【Pytorch】深度学习之损失函数
文章目录
- 二分类交叉熵损失函数
- 交叉熵损失函数
- L1损失函数
- MSE损失函数
- 平滑L1(Smooth L1)损失函数
- 目标泊松分布的负对数似然损失
- KL散度
- MarginRankingLoss
- 多标签边界损失函数
- 二分类损失函数
- 多分类的折页损失
- 三元组损失
- HingEmbeddingLoss
- 余弦相似度
- CTC损失函数
- 参考资料
学习目标:

二分类交叉熵损失函数
函数
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
input为sigmoid函数的输出或softmax函数的输出
label为{0, 1}
功能:计算二分类任务时的交叉熵(Cross Entropy)
参数说明
weight:给每个类别的loss设置权值
size_average:bool类型,值为True时,返回各样本loss平均值;值为False时,返回各样本loss之和
reduce:bool类型,值为True时,返回loss为标量
代码说明
m = nn.Sigmoid()
loss = nn.BCELoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(m(input), target)
output.backward()
print('BCELoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
交叉熵损失函数
函数
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
功能:计算交叉熵
计算公式
l o s s ( x , c l a s s ) = − l o g ( e x p ( x [ c l a s s ] ) ∑ j e x p ( x [ j ] ) ) = − x [ c l a s s ] + l o g ( ∑ j e x p ( x [ j ] ) ) loss(x, class) = -log(\frac{exp(x[class])}{\sum_jexp(x[j])}) = -x[class] + log(\sum_jexp(x[j])) loss(x,class)=−log(∑jexp(x[j])exp(x[class]))=−x[class]+log(j∑exp(x[j]))
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3, dtype=torch.long).random_(5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
L1损失函数
函数
torch.nn.L1Loss(size_aveage=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
功能:output和真实标签之间差值的绝对值
参数说明
reduction参数——决定计算模式
none——逐个元素计算,output和输入元素同尺寸
sum——所有元素求和,返回标量
mean——加权平均,返回标量
计算公式
L n = ∣ x n − y n ∣ L_n = |x_n-y_n| Ln=∣xn−yn∣
代码示例
loss = nn.L1Loss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
MSE损失函数
函数
torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
功能:计算output和真实标签target之差的平方
代码示例
loss = nn.MSELoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
平滑L1(Smooth L1)损失函数
torch.nn.SmoothLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', beta=1.0)
功能:L1损失函数的平滑输出,能够减轻离群点带来的影响
计算公式
l o s s ( x , y ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n z i loss(x,y)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^nz_i loss(x,y)=n1i=1∑nzi
其中, z i z_i zi的计算公式如下
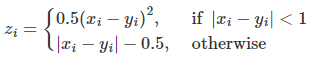
代码示例
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
对比平滑L1和L1
可视化两种损失函数曲线
inputs = torch.linspace(-10, 10, steps=5000)
target = torch.zeros_like(inputs)loss_f_smooth = nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='none')
loss_smooth = loss_f_smooth(inputs, target)
loss_f_l1 = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')
loss_l1 = loss_f_l1(inputs,target)plt.plot(inputs.numpy(), loss_smooth.numpy(), label='Smooth L1 Loss')
plt.plot(inputs.numpy(), loss_l1, label='L1 loss')
plt.xlabel('x_i - y_i')
plt.ylabel('loss value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
目标泊松分布的负对数似然损失
适用于回归任务,目标值(ground truth)服从泊松分布的回归问题,典型场景包括计数数据、连续型回归问题,如一天内发生的事件次数、网页访问次数
泊松分布: P ( Y = k ) = λ k k ! e − λ P(Y=k) = \frac{\lambda^k}{k!}e^{-\lambda} P(Y=k)=k!λke−λ
torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=false, size_average=None, eps=1e-08, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
参数解释
log_input:bool类型参数,用于说明输入是否为对数形式
full:bool类型,是否计算所有loss
eps:修正项,用于避免input为0时,log(input)为Nan的情况
计算公式
当参数log_input=True: l o s s ( x n , y n ) = e x n − x n ⋅ y n loss(x_n, y_n)=e^{x_n}-x_n\cdot y_n loss(xn,yn)=exn−xn⋅yn
当参数log_input=False: l o s s ( x n , y n ) = x n − y n ⋅ l o g ( x n + e p s ) loss(x_n, y_n) = x_n-y_n\cdot log(x_n+eps) loss(xn,yn)=xn−yn⋅log(xn+eps)
代码示例
loss = nn.PoissonNLLLoss()
log_input = torch.randn(5, 2, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(5, 2)
output = loss(log_input, target)
output.backward()
KL散度
torch.nn.KLDivLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', log_target=False)
功能:计算相对熵,度量连续分布的距离,对离散采用的连续输出空间分布进行回归
参数解释
reduction
取值有none/sum/mean/batchmean
none:逐个元素计算
sum:求和
mean:加权求和
batchmean:batchsize维度求平均值
计算公式
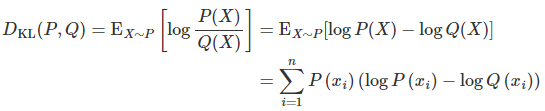
代码示例
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.3, 0.2], [0.2, 0.3, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[0.9, 0.05, 0.05], [0.1, 0.7, 0.2]], dtype=torch.float)
loss = nn.KLDivLoss()
output = loss(inputs,target)print('KLDivLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
MarginRankingLoss
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
功能:计算两个向量之间的相似度,用于排序任务,又称为排序损失函数

参数解释
margin:边界值,两个向量之间的差异值
计算公式
l o s s ( x 1 , x 2 , y ) = m a x ( 0 , − y ∗ ( x 1 − x 2 ) + m a r g i n ) loss(x_1, x_2, y) = max(0, -y*(x_1-x_2)+margin) loss(x1,x2,y)=max(0,−y∗(x1−x2)+margin)
代码示例
loss = nn.MarginRankingLoss()
input1 = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
input2 = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3).sign()
output = loss(input1, input2, target)
output.backward()print('MarginRankingLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
多标签边界损失函数
torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
关注的是样本和决策边界之间的间隔,使每个标签的得分都高于一个给定的阈值,并最小化样本与这些决策边界之间的间隔
计算公式
L ( y , f ( x ) ) = 1 N ∑ i = 1 N ∑ j = 1 C L i j L(y, f(x)) = \frac{1}{N}\sum^N_{i=1}\sum^C_{j=1}L_{ij} L(y,f(x))=N1∑i=1N∑j=1CLij
其中,N为样本数量,C为标签数量, L i j L_{ij} Lij为样本i对标签j的边界损失
L i j = m a x ( 0 , 1 − y i j ⋅ f ( x ) i j ) L_{ij}=max(0, 1-y_{ij}\cdot f(x)_{ij}) Lij=max(0,1−yij⋅f(x)ij)
y i j y_{ij} yij取值为 -1 或 1,表示标签 j 是否属于样本 i 的真实标签
若 y i j = 1 y_{ij}=1 yij=1,则要求 f ( x ) i j ≥ m a r g i n f(x)_{ij} \geq margin f(x)ij≥margin ;若 y i j = − 1 y_{ij}=-1 yij=−1,则要求 f ( x ) i j ≤ m a r g i n f(x)_{ij} \leq margin f(x)ij≤margin
代码示例
loss = nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss()
x = torch.FloatTensor([[0.9, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8]])
# for target y, only consider labels 3 and 0, not after label -1
y = torch.LongTensor([[3, 0, -1, -1]])# 真实的分类是,第3类和第0类,标签中的-1表示该标签不适用于该样本
output = loss(x, y)print('MultiLabelMarginLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
二分类损失函数
torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
功能:计算二分类的logistic损失,在训练SVM被经常使用,使得正确分类的样本得分与正确类别的边界之差大于一个预定义的边界值
计算公式
L ( y , f ( x ) ) = 1 N ∑ i = 1 N m a x ( 0 , 1 − y i ⋅ f ( x ) i ) L(y, f(x))=\frac{1}{N}\sum^N_{i=1}max(0, 1-y_{i}\cdot f(x)_{i}) L(y,f(x))=N1∑i=1Nmax(0,1−yi⋅f(x)i)
样本的真实标签和预测得分的乘积与1之差的最大值
若 y i ⋅ f ( x ) i ≥ 1 y_{i}\cdot f(x)_{i} \geq 1 yi⋅f(x)i≥1,样本被正确分类,损失为0
反之,样本离正确分类还有距离,加入损失
代码示例
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.7], [0.5, 0.5]]) # 两个样本,两个神经元
target = torch.tensor([[-1, 1], [1, -1]], dtype=torch.float) # 该 loss 为逐个神经元计算,需要为每个神经元单独设置标签loss_f = nn.SoftMarginLoss()
output = loss_f(inputs, target)print('SoftMarginLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
多分类的折页损失
torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1, margin=1.0, weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
参数解释
p:可选 1 或 2
weight:各类别loss的权值
计算公式
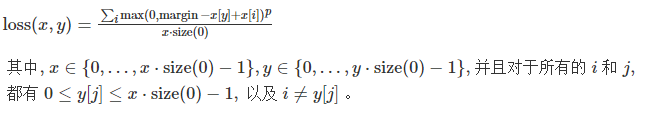
代码示例
inputs = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.7], [0.5, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([0, 1], dtype=torch.long) loss_f = nn.MultiMarginLoss()
output = loss_f(inputs, target)print('MultiMarginLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
三元组损失
torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2.0, eps=1e-06, swap=False, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
说明
三元组:特殊的数据存储格式,有很多具体的引用,如nlp的关系抽取任务中<实体1, 关系, 实体2>,又如项目中的<anchor, positive examples, negative examples>
损失函数倾向于使anchor与positive examples的距离更近,而与negative examples的距离更远
计算公式
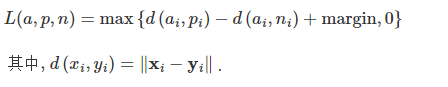
代码示例
triplet_loss = nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2)
anchor = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
positive = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
negative = torch.randn(100, 128, requires_grad=True)
output = triplet_loss(anchor, positive, negative)
output.backward()
print('TripletMarginLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
HingEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
计算公式
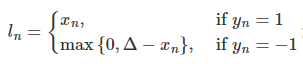
代码示例
loss_f = nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss()
inputs = torch.tensor([[1., 0.8, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([[1, 1, -1]])
output = loss_f(inputs,target)print('HingEmbeddingLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
余弦相似度
torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.0, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
计算公式
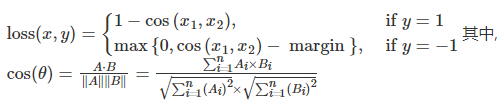
代码示例
loss_f = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss()
inputs_1 = torch.tensor([[0.3, 0.5, 0.7], [0.3, 0.5, 0.7]])
inputs_2 = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.5], [0.1, 0.3, 0.5]])
target = torch.tensor([1, -1], dtype=torch.float)
output = loss_f(inputs_1,inputs_2,target)print('CosineEmbeddingLoss损失函数的计算结果为',output)
CTC损失函数
CTC(Connectionist Temporal Classification)处理seq2seq任务,如语音识别、手写体识别,解决序列对齐问题,即在输入序列和目标序列长度不同的情况下,计算它们之间的对应关系
计算路径概率:对于给定的输入序列和目标标签,CTC损失考虑所有可能的对齐路径,在这些对齐路径对应的对齐方式中,重复字符被合并,空白标签被插入。CTC损失计算这些路径的概率之和
在反向传播中,CTC损失也会考虑所有可能的对齐方式
L ( y , y ^ ) = − l o g ( P ( y ^ ∣ y ) ) L(y, \hat y) = -log(P(\hat y|y)) L(y,y^)=−log(P(y^∣y))
torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='mean', zero_infinity=False)
功能:用于时序类数据的分类, 计算连续时间序列和目标序列之间的损失
参数解释
blank:blank label
zero_infinity:无穷大的值
代码示例
# Target are to be padded
T = 50 # Input sequence length
C = 20 # Number of classes (including blank)
N = 16 # Batch size
S = 30 # Target sequence length of longest target in batch (padding length)
S_min = 10 # Minimum target length, for demonstration purposes# Initialize random batch of input vectors, for *size = (T,N,C)
# 生成一批随机输入序列
# 这些input序列通过softmax函数沿着最后一个维度(detach函数)传递,对数化处理
input = torch.randn(T, N, C).log_softmax(2).detach().requires_grad_()# Initialize random batch of targets (0 = blank, 1:C = classes) 生成随机目标标签
target = torch.randint(low=1, high=C, size=(N, S), dtype=torch.long)# 初始化input序列长度和目标序列长度,input中每个序列长度都为样本最大序列长度T,target中每个序列长度为S_min到S之间的随机值
input_lengths = torch.full(size=(N,), fill_value=T, dtype=torch.long)
target_lengths = torch.randint(low=S_min, high=S, size=(N,), dtype=torch.long)
ctc_loss = nn.CTCLoss()
loss = ctc_loss(input, target, input_lengths, target_lengths)
loss.backward()
# Target are to be un-padded
T = 50 # Input sequence length
C = 20 # Number of classes (including blank)
N = 16 # Batch size# Initialize random batch of input vectors, for *size = (T,N,C)
input = torch.randn(T, N, C).log_softmax(2).detach().requires_grad_()
input_lengths = torch.full(size=(N,), fill_value=T, dtype=torch.long)# Initialize random batch of targets (0 = blank, 1:C = classes)
target_lengths = torch.randint(low=1, high=T, size=(N,), dtype=torch.long)
# target的生成方式变化,使用的是每个样本的长度来生成target
target = torch.randint(low=1, high=C, size=(sum(target_lengths),), dtype=torch.long)
ctc_loss = nn.CTCLoss()
loss = ctc_loss(input, target, input_lengths, target_lengths)
loss.backward()print('CTCLoss损失函数的计算结果为',loss)
关于seq2seq任务中的pading和unpadding:
填充:使所有序列达到相同的长度,以便进行批处理操作。通过在短序列两侧添加特殊标记(通常是0)来保持相同的长度。适用要求输入序列长度相同的模型,如循环神经网络(RNN)或卷积神经网络(CNN)等
不填充:模型可以直接根据输入序列的实际长度进行建模。适用于模型能够处理变长输入和目标序列的情况,如注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)或Connectionist Temporal Classification(CTC)损失
在CTC损失计算中,不填充的target使得目标序列与输入序列一一对应,不添加额外的标记,损失计算能够更接近实际任务
参考资料
- datawhale through-pytorch repo
- loss函数之PoissonNLLLoss, GaussianNLLLoss
- torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss文本排序
- 语音识别:深入理解CTC Loss原理
相关文章:
【Pytorch】深度学习之损失函数
文章目录 二分类交叉熵损失函数交叉熵损失函数L1损失函数MSE损失函数平滑L1(Smooth L1)损失函数目标泊松分布的负对数似然损失KL散度MarginRankingLoss多标签边界损失函数二分类损失函数多分类的折页损失三元组损失HingEmbeddingLoss余弦相似度CTC损失函数参考资料 学习目标&am…...

3.4 构造方法
思维导图: 3.4.1 定义构造方法 ### Java中的构造方法 #### **定义与目的** 构造方法,也称为构造器,是一个特殊的成员方法,用于在实例化对象时为对象赋值或执行初始化操作。其主要目的是确保对象在被创建时具有有效和合适的初始状…...

代码随想录
前言 代码随想录算法训练营day43 一、Leetcode 1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II 1.题目 有一堆石头,用整数数组 stones 表示。其中 stones[i] 表示第 i 块石头的重量。 每一回合,从中选出任意两块石头,然后将它们一起粉碎。假设石头的重量分…...
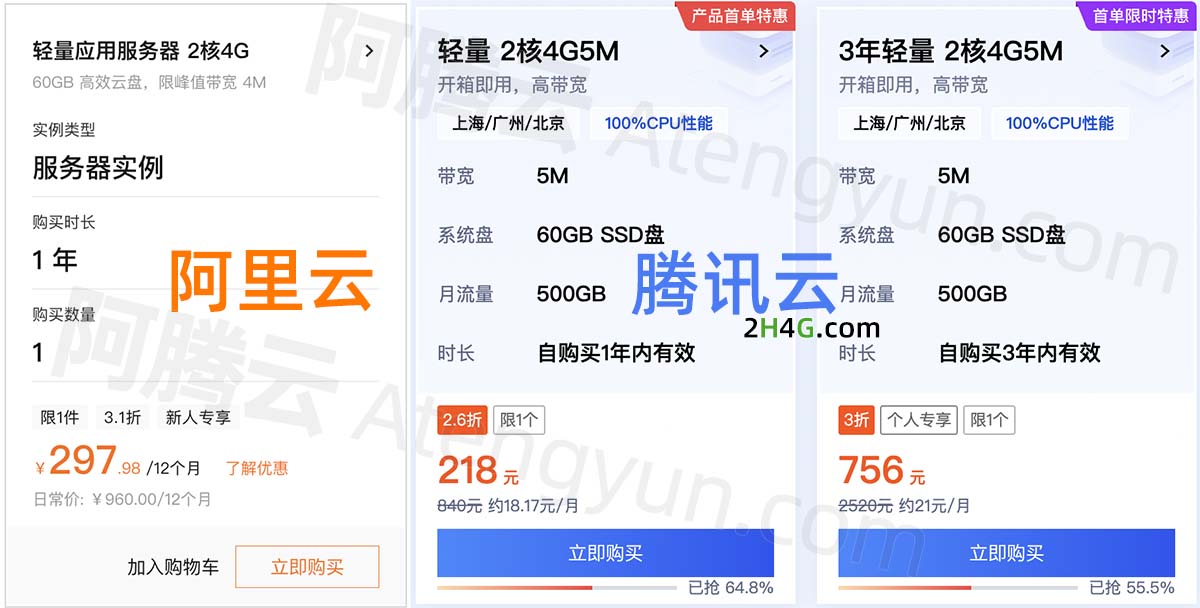
2核4G游戏服务器推荐(阿里云/腾讯云/华为云)
2核4G游戏服务器推荐,首选腾讯云2核4G5M带宽轻量应用服务器218元一年、阿里云2核4G4M带宽轻量应用服务器297元一年,华为云2核2G3M云耀L服务器95元一年,阿腾云来详细说下2核4G游戏服务器推荐配置大全: 目录 2核4G游戏服务器推荐 …...
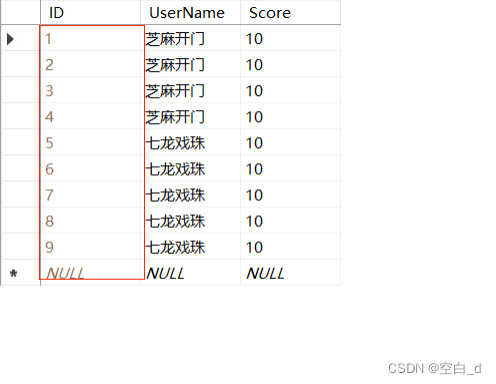
SQL标识列实现自动编号的步骤和技巧以及优势
目录 前言: 过程: 1.步骤: 2.标识种子和表示增量: 效果展示: 优势: 总结: 前言: 在.NET中的例子里面遇到这么一个问题,不能将NULL插入列‘ID’,表Login.dbo.Scores’;列不允许有NULL值。INSERT失败。这个问题很明显,我在SQL数据库中…...
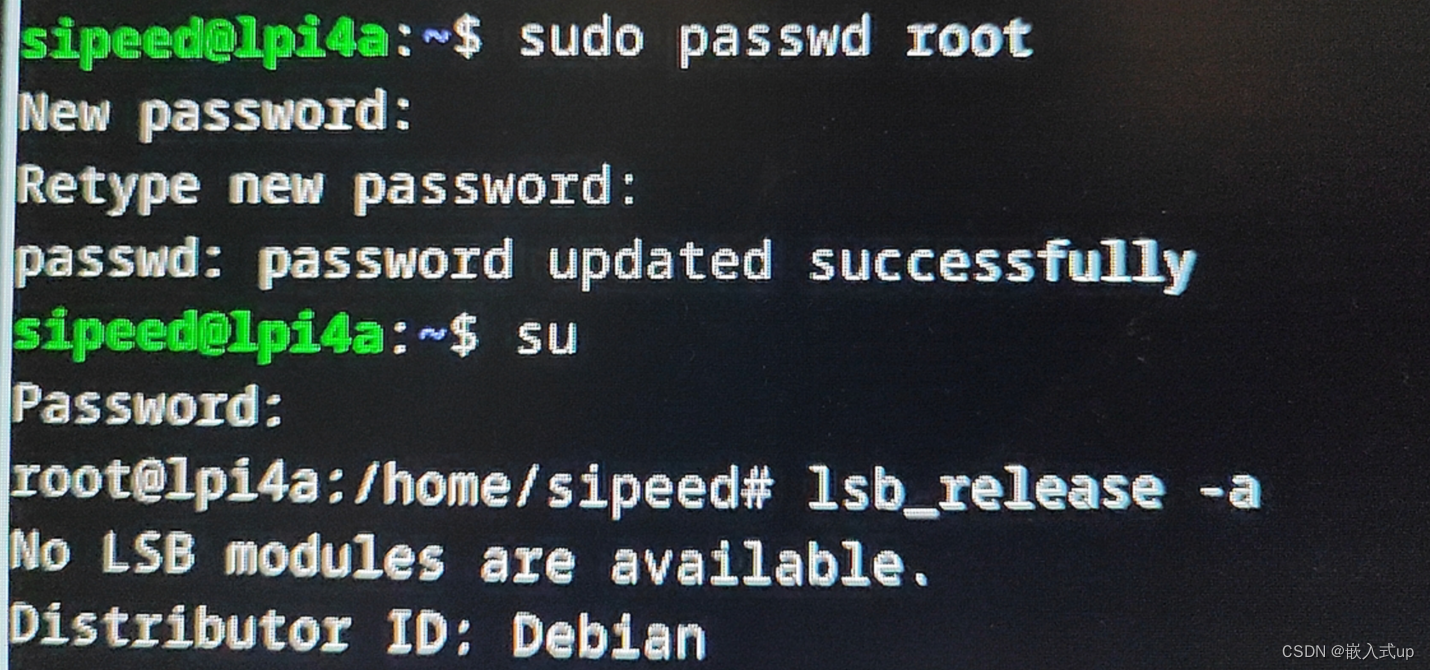
【Debian】报错:su: Authentication failure
项目场景: 今天我重新刷了一个debian系统。 系统版本: # 查看系统版本 lsb_release -a 我的系统版本: No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID:Debian Description: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookwormÿ…...

我测试用的mark down教程
Markdown 教程 欢迎使用 Markdown 你好,Markdown是一种类似 Word 的排版工具,你需要仔细阅读这篇文章,了解一下 Markdown 基础知识。 Markdown 功能和列表演示 Markdown 有以下功能,帮助你用它写博客: 数学公式代码高亮导航功能等等Markdown 的优点: 间接高效大厂支持…...
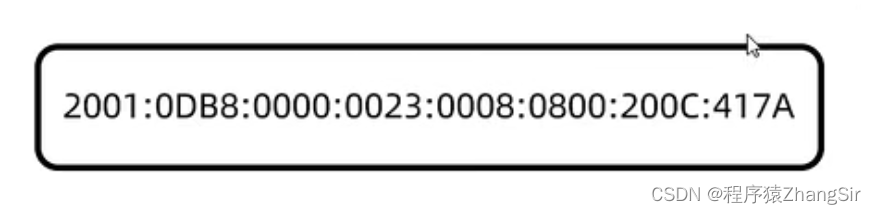
网络编程基础知识总结——IP,端口,协议
目录 1. 什么是网络编程? 2. 网络编程的三要素 3. IP 3.1 IP地址的概念 3.2 IP地址的分类 3.3 IPv4解析 3.4 Ipv6解析 4. IPv4 的使用细节 5. 特殊IP地址 4. 端口号 5. 协议 5.1 UDP协议 5.2 TCP协议 1. 什么是网络编程? 总的来说就是一句…...

【LeetCode力扣】297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
目录 1、题目介绍 2、解题思路 2.1、详细过程图解 2.2、代码描述 2.3、完整代码 1、题目介绍 原题链接:297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 - 力扣(LeetCode) 示例 1: 输入:root [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] 输出&#…...

Linux寄存器+Linux2.6内核进程调度队列+命令行参数+环境变量
目录 一、寄存器 二、Linux2.6内核进程调度队列 (一)优先级 (二)活动队列 (三)过期队列 (四)active指针和expired指针 三、命令行参数 (一)举例一 &…...
获取C(n,k)组合数列表的QT实现)
组合数(2)获取C(n,k)组合数列表的QT实现
1)工程文件 QT coreCONFIG c17 cmdline# You can make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs. # In order to do so, uncomment the following line. #DEFINES QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.…...

SparkCore编程RDD
RDD概述 中文名为弹性分布式数据集,是数据处理基本单位。代表一个弹性的,不可变,可分区,里面的数据可并行计算的集合。 RDD和Hadoop MR 的区别: RDD是先明确数据处理流程,数据在行动算子执行前实际上并未…...

VBA技术资料MF69:添加和删除工作表中的分页符
我给VBA的定义:VBA是个人小型自动化处理的有效工具。利用好了,可以大大提高自己的工作效率,而且可以提高数据的准确度。我的教程一共九套,分为初级、中级、高级三大部分。是对VBA的系统讲解,从简单的入门,到…...
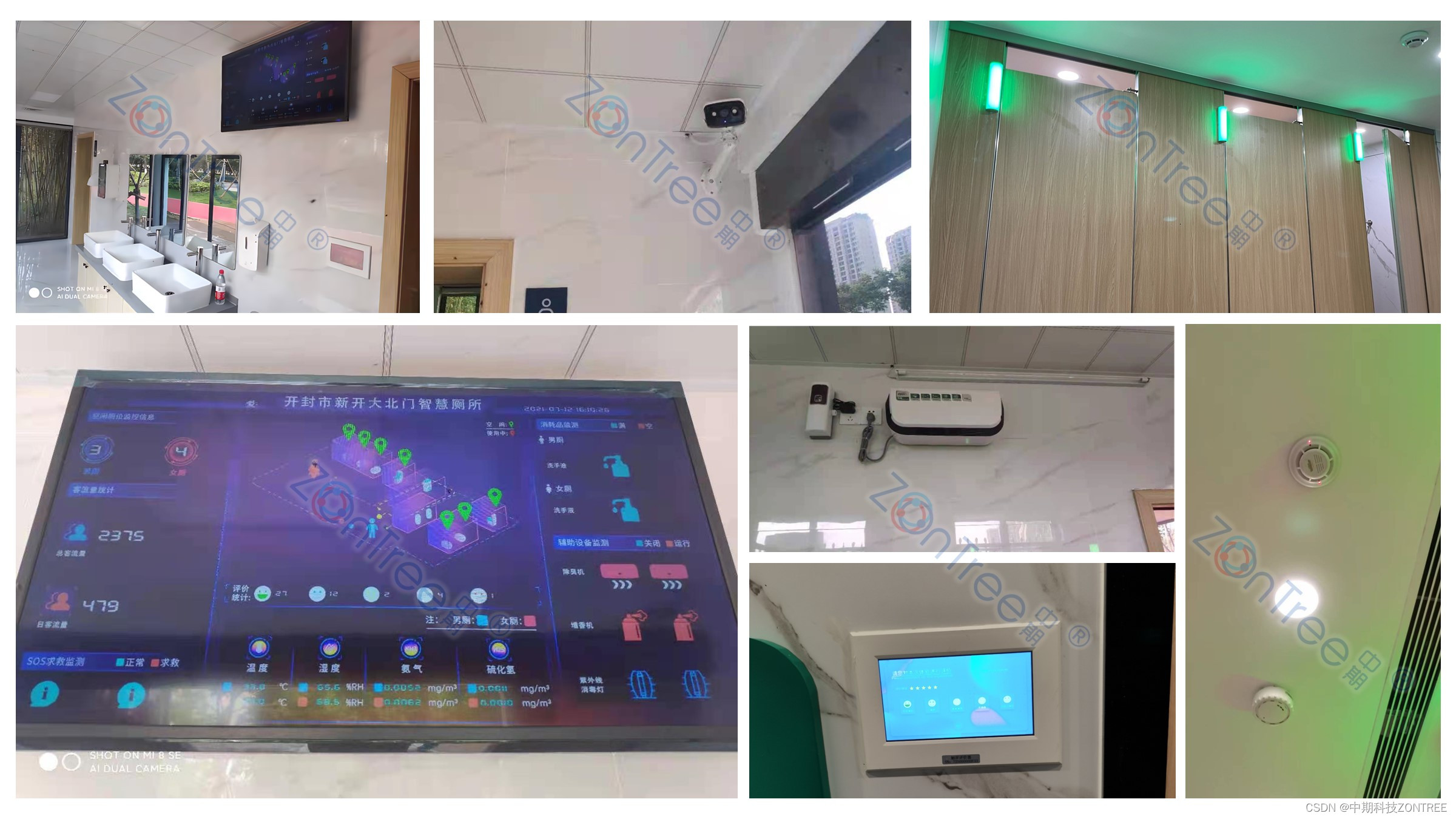

数字技术助力智慧公厕,让公厕变身为全新创新应用
在如今数字化的时代,数字技术的集成应用已经渗透到了生活的方方面面。其中一个令人瞩目的领域就是智慧公厕。以前只是简单的厕所,如今借助数字技术的力量,智慧公厕变得功能强大、智能高效。接下来,我们将以智慧公厕源头领航厂家广…...
electron 升级 v22 遇到问题
Electron 漏洞 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5LpSJb_5uV8EIDOl3fz9Tw 由于 23以上不在支持win 7 8 8.1 所以我选择安装 v22.3.24 electron 22.3.24 node-sass 6.0.1 sass-loader 10.4.1 对应的版本 npm i node-sass6.0.1 --sass_binary_sitehttps://npm.taobao.org/mirrors…...

跟我学c++中级篇——Pimpl
一、前向声明 前向声明或者前置声明(forward declaration),这个在c中用得还是比较多的。一般的框架或者库中,经常可以看到在一个类的前面声明了一个类,类似下面这样: class useclass; class mycall{...useclass *us; };前向声明…...
[补题记录] Atcoder Beginner Contest 295(E)
URL:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc295 目录 E Problem/题意 Thought/思路 Code/代码 E Problem/题意 给定长度为 N 的数组 A。进行如下操作: 若 Ai 0,将 Ai 等概率地变为 1 ~ M 中的任意一个数;对 A 排序; …...
解决git在window11操作很慢,占用很大cpu的问题
【git在window11操作很慢,占用很大cpu,最后也执行失败】 在谷歌输入:git very slow in window 11。通过下面链接终于找到了解决方案: https://www.reddit.com/r/vscode/comments/sulebx/slow_git_in_wsl_after_updating_to_window…...
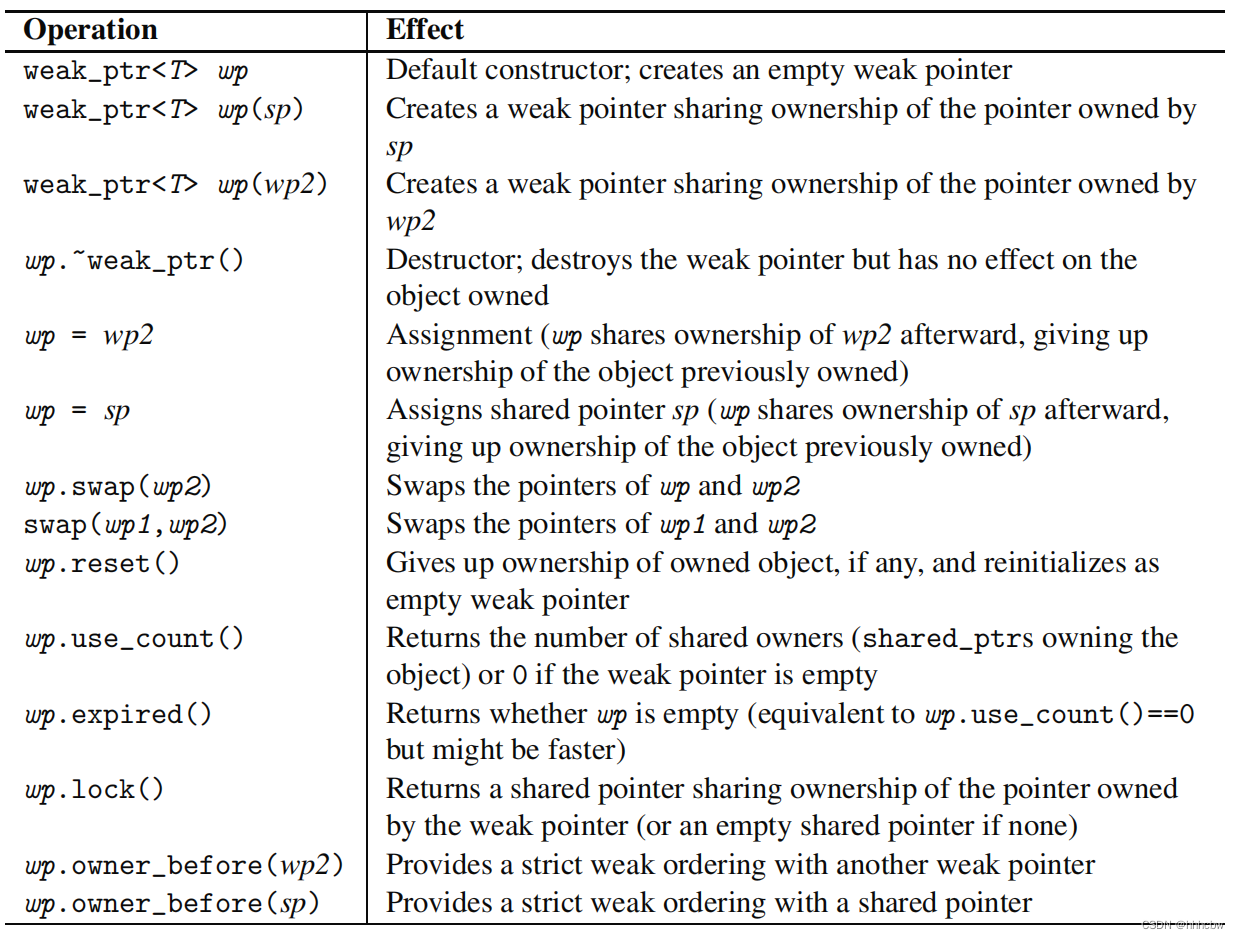
C++智能指针(二)——weak_ptr初探
文章目录 1. shared_ptr 存在的问题2. 使用weak_ptr2.1 初始化 weak_ptr2.2 访问数据 3. 附录4. 参考文献 1. shared_ptr 存在的问题 与 shared_ptr 的引入要解决普通指针存在的一些问题一样,weak_ptr 的引入,也是因为 shared_ptr 本身在某些情况下&…...
)
540 - Team Queue (UVA)
题目链接如下: Online Judge 对比刘汝佳的代码,我没有用queue来排整个队伍,因为那样的话遍历整个队伍太麻烦,vector比较方便。但vector删除元素比较耗时,所以就不删了,仅仅用pivot来指代目前队伍的开始。…...
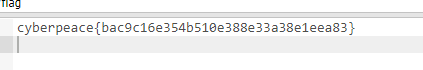
XCTF-web-easyupload
试了试php,php7,pht,phtml等,都没有用 尝试.user.ini 抓包修改将.user.ini修改为jpg图片 在上传一个123.jpg 用蚁剑连接,得到flag...
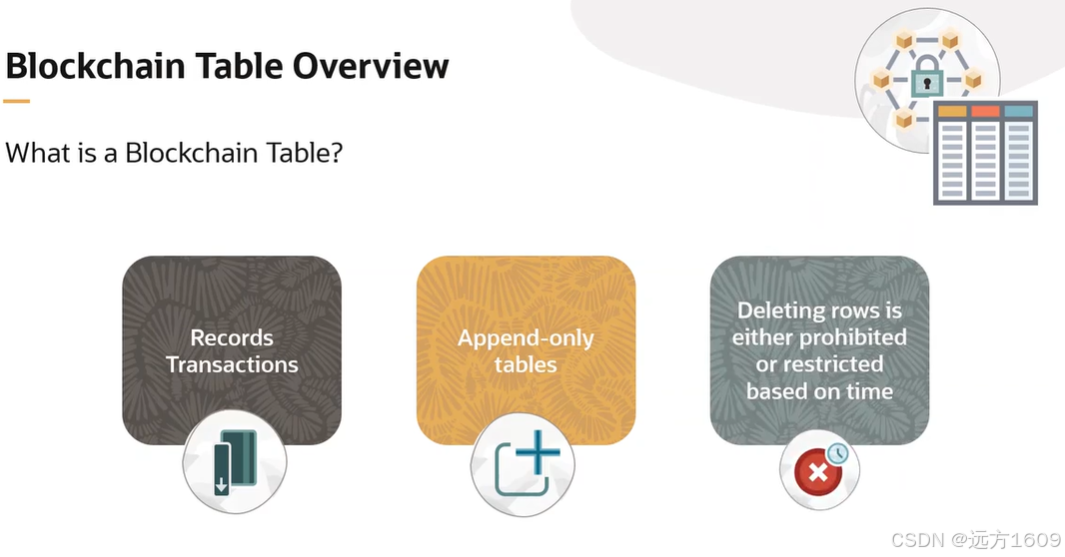
23-Oracle 23 ai 区块链表(Blockchain Table)
小伙伴有没有在金融强合规的领域中遇见,必须要保持数据不可变,管理员都无法修改和留痕的要求。比如医疗的电子病历中,影像检查检验结果不可篡改行的,药品追溯过程中数据只可插入无法删除的特性需求;登录日志、修改日志…...

Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Callable接口深度解析 一、Callable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Runnable接口的对比1.3 Future接口与FutureTask类 二、Callable接口的基本使用方法2.1 传统方式实现Callable接口2.2 使用Lambda表达式简化Callable实现2.3 使用FutureTask类执行Callable任务 三、…...
:滤镜命令)
ffmpeg(四):滤镜命令
FFmpeg 的滤镜命令是用于音视频处理中的强大工具,可以完成剪裁、缩放、加水印、调色、合成、旋转、模糊、叠加字幕等复杂的操作。其核心语法格式一般如下: ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf "滤镜参数" output.mp4或者带音频滤镜: ffmpeg…...

实现弹窗随键盘上移居中
实现弹窗随键盘上移的核心思路 在Android中,可以通过监听键盘的显示和隐藏事件,动态调整弹窗的位置。关键点在于获取键盘高度,并计算剩余屏幕空间以重新定位弹窗。 // 在Activity或Fragment中设置键盘监听 val rootView findViewById<V…...

[Java恶补day16] 238.除自身以外数组的乘积
给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。 题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。 请 不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度…...

聊一聊接口测试的意义有哪些?
目录 一、隔离性 & 早期测试 二、保障系统集成质量 三、验证业务逻辑的核心层 四、提升测试效率与覆盖度 五、系统稳定性的守护者 六、驱动团队协作与契约管理 七、性能与扩展性的前置评估 八、持续交付的核心支撑 接口测试的意义可以从四个维度展开,首…...

C++八股 —— 单例模式
文章目录 1. 基本概念2. 设计要点3. 实现方式4. 详解懒汉模式 1. 基本概念 线程安全(Thread Safety) 线程安全是指在多线程环境下,某个函数、类或代码片段能够被多个线程同时调用时,仍能保证数据的一致性和逻辑的正确性…...
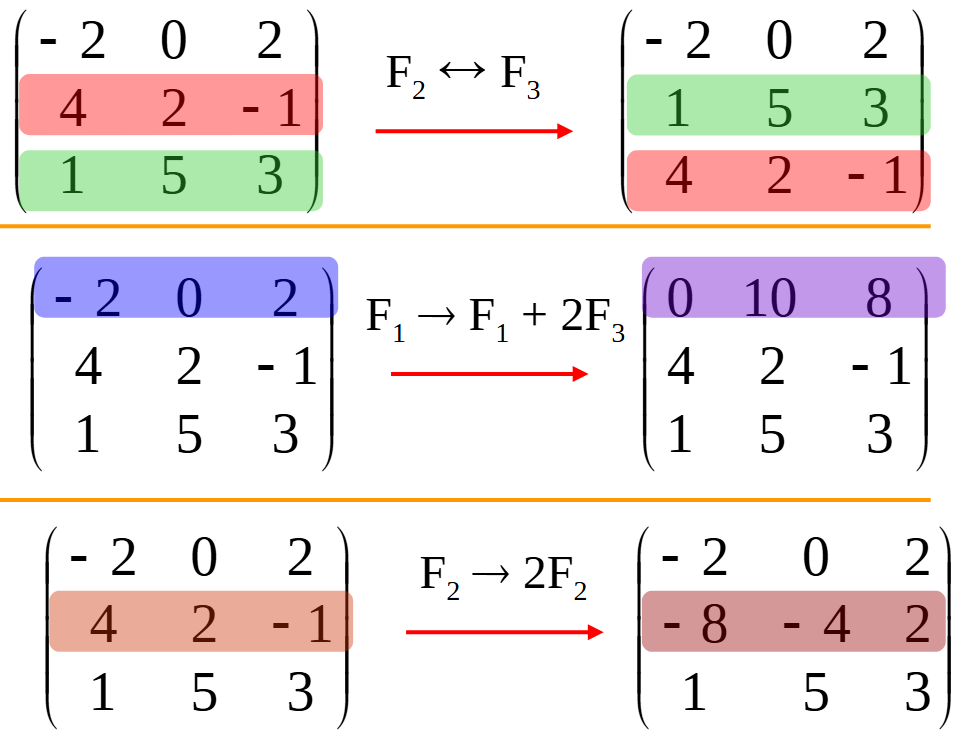
使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的高级操作
在科学计算和工程领域,向量和矩阵操作是解决问题的核心技能之一。Python 的 SymPy 库提供了强大的符号计算功能,能够高效地处理向量和矩阵的各种操作。本文将深入探讨如何使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的创建、合并以及维度拓展等操作,并通过具体…...

AirSim/Cosys-AirSim 游戏开发(四)外部固定位置监控相机
这个博客介绍了如何通过 settings.json 文件添加一个无人机外的 固定位置监控相机,因为在使用过程中发现 Airsim 对外部监控相机的描述模糊,而 Cosys-Airsim 在官方文档中没有提供外部监控相机设置,最后在源码示例中找到了,所以感…...
