Android之高级UI
系统ViewGroup原理解析
常见的布局容器: FrameLayout, LinearLayout,RelativeLayoout,GridLayout
后起之秀:ConstraintLayout,CoordinateLayout
Linearlayout
@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);} else {measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);}}
onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 源码如上所示,通过 mOrientation 分别处理垂直和水平两个方向的测量,其中的 mOrientation 变量则是我们在 xml 布局文件中通过 android:orientation=“vertical” 或者直接通过 setOrientation(@OrientationMode int orientation) 方法设置的 LinearLayout 文件方向变量
我们仅分析垂直方向的测量方法,也就是 measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)(水平方向的测量方法 measureHorizontal(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 是类似的原理,有兴趣的朋友可以自己分析)
初始化变量
需要初始化一些类变量 & 声明一些重要的局部变量
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//第一阶段,主要是一些变量的初始化mTotalLength = 0;// 所有 childView 的高度和 + 本身的 padding,注意:它和 LinearLayout 本身的高度是不同的int maxWidth = 0;// 所有 childView 中宽度的最大值int childState = 0;int alternativeMaxWidth = 0;// 所有 layout_weight <= 0 的 childView 中宽度的最大值int weightedMaxWidth = 0;// 所有 layout_weight >0 的 childView 中宽度的最大值boolean allFillParent = true;float totalWeight = 0;// 所有 childView 的 weight 之和final int count = getVirtualChildCount();final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);boolean matchWidth = false;boolean skippedMeasure = false;final int baselineChildIndex = mBaselineAlignedChildIndex;final boolean useLargestChild = mUseLargestChild;int largestChildHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int consumedExcessSpace = 0;int nonSkippedChildCount = 0;}
第一次测量
在测量第一阶段会计算那些没有设置 weight 的 childView 的高度、计算 mTotleLength,并且计算三个宽度相关的变量的值
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//第二阶段,第一次测量,接上面代码
// See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
//第一遍循环,看看每个childview的高度,并且记录最大宽度for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {//一层for循环final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);//获取到每一个childviewif (child == null) {mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);continue;}if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);continue;}nonSkippedChildCount++;if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;}final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();totalWeight += lp.weight;//计算总权重final boolean useExcessSpace = lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0;//使用了权重才会满足// 我们都知道,测量模式有三种:// * UNSPECIFIED:父控件对子控件无约束// * Exactly:父控件对子控件强约束,子控件永远在父控件边界内,越界则裁剪。如果要记忆的话,可以记忆为有对应的具体数值或者是Match_parent// * AT_Most:子控件为wrap_content的时候,测量值为ATif (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && useExcessSpace) {//确切高度,且height=0 权重>0// Optimization: don't bother measuring children who are only// laid out using excess space. These views will get measured// later if we have space to distribute.//先跳过测量模式为EXACTLY并且需要权重计算的childview // 在后面第三个 for 循环重新计算此 childView 大小final int totalLength = mTotalLength;mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);skippedMeasure = true;//后面跳过Measure} else {//高度不是确定可能是AT_MOST/UNSPECIFIEDif (useExcessSpace) {// The heightMode is either UNSPECIFIED or AT_MOST, and// this child is only laid out using excess space. Measure// using WRAP_CONTENT so that we can find out the view's// optimal height. We'll restore the original height of 0// after measurement.//把使用权重的childview的高度设置为wrap_contentlp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;}// Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or// previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to// use all available space (and we will shrink things later// if needed).//这是非常重要的一个方法,将会决定每个 childView 的大小//如果此 childView 及在此 childView 之前的 childView 中使用了 weight 属性,// 我们允许此 childView 使用所有的空间(后续如果需要,再做调整)final int usedHeight = totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0;//调用viewgroup中方法测量子viewmeasureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0,heightMeasureSpec, usedHeight);// 得到测量之后的 childView 的 childHeightfinal int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();if (useExcessSpace) {// Restore the original height and record how much space// we've allocated to excess-only children so that we can// match the behavior of EXACTLY measurement.lp.height = 0;consumedExcessSpace += childHeight;}// 将此 childView 的 childHeight 加入到 mTotalLength 中// 并加上 childView 的 topMargin 和 bottomMargin // getNextLocationOffset 方法返回 0,方便以后扩展使用final int totalLength = mTotalLength;mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));if (useLargestChild) {largestChildHeight = Math.max(childHeight, largestChildHeight);//记录最大子view高度}}// 下面两个 if 判断都和 `android:baselineAlignedChildIndex` 属性有关,这里不展开分析/*** If applicable, compute the additional offset to the child's baseline* we'll need later when asked {@link #getBaseline}.*/if ((baselineChildIndex >= 0) && (baselineChildIndex == i + 1)) {mBaselineChildTop = mTotalLength;}// if we are trying to use a child index for our baseline, the above// book keeping only works if there are no children above it with// weight. fail fast to aid the developer.if (i < baselineChildIndex && lp.weight > 0) {throw new RuntimeException("A child of LinearLayout with index "+ "less than mBaselineAlignedChildIndex has weight > 0, which "+ "won't work. Either remove the weight, or don't set "+ "mBaselineAlignedChildIndex.");}boolean matchWidthLocally = false;//该子view是否需要测量宽度// 所有 widthMode 是 `MeasureSpec.EXACTLY`,不会进入此 if 判断 if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// The width of the linear layout will scale, and at least one// child said it wanted to match our width. Set a flag// indicating that we need to remeasure at least that view when// we know our width.// 当父类(LinearLayout)不是match_parent或者精确值的时候,但子控件却是一个match_parent// 那么matchWidthLocally和matchWidth置为true// 意味着这个控件将会占据父类(水平方向)的所有空间matchWidth = true;matchWidthLocally = true;}// 计算三个和宽度相关的变量值final int margin = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;final int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + margin;maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, measuredWidth);childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());//获取子viewmeasure后的state状态allFillParent = allFillParent && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;if (lp.weight > 0) {//需要计算权重的/** Widths of weighted Views are bogus if we end up* remeasuring, so keep them separate.* alternative 可供选择的*/weightedMaxWidth = Math.max(weightedMaxWidth,matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);} else {//如果不需要计算权重走这里alternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);}i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);}//for循环结束// 如果存在没有跳过的 childView 并且需要绘制 end divider 则需要加上 end 位置的 divider 的高度if (nonSkippedChildCount > 0 && hasDividerBeforeChildAt(count)) {mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;}
measureChildBeforeLayout()
在此方法中将会计算每个 childView 的大小,调用 ViewGroup 的 measureChildWithMargins() 方法计算每个 childView 的大小,在测量垂直方向的 childView 时,有一个非常重要的参数需要注意,即:heightUsed,根据英文注释,heightUsed 是指在垂直方向,已经被 parentView 或者 parentView 的其他 childView 使用了的空间
void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,int totalHeight) {measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth,heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);}
第二次测量
如果进入这个 if 条件,会进行第二次的 for 循环遍历 childView,重新计算 mTotalLength
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//接上面代码
if (useLargestChild &&(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {mTotalLength = 0;//重新计算总高度:每个非gone的view的高度都按 上次循环记录的最大子view的高度计算,再加上marginfor (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);if (child == null) {mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);continue;}if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);continue;}final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)child.getLayoutParams();// Account for negative marginsfinal int totalLength = mTotalLength;mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + largestChildHeight +lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));}}
测量第三阶段
针对设置了 android:layout_weight 属性的布局,重新计算 mTotalLength
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//接上面代码// Add in our paddingmTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;int heightSize = mTotalLength;// Check against our minimum height// 通过 getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 得到建议最小高度,并和计算得到的// mTotalLength 比较取最大值heightSize = Math.max(heightSize, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());// Reconcile our calculated size with the heightMeasureSpec// 通过 heightMeasureSpec,调整 heightSize 的大小int heightSizeAndState = resolveSizeAndState(heightSize, heightMeasureSpec, 0);heightSize = heightSizeAndState & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;// Either expand children with weight to take up available space or// shrink them if they extend beyond our current bounds. If we skipped// measurement on any children, we need to measure them now.// 重新计算有 weight 属性的 childView 大小,// 如果还有可用的空间,则扩展 childView,计算其大小// 如果 childView 超出了 LinearLayout 的边界,则收缩 childViewint remainingExcess = heightSize - mTotalLength+ (mAllowInconsistentMeasurement ? 0 : consumedExcessSpace);if (skippedMeasure|| ((sRemeasureWeightedChildren || remainingExcess != 0) && totalWeight > 0.0f)) { // 根据 mWeightSum 计算得到 remainingWeightSum,mWeightSum 是通过 // `android:weightSum` 属性设置的,totalWeight 是通过第一次 for 循环计算得到的float remainingWeightSum = mWeightSum > 0.0f ? mWeightSum : totalWeight;// 将 mTotalLength 复位为 0mTotalLength = 0;// 权重childview的测量,开始真正的第二次 for 循环遍历每一个 childView,重新测量每一个 childViewfor (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);if (child == null || child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {continue;}final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();final float childWeight = lp.weight // 如果该 childView 设置了 `weight` 值,则进入 if 语句块if (childWeight > 0) {// 这是设置了 weight 的情况下,最重要的一行代码// remainingExcess 剩余高度 * ( childView 的 weight / remainingWeightSum)// share 便是此 childView 通过这个公式计算得到的高度, // 并重新计算剩余高度 remainingExcess 和剩余权重总和 remainingWeightSumfinal int share = (int) (childWeight * remainingExcess / remainingWeightSum);remainingExcess -= share;remainingWeightSum -= childWeight;// 通过下面的 if 条件重新计算,childHeight 是最终 childView 的真正高度final int childHeight;if (mUseLargestChild && heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {childHeight = largestChildHeight;} else if (lp.height == 0 && (!mAllowInconsistentMeasurement|| heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)) {// This child needs to be laid out from scratch using// only its share of excess space.childHeight = share;} else {// This child had some intrinsic height to which we// need to add its share of excess space.childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + share;}// 计算 childHeightMeasureSpec & childWidthMeasureSpec,并调用 child.measure() 方法final int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Math.max(0, childHeight), MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,lp.width);child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);// Child may now not fit in vertical dimension.childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState()& (MEASURED_STATE_MASK>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));}final int margin = lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;final int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + margin;maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, measuredWidth);boolean matchWidthLocally = widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY &&lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;alternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,matchWidthLocally ? margin : measuredWidth);allFillParent = allFillParent && lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;// 考虑 childView.topMargin & childView.bottomMargin,重新计算 mTotalLengthfinal int totalLength = mTotalLength;mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + child.getMeasuredHeight() +lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));}// Add in our padding// 完成 for 循环之后,加入 LinearLayout 本身的 mPaddingTop & mPaddingBottommTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;// TODO: Should we recompute the heightSpec based on the new total length?} else {// 重新计算 alternativeMaxWidthalternativeMaxWidth = Math.max(alternativeMaxWidth,weightedMaxWidth);// We have no limit, so make all weighted views as tall as the largest child.// Children will have already been measured once.if (useLargestChild && heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);if (child == null || child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {continue;}final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =(LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();float childExtra = lp.weight;if (childExtra > 0) {child.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(child.getMeasuredWidth(),MeasureSpec.EXACTLY),MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(largestChildHeight,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY));}}}}if (!allFillParent && widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {maxWidth = alternativeMaxWidth;}// 调整 width 大小maxWidth += mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight;// Check against our minimum widthmaxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());// 调用 setMeasuredDimension() 设置 LinearLayout 的大小setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),heightSizeAndState);//最后,设置LinearLayout的size大小和状态,如果LinearLayout有设置width为match_parent的话,将会调用forceUniformWidth再测量一次所有的subchild,这里主要是测量subchild的width大小if (matchWidth) {forceUniformWidth(count, heightMeasureSpec);}
假如一共有3个subchild且都有设置weight ,分别为3、2、1,我们假设剩余的space为120,则第一个view的大小为120 * 3/(3+2+1)=60,第二个view的大小为(120-60)*2/(2+1)=40,第3个view的大小为(60-40)*1/1 = 20
resolveSizeAndState
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);final int result;switch (specMode) {case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:if (specSize < size) {result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;} else {result = size;}break;case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:result = specSize;break;case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:default:result = size;}return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);}
总结
1.LinearLayout针对设置weight与不设置weight的情况分别处理
2.在 LinearLayout 中总共有 3 个 for 循环,分别处理不同的流程
- 第一个 for 循环,只会在不使用 weight 属性时进入,并有可能会测量每个 childView 的大小
- 第二个 for 循环,在使用 android:measureWithLargestChild 时才会进入,并且即使进入也不会调用 childView 的测量方法,只会更新 mTotalLength 变量
- 第三个 for 循环,只会在使用 weight 属性时进入,并测量每个 childView 的大小
自定义View总结
自定义UI基础
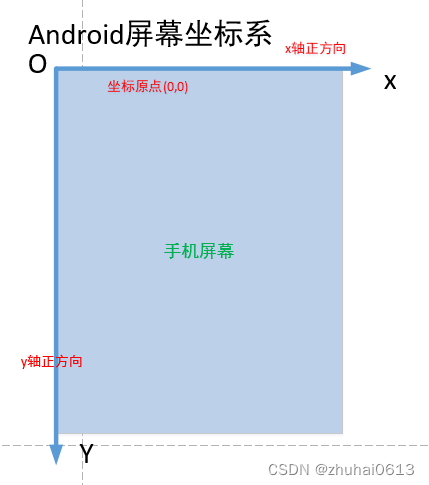
Android的坐标系
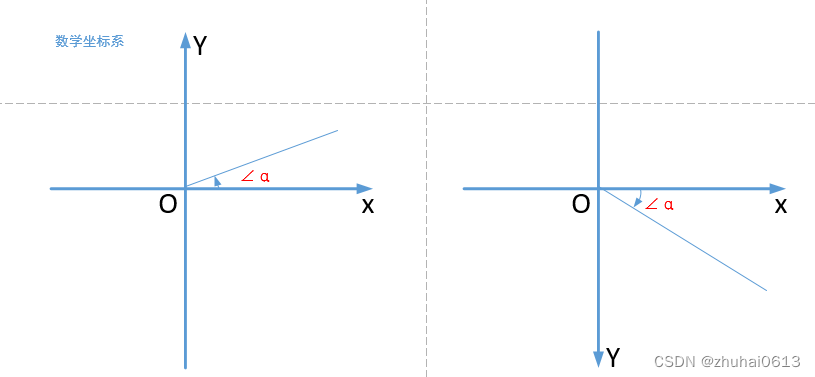
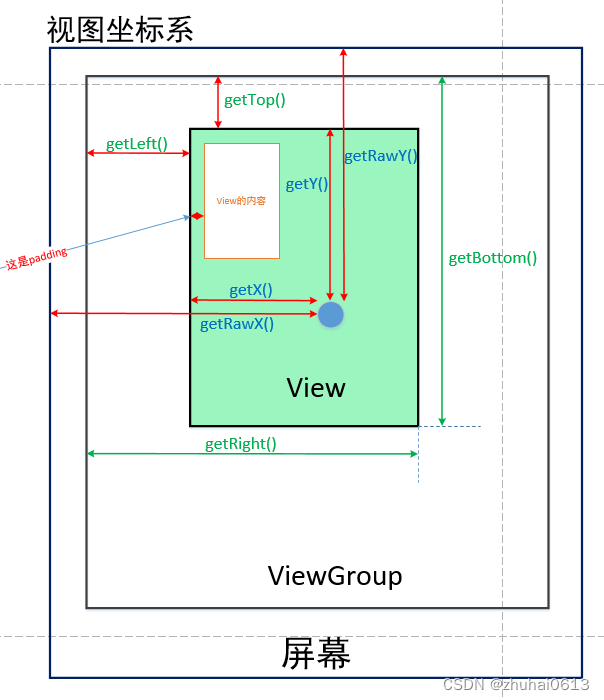
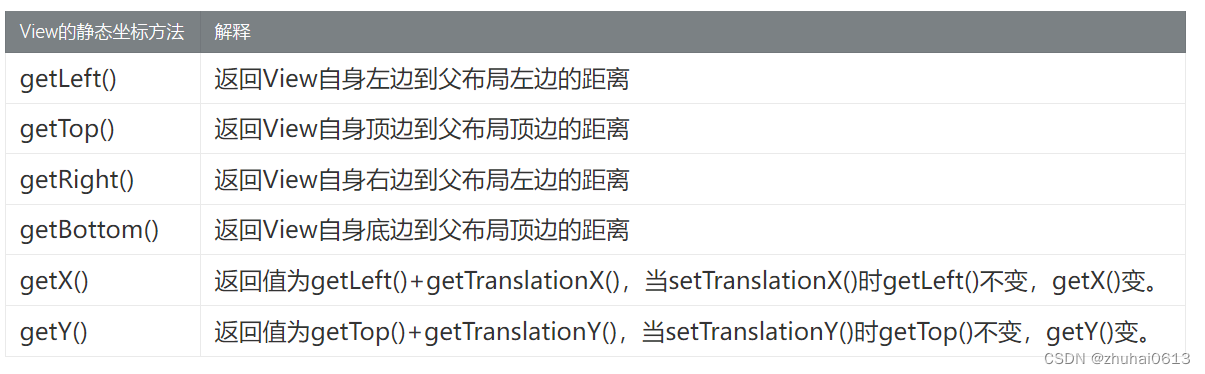
View的静态坐标方法
手指触摸屏幕时MotionEvent
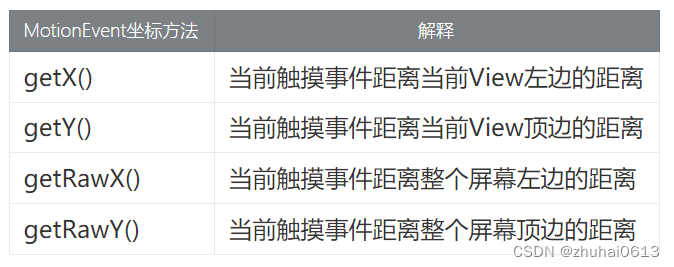
获取宽高
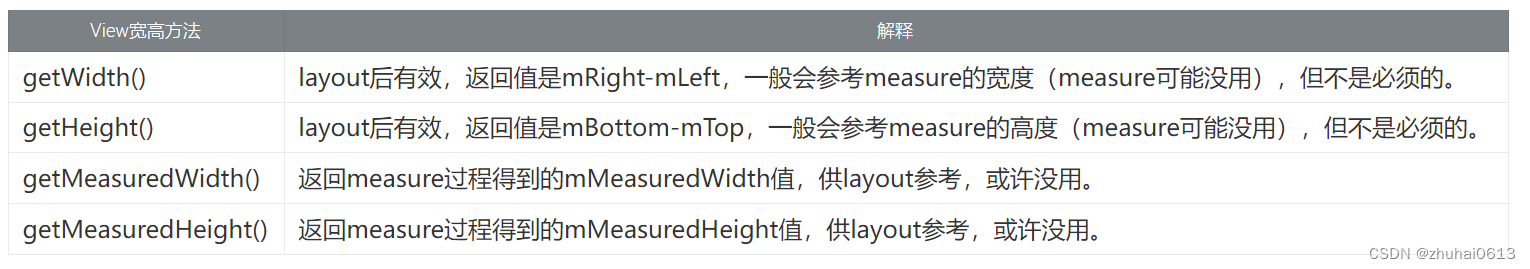
获取view位置
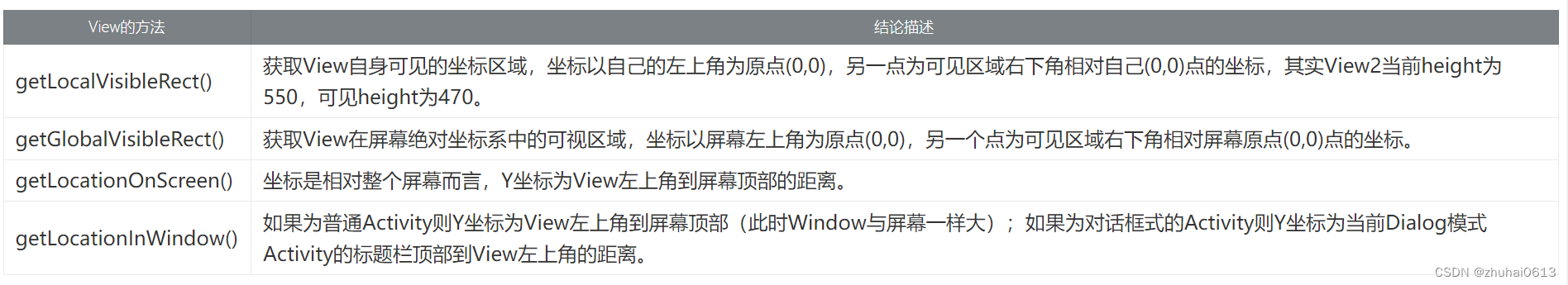
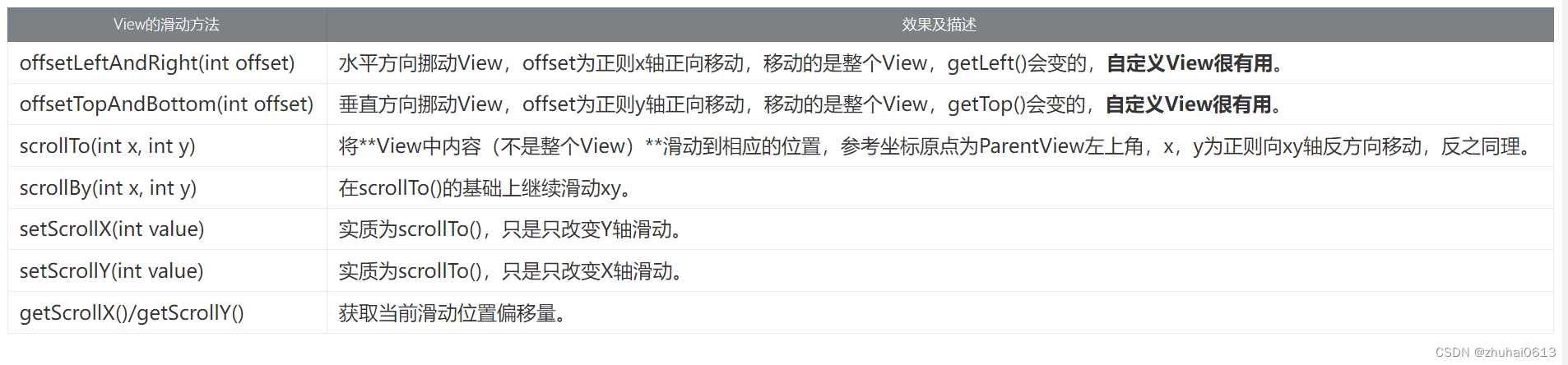
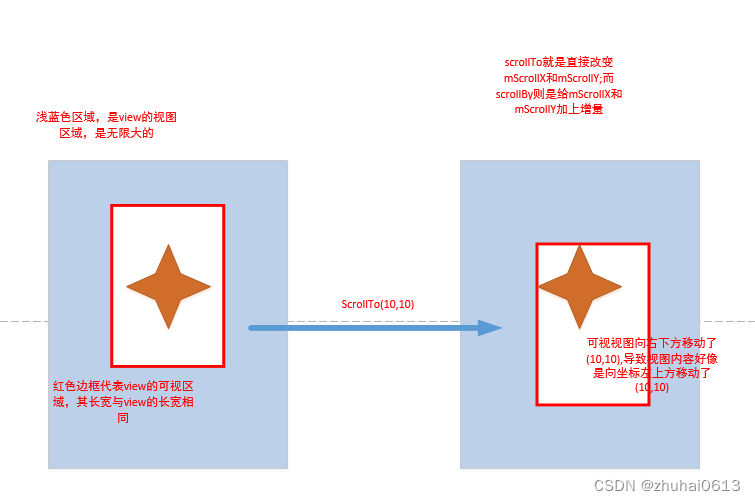
View滑动相关坐标系
View的scrollTo()和scrollBy()是用于滑动View中的内容,而不是改变View的位置;改变View在屏幕中的位置可以使用offsetLeftAndRight()和offsetTopAndBottom()方法,他会导致getLeft()等值改变
自定义view分类
- 自定义View的基本方法
自定义View的最基本的三个方法分别是: onMeasure()、onLayout()、onDraw();
View在Activity中显示出来,要经历测量、布局和绘制三个步骤,分别对应三个动作:measure、layout和draw。
测量:onMeasure()决定View的大小;
布局:onLayout()决定View在ViewGroup中的位置;
绘制:onDraw()决定绘制这个View。
- 自定义控件分类
自定义View: 只需要重写onMeasure()和onDraw()
自定义ViewGroup: 则只需要重写onMeasure()和onLayout()
- 视图View主要分为两类

View类简介
View类是Android中各种组件的基类,如View是ViewGroup基类
View表现为显示在屏幕上的各种视图
Android中的UI组件都由View、ViewGroup组成。
View的构造函数:共有4个
// 如果View是在Java代码里面new的,则调用第一个构造函数public CustomView(Context context) {super(context);}// 如果View是在.xml里声明的,则调用第二个构造函数// 自定义属性是从AttributeSet参数传进来的public CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);}// 不会自动调用// 一般是在第二个构造函数里主动调用// 如View有style属性时public CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);}//API21之后才使用// 不会自动调用// 一般是在第二个构造函数里主动调用// 如View有style属性时public CustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);}
- AttributeSet与自定义属性
系统自带的View可以在xml中配置属性,对于写的好的自定义View同样可以在xml中配置属性,为了使自定义的View的属性可以在xml中配置,需要以下4个步骤:
通过为自定义View添加属性
在xml中为相应的属性声明属性值
在运行时(一般为构造函数)获取属性值
将获取到的属性值应用到View
- View视图结构
1 PhoneWindow是Android系统中最基本的窗口系统,继承自Windows类,负责管理界面显示以及事件响应。它是Activity与View系统交互的接口
2 DecorView是PhoneWindow中的起始节点View,继承于View类,作为整个视图容器来使用。用于设置窗口属性。它本质上是一个FrameLayout
3 ViewRoot在Activtiy启动时创建,负责管理、布局、渲染窗口UI等等
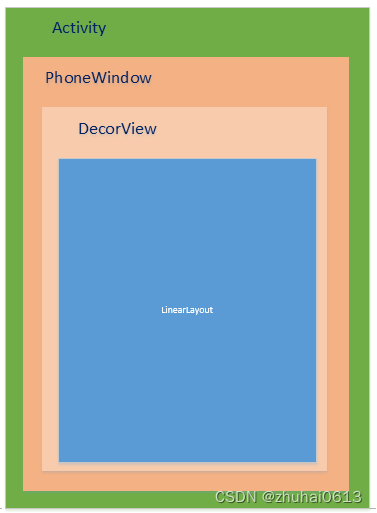
上图是 Activity 的结构。我们先进行大致的描述,然后在进入源码体会这一过程。
我们可以清晰的知道一个 Activity 会对应着有一个 Window,而 Window 的唯一实现类为 PhoneWindow,PhoneWindow 的初始化是在 Activity 的 attach 方法中,我们前面也有提到 attach 方法。
在往下一层是一个 DecorView,被 PhoneWindow 持有着,DecorView 的初始化在 setContentView 中,这个我们待会会进行详细分析。DecorView 是我们的顶级View,我们设置的布局只是其子View。
DecorView 是一个 FrameLayout。但在 setContentView 中,会给他加入一个线性的布局(LinearLayout)。该线性布局的子View 则一般由 TitleBar 和 ContentView 进行组成。TitleBar 我们可以通过 requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); 进行去除,而 ContentView 则是来装载我们设置的布局文件的 ViewGroup 了
对于多View的视图,结构是树形结构:最顶层是ViewGroup,ViewGroup下可能有多个ViewGroup或View,如下图:
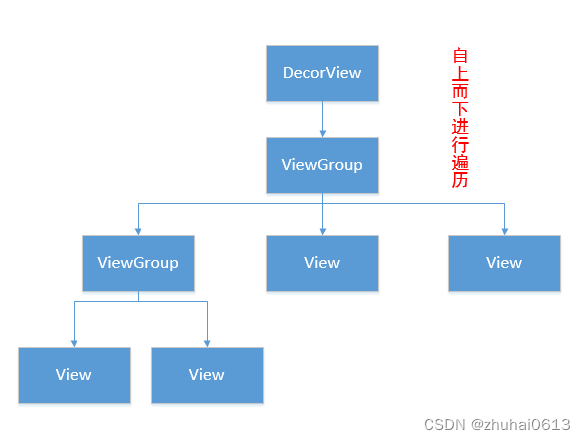
一定要记住:无论是measure过程、layout过程还是draw过程,永远都是从View树的根节点开始测量或计算(即从树的顶端开始),一层一层、一个分支一个分支地进行(即树形递归),最终计算整个View树中各个View,最终确定整个View树的相关属性
view的生命周期
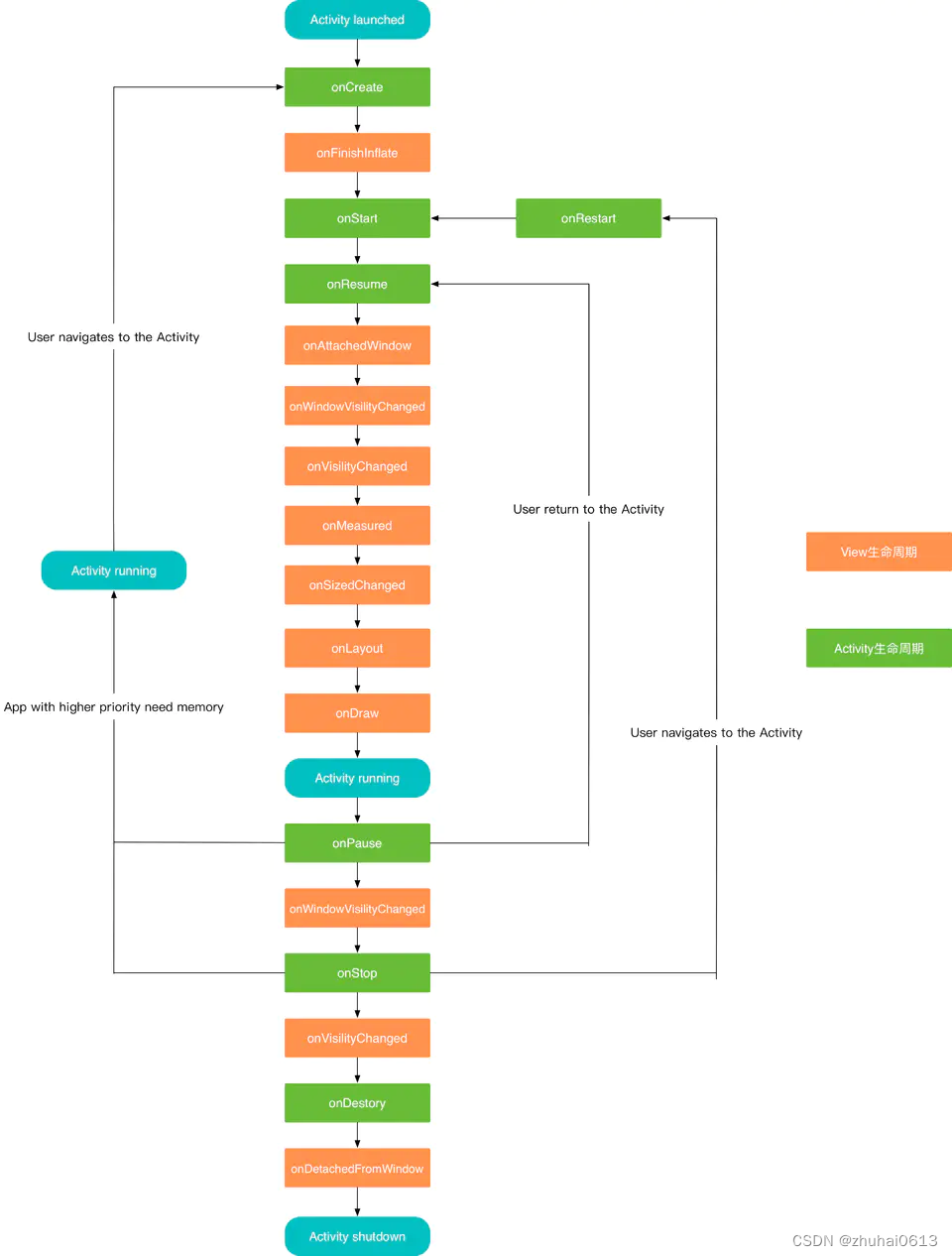
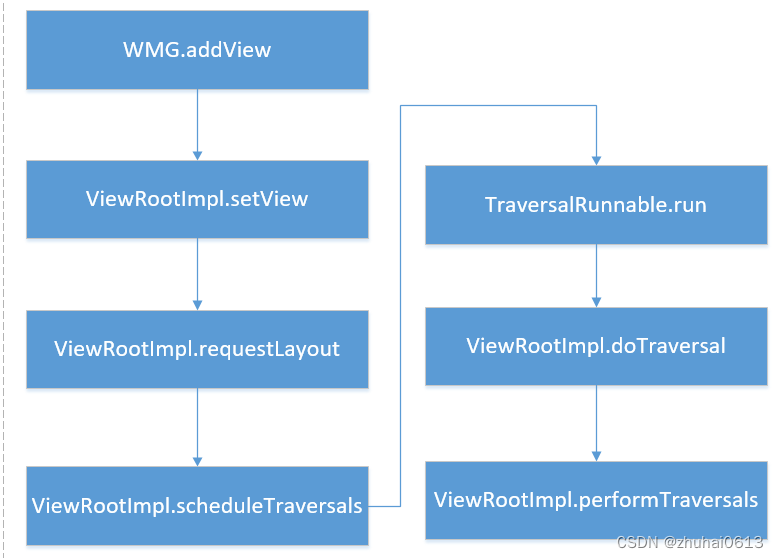
绘制流程从何而起
我们一说到绘制流程,就会想到或是听过onMeasure、onLayout、onDraw这三个方法,但是有没想过为什么我们开启一个App或是点开一个Activity,就会触发这一系列流程呢?想知道绘制流程从何而起,我们就有必要先解释 App启动流程 和 Activity的启动流程。我们都知道
ActivityThread 的 main 是一个App的入口。我们来到 main 方法看看他做了什么启动操作。ActivityThread 的 main方法是由 ZygoteInit 类中最终通过 RuntimeInit类的invokeStaticMain 方法进行反射调用

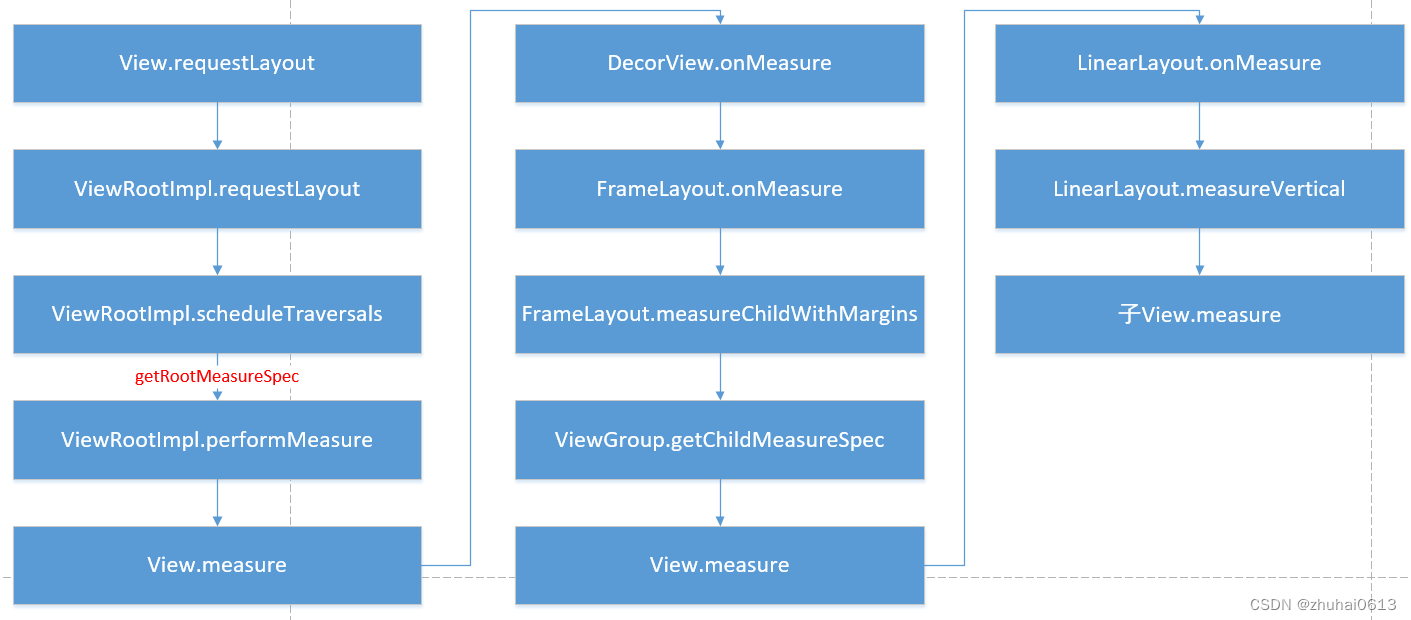
measure流程
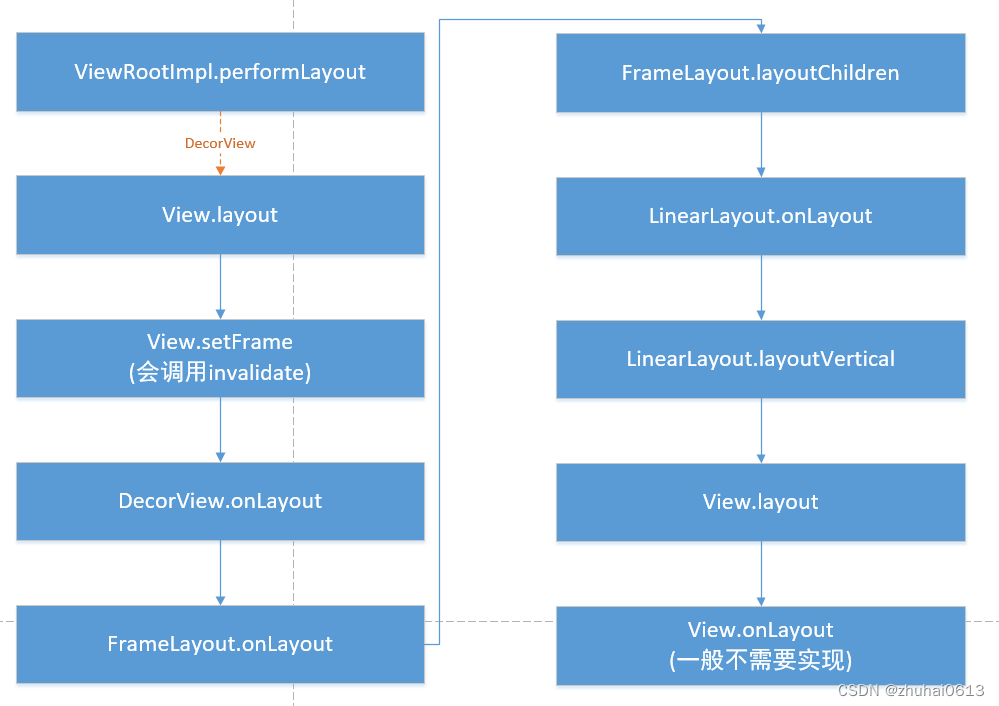
layout流程
draw流程
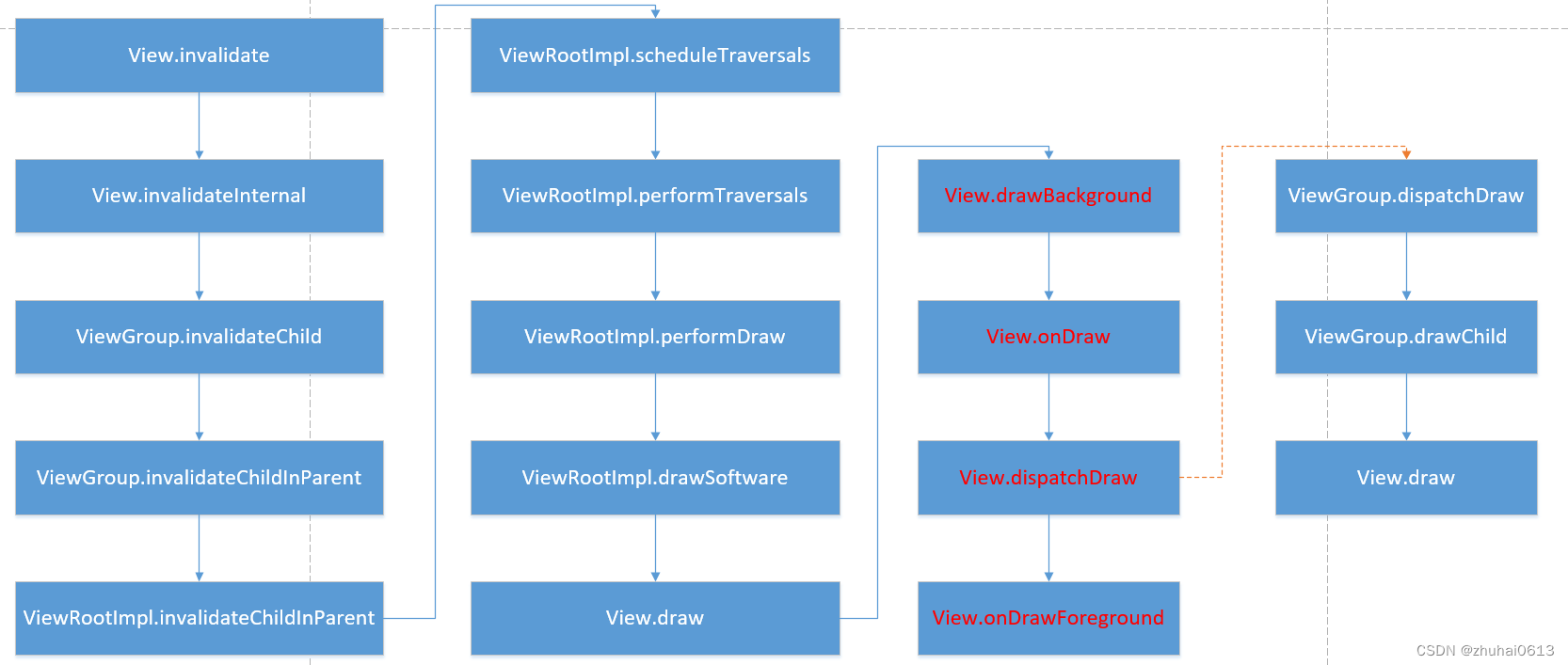
刷新
测量是如何进行的
-
测量遍历在 measure(int, int) 中实现,是 View 树的自上而下遍历。在递归过程中,每个 View
都会将维度规范下推到布局树。在测量遍历结束时,每个 View 均存储了其测量值。第二次遍历发生在 layout(int, int,
int, int) 中,也是自上而下遍历。在此次遍历中,每个父级负责使用测量遍历中计算的尺寸来定位其所有的子级。当返回 View 对象的
measure() 方法时,必须设置其 getMeasuredWidth() 和 getMeasuredHeight() 值,以及该
View 对象的所有子级的值。View 对象的测量宽度值和测量高度值必须遵守 View
对象的父级所施加的限制。这就保证了在测量遍历结束时,所有父级都会接受其子级的所有测量值。父级 View 可以对其子级多次调用
measure()。例如,父级可以使用未指定的维度测量每个子级一次,以确定它们希望的大小;然后,如果所有子级不受限制的尺寸的总和过大或过小,则再次使用实际的数字对它们调用
measure()(即,如果子级未就各自获得多少空间达成一致,则父级将会介入并针对第二次遍历设置规则)。 -
测量遍历使用两个类来传达维度。View 对象使用 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 类来告知父级它们想要如何测量和定位。基本的
ViewGroup.LayoutParams 类仅描述了 View 希望的宽度和高度。针对每个维度,它可以指定以下某一项: -
一个确切的数字
-
MATCH_PARENT,该参数意味着 View 想要和它的父级一样大(负填充)
-
WRAP_CONTENT,该参数意味着 View 想要足够大,以包含其内容(正填充)。
有适用于 ViewGroup 的不同子类的 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 子类。例如,RelativeLayout 有自己的 ViewGroup.LayoutParams 子类,其中包括使子级 View 对象水平和垂直居中的功能。
MeasureSpec 对象用于在树中将要求从父级下推到子级。MeasureSpec 可以为以下三种模式之一:
- UNSPECIFIED:父级使用该模式来确定子级 View 所需的维度。例如,LinearLayout 可能会对其高度设置为 UNSPECIFIED 和宽度设置为 EXACTLY 240 的子级调用 measure(),从而确定宽度为 240 像素的子级 View 所需的高度。
- EXACTLY:父级使用该模式来强制子级使用某个确切尺寸。子级必须使用该尺寸,并保证其所有的子项都能放入该尺寸。
- AT MOST:父级使用该模式来强制规定子级的最大尺寸。子级必须保证它及其所有的子项都能放入该尺寸

// ViewGroup 类
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);int resultSize = 0;int resultMode = 0;switch (specMode) {// 父视图为确定的大小的模式case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:/*** 根据子视图的大小,进行不同模式的组合:* 1、childDimension 大于 0,说明子视图设置了具体的大小* 2、childDimension 为 {@link LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT},说明大小和其父视图一样大* 3、childDimension 为 {@link LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT},说明子视图想为其自己的大小,但* 不能超过其父视图的大小。*/if (childDimension >= 0) {resultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size. So be it.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;// 父视图已经有一个最大尺寸限制case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:/*** 根据子视图的大小,进行不同模式的组合:* 1、childDimension 大于 0,说明子视图设置了具体的大小* 2、childDimension 为 {@link LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT},* -----说明大小和其父视图一样大,但是此时的父视图还不能确定其大小,所以只能让子视图不超过自己* 3、childDimension 为 {@link LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT},* -----说明子视图想为其自己的大小,但不能超过其父视图的大小。*/if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... so be itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... let him have itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should// beresultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how// big it should beresultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;}break;}return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);}
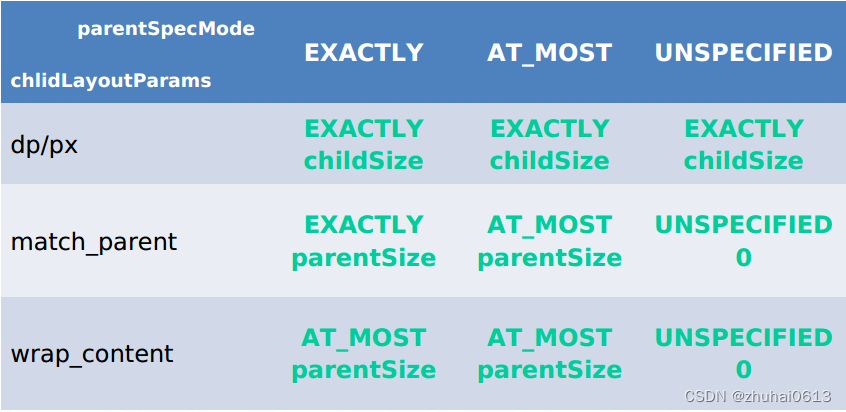
针对上表,这里再做一下具体的说明
- 对于应用层 View ,其 MeasureSpec 由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和自身的 LayoutParams 来共同决定
- 对于不同的父容器和view本身不同的LayoutParams,view就可以有多种MeasureSpec。
- 当view采用固定宽高的时候,不管父容器的MeasureSpec是什么,view的MeasureSpec都是精确模式并且其大小遵循Layoutparams中的大小;
- 当view的宽高是match_parent时,这个时候如果父容器的模式是精准模式,那么view也是精准模式并且其大小是父容器的剩余空间,如果父容器是最大模式,那么view也是最大模式并且其大小不会超过父容器的剩余空间;
- 当view的宽高是wrap_content时,不管父容器的模式是精准还是最大化,view的模式总是最大化并且大小不能超过父容器的剩余空间。
- Unspecified模式,这个模式主要用于系统内部多次measure的情况下,一般来说,我们不需要关注此模式(这里注意自定义View放到ScrollView的情况 需要处理)。
onMeasure()方法中常用的方法 - getChildCount():获取子View的数量;
- getChildAt(i):获取第i个子控件;
- subView.getLayoutParams().width/height:设置或获取子控件的宽或高;
- measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec):测量子View的宽高;
- child.getMeasuredHeight/width():执行完measureChild()方法后就可以通过这种方式获取子View的宽高值;
- getPaddingLeft/Right/Top/Bottom():获取控件的四周内边距;
- setMeasuredDimension(width, height):重新设置控件的宽高
自定义View需要注意的地方
- 让View支持wrap_conent
- 让View支持padding
- 尽量避免使用Handler,一般都可以用View自带的post方法代替
- 在onDeatchFromWindow时,停止View的动画或线程(如果有的话)
- 如果存在嵌套滑动,处理好滑动冲突
自定义View如何测量
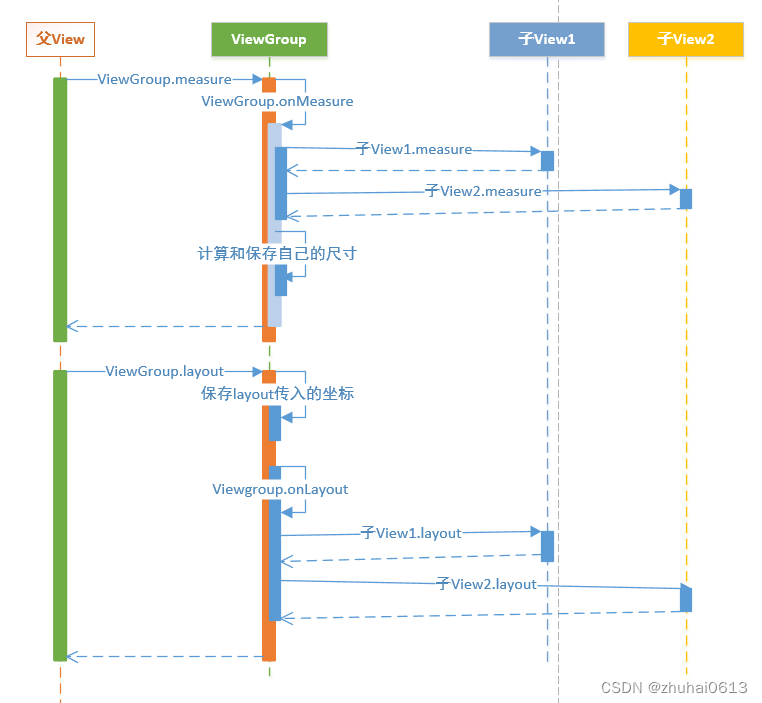
自定义绘制
1.Canvas常用方法
- 绘制图形(点、线、矩形、椭圆、圆等)
- 绘制文本(文本的居中问题,需要Paint知识)
- 画布的基本变化(平移、缩放、旋转、倾斜)
- 画布的裁剪
- 画布的保存
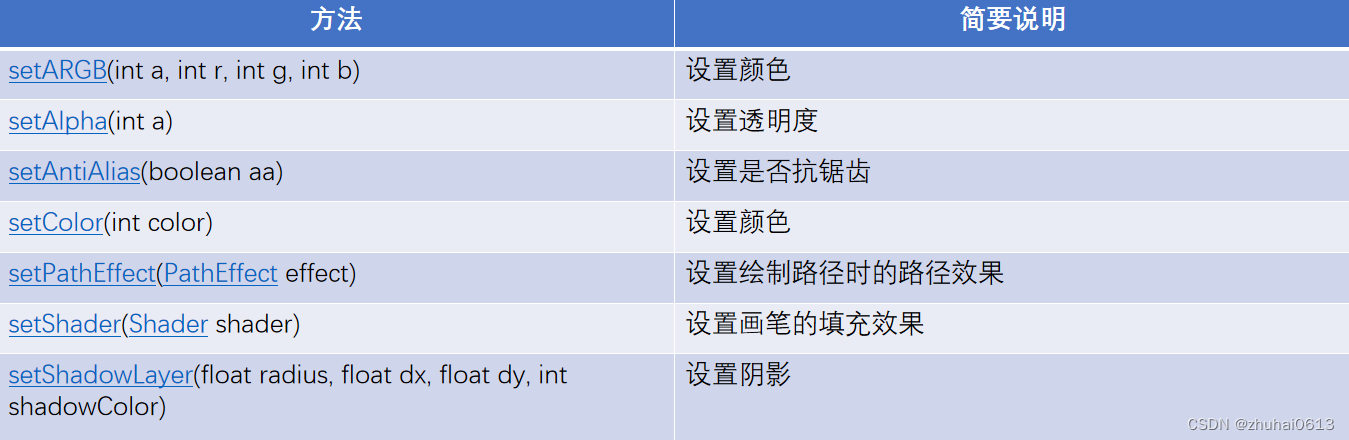
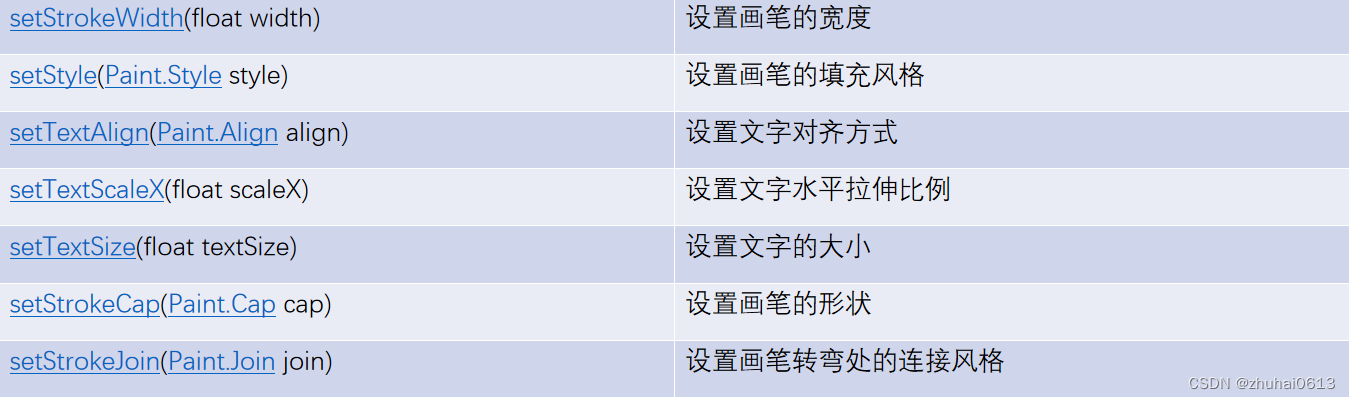
2.Paint类主要用于设置绘制风格:包括画笔的颜色画笔触笔粗细、填充风格及文字的特征
-
Paint常用方法
-
颜色
-
类型(填充、描边)
-
字体大小
-
宽度
-
对齐方式
-
文字位置属性测量
-
文字宽度测量
-
Path常用方法
-
添加路径
-
移动起点
-
贝塞尔(二阶、三阶)
-
逻辑运算
-
重置路径
-
PathEffect
-
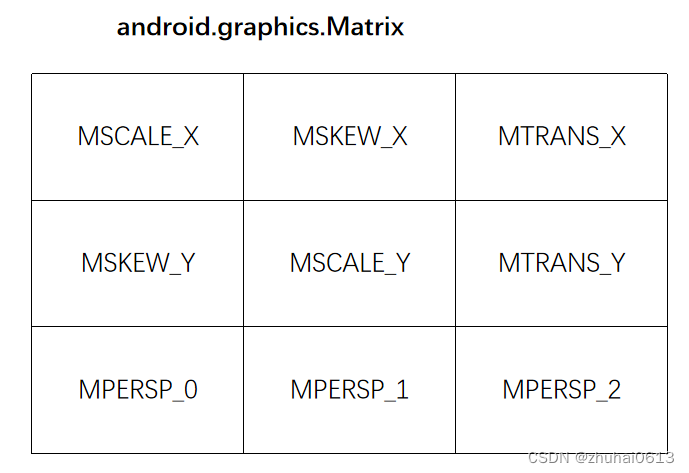
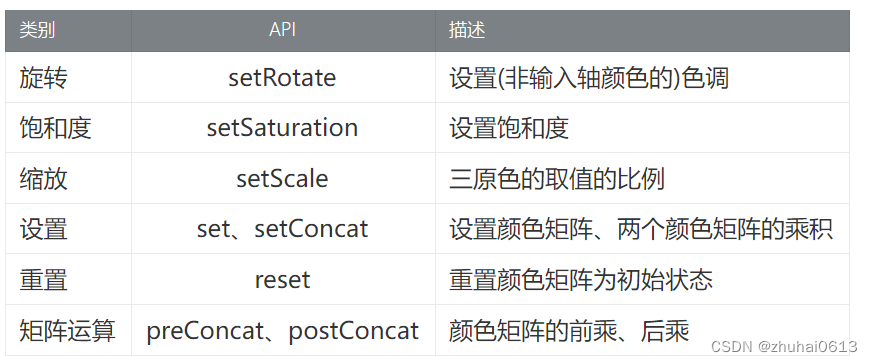
Matrix
-
PathMeasure:来操作和获取有关 Path 对象信息的工具类。
-
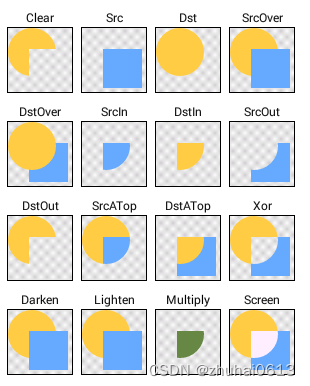
PorterDuffXfermode
-
Matrix
-
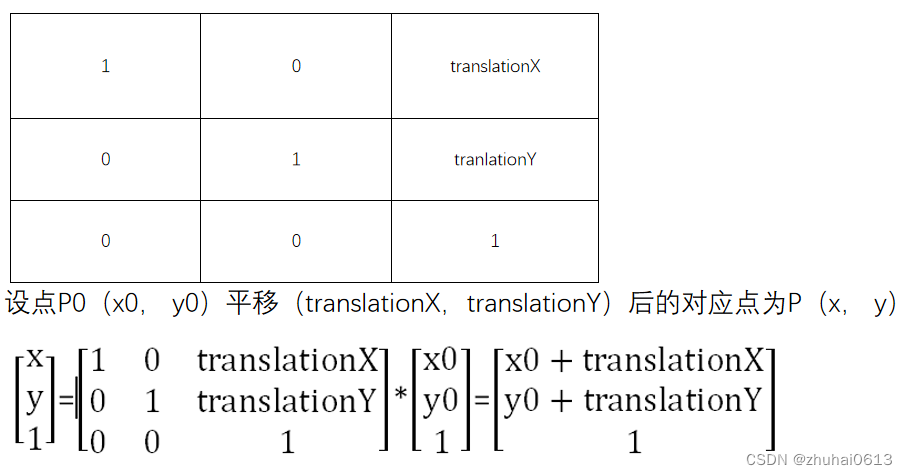
平移矩阵
-
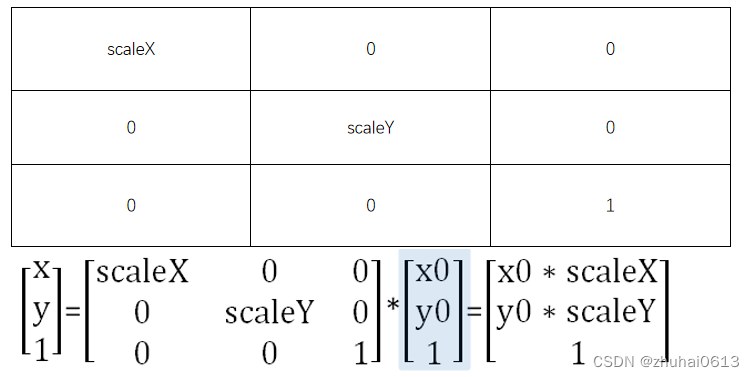
缩放矩阵
-
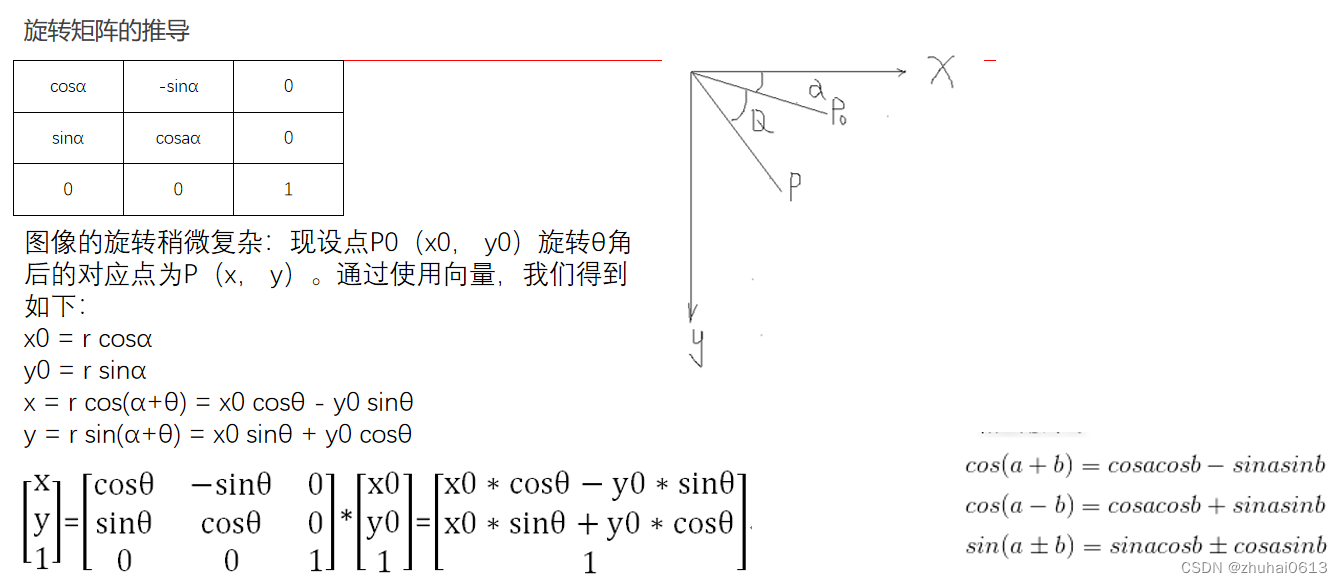
旋转矩阵
-
ColorMatrix
4 动画
- ObjectAnimator
- ValueAnimator
- AnimatorSet
- 差值器
- 估值器
事件分发
-
事件序列 DOWN -> … MOVE … -> UP/CANCEL
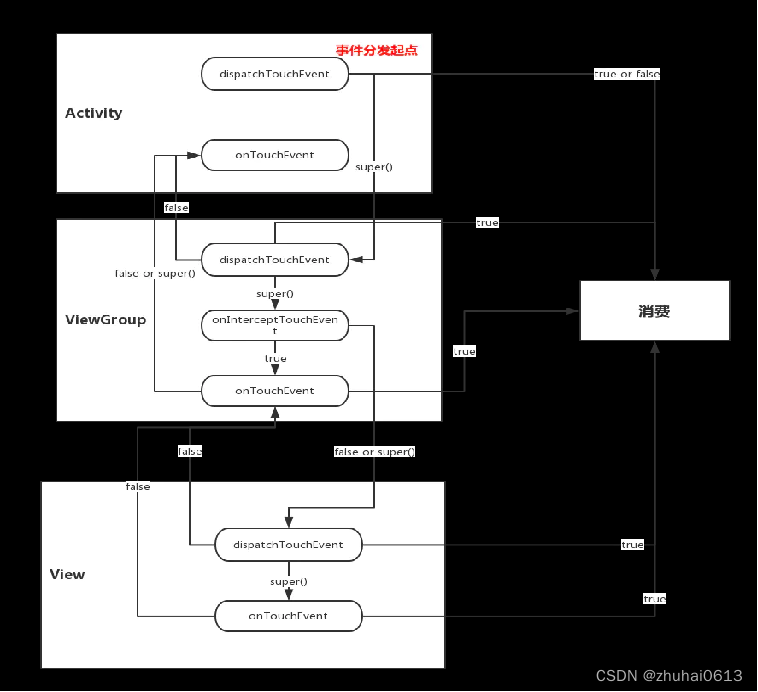
-
父容器调用哪个方法可以拦截子View的事件?为什么?
- 调用onInterceptTouchEvent()并返回true。因为该方法返回true后,会导致变量 intercepted =
true,从而导致不会走后面分发事件的代码。 -
子View调用哪个方法可以请求父容器不拦截自己?为什么?
- requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true)。因为 onInterceptTouchEvent()
方法的执行条件是disallowIntercept = false,而子View调用requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true)方法可以导致disallowIntercept
= true,从而onInterceptTouchEvent方法不会执行,父容器就不能拦截自己了。 -
父容器一旦在down事件拦截子View,就算子View调用了requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent方法还是拿不到事件,为什么?
- 因为down事件时,父容器会调用resetTouchState,导致disallowIntercept始终为false,即onInterceptTouchEvent方法始终会执行。
-
按钮的onClick方法是在哪个事件响应的?
- A.MotionEvent.ACTION_UP
- B.MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
- C.MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE
-
解决事件冲突的主要方法有哪些?
- 内部拦截法、外部拦截法
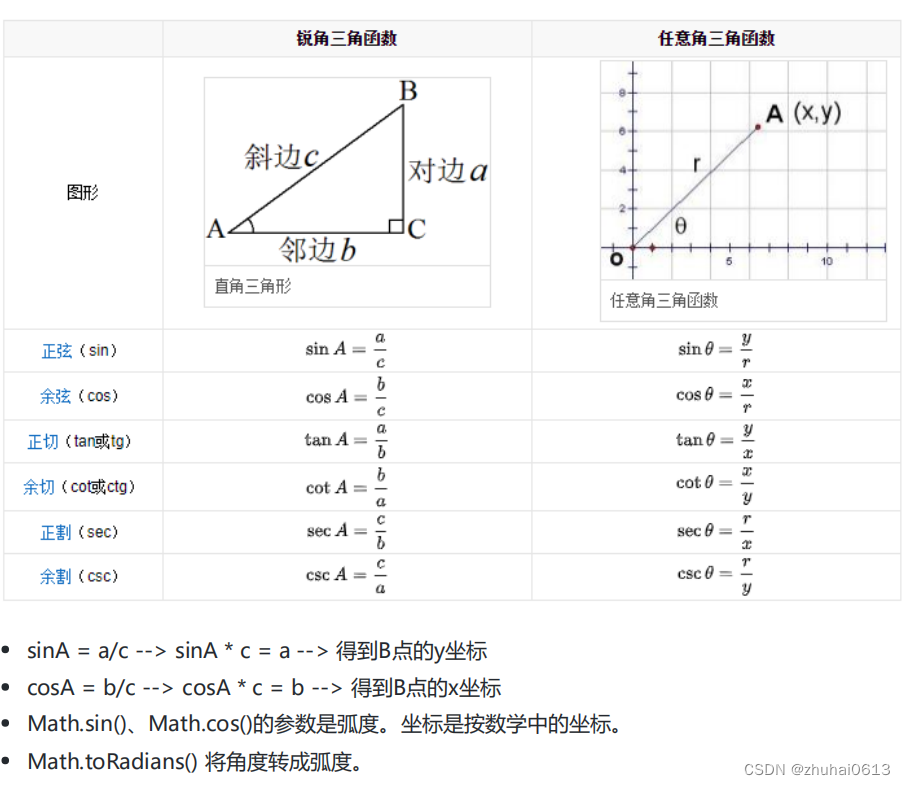
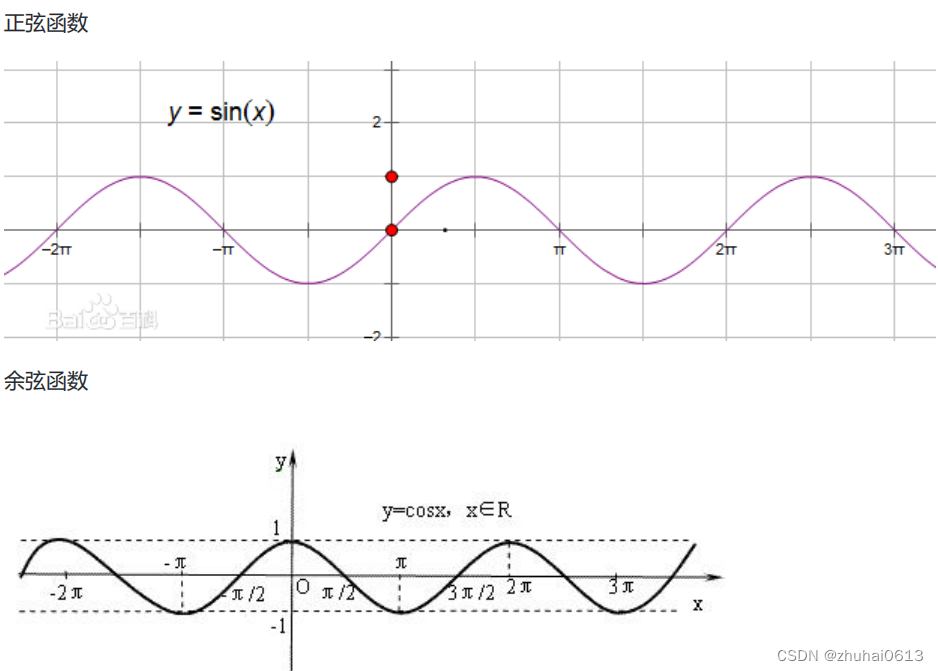
三角函数
Android底层绘制原理:
1.Linux Kernel(Linux内核) :
Graphics Driver(图形驱动):Linux内核包含用于管理硬件资源的图形驱动,如GPU(图形处理单元)。它负责底层的图形渲染和硬件加速。
2.Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)(硬件抽象层):
Graphics HAL:这一层抽象了硬件的细节,为上层提供统一的接口。在这里,Android系统与具体的硬件设备进行交互,例如图形和显示硬件。
3.Android Runtime and Libraries(Android运行时和库):
Skia:Android中用于2D图形绘制的库。它被用于处理形状、文本、图像等基本绘图操作。
OpenGL ES:用于3D图形渲染的库。Android应用通过OpenGL ES API进行复杂的3D绘图。
SurfaceFlinger:Android的合成器,负责将多个应用的图形内容合成到屏幕上。它管理应用创建的Surface(绘图表面)。
4.Android Framework(Android框架):
View System:Android框架的一部分,负责布局和绘制用户界面。每个View负责绘制自身。
Canvas API:提供了一个绘图表面,开发者可以在上面绘制图形(如线条、圆形、文本等)。
Hardware Acceleration(硬件加速):自Android 3.0(Honeycomb)起,UI的绘制可以通过GPU进行加速。
5.Android Applications(Android应用):
Application Code(应用代码):开发者编写的代码,使用Android提供的API(如View、Canvas)来创建和管理用户界面。
Rendering(渲染):应用通过View系统进行界面布局,然后通过Canvas或OpenGL ES绘制内容。完成的绘制内容传递给SurfaceFlinger进行合成。
在整个过程中,从应用发起的绘制请求(如一个按钮或图像的显示),首先通过Android框架层处理,然后通过硬件抽象层和Linux内核中的驱动与实际的硬件(如GPU)交互,最终将内容渲染到屏幕上。
最后给大家带来一个好玩的公式:
e i π + 1 = 0 e ^{iπ}+1=0 eiπ+1=0
- e 是自然对数的底数。
- i 是虚数单位。
- π是圆周率。
相关文章:

Android之高级UI
系统ViewGroup原理解析 常见的布局容器: FrameLayout, LinearLayout,RelativeLayoout,GridLayout 后起之秀:ConstraintLayout,CoordinateLayout Linearlayout Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {if (mOrientation …...

Qt:解决跨线程调用socket/IO类,导致报错的问题
Qt有很多IO相关的类,比如说QTcpSocket、QFile,总的来说,在Qt的框架内使用,还是非常方便的。 但是用过其他框架IO类的人,可能有一个很不习惯,就是Qt的所有IO类,都不推荐或者不可以跨线程操作&…...

长沙电信大楼火灾调查报告发布:系烟头引发。FIS来护航安全
近日,长沙电信大楼的火灾调查报告引起广泛关注。调查发现,火灾是由未熄灭的烟头引发,烟头点燃了室外平台的易燃物,迅速蔓延至整个建筑。这起悲剧再次提醒我们,小小的疏忽可能酿成大灾难。但如果我们能及时发现并处理这…...

【Web系列二十七】Vue实现dom元素拖拽并限制移动范围
目录 需求 拖拽功能封装 使用拖拽功能 vite-env.d.ts main.ts test.vue 需求 dom元素拖拽并限制在父组件范围内 拖拽功能封装 export const initVDrag (vue) > {vue.directive(drag, (el) > {const oDiv el // 当前元素oDiv.onmousedown (e) > {let target…...

【IEEE独立出版】2024第四届神经网络、信息与通信工程国际学术会议(NNICE 2024)
2024第四届神经网络、信息与通信工程国际学术会议(NNICE 2024) 2024 4th International Conference on Neural Networks, Information and Communication Engineering 2024第四神经网络、信息与通信工程国际学术会议(NNICE 2024࿰…...

docker 推送tar包到远程仓库
tar 包 推送到远程仓库的步骤 - 导入镜像(docker load -i 镜像名称)示例:docker load -i yiyi-admin.tar- 打标签(docker tag 镜像id registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/空间名称/镜像名称:版本号)示例:docker tag $image_id reg…...

全志XR806基于FreeRTOS下部署竞技机器人先进模糊控制器
前言 很荣幸参与到由“极术社区和全志在线联合组织”举办的XR806开发板试用活动。本人热衷于各种的开发板的开发,同时更愿意将其实现到具体项目中。秉承以上原则,发现大家的重心都放在开发中的环境构建过程,缺少了不少实际应用场景的运用&am…...

python动态加载内容抓取问题的解决实例
问题背景 在网页抓取过程中,动态加载的内容通常无法通过传统的爬虫工具直接获取,这给爬虫程序的编写带来了一定的技术挑战。腾讯新闻(https://news.qq.com/)作为一个典型的动态网页,展现了这一挑战。 问题分析 动态…...

系列二十三、将一个第三方的类配置成bean的方式
一、将一个第三方的类配置成bean的方式 1.1、概述 日常的JavaEE开发中,难免不会遇到需要使用第三方的类的情况,比如:MyBatisPlus、RedisTemplate、DruidDataSource...,这些外部组件是不同的组织或个人提供的,我们为什…...
【长文干货】Python可视化教程
文章目录 数据介绍Matplotlib散点图折线图柱形图直方图 Seaborn散点图折线图柱形图直方图 Bokeh散点图折线条形图交互式 Plotly基本组合优化:定制化下拉菜单 总结 数据介绍 在这个小费数据集中,我们记录了20世纪90年代初期餐厅顾客在两个半月内给出的小…...
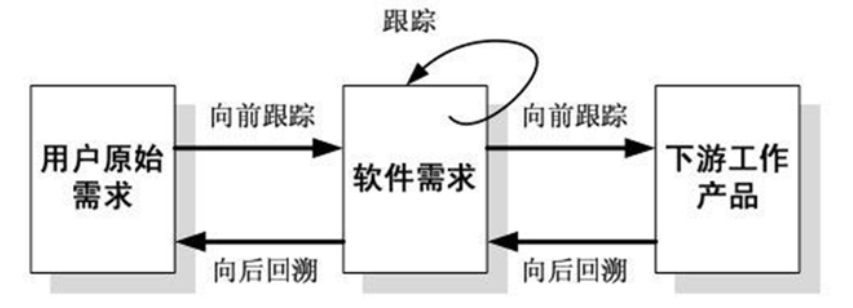
软件工程--需求工程--学习笔记(超详细)
软件需求工程是软件开发周期的第一个阶段,也是关系到软件开发成败最关键阶段,本章讲解需求的基础知识和需求工程的关键活动。这些知识对于结构化方法、面向对象方法、面向服务方法等都是适用的 本文参考教材:沈备军老师的《软件工程原理》 目…...

TemplateHit中提取query和hit比对上序列索引的映射字典
template_hits(Sequence[TemplateHit]数据格式)来自结构数据库搜索结果 python运行hhsearch二进制命令的包装器类 映射索引计算:TemplateHit 中含有 indices_query,需要换算成在原始query序列中的index,hit 中indices_hit 需要减去最小index…...
富必达API:一站式无代码开发集成电商平台、CRM和营销系统
一站式无代码开发的连接解决方案 电子商务、客户服务系统以及其它商业应用,是现代企业运营的重要部分。然而,将这些系统进行有效的整合往往需要复杂的API开发,这对很多企业来说是一个巨大的挑战。富必达API以其一站式的无代码开发解决方案&a…...

聊聊接口最大并发处理数
文章目录 前言并发和并行并发(Concurrency)并行(Parallelism)思考一下 前言 生活在 2023 年的互联网时代下,又是在国内互联网越发内卷的背景下,相信大家面试找工作、网上学习查资料时都了解过互联网系统设…...
6.如何利用LIO-SAM生成可用于机器人/无人机导航的二维/三维栅格地图--以octomap为例
目录 1 octomap的安装 2 二维导航节点的建立及栅格地图的构建 3 三维栅格地图的建立 1 octomap的安装 这里采用命令安装: sudo apt install ros-melodic-octomap-msgs ros-melodic-octomap-ros ros-melodic-octomap-rviz-plugins ros-melodic-octomap-server 这样…...
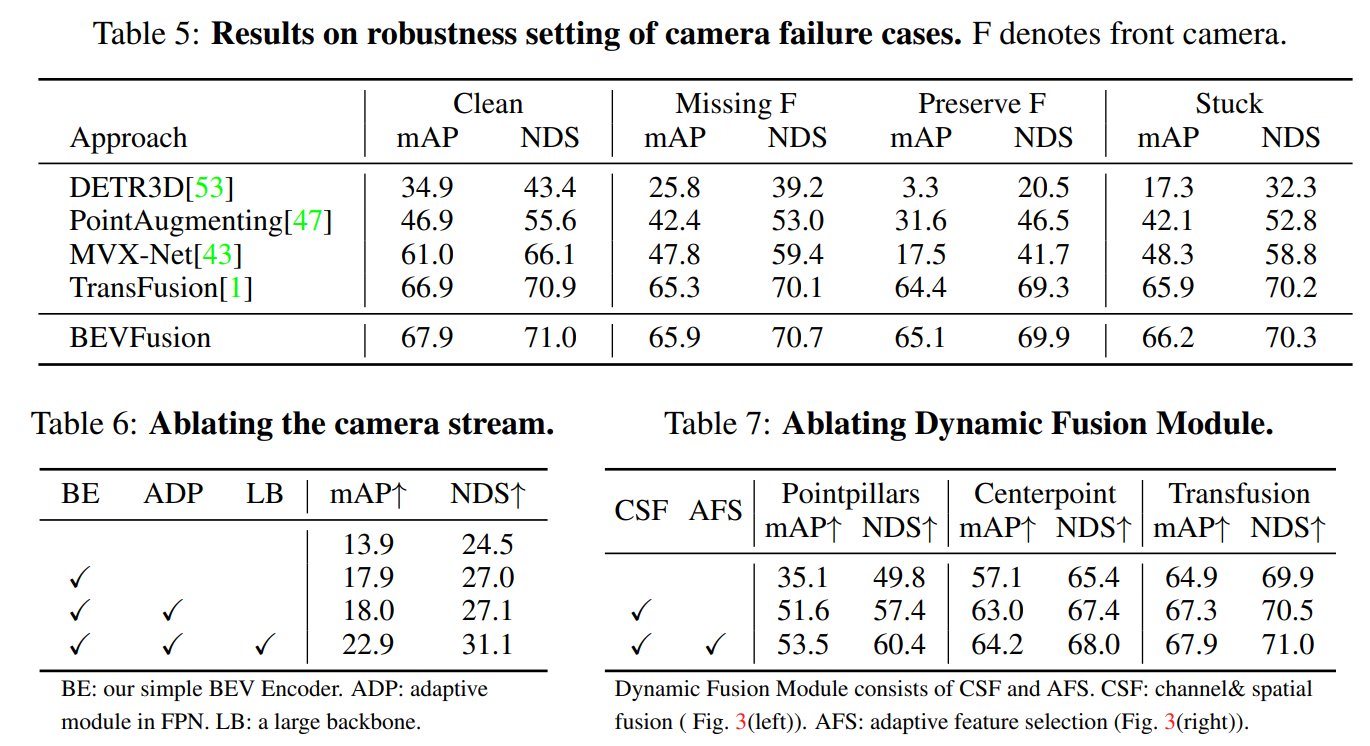
【多传感器融合】BEVFusion: 激光雷达和视觉融合框架 NeurIPS 2022
前言 BEVFusion其实有两篇, 【1】BEVFusion: A Simple and Robust LiDAR-Camera Fusion Framework. NeurIPS 2022 | 北大&阿里提出 【2】BEVFusion: Multi-Task Multi-Sensor Fusion with Unified Bird’s-Eye View Representation 2022 | MIT提出 本文先分…...
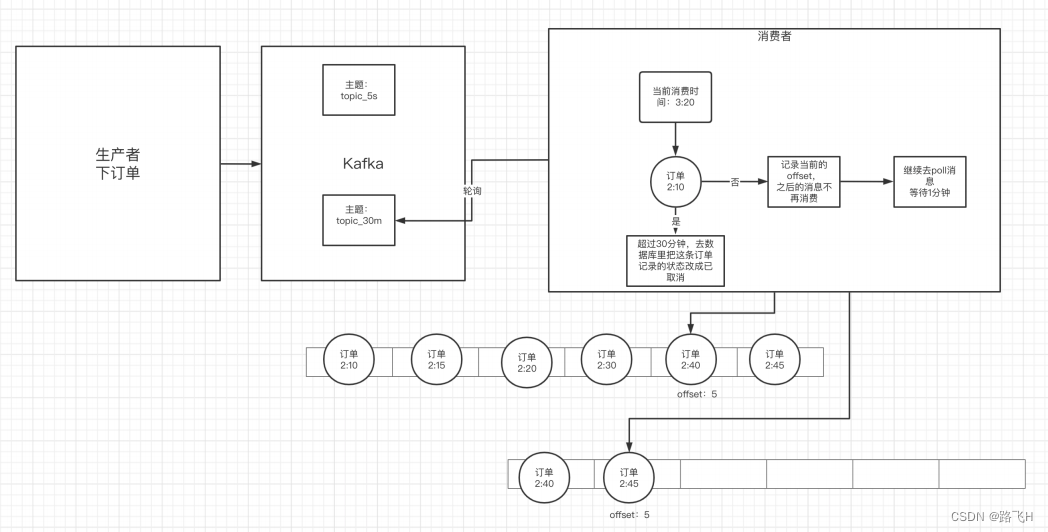
kafka中的常见问题处理
文章目录 1. 如何防⽌消息丢失2. 如何防⽌重复消费3. 如何做到消息的顺序消费4. 如何解决消息积压问题4.1 消息积压问题的出现4.2 消息积压的解决⽅案 5. 实现延时队列的效果5.1 应用场景5.2 具体方案 1. 如何防⽌消息丢失 ⽣产者:1)使⽤同步发送 2&…...
——@Styles装饰器:定义组件重用样式)
HarmonyOS(八)——@Styles装饰器:定义组件重用样式
前言 在前面我们介绍过Builder装饰器和BuilderParam装饰器。今天我们继续介绍另外一个装饰器——Styles装饰器:定义组件重用样式。 如果每个组件的样式都需要单独设置,在开发过程中会出现大量代码在进行重复样式设置,虽然可以复制粘贴&…...

手写VUE后台管理系统5 - 整合状态管理组件pinia
整合状态管理组件 安装整合创建实例挂载使用 pinia 是一个拥有组合式 API 的 Vue 状态管理库。 pinia 官方文档:https://pinia.vuejs.org/zh/introduction.html 安装 yarn add pinia整合 所有与状态相关的文件都放置于项目 src/store 目录下,方便管理 在…...
解决webpack打包生成gz格式css/js文件没法在nginx使用的问题--全网唯一正确
本文绝对是全网解决这个问题唯一正确的文章,没有之一! 很多人都说开启nginx gzip压缩,这些人完全是胡说八道!你们到底懂不懂叫gzip压缩啊?! 不信你就试试,如果css/js只有gz文件,ng…...
练习(含atoi的模拟实现,自定义类型等练习)
一、结构体大小的计算及位段 (结构体大小计算及位段 详解请看:自定义类型:结构体进阶-CSDN博客) 1.在32位系统环境,编译选项为4字节对齐,那么sizeof(A)和sizeof(B)是多少? #pragma pack(4)st…...
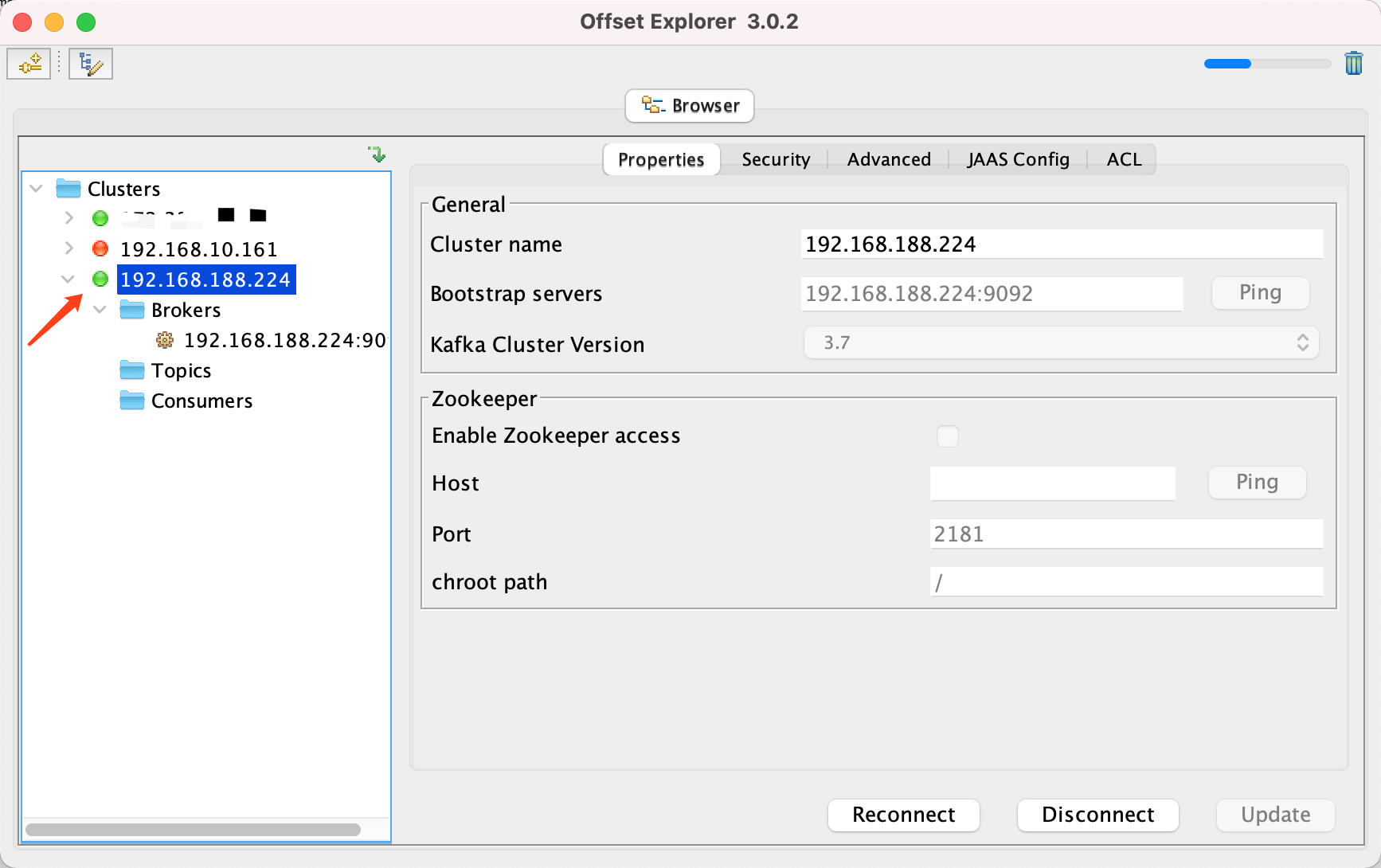
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程一、说明二、环境准备三、编写 Docker Compose 和 jaas文件docker-compose.yml代码说明:server_jaas.conf 四、启动服务五、验证服务六、连接kafka服务七、总结 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认…...
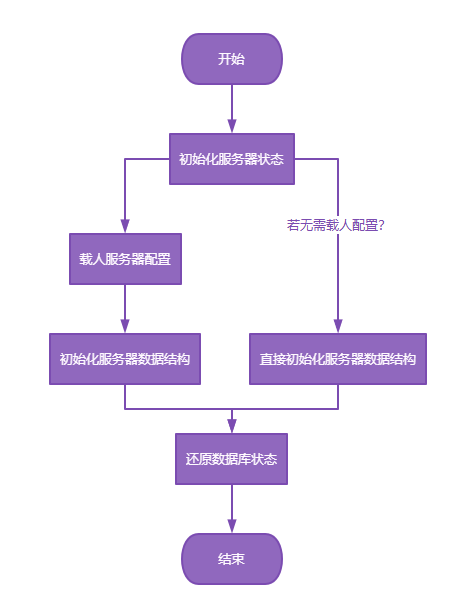
【Redis技术进阶之路】「原理分析系列开篇」分析客户端和服务端网络诵信交互实现(服务端执行命令请求的过程 - 初始化服务器)
服务端执行命令请求的过程 【专栏简介】【技术大纲】【专栏目标】【目标人群】1. Redis爱好者与社区成员2. 后端开发和系统架构师3. 计算机专业的本科生及研究生 初始化服务器1. 初始化服务器状态结构初始化RedisServer变量 2. 加载相关系统配置和用户配置参数定制化配置参数案…...

工业自动化时代的精准装配革新:迁移科技3D视觉系统如何重塑机器人定位装配
AI3D视觉的工业赋能者 迁移科技成立于2017年,作为行业领先的3D工业相机及视觉系统供应商,累计完成数亿元融资。其核心技术覆盖硬件设计、算法优化及软件集成,通过稳定、易用、高回报的AI3D视觉系统,为汽车、新能源、金属制造等行…...
)
是否存在路径(FIFOBB算法)
题目描述 一个具有 n 个顶点e条边的无向图,该图顶点的编号依次为0到n-1且不存在顶点与自身相连的边。请使用FIFOBB算法编写程序,确定是否存在从顶点 source到顶点 destination的路径。 输入 第一行两个整数,分别表示n 和 e 的值(1…...
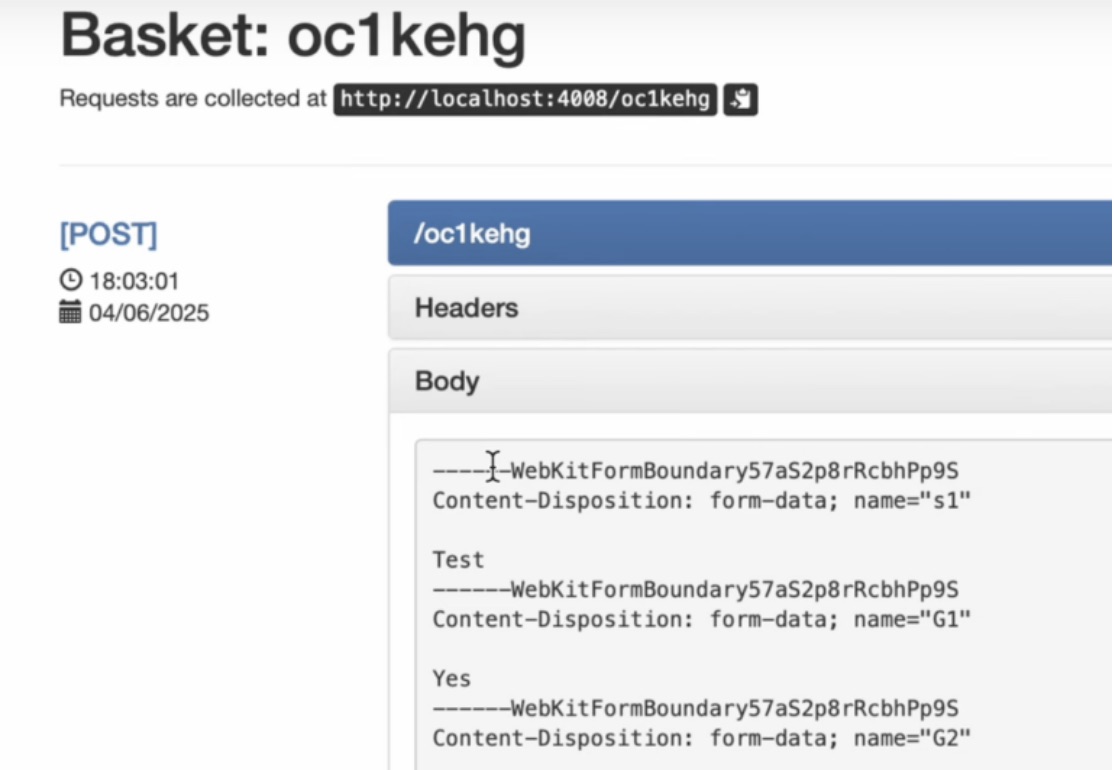
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...

Python 包管理器 uv 介绍
Python 包管理器 uv 全面介绍 uv 是由 Astral(热门工具 Ruff 的开发者)推出的下一代高性能 Python 包管理器和构建工具,用 Rust 编写。它旨在解决传统工具(如 pip、virtualenv、pip-tools)的性能瓶颈,同时…...

tomcat入门
1 tomcat 是什么 apache开发的web服务器可以为java web程序提供运行环境tomcat是一款高效,稳定,易于使用的web服务器tomcathttp服务器Servlet服务器 2 tomcat 目录介绍 -bin #存放tomcat的脚本 -conf #存放tomcat的配置文件 ---catalina.policy #to…...

Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析
Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析 在 Qt 事件处理中,return 语句的使用是另一个关键概念,它与 event->accept()/event->ignore() 密切相关但作用不同。让我们详细分析一下它们之间的关系和工作原理。 核心区别:不同层级的事件处理 方…...

在树莓派上添加音频输入设备的几种方法
在树莓派上添加音频输入设备可以通过以下步骤完成,具体方法取决于设备类型(如USB麦克风、3.5mm接口麦克风或HDMI音频输入)。以下是详细指南: 1. 连接音频输入设备 USB麦克风/声卡:直接插入树莓派的USB接口。3.5mm麦克…...
