2023.11.15 每日一题(AI自生成应用)【C++】【Python】【Java】【Go】 动态路径分析
目录
一、题目
二、解决方法
三、改进

一、题目
背景: 在一个城市中,有数个交通节点,每个节点间有双向道路相连。每条道路具有一个初始权重,代表通行该路段的成本(例如时间、费用等)。随着时间的变化,道路的权重可能会发生变化,比如由于交通堵塞或道路维修。
问题: 设计一个算法,以处理以下两种类型的查询:
- 更新查询:给定两个节点及新的权重值,更新这两个节点之间道路的权重。
- 最短路径查询:给定两个节点,找出这两个节点之间的最短路径及其权重。
输入格式:

输出格式:
- 对于每个最短路径查询,输出一个整数,表示最短路径的权重。如果两个节点之间没有路径,则输出
-1。
实际应用: 这个问题可以应用于交通管理系统,例如实时更新交通状况并为司机提供最优路线。也适用于网络数据流量管理,其中节点代表数据中心,道路代表连接它们的网络。
挑战:
- 设计一个高效的数据结构来存储和更新节点间的道路权重。
- 实现一个算法来快速回答最短路径查询,考虑到道路权重可能频繁变化。
二、解决方法
解决:
为了解决这个动态路径分析问题,我们可以采用以下策略:
- 数据结构:使用邻接表来表示图,其中每个节点都有一个列表存储它与其他节点的连接及其权重。
- 路径更新:对于更新操作,我们只需要修改邻接表中对应的权重。
- 最短路径查询:使用 Dijkstra 算法来找到最短路径。由于权重可能会频繁变化,我们在每次查询时都从头开始执行 Dijkstra 算法。
C++实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <climits>using namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> pii; // pair of (weight, node)class Graph {int V; // Number of verticesvector<vector<pii>> adj; // Adjacency listpublic:Graph(int V) : V(V), adj(V) {}void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {adj[u].push_back({w, v});adj[v].push_back({w, u}); // For undirected graph}void updateEdge(int u, int v, int w) {// Update weight for edge u-vfor (auto &p : adj[u]) {if (p.second == v) {p.first = w;break;}}for (auto &p : adj[v]) {if (p.second == u) {p.first = w;break;}}}int shortestPath(int source, int destination) {priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii>> pq;vector<int> dist(V, INT_MAX);pq.push({0, source});dist[source] = 0;while (!pq.empty()) {int u = pq.top().second;pq.pop();for (auto &[w, v] : adj[u]) {if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {dist[v] = dist[u] + w;pq.push({dist[v], v});}}}return (dist[destination] == INT_MAX) ? -1 : dist[destination];}
};int main() {int N, M, u, v, w;cin >> N >> M;Graph g(N);for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {cin >> u >> v >> w;g.addEdge(u, v, w);}// Querieschar queryType;while (cin >> queryType) {if (queryType == 'U') {cin >> u >> v >> w;g.updateEdge(u, v, w);} else if (queryType == 'Q') {cin >> u >> v;cout << g.shortestPath(u, v) << endl;}}return 0;
}
Python:
import heapqclass Graph:def __init__(self, V):self.V = Vself.graph = {i: {} for i in range(V)}def add_edge(self, u, v, w):self.graph[u][v] = wself.graph[v][u] = wdef update_edge(self, u, v, w):if v in self.graph[u]:self.graph[u][v] = wif u in self.graph[v]:self.graph[v][u] = wdef shortest_path(self, source, destination):dist = [float('inf')] * self.Vdist[source] = 0pq = [(0, source)]while pq:d, u = heapq.heappop(pq)if d > dist[u]:continuefor v, w in self.graph[u].items():if dist[u] + w < dist[v]:dist[v] = dist[u] + wheapq.heappush(pq, (dist[v], v))return dist[destination] if dist[destination] != float('inf') else -1# Example usage
g = Graph(N) # N is the number of vertices
# Add edges and handle queries similarly to the C++ example
JAVA:
import java.util.*;public class Graph {private int V;private Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> adj;public Graph(int V) {this.V = V;this.adj = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {adj.put(i, new HashMap<>());}}public void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {adj.get(u).put(v, w);adj.get(v).put(u, w);}public void updateEdge(int u, int v, int w) {if (adj.get(u).containsKey(v)) {adj.get(u).put(v, w);}if (adj.get(v).containsKey(u)) {adj.get(v).put(u, w);}}public int shortestPath(int source, int destination) {int[] dist = new int[V];Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);dist[source] = 0;PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));pq.add(new int[]{source, 0});while (!pq.isEmpty()) {int[] current = pq.poll();int u = current[0];if (u == destination) {break;}for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : adj.get(u).entrySet()) {int v = entry.getKey();int weight = entry.getValue();if (dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;pq.add(new int[]{v, dist[v]});}}}return dist[destination] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : dist[destination];}// Example usagepublic static void main(String[] args) {Graph g = new Graph(N); // N is the number of vertices// Add edges and handle queries similarly to the C++ example}
}
Go语言:
package mainimport ("container/heap""fmt""math"
)type Edge struct {node, weight int
}type Graph struct {V intedges map[int]map[int]int
}func NewGraph(V int) *Graph {g := &Graph{V: V,edges: make(map[int]map[int]int),}for i := 0; i < V; i++ {g.edges[i] = make(map[int]int)}return g
}
func (g *Graph) UpdateEdge(u, v, w int) {if _, ok := g.edges[u][v]; ok {g.edges[u][v] = w}if _, ok := g.edges[v][u]; ok {g.edges[v][u] = w}
}func (g *Graph) ShortestPath(source, destination int) int {dist := make([]int, g.V)for i := range dist {dist[i] = math.MaxInt32}dist[source] = 0pq := make(PriorityQueue, 0)heap.Init(&pq)heap.Push(&pq, &Item{value: source,priority: 0,})for pq.Len() > 0 {item := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Item)u := item.valueif u == destination {break}for v, w := range g.edges[u] {if dist[u]+w < dist[v] {dist[v] = dist[u] + wheap.Push(&pq, &Item{value: v,priority: dist[v],})}}}if dist[destination] == math.MaxInt32 {return -1}return dist[destination]
}// Define the priority queue used for Dijkstra's algorithm
type Item struct {value int // The node indexpriority int // The node's priority (distance)index int // The index of the item in the heap
}type PriorityQueue []*Itemfunc (pq PriorityQueue) Len() int { return len(pq) }func (pq PriorityQueue) Less(i, j int) bool {return pq[i].priority < pq[j].priority
}func (pq PriorityQueue) Swap(i, j int) {pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i]pq[i].index = ipq[j].index = j
}func (pq *PriorityQueue) Push(x interface{}) {n := len(*pq)item := x.(*Item)item.index = n*pq = append(*pq, item)
}func (pq *PriorityQueue) Pop() interface{} {old := *pqn := len(old)item := old[n-1]old[n-1] = nilitem.index = -1*pq = old[0 : n-1]return item
}func main() {// Example usageg := NewGraph(N) // N is the number of vertices// Add edges and handle queries similarly to the C++ example
}
三、改进
- 效率问题:每次查询最短路径时都需要从头执行 Dijkstra 算法。在频繁更新边权重的场景中,这可能导致效率低下。
- 数据结构选择:现有实现使用邻接表来存储图,这对于稀疏图是合适的。但对于密集图,这种表示方式可能导致内存使用不经济。
改进:
- 增量更新算法:对于频繁更新的场景,可以考虑使用更高级的图算法,如“动态最短路径算法”。这类算法可以在不重新计算整个图的情况下,有效更新最短路径。
- 数据结构优化:针对不同类型的图(稀疏或密集),选择合适的数据结构。例如,对于密集图,可以使用邻接矩阵来代替邻接表。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <climits>using namespace std;const int MAX_V = 1000; // 假设图中最多有1000个节点class Graph {int V; // 顶点数vector<vector<int>> adjMatrix; // 邻接矩阵public:Graph(int V) : V(V), adjMatrix(V, vector<int>(V, INT_MAX)) {}void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {adjMatrix[u][v] = w;adjMatrix[v][u] = w;}void updateEdge(int u, int v, int w) {adjMatrix[u][v] = w;adjMatrix[v][u] = w;}int shortestPath(int source, int destination) {vector<int> dist(V, INT_MAX);vector<bool> sptSet(V, false);dist[source] = 0;for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);sptSet[u] = true;for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {if (!sptSet[v] && adjMatrix[u][v] != INT_MAX && dist[u] != INT_MAX &&dist[u] + adjMatrix[u][v] < dist[v]) {dist[v] = dist[u] + adjMatrix[u][v];}}}return (dist[destination] == INT_MAX) ? -1 : dist[destination];}private:int minDistance(const vector<int> &dist, const vector<bool> &sptSet) {int min = INT_MAX, min_index;for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {if (!sptSet[v] && dist[v] <= min) {min = dist[v];min_index = v;}}return min_index;}
};int main() {// 示例用法int N, M, u, v, w;cin >> N >> M;Graph g(N);for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {cin >> u >> v >> w;g.addEdge(u, v, w);}// 处理查询// ...
}
这个实现针对密集图进行了优化,但它不包括动态最短路径算法的实现。动态最短路径算法通常更复杂,可能需要使用更高级的数据结构和算法技巧。这种算法的实现和优化通常是图算法研究的前沿话题。
相关文章:

2023.11.15 每日一题(AI自生成应用)【C++】【Python】【Java】【Go】 动态路径分析
目录 一、题目 二、解决方法 三、改进 一、题目 背景: 在一个城市中,有数个交通节点,每个节点间有双向道路相连。每条道路具有一个初始权重,代表通行该路段的成本(例如时间、费用等)。随着时间的变化&am…...

【libGDX】初识libGDX
1 前言 libGDX 是一个开源且跨平台的 Java 游戏开发框架,于 2010 年 3 月 11 日推出 0.1 版本,它通过 OpenGL ES 2.0/3.0 渲染图像,支持 Windows、Linux、macOS、Android、iOS、Web 等平台,提供了统一的 API,用户只需要…...
VIVADO+FPGA调试记录
vivadoFPGA调试记录 vitis编译vivado导出的硬件平台,提示xxxx.h file cant find vitis编译vivado导出的硬件平台,提示’xxxx.h file cant find’ 此硬件平台中,包含有AXI接口类型的ip。在vitis编译硬件平台时,经常会报错…...
Android——Gradle插件gradle-wrapper.properties
一、Android Studio版本,Android Gradle插件版本,Gradle版本 Android Studio 通过Android Gradle插件 使用 Gradle来构建代码; Android Studio每次升级后, Android Gradle 插件自动更新,对应的Gradle版本也会变动&…...

iOS应用加固方案解析:ipa加固安全技术全面评测
在移动应用开发领域,iOS应用的安全性一直备受关注。ipaguard作为一款专业的iOS应用加固方案,采用混淆加密技术,旨在保护应用免受破解、逆向和篡改等风险。本文将深入探讨ipaguard的产品功能、安全技术及其在iOS应用加固领域中的核心优势和特色…...
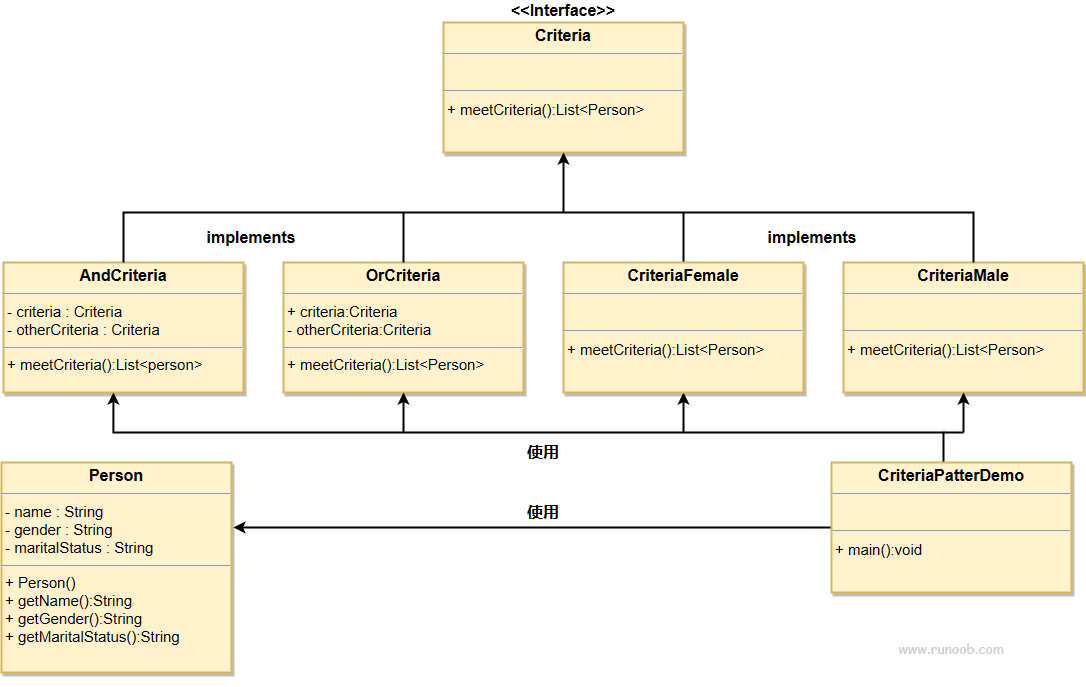
过滤器模式 rust和java的实现
文章目录 过滤器模式实现 过滤器模式实现javarustjavarust rust代码仓库 过滤器模式 过滤器模式(Filter Pattern)或标准模式(Criteria Pattern)是一种设计模式,这种模式允许开发人员使用不同的标准来过滤一组对象&…...
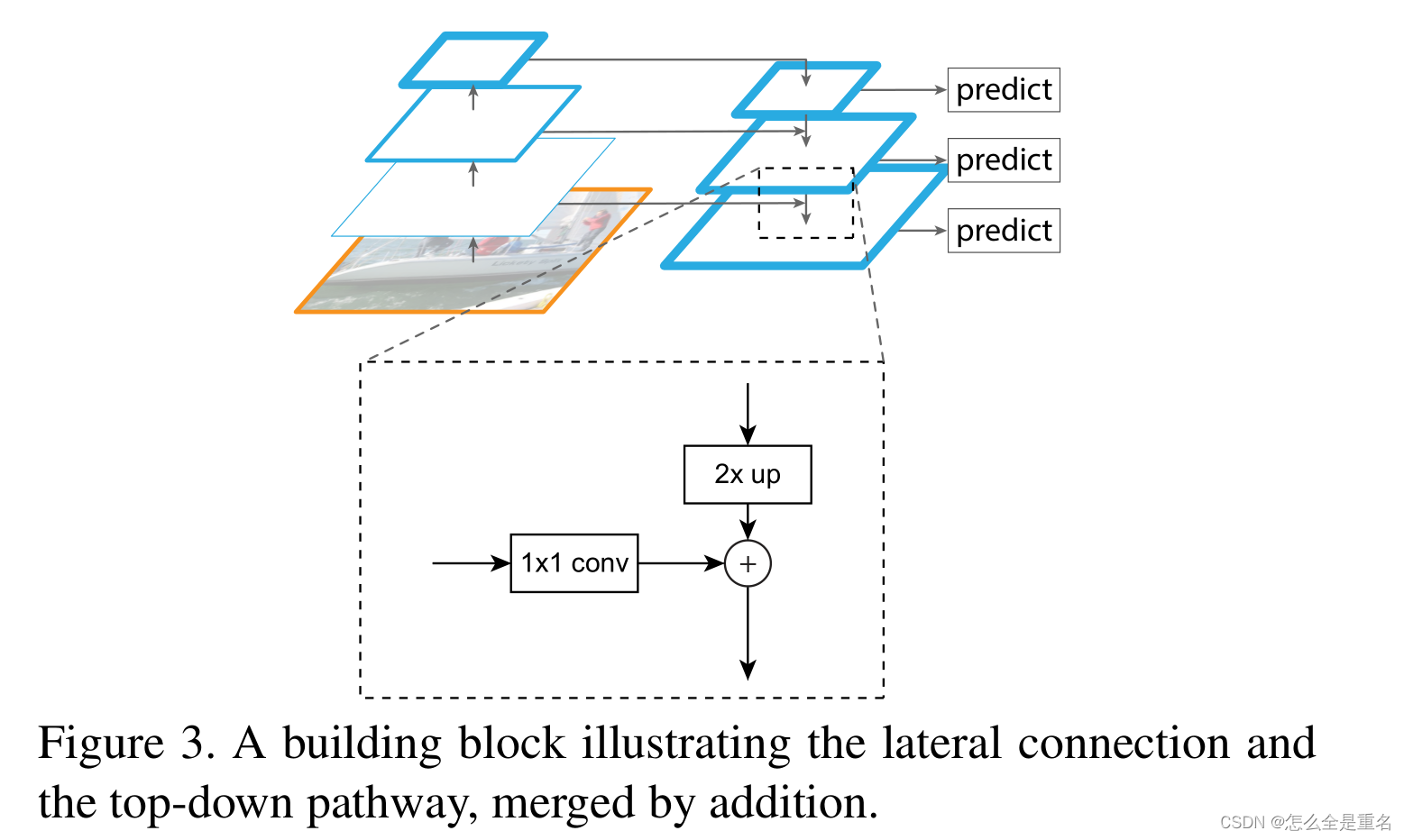
Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection(2017.4)
文章目录 Abstract1. Introduction3. Feature Pyramid NetworksBottom-up pathwayTop-down pathway and lateral connections 7. Conclusion FPN Abstract 特征金字塔是识别系统中检测不同尺度物体的基本组成部分。但最近的深度学习对象检测器避免了金字塔表示,部分…...

Python3基础模块 random
Python3基础模块 random import random #作用:生成随机数使用dir(module)查看模块内容 >>> import random >>> dir(random) [BPF, LOG4, NV_MAGICCONST, RECIP_BPF, Random, SG_MAGICCONST, SystemRandom, TWOPI, _BuiltinMethodType, _MethodT…...

ubuntu安装pgsql16
ubuntu安装postgresSQL 官网地址: https://www.postgresql.org/download/ 1.安装 # 添加源 sudo sh -c echo "deb https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list # 安装数字签名 w…...

数据管理70个名词解析
数据标准化70个名词解析 1、数据 是指任何以电子或者其他方式对信息的记录。在计算机科学技术中,“数据”是客观事物的符号表示,指所有可被输入到计算机中并可被计算机程序处理的符号的总称;在管理科学技术中,“数据”是描述事件或事物的属性…...
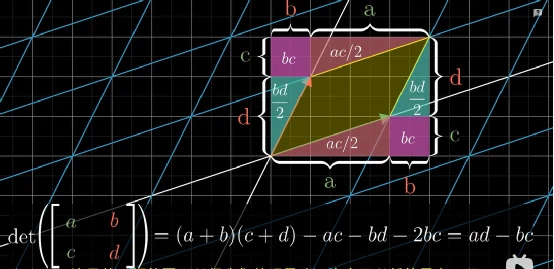
线性代数本质系列(二)矩阵乘法与复合线性变换,行列式,三维空间线性变换
本系列文章将从下面不同角度解析线性代数的本质,本文是本系列第二篇 向量究竟是什么? 向量的线性组合,基与线性相关 矩阵与线性相关 矩阵乘法与复合线性变换 三维空间中的线性变换 行列式 逆矩阵,列空间,秩与零空间 克…...

Linux-CentOS重要模块
软件包管理器:CentOS使用Yum(Yellowdog Updater, Modified)作为其包管理器。Yum提供了一种方便的方式来安装、更新和删除软件包,并自动解决依赖关系。 RPM:RPM(RPM Package Manager)是CentOS中…...
posix定时器的使用
POSIX定时器是基于POSIX标准定义的一组函数,用于实现在Linux系统中创建和管理定时器。POSIX定时器提供了一种相对较高的精度,可用于实现毫秒级别的定时功能。 POSIX定时器的主要函数包括: timer_create():用于创建一个定时器对象…...
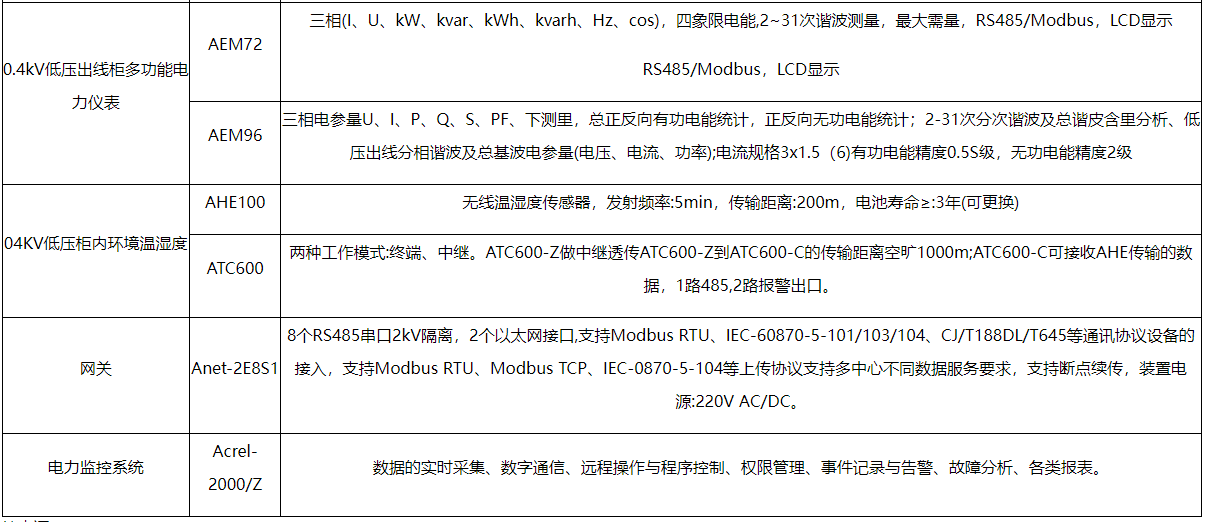
安科瑞煤矿电力监控系统的研究与应用
摘要:作为一个巨大的能源消耗国家,我国每年对煤炭的市场需求巨大。煤炭作为我国点力气和供暖企业的重要原材料,煤矿的开采过程存在着难以消除的风险,我国的煤炭安全问题长期困扰着相关企业和监督部门,也受到社会的广泛…...
)
高教社杯数模竞赛特辑论文篇-2023年A题:基于机理分析法的定日镜场优化设计模型(附获奖论文及MATLAB代码实现)
目录 摘要 一、 问题重述 1 . 1 问题背景 1 . 2 问题要求 二、 问题分析...
缩点+图论路径网络流:1114T4
http://cplusoj.com/d/senior/p/SS231114D 重新梳理一下题目 我们先建图 x → y x\to y x→y,然后对点分类:原串出现点,原串未出现点。 假如我们对一个原串出现点进行了操作,那么它剩余所有出边我们立刻去操作必然没有影响。所…...
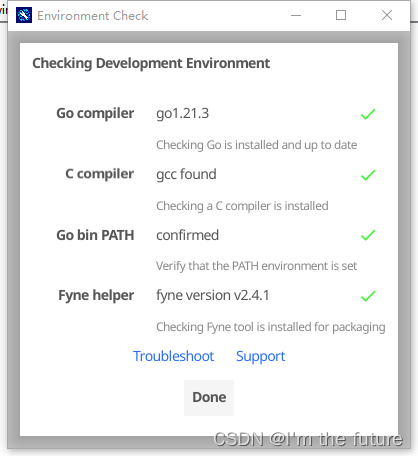
Go语言fyne开发桌面应用程序-环境安装
环境安装 参考https://developer.fyne.io/started/#prerequisites网站 之前的文章介绍了如何安装GO语言这里不在叙述 msys2 首先安装msys2,https://www.msys2.org/ 开始菜单打开MSYS2 执行 $ pacman -Syu$ pacman -S git mingw-w64-x86_64-toolchain注意&#…...
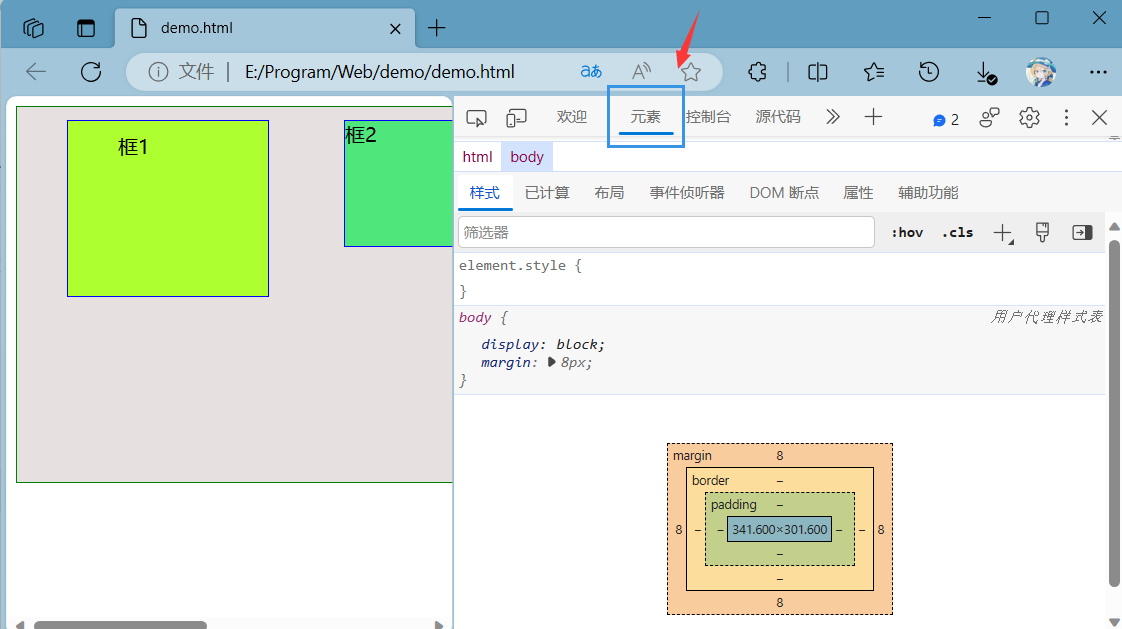
JavaWeb——CSS3的使用
目录 1. CSS概述 2. CSS引入方式 3. CSS颜色显示 4. CSS选择器 4.1. 元素(标签)选择器 4.2. id选择器 4.3. 类选择器 4.4. 三者优先级 5. 盒子模型 1. CSS概述 CSS,全称为“Cascading Style Sheets”,中文译为“层叠样式…...

AR导览小程序开发方案
一、背景介绍 随着科技的不断发展,虚拟现实(VR)和增强现实(AR)技术逐渐被应用于各个领域。其中,AR导览小程序作为一种新兴的导览方式,以其独特的视觉体验和互动性受到了广泛的关注。AR导览小程…...
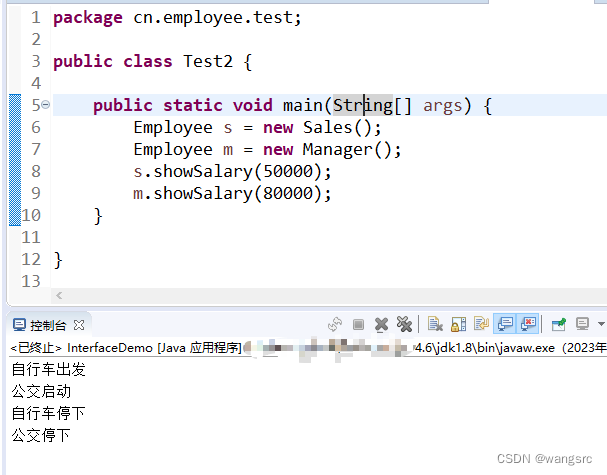
继承、多态
复习 需求: 编写一个抽象类:职员Employee,其中定义showSalary(int s)抽象方法;编写Employee的子类,分别是销售员Sales和经理Manager,分别在子类中实现对父类抽象方法的重写,并编写测试类Test查看输出结果 package cn.…...

华为云AI开发平台ModelArts
华为云ModelArts:重塑AI开发流程的“智能引擎”与“创新加速器”! 在人工智能浪潮席卷全球的2025年,企业拥抱AI的意愿空前高涨,但技术门槛高、流程复杂、资源投入巨大的现实,却让许多创新构想止步于实验室。数据科学家…...

HTML 语义化
目录 HTML 语义化HTML5 新特性HTML 语义化的好处语义化标签的使用场景最佳实践 HTML 语义化 HTML5 新特性 标准答案: 语义化标签: <header>:页头<nav>:导航<main>:主要内容<article>&#x…...

C++初阶-list的底层
目录 1.std::list实现的所有代码 2.list的简单介绍 2.1实现list的类 2.2_list_iterator的实现 2.2.1_list_iterator实现的原因和好处 2.2.2_list_iterator实现 2.3_list_node的实现 2.3.1. 避免递归的模板依赖 2.3.2. 内存布局一致性 2.3.3. 类型安全的替代方案 2.3.…...

SciencePlots——绘制论文中的图片
文章目录 安装一、风格二、1 资源 安装 # 安装最新版 pip install githttps://github.com/garrettj403/SciencePlots.git# 安装稳定版 pip install SciencePlots一、风格 简单好用的深度学习论文绘图专用工具包–Science Plot 二、 1 资源 论文绘图神器来了:一行…...

Python ROS2【机器人中间件框架】 简介
销量过万TEEIS德国护膝夏天用薄款 优惠券冠生园 百花蜂蜜428g 挤压瓶纯蜂蜜巨奇严选 鞋子除臭剂360ml 多芬身体磨砂膏280g健70%-75%酒精消毒棉片湿巾1418cm 80片/袋3袋大包清洁食品用消毒 优惠券AIMORNY52朵红玫瑰永生香皂花同城配送非鲜花七夕情人节生日礼物送女友 热卖妙洁棉…...

LOOI机器人的技术实现解析:从手势识别到边缘检测
LOOI机器人作为一款创新的AI硬件产品,通过将智能手机转变为具有情感交互能力的桌面机器人,展示了前沿AI技术与传统硬件设计的完美结合。作为AI与玩具领域的专家,我将全面解析LOOI的技术实现架构,特别是其手势识别、物体识别和环境…...
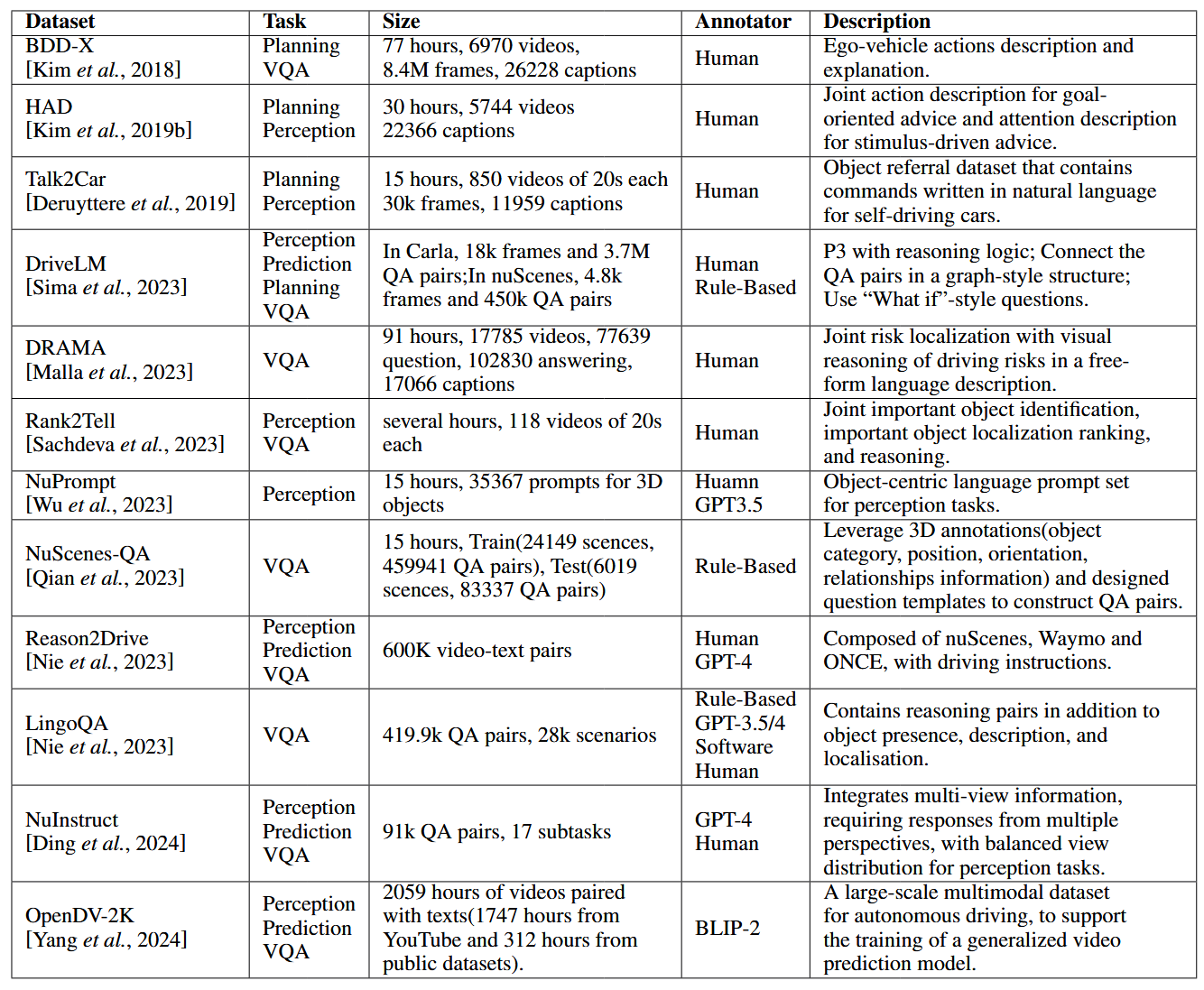
论文阅读:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
地址:LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving 摘要翻译 自动驾驶技术作为推动交通和城市出行变革的催化剂,正从基于规则的系统向数据驱动策略转变。传统的模块化系统受限于级联模块间的累积误差和缺乏灵活性的预设规则。…...
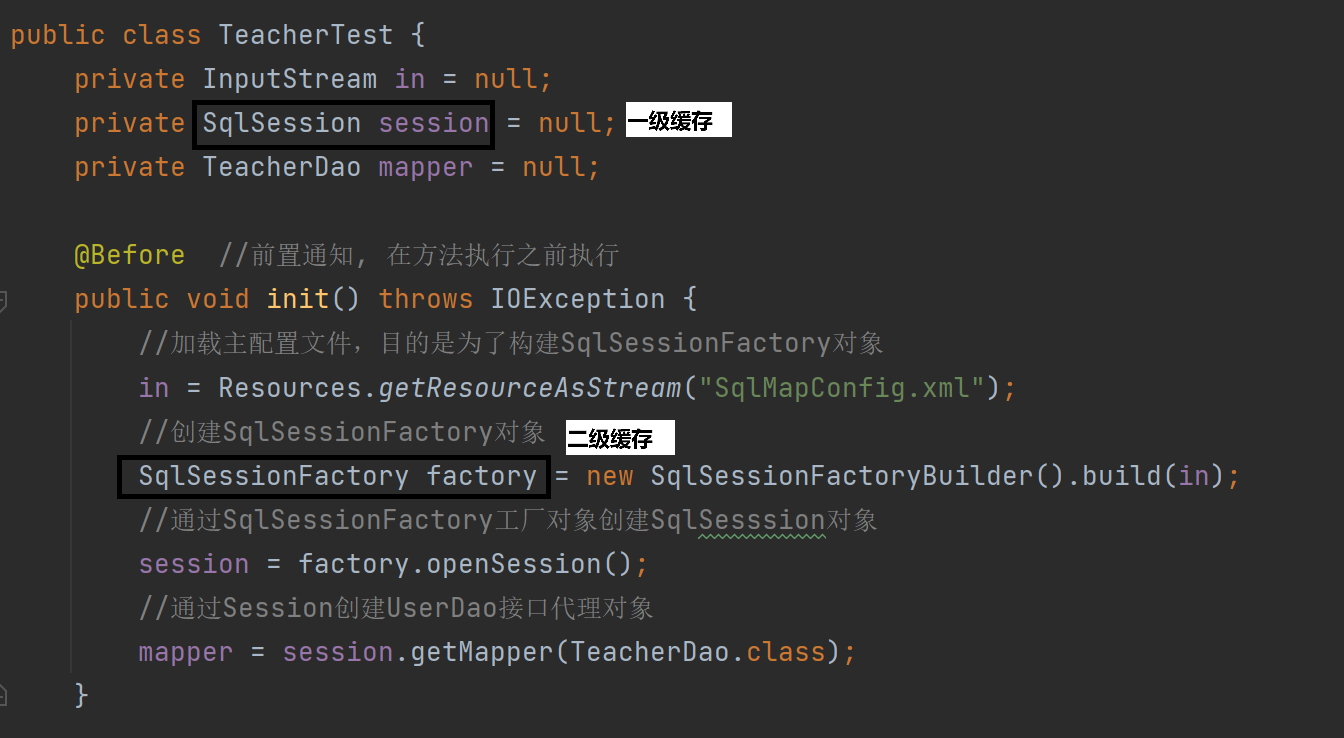
MyBatis中关于缓存的理解
MyBatis缓存 MyBatis系统当中默认定义两级缓存:一级缓存、二级缓存 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启(sqlSession级别的缓存)二级缓存需要手动开启配置,需要局域namespace级别的缓存 一级缓存(本地缓存&#…...

Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析
Java多线程实现之Runnable接口深度解析 一、Runnable接口概述1.1 接口定义1.2 与Thread类的关系1.3 使用Runnable接口的优势 二、Runnable接口的基本实现方式2.1 传统方式实现Runnable接口2.2 使用匿名内部类实现Runnable接口2.3 使用Lambda表达式实现Runnable接口 三、Runnabl…...

RushDB开源程序 是现代应用程序和 AI 的即时数据库。建立在 Neo4j 之上
一、软件介绍 文末提供程序和源码下载 RushDB 改变了您处理图形数据的方式 — 不需要 Schema,不需要复杂的查询,只需推送数据即可。 二、Key Features ✨ 主要特点 Instant Setup: Be productive in seconds, not days 即时设置 :在几秒钟…...
