者不管水位直接分配,这就对应ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS标识。
在zone结构中,有vm_stat字段,是一个数组,记录各个状态的页面的数量,其中就包含空闲页面,对应NR_FREE_PAGES,携带watermark标识的分配,
需要验证空闲页面是否大于对应的水位,只有在大于水位了才允许分配,否则需要根据情况对页面进行回收reclaim,如果无法回收或者回收后仍然不满足条件,则直接返回了。
在一些急迫的事务中,可以指定ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS,这样会不会对水位进行验证,直接调用buffered_rmqueue分配页面。
zone_watermark_ok函数检查标志
设置的标志在zone_watermark_ok函数中检查, 该函数根据设置的标志判断是否能从给定的内存域分配内存。
/mm/page_alloc.c
bool zone_watermark_ok(struct zone *z, unsigned int order, unsigned long mark,int classzone_idx, unsigned int alloc_flags)
{return __zone_watermark_ok(z, order, mark, classzone_idx, alloc_flags, --------------- 完成了检查的工作zone_page_state(z, NR_FREE_PAGES));
}/** Return true if free base pages are above 'mark'. For high-order checks it* will return true of the order-0 watermark is reached and there is at least* one free page of a suitable size. Checking now avoids taking the zone lock* to check in the allocation paths if no pages are free.*/
bool __zone_watermark_ok(struct zone *z, unsigned int order, unsigned long mark,int classzone_idx, unsigned int alloc_flags,long free_pages)
{long min = mark;int o;const bool alloc_harder = (alloc_flags & (ALLOC_HARDER|ALLOC_OOM));/* free_pages may go negative - that's OK *//* free_pages可能变为负值, 没有关系 */free_pages -= (1 << order) - 1;if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HIGH)min -= min / 2;/** If the caller does not have rights to ALLOC_HARDER then subtract* the high-atomic reserves. This will over-estimate the size of the* atomic reserve but it avoids a search.*/if (likely(!alloc_harder)) {free_pages -= z->nr_reserved_highatomic;} else {/** OOM victims can try even harder than normal ALLOC_HARDER* users on the grounds that it's definitely going to be in* the exit path shortly and free memory. Any allocation it* makes during the free path will be small and short-lived.*/if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_OOM)min -= min / 2;elsemin -= min / 4;}#ifdef CONFIG_CMA/* If allocation can't use CMA areas don't use free CMA pages */if (!(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA))free_pages -= zone_page_state(z, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES); //得到空闲页的个数
#endif/** Check watermarks for an order-0 allocation request. If these* are not met, then a high-order request also cannot go ahead* even if a suitable page happened to be free.*///该函数会检查空闲页的数目free_pages是否小于最小值与lowmem_reserve中指定的紧急分配值min之和.if (free_pages <= min + z->lowmem_reserve[classzone_idx])return false;/* If this is an order-0 request then the watermark is fine */if (!order)return true;/* For a high-order request, check at least one suitable page is free *//* 在下一阶,当前阶的页是不可用的 */for (o = order; o < MAX_ORDER; o++) {struct free_area *area = &z->free_area[o];int mt;if (!area->nr_free)continue;/* 所需高阶空闲页的数目相对较少 */for (mt = 0; mt < MIGRATE_PCPTYPES; mt++) {if (!list_empty(&area->free_list[mt]))return true;}#ifdef CONFIG_CMAif ((alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA) &&!list_empty(&area->free_list[MIGRATE_CMA])) {return true;}
#endifif (alloc_harder &&!list_empty(&area->free_list[MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC]))return true;}return false;
}
如果内核遍历所有的低端内存域之后,发现内存不足, 则不进行内存分配。
alloc_flags和gfp_mask之间的区别,gfp_mask是使用alloc_pages申请内存时所传递的申请标记,而alloc_flags是在内存管理子系统内部使用的另一个标记。关于alloc_flags的定义有如下几个:
/* The ALLOC_WMARK bits are used as an index to zone->watermark */
#define ALLOC_WMARK_MIN WMARK_MIN
#define ALLOC_WMARK_LOW WMARK_LOW
#define ALLOC_WMARK_HIGH WMARK_HIGH
#define ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS 0x04 /* don't check watermarks at all */#define ALLOC_HARDER 0x10 /* try to alloc harder */
#define ALLOC_HIGH 0x20 /* __GFP_HIGH set */
#define ALLOC_CPUSET 0x40 /* check for correct cpuset */
#define ALLOC_CMA 0x80 /* allow allocations from CMA areas */
#define ALLOC_FAIR 0x100 /* fair zone allocation */
get_page_from_freelist
get_page_from_freelist是伙伴系统使用的另一个重要的辅助函数。它通过标志集和分配阶来判断是否能进行分配。如果可以,则发起实际的分配操作。 get_page_from_freelist将那些相关联的参数封装成一个结构:
static struct page *
get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags, const struct alloc_context *ac)
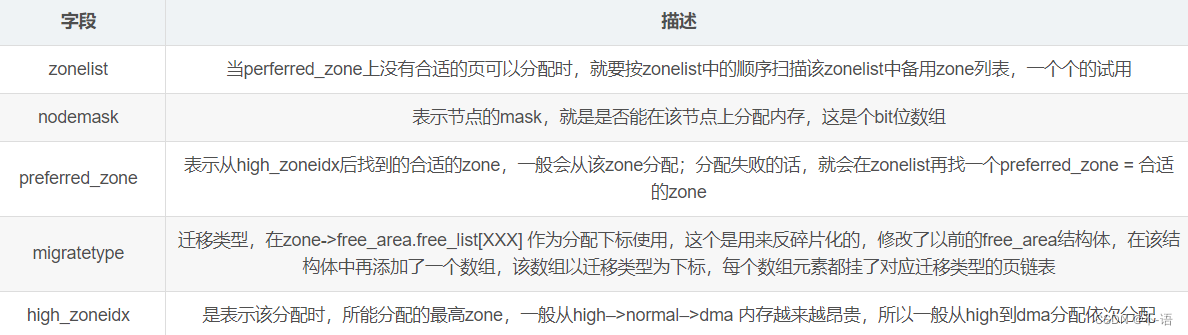
封装好的结构是struct alloc_context:
/** Structure for holding the mostly immutable allocation parameters passed* between functions involved in allocations, including the alloc_pages** family of functions.** nodemask, migratetype and high_zoneidx are initialized only once in* __alloc_pages_nodemask() and then never change.** zonelist, preferred_zone and classzone_idx are set first in* __alloc_pages_nodemask() for the fast path, and might be later changed* in __alloc_pages_slowpath(). All other functions pass the whole strucure* by a const pointer.*/
struct alloc_context {struct zonelist *zonelist;nodemask_t *nodemask;struct zoneref *preferred_zoneref;int migratetype;enum zone_type high_zoneidx;bool spread_dirty_pages;
};
__get_free_pages
如果无须用到 struct page,可以调用__get_free_pages。这个函数与 alloc_pages 作用相同,不过它直接返回所请求的第一个页的逻辑地址。因为页是连续的,因此其他页也会紧随其后。
Kernel-4.19/mm/page_alloc.c
unsigned long __get_free_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{struct page *page;page = alloc_pages(gfp_mask & ~__GFP_HIGHMEM, order); ----------- __get_free_pages调用alloc_pages完成内存分配, 而alloc_pages又借助于alloc_pages_nodeif (!page)return 0;return (unsigned long) page_address(page);-------- 该函数分配 2^order 个连续的物理页,并返回一个指向第一页的 page 结构体指针,如果出错就返回 NULL, 把给定的页转换成它的逻辑地址。
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__get_free_pages);
分配单页的函数alloc_page和__get_free_page, 还有__get_dma_pages借助于宏定义。
Kernel-4.19/include/linux/gfp.h
#define alloc_page(gfp_mask) alloc_pages(gfp_mask, 0)#define __get_free_page(gfp_mask) \__get_free_pages((gfp_mask), 0)`#define __get_dma_pages(gfp_mask, order) \__get_free_pages((gfp_mask) | GFP_DMA, (order))
获得填充为0的页
如果需要让返回页的内容全为0,可以使用下面这个函数。get_zeroed_page的实现,是对__get_free_pages使用__GFP_ZERO标志,即可分配填充字节0的页. 再返回与页关联的内存区地址即可.
Kernel-4.19/mm/page_alloc.c
unsigned long get_zeroed_page(gfp_t gfp_mask)
{return __get_free_pages(gfp_mask | __GFP_ZERO, 0);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(get_zeroed_page);
释放页
当不再需要页时可以使用以下函数来释放。释放页时要谨慎,只能释放属于你的页。传递了错误的 struct page 或地址,用了错误的 order 值都可能导致系统崩溃。
void __free_pages( struct page *page, unsigned int order );
void free_pages( unsigned long addr, unsigned int order );
void free_page( unsigned long addr );
kmalloc
<linux/slab.h>
对于以字节为单位的分配,内核提供的函数是kmalloc。所分配的内存区在物理上是连续的,虚拟地址自然也是连续的。在出错时,返回NULL。调用之后,要检查返回值是否为空。
void *kmalloc( size_t size, int flags );
kfree()函数释放由 kmalloc()分配出来的内存块, 注意配对使用,以避免内存泄漏和其他BUG。
vmalloc
vmalloc 的工作方式是类似于 kmalloc,不同点:
vmalloc()分配的内存:虚拟地址连续,物理地址不一定连续。
kmalloc()分配的内存:虚拟地址连续,物理地址也连续。
内核多用kmalloc()来分配内存,主要是基于性能的考虑:vmalloc()函数为了把物理上不连续的页转换为虚拟地址空间上连续的页,必须专门建立页表项,vmalloc()获得的页必须一个一个进行映射,这会导致比直接内存映射大得多的TLB抖动。
vmalloc()函数声明<linux/vmalloc.h>中,用法与用户空间malloc相同。
void *vmalloc(unsigned long size);
该函数返回一个指针,指向逻辑上连续的一块内存区,大小至少为size;发生错误时函数返回NULL。
函数可能睡眠,因此不能在中断上下文 ,也不能在不允许阻塞的情况下进行调用。
释放vmalloc()分配的页,通过配对函数Vfree()
void vfree(const void *addr);
该函数也可以睡眠,没有返回值。
参考资料
linux内核设计与实现
alloc_page分配内存
节点、管理区、页描述符
相关文章:

内存管理框架---页(一)
文章目录物理内存的模型非一致内存访问--NUMA一致内存访问模型--UMA内存管理架构页页框管理页描述符页描述符字段flags字段详解gfp_mask 标志获得页alloc_pages__get_free_pages获得填充为0的页释放页kmallocvmalloc参考资料你用心写的每一篇文章,可能会带别人和自己…...
)
华为OD机试真题Python实现【流水线】真题+解题思路+代码(20222023)
流水线 题目 一个工厂有m条流水线 来并行完成n个独立的作业 该工厂设置了一个调度系统 在安排作业时,总是优先执行处理时间最短的作业 现给定流水线个数m 需要完成的作业数n 每个作业的处理时间分别为 t1,t2...tn 请你编程计算处理完所有作业的耗时为多少 当n > m时 首先…...
「JVM 编译优化」Graal 编译器
文章目录1. 历史背景2. 构建编译调试环境3. JVMCI 编译器接口4. 代码中间表示5. 代码优化与生成1. 历史背景 Graal 编译器在 JDK 9 以 Jaotc 提前编译工具的形式首次加入到官方的 JDK 中,JDK 10 开始提供替换(得益于 HotSpot 编译器接口,Jav…...

蓝牙标签操作指南
一、APP安装指南 1.APP权限问题 电子标签APP安装之后,会提示一些权限的申请,点击允许。否则某些会影响APP的正常运行。安装后,搜索不到蓝牙标签,可以关闭App,重新打开。 2.手机功能 运行APP时候,需要打开…...

嵌入式 Linux Shell编程
目录 1、shell脚本 2、执行shell脚本 3、shell脚本编写 3.1 shell变量 3.2 标准变量或环境变量 3.4 变量赋值有五种格式 3.5 运算符和表达式 关系运算符 布尔运算符 3.6 Test命令用法 1、判断表达式 2、判断字符串 3.判断整数 4、判断文件 3.7 数组 1、数组定义…...
Web前端学习:一
编辑器的基础使用 编辑器推荐使用: HBuilderx(免费中文)(建议使用) Sublime(免费英文) Sublime中文设置方法,下载语言插件: 1、进入Sublime后,ShiftCtrlP…...

SpringBoot集成Redis实现分布式会话
在单体应用的时代,Session 会话直接保存在服务器中,实现非常简单,但是随着微服务的流行,现代应用架构基本都是分布式架构,请求随机的分配到后端的多个应用中,此时session就需要共享,而存储在red…...
2023年关于身份安全的4 个预测
如果您身处技术领域,就会知道现在是时候盘点过去的一年,展望未来 365 天将影响业务、创新以及我们工作方式的因素的季节。这不是一门精确的科学,我们也不总是对的。但是推测很有趣,当我们看到其中一些趋势成为现实时会更有趣。本文…...

Linux期末考试应急
Linux期末考试应急 虚拟机添加硬盘、分区、格式化、挂载、卸载 fdisk -l#查看系统现有分区fdisk <指定磁盘>#指定磁盘分区sudo mkfs.ext3 <指定分区>#格式化磁盘###挂载磁盘1.新建一个目录sudo mkdir /mnt/test2.将指定分区挂载到对应目录sudo mount /dev/sdb10 /…...
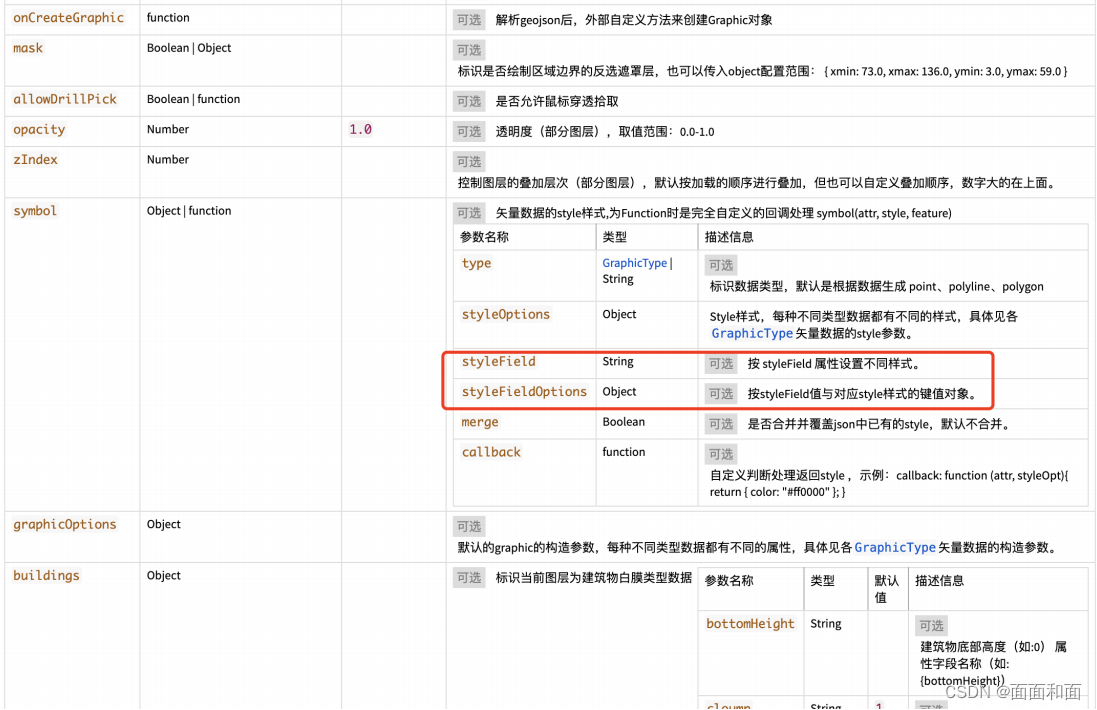
mars3d对geojson图层分属性设置样式
开发中可能会遇到如下需求,在全省的数据中按某个属性⾼亮展示某市区。此时就需要使⽤分属性样式的api了。⽂档如下。GeoJsonLayer - Mars3D API文档属性是根据⽮量数据的属性进⾏匹配。可以通过 layer.graphics[0]?.attr ⽅式获取。 指导有哪些属性之后先设置…...
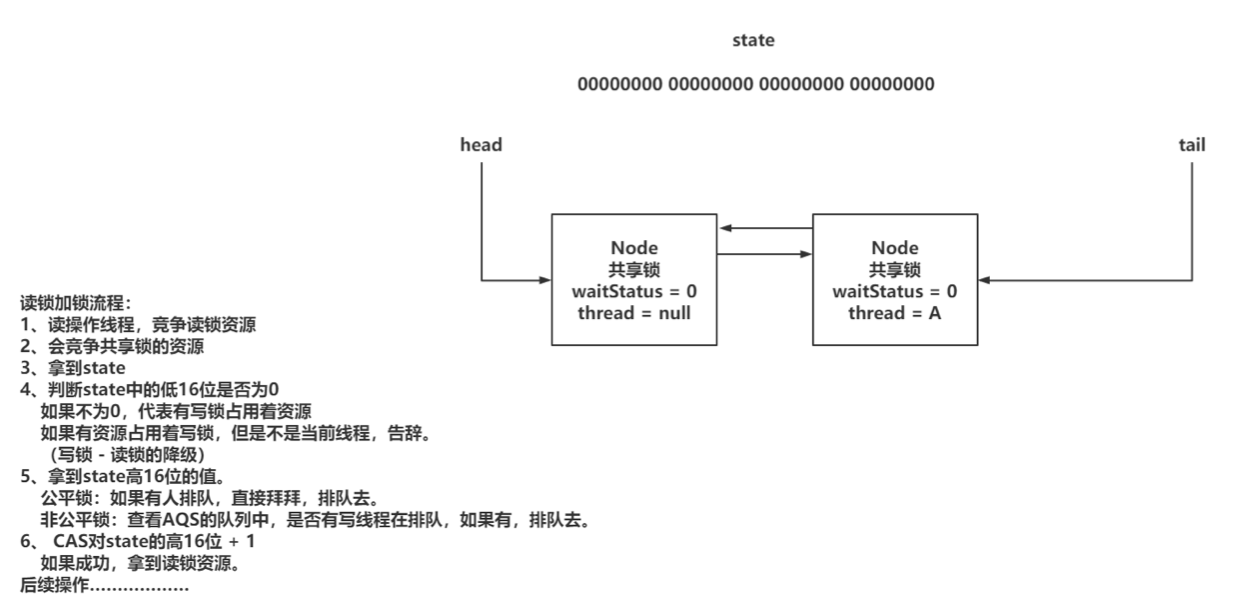
三、锁相关知识
文章目录锁的分类可重入锁、不可重入锁乐观锁、悲观锁公平锁、非公平锁互斥锁、共享锁深入synchronized类锁、对象锁synchronized的优化synchronized实现原理synchronized的锁升级重量锁底层ObjectMonitor深入ReentrantLockReentrantLock和synchronized的区别AQS概述加锁流程源…...

C语言数据类型
C 数据类型 在 C 语言中,数据类型指的是用于声明不同类型的变量或函数的一个广泛的系统。变量的类型决定了变量存储占用的空间,以及如何解释存储的位模式。 C 中的类型可分为以下几种: 1 基本类型: 它们是算术类型,…...
)
华为OD机试真题Python实现【水仙花数】真题+解题思路+代码(20222023)
水仙花数 题目 所谓的水仙花数是指一个n位的正整数其各位数字的n次方的和等于该数本身, 例如153 = 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3,153是一个三位数 🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥👉👉👉👉👉👉 华为OD机试(Python)真题目录汇总 输入 第一行输入一个整数N, 表示 N 位的正整数 N 在3…...

【华为OD机试模拟题】用 C++ 实现 - 非严格递增连续数字序列(2023.Q1)
最近更新的博客 华为OD机试 - 入栈出栈(C++) | 附带编码思路 【2023】 华为OD机试 - 箱子之形摆放(C++) | 附带编码思路 【2023】 华为OD机试 - 简易内存池 2(C++) | 附带编码思路 【2023】 华为OD机试 - 第 N 个排列(C++) | 附带编码思路 【2023】 华为OD机试 - 考古…...

RN面试题
RN面试题1.React Native相对于原生的ios和Android有哪些优势?1.性能媲美原生APP 2.使用JavaScript编码,只要学习这一种语言 3.绝大部分代码安卓和IOS都能共用 4.组件式开发,代码重用性很高 5.跟编写网页一般,修改代码后即可自动刷…...
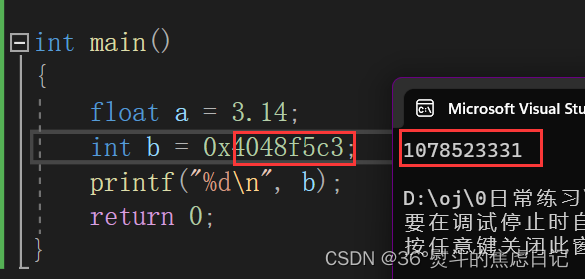
【数据存储】浮点型在内存中的存储
目录 一、存储现象 二、IEEE标准规范 1.存储 2.读取 三、举例验证 1.存储 2.读取 浮点型存储的标准是IEEE(电气电子工程师学会)754制定的。 一、存储现象 浮点数由于其有小数点的特殊性,有很多浮点数是不能精确存储的,如&#…...
:异常处理)
Servlet笔记(8):异常处理
1、错误页面配置 web.xml <!-- servlet 定义 --> <servlet><servlet-name>ErrorHandler</servlet-name><servlet-class>ErrorHandler</servlet-class> </servlet> <!-- servlet 映射 --> <servlet-mapping><servle…...

stm32f407探索者开发板(二十一)——窗口看门狗
文章目录一、窗口看门狗概述1.1 看门狗框图1.2 窗口看门狗工作过程总结1.3 超时时间1.4 为什么需要窗口看门狗1.5 其他注意事项二、常用寄存器和库函数2.1 控制寄存器WWDG_ CR2.2 配置寄存器WWDG_ CFR2.3 状态寄存器WWDG_SR三、手写窗口看门狗3.1 配置过程3.2 初始化窗口看门狗…...
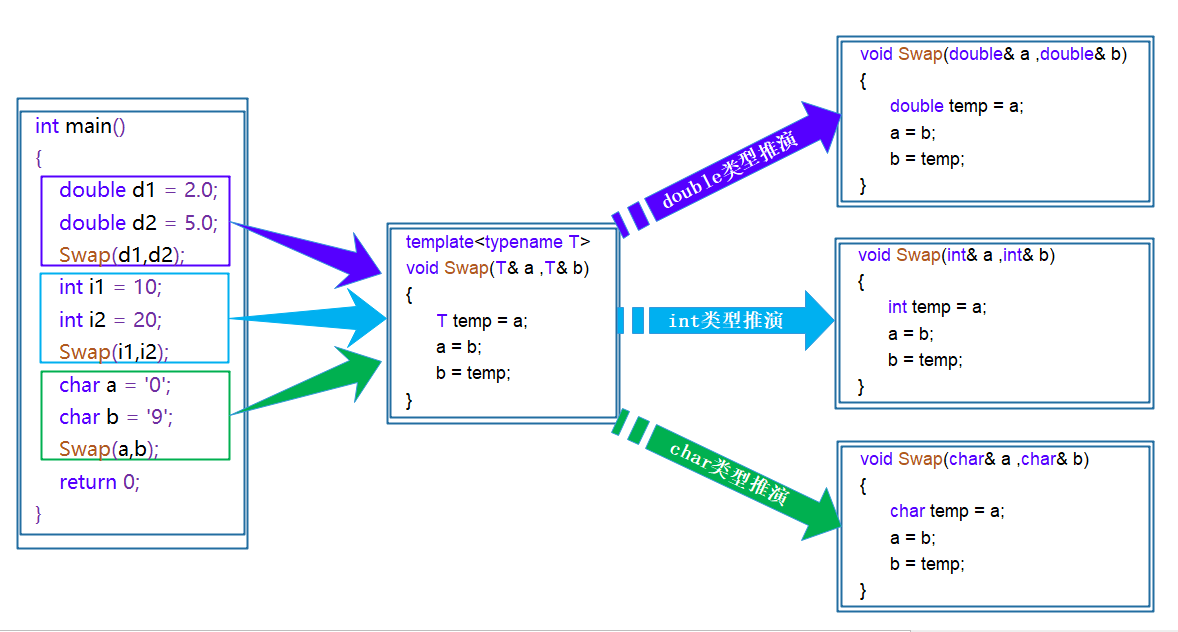
C++ 模板
1. 泛型编程实现一个通用的交换函数,使用函数重载虽然可以实现,但是有以 下几个不好的地方:1. 重载的函数仅仅是类型不同,代码复用率比较低,只要有新类型出现时,就需要用户自己增加对应的函数2. 代码的可维…...

C++中的友元及运算符重载
友元 意义 程序中,有些私有属性也想让类外特殊的一些函数或者类进行访问,就要用到友元技术 关键字 friend 友元的三种实现 全局函数做友元 class Room{friend void test(Person &p);//friend class test;public:string phone_number;private:string…...
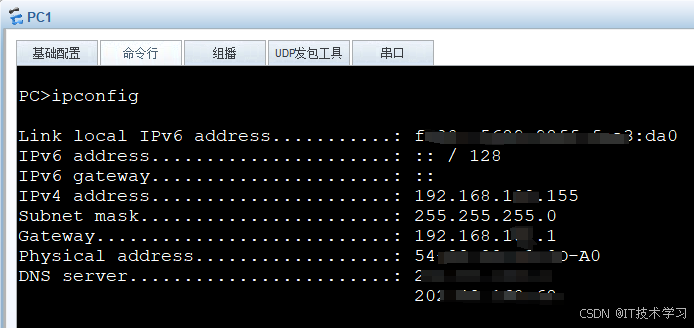
eNSP-Cloud(实现本地电脑与eNSP内设备之间通信)
说明: 想象一下,你正在用eNSP搭建一个虚拟的网络世界,里面有虚拟的路由器、交换机、电脑(PC)等等。这些设备都在你的电脑里面“运行”,它们之间可以互相通信,就像一个封闭的小王国。 但是&#…...
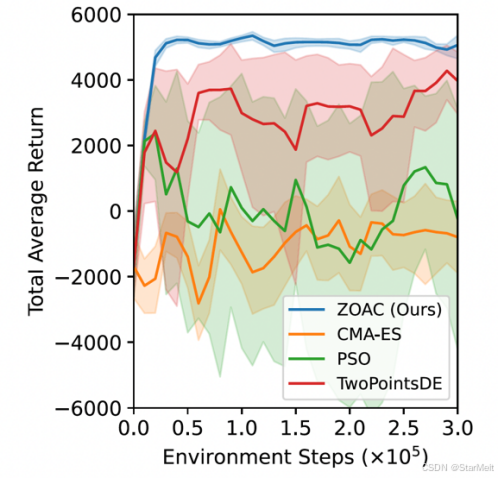
突破不可导策略的训练难题:零阶优化与强化学习的深度嵌合
强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)是工业领域智能控制的重要方法。它的基本原理是将最优控制问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后使用强化学习的Actor-Critic机制(中文译作“知行互动”机制),逐步迭代求解…...

Objective-C常用命名规范总结
【OC】常用命名规范总结 文章目录 【OC】常用命名规范总结1.类名(Class Name)2.协议名(Protocol Name)3.方法名(Method Name)4.属性名(Property Name)5.局部变量/实例变量(Local / Instance Variables&…...

【android bluetooth 框架分析 04】【bt-framework 层详解 1】【BluetoothProperties介绍】
1. BluetoothProperties介绍 libsysprop/srcs/android/sysprop/BluetoothProperties.sysprop BluetoothProperties.sysprop 是 Android AOSP 中的一种 系统属性定义文件(System Property Definition File),用于声明和管理 Bluetooth 模块相…...
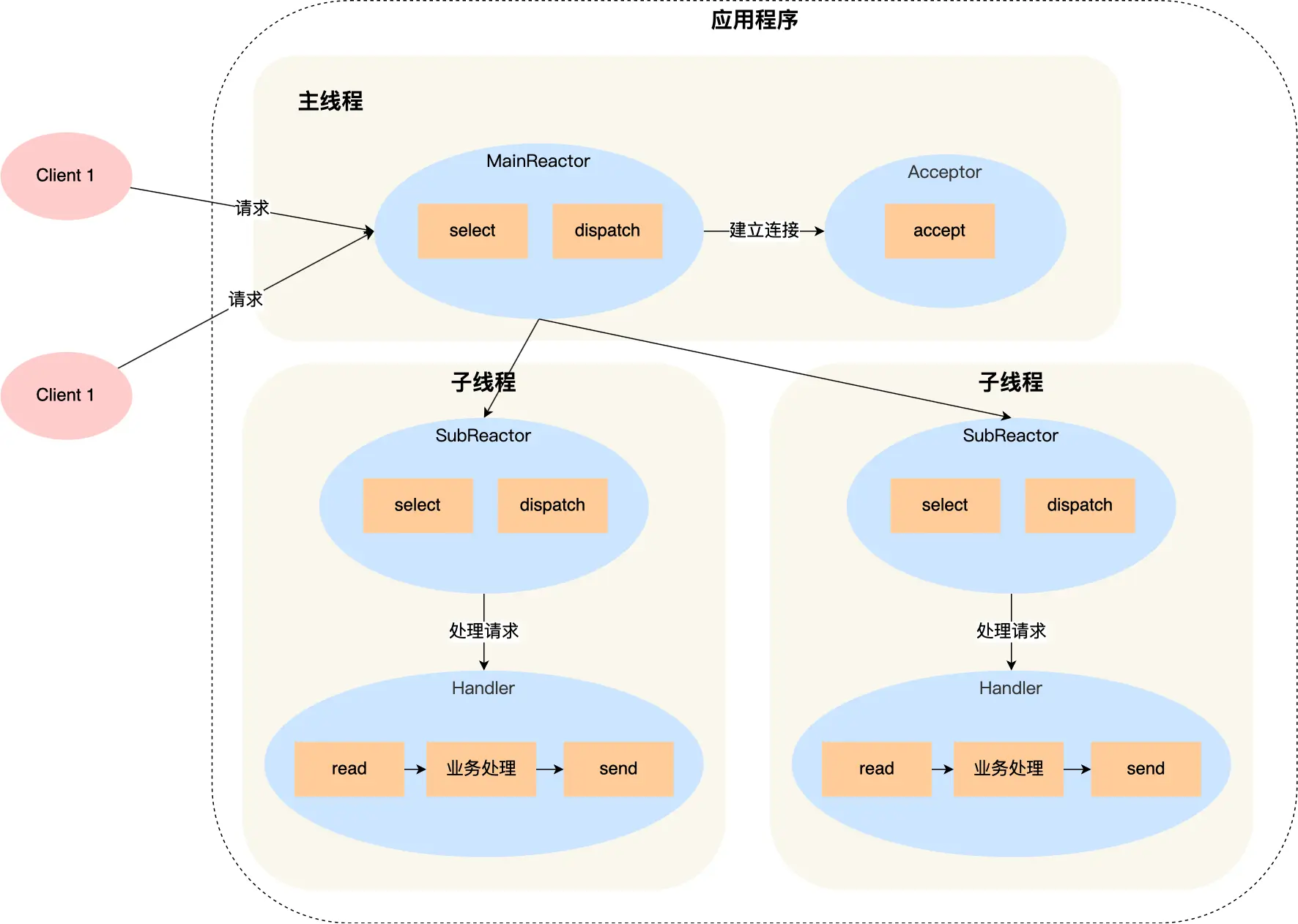
select、poll、epoll 与 Reactor 模式
在高并发网络编程领域,高效处理大量连接和 I/O 事件是系统性能的关键。select、poll、epoll 作为 I/O 多路复用技术的代表,以及基于它们实现的 Reactor 模式,为开发者提供了强大的工具。本文将深入探讨这些技术的底层原理、优缺点。 一、I…...

智能AI电话机器人系统的识别能力现状与发展水平
一、引言 随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI电话机器人系统已经从简单的自动应答工具演变为具备复杂交互能力的智能助手。这类系统结合了语音识别、自然语言处理、情感计算和机器学习等多项前沿技术,在客户服务、营销推广、信息查询等领域发挥着越来越重要…...
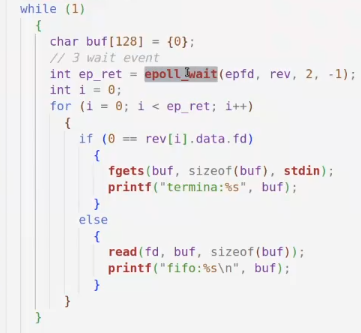
day36-多路IO复用
一、基本概念 (服务器多客户端模型) 定义:单线程或单进程同时监测若干个文件描述符是否可以执行IO操作的能力 作用:应用程序通常需要处理来自多条事件流中的事件,比如我现在用的电脑,需要同时处理键盘鼠标…...

go 里面的指针
指针 在 Go 中,指针(pointer)是一个变量的内存地址,就像 C 语言那样: a : 10 p : &a // p 是一个指向 a 的指针 fmt.Println(*p) // 输出 10,通过指针解引用• &a 表示获取变量 a 的地址 p 表示…...
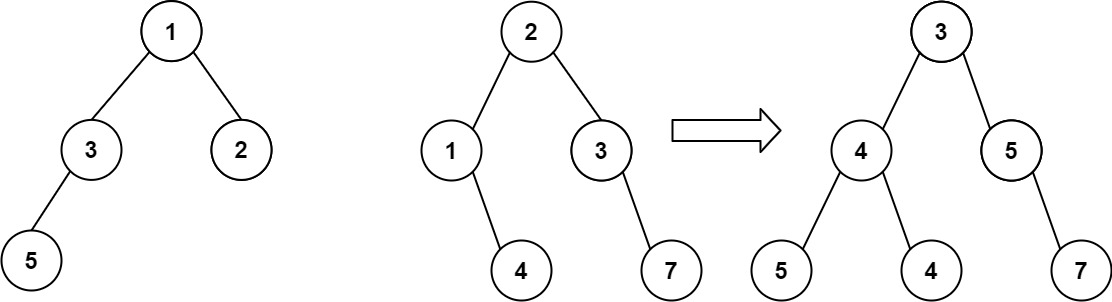
算法打卡第18天
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 (力扣106题) 给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。 示例 1: 输入:inorder [9,3,15,20,7…...

Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫
Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫 构建坚不可摧的数字堡垒 引言:攻防对抗的新纪元 在日益复杂的网络威胁环境中,Linux系统安全已从被动防御转向主动免疫。2023年全球网络安全报告显示,高级持续性威胁(APT)攻击同比增长65%,平均入侵停留时间缩短至48小时。本章将从…...
