CUDA中的数学方法
CUDA中的数学方法

文章目录
- CUDA中的数学方法
- 1. Standard Functions
- Single-Precision Floating-Point Functions
- Double-Precision Floating-Point Functions
- 2. Intrinsic Functions
- Single-Precision Floating-Point Functions
- Double-Precision Floating-Point Functions
参考手册列出了设备代码中支持的 C/C++ 标准库数学函数的所有函数及其描述,以及所有内部函数(仅在设备代码中支持)。
本附录在适用时提供了其中一些功能的准确性信息。它使用 ULP 进行量化。有关最后位置单元 (ULP: Unit in the Last Place, 上面是直译的,这里可以理解为最小精度单元) 定义的更多信息,请参阅 Jean-Michel Muller’s paper On the definition of ulp(x), RR-5504, LIP RR-2005-09, INRIA, LIP. 2005, pp.16 at https://hal.inria.fr/inria-00070503/document
设备代码中支持的数学函数不设置全局 errno 变量,也不报告任何浮点异常来指示错误;因此,如果需要错误诊断机制,用户应该对函数的输入和输出实施额外的筛选。用户负责指针参数的有效性。用户不得将未初始化的参数传递给数学函数,因为这可能导致未定义的行为:函数在用户程序中内联,因此受到编译器优化的影响。
1. Standard Functions
本节中的函数可用于主机和设备代码。
本节指定每个函数在设备上执行时的错误范围,以及在主机不提供函数的情况下在主机上执行时的错误范围。
错误界限是从广泛但并非详尽的测试中生成的,因此它们不是保证界限。
Single-Precision Floating-Point Functions
加法和乘法符合 IEEE 标准,因此最大误差为 0.5 ulp。
将单精度浮点操作数舍入为整数的推荐方法是 rintf(),而不是 roundf()。 原因是 roundf() 映射到设备上的 4 条指令序列,而 rintf() 映射到单个指令。 truncf()、ceilf() 和 floorf() 也都映射到一条指令。
| Function | Maximum ulp error |
|---|---|
| x+y | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| x*y | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| x/y | 0 for compute capability ≥ 2 when compiled with -prec-div=true 2 (full range), otherwise |
| 1/x | 0 for compute capability ≥ 2 when compiled with -prec-div=true 1 (full range), otherwise |
| rsqrtf(x) 1/sqrtf(x) | 2 (full range) Applies to 1/sqrtf(x) only when it is converted to rsqrtf(x) by the compiler. |
| sqrtf(x) | 0 when compiled with -prec-sqrt=true Otherwise 1 for compute capability ≥ 5.2 and 3 for older architectures |
| cbrtf(x) | 1 (full range) |
| rcbrtf(x) | 1 (full range) |
| hypotf(x,y) | 3 (full range) |
| rhypotf(x,y) | 2 (full range) |
| norm3df(x,y,z) | 3 (full range) |
| rnorm3df(x,y,z) | 2 (full range) |
| norm4df(x,y,z,t) | 3 (full range) |
| rnorm4df(x,y,z,t) | 2 (full range) |
| normf(dim,arr) | An error bound can't be provided because a fast algorithm is used with accuracy loss due to round-off |
| rnormf(dim,arr) | An error bound can't be provided because a fast algorithm is used with accuracy loss due to round-off |
| expf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| exp2f(x) | 2 (full range) |
| exp10f(x) | 2 (full range) |
| expm1f(x) | 1 (full range) |
| logf(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log2f(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log10f(x) | 2 (full range) |
| log1pf(x) | 1 (full range) |
| sinf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| cosf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| tanf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| sincosf(x,sptr,cptr) | 2 (full range) |
| sinpif(x) | 2 (full range) |
| cospif(x) | 2 (full range) |
| sincospif(x,sptr,cptr) | 2 (full range) |
| asinf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| acosf(x) | 3 (full range) |
| atanf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| atan2f(y,x) | 3 (full range) |
| sinhf(x) | 3 (full range) |
| coshf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| tanhf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| asinhf(x) | 3 (full range) |
| acoshf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| atanhf(x) | 3 (full range) |
| powf(x,y) | 9 (full range) |
| erff(x) | 2 (full range) |
| erfcf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| erfinvf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| erfcinvf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| erfcxf(x) | 4 (full range) |
| normcdff(x) | 5 (full range) |
| normcdfinvf(x) | 5 (full range) |
| lgammaf(x) | 6 (outside interval -10.001 ... -2.264; larger inside) |
| tgammaf(x) | 11 (full range) |
| fmaf(x,y,z) | 0 (full range) |
| frexpf(x,exp) | 0 (full range) |
| ldexpf(x,exp) | 0 (full range) |
| scalbnf(x,n) | 0 (full range) |
| scalblnf(x,l) | 0 (full range) |
| logbf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| ilogbf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| j0f(x) | 9 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| j1f(x) | 9 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| jnf(n,x) | For n = 128, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| y0f(x) | 9 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| y1f(x) | 9 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| ynf(n,x) | ceil(2 + 2.5n) for |x| < n otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 2.2 x 10-6 |
| cyl_bessel_i0f(x) | 6 (full range) |
| cyl_bessel_i1f(x) | 6 (full range) |
| fmodf(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| remainderf(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| remquof(x,y,iptr) | 0 (full range) |
| modff(x,iptr) | 0 (full range) |
| fdimf(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| truncf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| roundf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| rintf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| nearbyintf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| ceilf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| floorf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| lrintf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| lroundf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| llrintf(x) | 0 (full range) |
| llroundf(x) | 0 (full range) |
Double-Precision Floating-Point Functions
将双精度浮点操作数舍入为整数的推荐方法是 rint(),而不是 round()。 原因是 round() 映射到设备上的 5 条指令序列,而 rint() 映射到单个指令。 trunc()、ceil() 和 floor() 也都映射到一条指令。
| Function | Maximum ulp error |
|---|---|
| x+y | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| x*y | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| x/y | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| 1/x | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| sqrt(x) | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| rsqrt(x) | 1 (full range) |
| cbrt(x) | 1 (full range) |
| rcbrt(x) | 1 (full range) |
| hypot(x,y) | 2 (full range) |
| rhypot(x,y) | 1 (full range) |
| norm3d(x,y,z) | 2 (full range) |
| rnorm3d(x,y,z) | 1 (full range) |
| norm4d(x,y,z,t) | 2 (full range) |
| rnorm4d(x,y,z,t) | 1 (full range) |
| norm(dim,arr) | An error bound can't be provided because a fast algorithm is used with accuracy loss due to round-off |
| rnorm(dim,arr) | An error bound can't be provided because a fast algorithm is used with accuracy loss due to round-off |
| exp(x) | 1 (full range) |
| exp2(x) | 1 (full range) |
| exp10(x) | 1 (full range) |
| expm1(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log2(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log10(x) | 1 (full range) |
| log1p(x) | 1 (full range) |
| sin(x) | 2 (full range) |
| cos(x) | 2 (full range) |
| tan(x) | 2 (full range) |
| sincos(x,sptr,cptr) | 2 (full range) |
| sinpi(x) | 2 (full range) |
| cospi(x) | 2 (full range) |
| sincospi(x,sptr,cptr) | 2 (full range) |
| asin(x) | 2 (full range) |
| acos(x) | 2 (full range) |
| atan(x) | 2 (full range) |
| atan2(y,x) | 2 (full range) |
| sinh(x) | 2 (full range) |
| cosh(x) | 1 (full range) |
| tanh(x) | 1 (full range) |
| asinh(x) | 2 (full range) |
| acosh(x) | 2 (full range) |
| atanh(x) | 2 (full range) |
| pow(x,y) | 2 (full range) |
| erf(x) | 2 (full range) |
| erfc(x) | 5 (full range) |
| erfinv(x) | 5 (full range) |
| erfcinv(x) | 6 (full range) |
| erfcx(x) | 4 (full range) |
| normcdf(x) | 5 (full range) |
| normcdfinv(x) | 8 (full range) |
| lgamma(x) | 4 (outside interval -11.0001 ... -2.2637; larger inside) |
| tgamma(x) | 8 (full range) |
| fma(x,y,z) | 0 (IEEE-754 round-to-nearest-even) |
| frexp(x,exp) | 0 (full range) |
| ldexp(x,exp) | 0 (full range) |
| scalbn(x,n) | 0 (full range) |
| scalbln(x,l) | 0 (full range) |
| logb(x) | 0 (full range) |
| ilogb(x) | 0 (full range) |
| j0(x) | 7 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| j1(x) | 7 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| jn(n,x) | For n = 128, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| y0(x) | 7 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| y1(x) | 7 for |x| < 8 otherwise, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| yn(n,x) | For |x| > 1.5n, the maximum absolute error is 5 x 10-12 |
| cyl_bessel_i0(x) | 6 (full range) |
| cyl_bessel_i1(x) | 6 (full range) |
| fmod(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| remainder(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| remquo(x,y,iptr) | 0 (full range) |
| modf(x,iptr) | 0 (full range) |
| fdim(x,y) | 0 (full range) |
| trunc(x) | 0 (full range) |
| round(x) | 0 (full range) |
| rint(x) | 0 (full range) |
| nearbyint(x) | 0 (full range) |
| ceil(x) | 0 (full range) |
| floor(x) | 0 (full range) |
| lrint(x) | 0 (full range) |
| lround(x) | 0 (full range) |
| llrint(x) | 0 (full range) |
| llround(x) | 0 (full range) |
2. Intrinsic Functions
本节中的函数只能在设备代码中使用。
在这些函数中,有一些标准函数的精度较低但速度更快的版本。它们具有相同的名称,前缀为 __(例如 __sinf(x))。 它们更快,因为它们映射到更少的本机指令。 编译器有一个选项 (-use_fast_math),它强制下表 中的每个函数编译为其内在对应项。 除了降低受影响函数的准确性外,还可能导致特殊情况处理的一些差异。 一种更健壮的方法是通过调用内联函数来选择性地替换数学函数调用,仅在性能增益值得考虑的情况下以及可以容忍更改的属性(例如降低的准确性和不同的特殊情况处理)的情况下。
| Operator/Function | Device Function |
|---|---|
| x/y | __fdividef(x,y) |
| sinf(x) | __sinf(x) |
| cosf(x) | __cosf(x) |
| tanf(x) | __tanf(x) |
| sincosf(x,sptr,cptr) | __sincosf(x,sptr,cptr) |
| logf(x) | __logf(x) |
| log2f(x) | __log2f(x) |
| log10f(x) | __log10f(x) |
| expf(x) | __expf(x) |
| exp10f(x) | __exp10f(x) |
| powf(x,y) | __powf(x,y) |
Single-Precision Floating-Point Functions
__fadd_[rn,rz,ru,rd]() 和 __fmul_[rn,rz,ru,rd]() 映射到编译器从不合并到 FMAD 中的加法和乘法运算。相比之下,由“*”和“+”运算符生成的加法和乘法将经常组合到 FMAD 中。
以 _rn 为后缀的函数使用舍入到最接近的偶数舍入模式运行。
以 _rz 为后缀的函数使用向零舍入模式进行舍入操作。
以 _ru 为后缀的函数使用向上舍入(到正无穷大)舍入模式运行。
以 _rd 为后缀的函数使用向下舍入(到负无穷大)舍入模式进行操作。
浮点除法的准确性取决于代码是使用 -prec-div=false 还是 -prec-div=true 编译的。使用-prec-div=false编译代码时,正则除法/运算符和__fdividef(x,y)精度相同,但对于2126 < |y| <2128,__fdividef(x,y) 提供的结果为零,而 / 运算符提供的正确结果在下表 中规定的精度范围内。此外,对于 2126 < |y| <2128,如果 x 为无穷大,则 __fdividef(x,y) 提供 NaN(作为无穷大乘以零的结果),而 / 运算符返回无穷大。另一方面,当使用 -prec-div=true 或根本没有任何 -prec-div 选项编译代码时, / 运算符符合 IEEE 标准,因为它的默认值为 true。
| Function | Error bounds |
|---|---|
| __fadd_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fsub_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fmul_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fmaf_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y,z) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __frcp_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fsqrt_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __frsqrt_rn(x) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fdiv_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fdividef(x,y) | For |y| in [2-126, 2126], the maximum ulp error is 2. |
| __expf(x) | The maximum ulp error is 2 + floor(abs(1.16 * x)). |
| __exp10f(x) | The maximum ulp error is 2+ floor(abs(2.95 * x)). |
| __logf(x) | For x in [0.5, 2], the maximum absolute error is 2-21.41, otherwise, the maximum ulp error is 3. |
| __log2f(x) | For x in [0.5, 2], the maximum absolute error is 2-22, otherwise, the maximum ulp error is 2. |
| __log10f(x) | For x in [0.5, 2], the maximum absolute error is 2-24, otherwise, the maximum ulp error is 3. |
| __sinf(x) | For x in [-π,π], the maximum absolute error is 2-21.41, and larger otherwise. |
| __cosf(x) | For x in [-π,π], the maximum absolute error is 2-21.19, and larger otherwise. |
| __sincosf(x,sptr,cptr) | Same as __sinf(x) and __cosf(x). |
| __tanf(x) | Derived from its implementation as __sinf(x) * (1/__cosf(x)). |
| __powf(x, y) | Derived from its implementation as exp2f(y * __log2f(x)). |
Double-Precision Floating-Point Functions
__dadd_rn() 和 __dmul_rn() 映射到编译器从不合并到 FMAD 中的加法和乘法运算。 相比之下,由“*”和“+”运算符生成的加法和乘法将经常组合到 FMAD 中。
| Function | Error bounds |
|---|---|
| __dadd_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __dsub_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __dmul_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __fma_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y,z) | IEEE-compliant. |
| __ddiv_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x,y)(x,y) | IEEE-compliant. Requires compute capability > 2. |
| __drcp_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x) | IEEE-compliant. Requires compute capability > 2. |
| __dsqrt_[rn,rz,ru,rd](x) | IEEE-compliant. Requires compute capability > 2. |
相关文章:

CUDA中的数学方法
CUDA中的数学方法 文章目录CUDA中的数学方法1. Standard FunctionsSingle-Precision Floating-Point FunctionsDouble-Precision Floating-Point Functions2. Intrinsic FunctionsSingle-Precision Floating-Point FunctionsDouble-Precision Floating-Point Functions参考手册…...
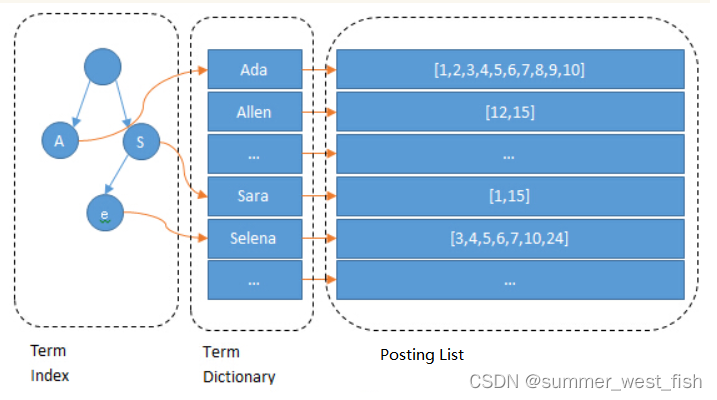
Elasticsearch基本概念和索引原理
一、Elasticsearch是什么? Elasticsearch是一个基于文档的NoSQL数据库,是一个分布式、RESTful风格的搜索和数据分析引擎,同时也是Elastic Stack的核心,集中存储数据。Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana经常被用作日志分析系统&…...

《NFL橄榄球》:堪萨斯城酋长·橄榄1号位
堪萨斯城酋长队(Kansas City Chiefs)是位于密苏里州堪萨斯城的职业美式橄榄球队;目前在全国橄榄球联盟隶属于美国橄榄球联合会(AFC)西区;其夏季训练营在威斯康星大学河瀑校区举行。 酋长队的前身是达拉斯得州佬队,这支…...
python+django在线教学网上授课系统vue
随着科技的进步,互联网已经开始慢慢渗透到我们的生活和学习中,并且在各个领域占据着越来越重要的部分,很多传统的行业都将面临着巨大的挑战,包括学习也不例外。现在学习竞争越来越激烈,人才的需求量越来越大࿰…...
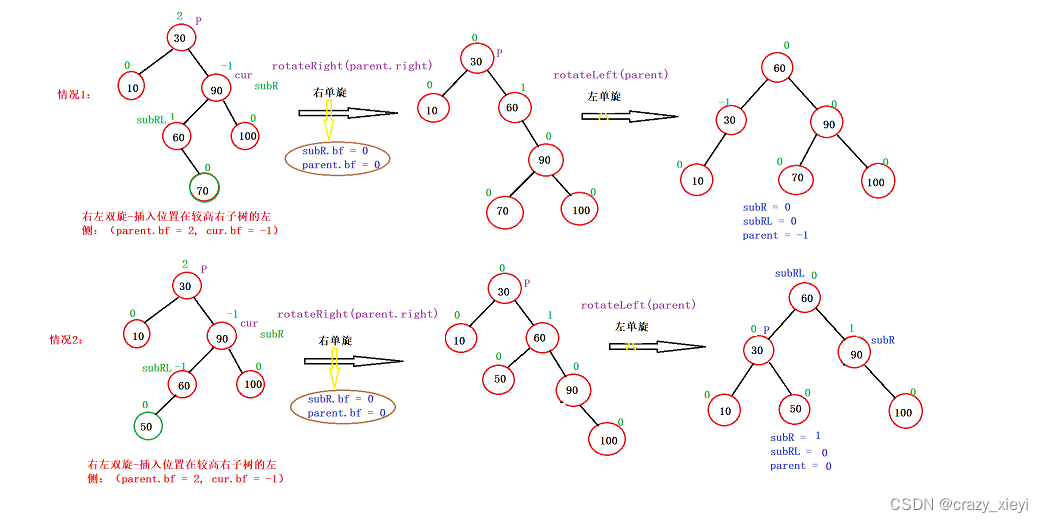
二叉搜索树之AVL树
AVL树的概念二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,两位俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii和E.M.Landis在1962年 发明了一种解决上…...
全栈自动化测试技术笔记(二):准备工作的切入点
自动化测试技术笔记(二):准备工作的切入点 上篇整理的技术笔记,聊了自动化测试的前期调研工作如何开展,最后一部分也提到了工作的优先级区分。 这篇文章,接上篇文章的内容,来聊聊自动化测试前期的准备工作࿰…...
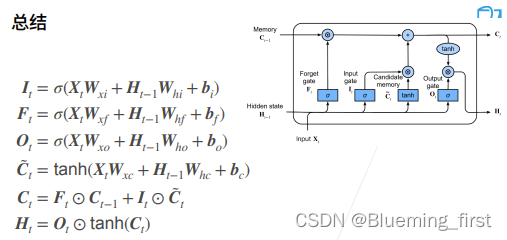
57 长短期记忆网络(LSTM)【动手学深度学习v2】
57 长短期记忆网络(LSTM)【动手学深度学习v2】 深度学习学习笔记 学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1JU4y1H7PC/?spm_id_fromautoNext&vd_source75dce036dc8244310435eaf03de4e330 长短期记忆网络(LSTM)…...
算法第十五期——动态规划(DP)之各种背包问题
目录 0、背包问题分类 1、 0/1背包简化版 【代码】 2、0/ 1背包的方案数 【思路】 【做法】 【代码】 空间优化1:交替滚动 空间优化2:自我滚动 3、完全背包 【思路】 【代码】 4、分组背包 核心代码 5、多重背包 多重背包解题思路1:转化…...
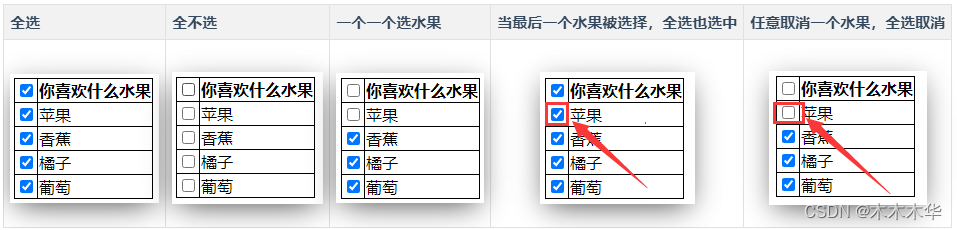
实现复选框全选和全不选的切换
今天,复看了一下JS的菜鸟教程,发现评论里面都是精华呀!! 看到函数这一节,发现就复选框的全选和全不选功能展开了讨论。我感觉挺有意思的,尝试实现了一下。 1. 全选、全不选,两个按钮ÿ…...
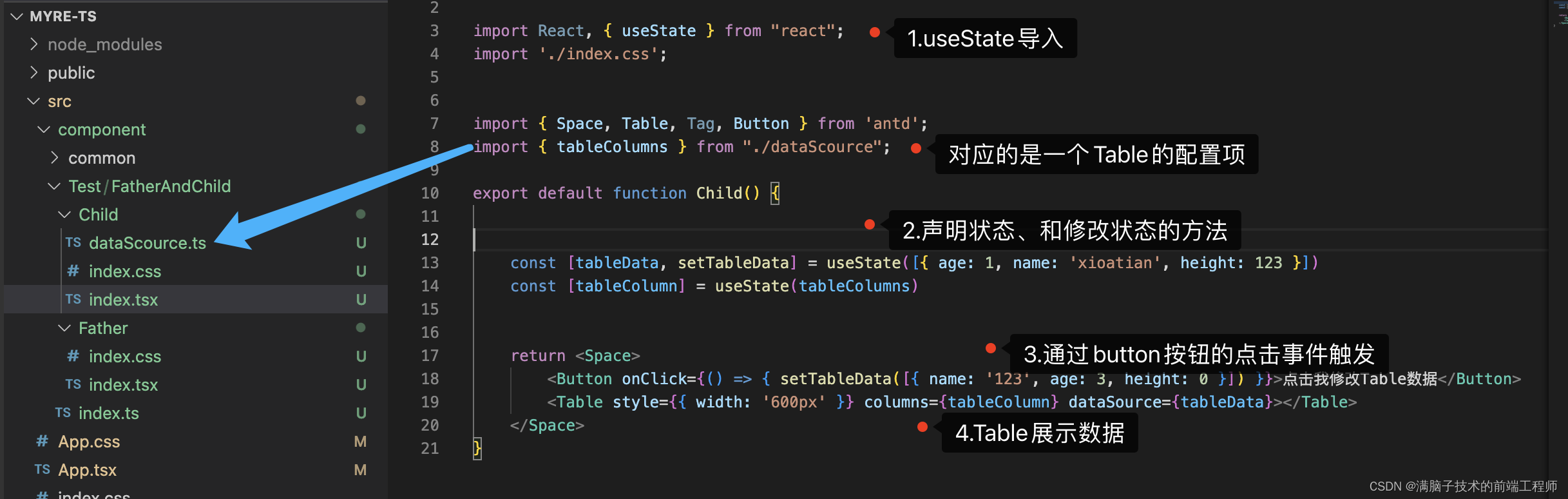
React hooks之useState用法(一)
系列文章目录 学习React已经有很长的一段时间了,今天决定重新回顾一下跟React相关的一些知识点 文章目录系列文章目录结构如下一、hooks是什么?useState可以能做什么二、如何使用useState()第一步:创建【函数组件&…...
spring的简单理解
目录 1 .ioc容器(控制反转) 2. Aop面向切面编程 3. 事务申明 4. 注解的方式启动 5. spring是什么与他的优势 6. 代理设计模式(比如aop) 7. springmvc中相应json数据 8. 使用lombok来进行对代码的简化 9. 使用logback记录…...
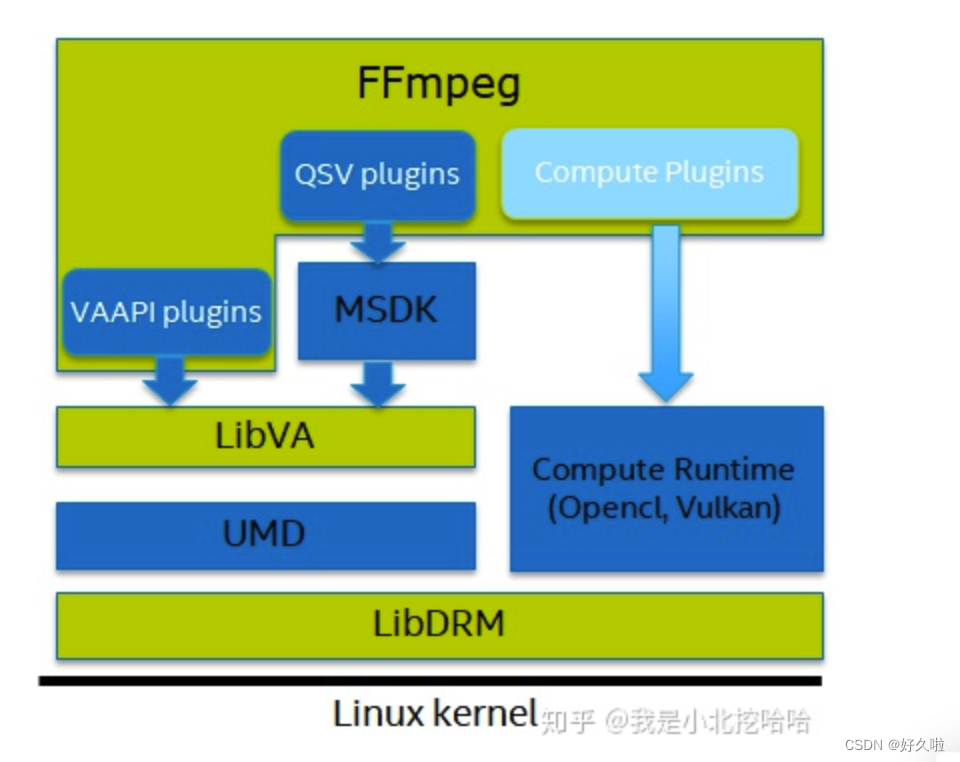
Docker调用Intel集显实现FFmpeg硬解码
文章目录Docker调用Intel集显实现FFmpeg硬解码参考FFmpeg 集成qsv方式一 容器完成所有步骤方式二 容器完成部分步骤方式三 dockerfile部署Docker调用Intel集显实现FFmpeg硬解码 参考 ffmpeg_qsv_docker拉取该镜像可以实现FFmpeg集成vaapi的硬加速,通过dockerfile文…...

端到端模型(end-to-end)与非端到端模型
一、端到端(end to end) 从输入端到输出端会得到一个预测结果,将预测结果和真实结果进行比较得到误差,将误差反向传播到网络的各个层之中,调整网络的权重和参数直到模型收敛或者达到预期的效果为止,中间所…...
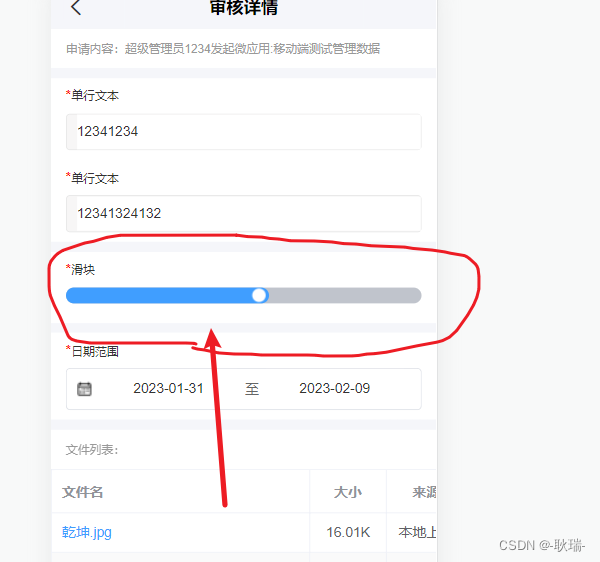
uniApp封装一个滑块组件
最近 项目中有一个需求 PC端动态设计的表单 移动端要能渲染出来 那么 就要去找到对应的组件 而其中 没有的 就包括滑块 没有又能怎么办 只能自己封装一个 我们直接上代码 <template><view class"u-slider" tap"onClick" :class"[disabled…...

运动基元(二):贝塞尔曲线
贝塞尔曲线是我第一个深入接触并使用于路径规划的运动基元。N阶贝塞尔曲线具有很多优良的特性,例如端点性、N阶可导性、对称性、曲率连续性、凸包性、几何不变性、仿射不变性以及变差缩减性。本章主要介绍贝塞尔曲线用于运动基元时几个特别有用的特性。 一、贝塞尔曲线的定义 …...

Android 11.0 关于Launcher3中调用截图功能总是返回null的解决方案
1.1概述 在11.0的系统产品开发中,在某些时候需要调用截图接口来进行截屏功能实现,而在Launcher3中发现调用系统截屏接口SurfaceControl.screenshot进行截图的时候始终为null, 获取不到系统当前页面的截屏功能,所以需要找到当前截屏失败的原因然后来实现截屏功能的实现,下面来…...

random随机数
random随机数 1.概述 random用来生成一些随机数,下面介绍random模块提供的方法根据需求生成不同的随机数。 2.random常用操作 2.1.random默认随机数 random()函数返回一个随机的浮点值,默认返回值范围在0 < n < 1.0区间 import randomfor i …...
【金三银四系列】Spring面试题-上(2023版)
Spring面试专题 1.Spring应该很熟悉吧?来介绍下你的Spring的理解 有些同学可能会抢答,不熟悉!!! 好了,不开玩笑,面对这个问题我们应该怎么来回答呢?我们给大家梳理这个几个维度来回答 1.1 Spring的发展历程 先介绍…...

linux基本功系列之tar命令实战
文章目录前言一. tar命令介绍二. 语法格式及常用选项三. 参考案例3.1 仅打包不压缩3.2 打包后使用调用压缩命令进行压缩3.3 列出文件的内容3.4 追加文件到tar命令中3.5 释放文件到指定的目录四 . 各种压缩方式的比较总结前言 大家好,又见面了,我是沐风晓…...
Prometheus服务发现
Prometheus服务发现介绍 Prometheus默认是采用pull的方式拉取监控数据的,每一个被抓取的目标都要暴露一个HTTP接口,prometheus通过这个接口来获取相应的指标数据,这种方式需要由prometheus-server决定采集的目标服务器有哪些,通过…...

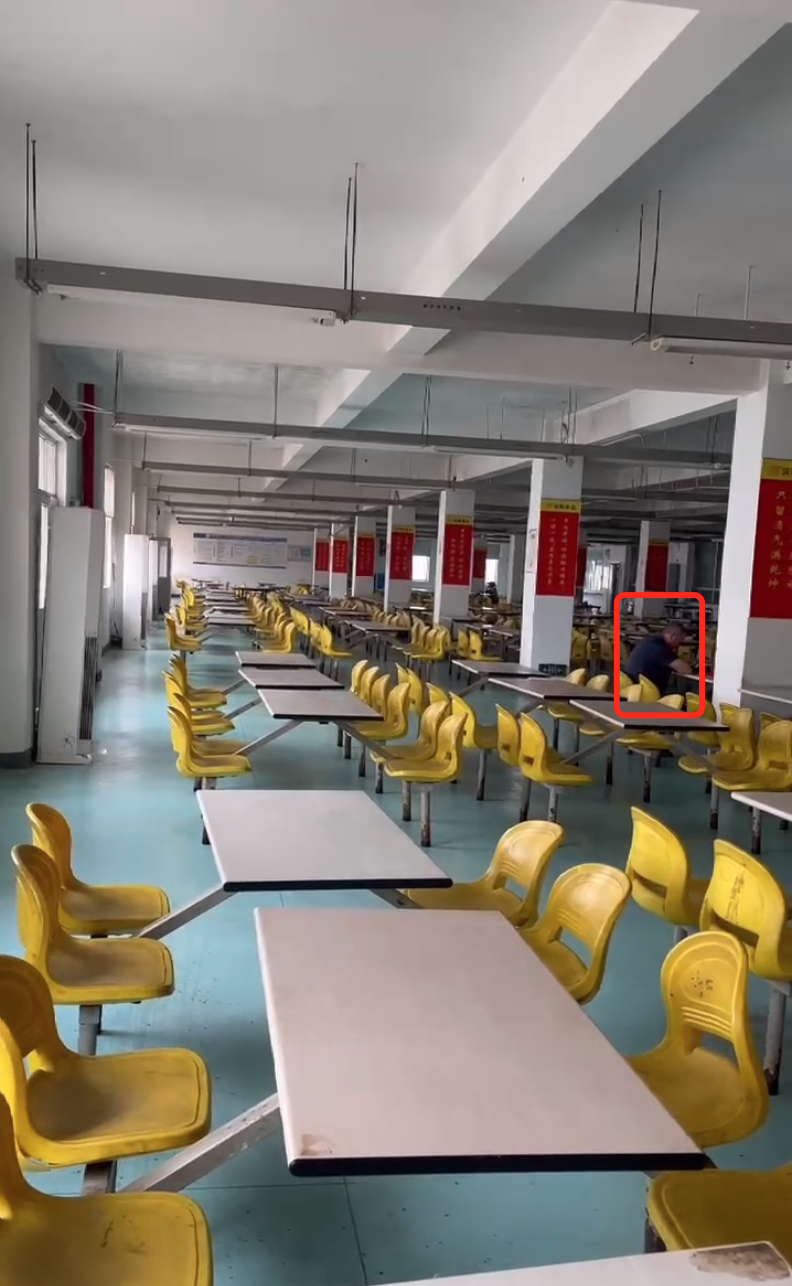
手游刚开服就被攻击怎么办?如何防御DDoS?
开服初期是手游最脆弱的阶段,极易成为DDoS攻击的目标。一旦遭遇攻击,可能导致服务器瘫痪、玩家流失,甚至造成巨大经济损失。本文为开发者提供一套简洁有效的应急与防御方案,帮助快速应对并构建长期防护体系。 一、遭遇攻击的紧急应…...
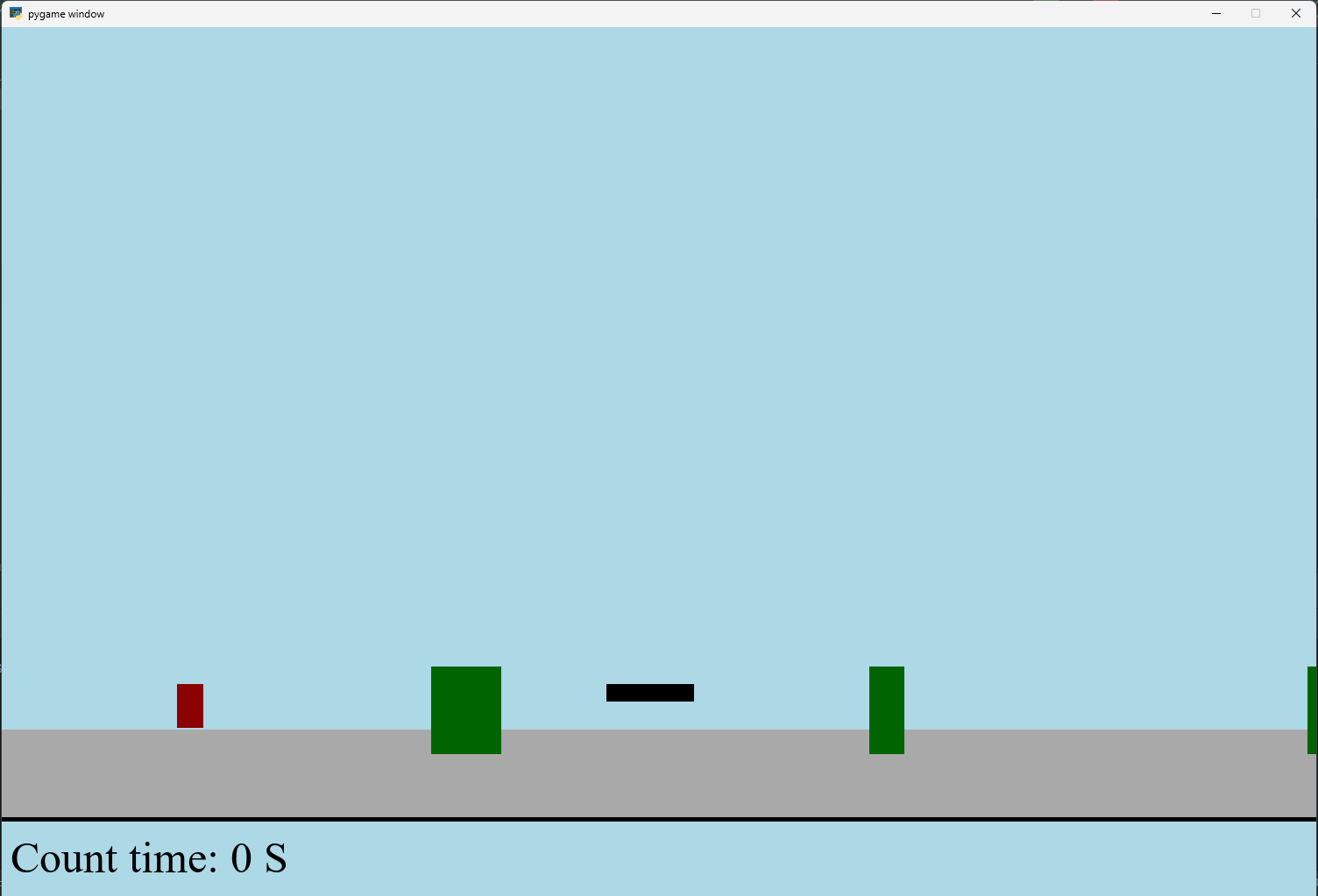
【Python】 -- 趣味代码 - 小恐龙游戏
文章目录 文章目录 00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架代码结构和功能游戏流程总结01 小恐龙游戏程序设计02 百度网盘地址00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架 这段代码是一个基于 Pygame 的简易跑酷游戏的完整实现,玩家控制一个角色(龙)躲避障碍物(仙人掌和乌鸦)。以下是代码的详细介绍:…...

工业安全零事故的智能守护者:一体化AI智能安防平台
前言: 通过AI视觉技术,为船厂提供全面的安全监控解决方案,涵盖交通违规检测、起重机轨道安全、非法入侵检测、盗窃防范、安全规范执行监控等多个方面,能够实现对应负责人反馈机制,并最终实现数据的统计报表。提升船厂…...

生成 Git SSH 证书
🔑 1. 生成 SSH 密钥对 在终端(Windows 使用 Git Bash,Mac/Linux 使用 Terminal)执行命令: ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_emailexample.com" 参数说明: -t rsa&#x…...
ArcGIS Pro制作水平横向图例+多级标注
今天介绍下载ArcGIS Pro中如何设置水平横向图例。 之前我们介绍了ArcGIS的横向图例制作:ArcGIS横向、多列图例、顺序重排、符号居中、批量更改图例符号等等(ArcGIS出图图例8大技巧),那这次我们看看ArcGIS Pro如何更加快捷的操作。…...

【生成模型】视频生成论文调研
工作清单 上游应用方向:控制、速度、时长、高动态、多主体驱动 类型工作基础模型WAN / WAN-VACE / HunyuanVideo控制条件轨迹控制ATI~镜头控制ReCamMaster~多主体驱动Phantom~音频驱动Let Them Talk: Audio-Driven Multi-Person Conversational Video Generation速…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...

解读《网络安全法》最新修订,把握网络安全新趋势
《网络安全法》自2017年施行以来,在维护网络空间安全方面发挥了重要作用。但随着网络环境的日益复杂,网络攻击、数据泄露等事件频发,现行法律已难以完全适应新的风险挑战。 2025年3月28日,国家网信办会同相关部门起草了《网络安全…...
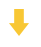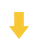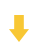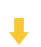
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统开发:打造互动性强的购物平台
淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统的开发,旨在打造一个互动性强的购物平台,让用户在购物的同时,能够享受到更多的乐趣和惊喜。 淘宝扭蛋机小程序系统拥有丰富的互动功能。用户可以通过虚拟摇杆操作扭蛋机,实现旋转、抽拉等动作,增…...
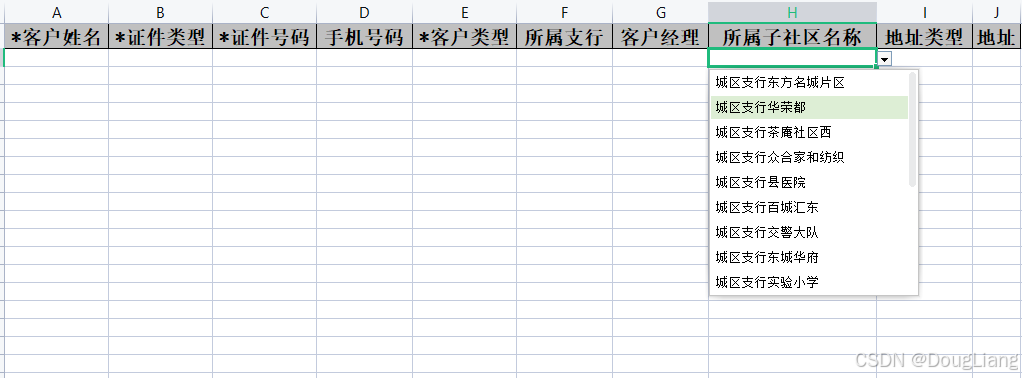
关于easyexcel动态下拉选问题处理
前些日子突然碰到一个问题,说是客户的导入文件模版想支持部分导入内容的下拉选,于是我就找了easyexcel官网寻找解决方案,并没有找到合适的方案,没办法只能自己动手并分享出来,针对Java生成Excel下拉菜单时因选项过多导…...
