C++的线程管理
C++的线程管理
- 线程类(Thread)
- 线程构造器
- 约定构造器
- 初始化构造器
- 复制构造器
- 移动构造器
- 多线程
- atomic
- condition_variable
- 应用实列
- future
- promise
- 应用实列
- future
- 应用实列
线程类(Thread)
执行线程是一个指令序列,它可以在多线程环境中,与其他此类指令序列同时执行,同时共享相同的地址空间。
一个初始化的线程对象代表一个活动的执行线程;这样的线程对象是可连接的,并且具有唯一的线程ID。
默认构造的(未初始化的)线程对象是不可连接的,并且它的线程 id 对于所有不可连接的线程都是通用的。
如果从可连接线程移出,或者对它们调用 join 或 detach,则该线程将变得不可连接。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;void foo()
{sleep(10); // sleep 10 secondscout << "I'm foo, awake now" << endl;
}void bar(int x)
{sleep(5); // sleep 10 secondscout << "I'm bar, awake now" << endl;
}int main()
{thread T1 (foo); // spawn new thread that calls foo()thread T2 (bar,0); // spawn new thread that calls bar(0)cout << "main, foo and bar now execute concurrently...\n";// synchronize threads:T1.join(); // pauses until first finishesT2.join(); // pauses until second finishescout << "foo and bar completed.\n";return 0;
}
程序运行屏幕输出
main, foo and bar now execute concurrently...
I'm bar, awake now
I'm foo, awake now
foo and bar completed.
线程构造器
- thread() noexcept;- template <class Fn, class... Args>explicit thread (Fn&& fn, Args&&... args); - thread (const thread&) = delete; - thread (thread&& x) noexcept;
约定构造器
thread() noexcept;
构造一个线程对象, 它不包含任何执行线程。
初始化构造器
template <class Fn, class... Args>explicit thread (Fn&& fn, Args&&... args);
构造一个线程对象,它拥有一个可连接执行线程。
新的执行线程调用 fn, 并传递 args 作为参数。
此构造的完成与 fn 的副本开始运行同步。
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <utility>using namespace std;void f1(int n)
{for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i){cout << "Thread 1 executing\n";++n;this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(10));}
}void f2(int& n, int sz)
{for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i){cout << "Thread 2 executing\n";++n;this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(10));}
}int main()
{int n = 0;thread t2(f1, n + 1); // pass by valuethread t3(f2, ref(n), 6); // pass by referencet2.join();t3.join();cout << "Final value of n is " << n << '\n';
}
程序运行屏幕输出
Thread 1 executing
Thread 2 executing
Thread 1 executing
Thread 2 executing
Thread 2 executing
Thread 1 executing
Thread 1 executing
Thread 2 executing
Thread 1 executing
Thread 2 executing
Thread 2 executing
Final value of n is 6
复制构造器
thread (const thread&) = delete;
删除构造函数,线程对象不能复制。
移动构造器
thread (thread&& x) noexcept;
构造一个线程对象,该对象获取 x 表示的执行线程(如果有)。此操作不会以任何方式影响移动线程的执行,它只是传输其处理程序。
x 对象不再代表任何执行线程。
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <utility>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;void f2(int& n)
{thread::id this_id = this_thread::get_id();cout << "Thread " << this_id << " executing" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i){++n;this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));}
}int main()
{int n = 0;thread t3(f2, ref(n));thread t4(move(t3));t4.join();cout << "Final value of n is " << n << '\n';
}程序运行屏幕输出
Thread 140291256411904 executing
Final value of n is 5
多线程
atomic
atomic类型是封装值的类型,保证其访问不会导致数据争用,并且可用于同步不同线程之间的内存访问。
#include <iostream>
#include <atomic>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <random>using namespace std;atomic<bool> ready (false);
atomic_flag winner = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;void count1m (int id) {random_device dev;mt19937 rng(dev());uniform_int_distribution<mt19937::result_type> dist6(50,100); // distribution in range [1, 6]while (!ready) { this_thread::yield(); }int val = dist6(rng); this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(val));if (!winner.test_and_set()) { cout << "thread #" << id << " won!\n"; }
}int main ()
{vector<thread> threads;cout << "5 threads compete...\n";for (int i=1; i<=5; ++i) threads.push_back(thread(count1m,i));ready = true;for (auto& th : threads) th.join();return 0;
}
程序运行2次,屏幕输出
threads$ ./atomic
5 threads compete...
thread #3 won!
threads$ ./atomic
5 threads compete...
thread #4 won!
condition_variable
条件变量是一个能够阻塞调用线程,直到通知恢复的对象。
当调用其等待函数之一时,它使用 unique_lock(通过互斥锁)来锁定线程。该线程将保持阻塞状态,直到被另一个对同一 condition_variable 对象调用通知函数的线程唤醒。
Condition_variable 类型的对象始终使用 unique_lock 进行等待。
应用实列
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <vector>
#include <condition_variable>using namespace std;mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;
bool ready = false;void wait_init_ready (int id) {unique_lock<mutex> lck(mtx);cout << "Init " << id << " start ..." << endl;while (!ready) cv.wait(lck);cout << "Init " << id << " done !!!" << '\n';
}void init_complete() {unique_lock<mutex> lck(mtx);ready = true;cv.notify_all();
}int main ()
{vector<thread> threads;for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)threads.push_back(thread(wait_init_ready, i));init_complete();for (auto& th : threads) th.join();return 0;
}
程序运行屏幕输出
Init 0 start ...
Init 1 start ...
Init 3 start ...
Init 3 done !!!
Init 1 done !!!
Init 4 start ...
Init 4 done !!!
Init 0 done !!!
Init 2 start ...
Init 2 done !!!
future
具有允许异步访问特定提供程序(可能在不同线程中)设置的值的功能的标头。
这些提供者中的每一个(要么是promise或packaged_task对象,要么是对async的调用)与未来对象共享对共享状态的访问:提供者使共享状态准备就绪的点与未来对象访问共享状态的点同步状态。
promise
Promise 是一个对象,它可以存储类型 T 的值,以便将来的对象(可能在另一个线程中)检索,从而提供同步点。
在构造时,Promise 对象与一个新的共享状态相关联,它们可以在该状态上存储类型 T 的值或从 std::exception 派生的异常。
通过调用成员 get_future,可以将该共享状态关联到未来对象。调用后,两个对象共享相同的共享状态:
- Promise 对象是异步提供者,预计会在某个时刻为共享状态设置一个值。
- future 对象是一个异步返回对象,可以检索共享状态的值,并在必要时等待它准备好。
共享状态的生命周期至少持续到与其关联的最后一个对象释放它或被销毁为止。因此,如果也与 future 相关联,它可以在最初获得它的 Promise 对象中存活下来。
应用实列
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <thread>
#include <future>using namespace std;struct data_pkt {int id;uint8_t data[20];
};void wait_new_value (future<data_pkt>& fut) {data_pkt x = fut.get();cout << "value: " << x.id << '\n';
}int main ()
{data_pkt pkt;promise<data_pkt> prom; // create promisefuture<data_pkt> fut = prom.get_future(); // engagement with futurethread th1 (wait_new_value, ref(fut)); // send future to new threadpkt.id = 1;prom.set_value (pkt); // fulfill promise// (synchronizes with getting the future)th1.join();return 0;
}程序运行屏幕输出
value: 1
future
future 是一个可以从某些提供程序对象或函数检索值的对象,如果在不同的线程中,则可以正确同步此访问。
“有效”未来是与共享状态关联的未来对象,并通过调用以下函数之一来构造:
异步
承诺::get_future
打包任务::获取未来
future 对象仅在有效时才有用。默认构造的未来对象无效(除非移动分配了有效的未来)。
在有效的 future 上调用 future::get 会阻塞线程,直到提供者使共享状态准备就绪(通过设置值或异常)。这样,两个线程可以通过一个等待另一个线程设置值来同步。
共享状态的生命周期至少持续到与其关联的最后一个对象释放它或被销毁为止。因此,如果与未来相关联,共享状态可以在最初获取它的对象(如果有)中继续存在。
应用实列
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include <chrono>
#include <signal.h>using namespace std;bool ready = false;
mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;struct data_pkt {int code;uint8_t data[32];
};void term(int signum)
{if (signum == SIGINT){ printf("Received SIGINT(ctrl+c), exiting ... \n");unique_lock<mutex> lck(mtx);ready = true;cv.notify_all();}else{time_t mytime = time(0);printf("%d: %s\n", signum, asctime(localtime(&mytime)));printf("%d\n",signum);}
}bool async_promise (data_pkt &pkt) {cout << "async_promise start ..." << endl;struct sigaction act;act.sa_handler = term;sigaction(SIGQUIT, &act, NULL);sigaction(SIGINT, &act, NULL);unique_lock<mutex> lck(mtx); while (!ready) cv.wait(lck);cout << "async_promise condition variable ready" << endl; pkt.code = 1900;return true;
}int main ()
{data_pkt pkt;// call function asynchronously:future<bool> fut = async (async_promise, ref(pkt)); // do something while waiting for function to set future:cout << "checking, please wait";chrono::milliseconds span (100);while (fut.wait_for(span) == future_status::timeout)cout << '.' << flush;bool x = fut.get(); // retrieve return valuecout << pkt.code << endl;return 0;
}
checking, please waitasync_promise start ...
............................^CReceived SIGINT(ctrl+c), exiting ...
async_promise condition variable ready
1900
函数模板 std::async 异步运行函数 f ,可能在一个单独的线程中,该线程可能是线程池的一部分,并返回一个 std::future ,它最终将保存该函数调用的结果。
相关文章:

C++的线程管理
C的线程管理 线程类(Thread)线程构造器约定构造器初始化构造器复制构造器移动构造器 多线程atomiccondition_variable应用实列 futurepromise应用实列 future应用实列 线程类(Thread) 执行线程是一个指令序列,它可以在…...

捷配笔记-如何设计PCB板布线满足生产标准?
PCB板布线是铺设连接各种设备与通电信号的路径的过程。PCB板布线是铺设连接各种设备与通电信号的路径的过程。 在PCB设计中,布线是完成产品设计的重要步骤。可以说,之前的准备工作已经为它做好了。在整个PCB设计中,布线设计过程具有最高的极限…...

【Java数据结构】初识线性表之一:顺序表
使用Java简单实现一个顺序表 顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。 线性表大致包含如下的一些方法: public class MyArrayList { private int[] array; pri…...

对接高德开放平台API
高德开放平台API: https://lbs.amap.com/ 一、天气查询 天气查询: https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/guide/api/weatherinfo adcode城市码表下载: https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/download Component public class WeatherUtil {Resourceprivate GdCon…...

Linux 初识
目录 编辑 1.Linux发展史 1.1UNIX发展历史 1.2Linux发展历史 2.Linux的开源属性 2.1 开源软件的定义 2.2 Linux的开源许可证 2.3 开源社区与协作 3.Linux的企业应用现状 3.1 服务器 3.1.1 Web服务器 3.1.2 数据库服务器 3.1.3 文件服务器 3.1.4 电子邮件服务器 …...

CSS技巧专栏:一日一例 4.纯CSS实现两款流光溢彩的酷炫按钮特效
大家好,今天是 CSS技巧专栏:一日一例 第三篇《纯CSS实现两款流光溢彩的酷炫按钮特效》 先看图: 特此说明: 本专题专注于讲解如何使用CSS制作按钮特效。前置的准备工作和按钮的基本样式,都在本专栏第一篇文章中又详细…...

int类型变量表示范围的计算原理
文章目录 1. 了解2. 为什么通常情况下int类型整数的取值范围是-2147483648 ~ 21474836473. int类型究竟占几个字节4. 推荐 1. 了解 通常情况下int类型变量占4个字节,1个字节有8位,每位都有0和1两种状态,所以int类型变量一共可以表示 2^32 种状…...

STM32崩溃问题排查
文章目录 前言1. 问题说明2. STM32(Cortex M4内核)的寄存器3. 崩溃问题分析3.1 崩溃信息的来源是哪里?3.2 崩溃信息中的每个关键字代表的含义3.3 利用崩溃信息去查找造成崩溃的点3.4 keil5中怎么根据地址找到问题点3.5 keil5上编译时怎么输出…...

CSS 【详解】样式选择器(含ID、类、标签、通配、属性、伪类、伪元素、Content属性、子代、后代、兄弟、相邻兄弟、交集、并集等选择器)
CSS 样式选择器,用于选中页面中的 html 元素,以便添加 CSS 样式。 按渲染性能由高到低 依次是: ID 选择器 #id 通过元素的 id 属性选中元素,区分大小写 <p id"p1" >第一段</p>#p1{color: red; }但不推荐使…...

CMakeLists.txt编写思路
近期在linux编写CMakeLists.txt文件,整理了一些思路。 一、编写CMakeLists.txt的基本步骤和思路: 初始化CMake: 使用cmake_minimum_required指令指定CMake的最小版本要求,以确保兼容性。使用project指令定义项目名称和可选的语言…...

红日靶场----(三)2.漏洞利用
上期的通过一句话木马实现对目标主机的持久后门 我使用的是蚁剑,蚁剑安装及使用参考: 下载地址: GitHub - AntSwordProject/AntSword-Loader: AntSword 加载器 安装即使用: 1. 快速入门 语雀 通过YXCMS的后台GETSHELL 利用…...
滑动窗口)
LeetCode HOT100(三)滑动窗口
子数组最大平均数 I (非hot100,但是滑动窗口的思想可以很好的体现,入门滑动窗口很好的题) 给你一个由 n 个元素组成的整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k 。 请你找出平均数最大且 长度为 k 的连续子数组,并输出该最大平均数…...

数学系C++ 排序算法简述(八)
目录 排序 选择排序 O(n2) 不稳定:48429 归并排序 O(n log n) 稳定 插入排序 O(n2) 堆排序 O(n log n) 希尔排序 O(n log2 n) 图书馆排序 O(n log n) 冒泡排序 O(n2) 优化: 基数排序 O(n k) 快速排序 O(n log n)【分治】 不稳定 桶排序 O(n…...

记一下blender曲线阵列
先说一下如何正常使用这个 这一次我是用来贴瓷砖 随便创建一个mesh 然后添加一个阵列修改器,然后再给他添加一个curve修改器,使用constant offset去偏移他 这里有个小细节 我第一次创建的curve 我选取之后,死活无法沿着曲线阵列ÿ…...
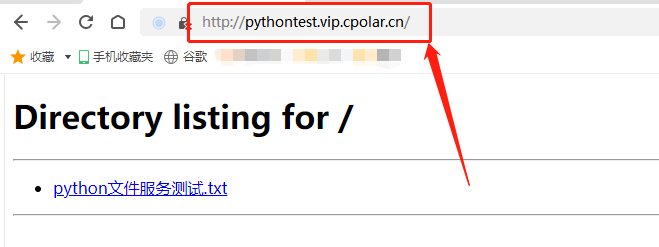
Windows电脑安装Python结合内网穿透轻松搭建可公网访问私有网盘
文章目录 前言1.本地文件服务器搭建1.1.Python的安装和设置1.2.cpolar的安装和注册 2.本地文件服务器的发布2.1.Cpolar云端设置2.2.Cpolar本地设置 3.公网访问测试4.结语 前言 本文主要介绍如何在Windows系统电脑上使用python这样的简单程序语言,在自己的电脑上搭建…...

react hooks antd 父组件取子组件form表单的值
在React中,父组件可以使用ref来访问子组件的方法或属性。子组件包含一个表单, 使用forwardRef、useImperativeHandle:forwardRef允许组件使用ref将 DOM 节点暴露给父组件,使用useImperativeHandle暴露方法给父组件。 子组件&#…...

【ARMv8/v9 GIC 系列 1.7 -- GIC PPI | SPI | SGI | LPI 中断使能配置概述】
请阅读【ARM GICv3/v4 实战学习 】 文章目录 GIC 各种中断使能配置PPIs(每个处理器私有中断)SPIs(共享外设中断)SGIs(软件生成的中断)LPIs(局部中断)GIC 各种中断使能配置 在ARM GICv3和GICv4架构中,不同类型的中断(如PPIs、SPIs、SGIs和LPIs)可以通过不同的方式进…...

大数据如何推动工业数字化发展?
随着工业领域的深刻变革,数字化成为了驱动行业前行的核心力量。在这一转变中,大数据扮演着不可或缺的角色。它不仅为企业提供了洞察市场趋势、消费者行为等关键信息的窗口,还为企业优化生产流程、提升产品质量以及推动创新提供了强有力的支持…...

计算机网络浅谈—什么是 OSI 模型?
开放系统通信(OSI)模型是一个代表网络通信工作方式的概念模型。 思维导图 什么是 OSI 模型? 开放系统互连 (OSI) 模型是由国际标准化组织创建的概念模型,支持各种通信系统使用标准协议进行通信。简单而言,OSI 为保证…...

浪潮服务器内存物理插槽位置
浪潮服务器内存物理插槽位置 如下图所示...

Docker 离线安装指南
参考文章 1、确认操作系统类型及内核版本 Docker依赖于Linux内核的一些特性,不同版本的Docker对内核版本有不同要求。例如,Docker 17.06及之后的版本通常需要Linux内核3.10及以上版本,Docker17.09及更高版本对应Linux内核4.9.x及更高版本。…...

地震勘探——干扰波识别、井中地震时距曲线特点
目录 干扰波识别反射波地震勘探的干扰波 井中地震时距曲线特点 干扰波识别 有效波:可以用来解决所提出的地质任务的波;干扰波:所有妨碍辨认、追踪有效波的其他波。 地震勘探中,有效波和干扰波是相对的。例如,在反射波…...

SCAU期末笔记 - 数据分析与数据挖掘题库解析
这门怎么题库答案不全啊日 来简单学一下子来 一、选择题(可多选) 将原始数据进行集成、变换、维度规约、数值规约是在以下哪个步骤的任务?(C) A. 频繁模式挖掘 B.分类和预测 C.数据预处理 D.数据流挖掘 A. 频繁模式挖掘:专注于发现数据中…...

大语言模型如何处理长文本?常用文本分割技术详解
为什么需要文本分割? 引言:为什么需要文本分割?一、基础文本分割方法1. 按段落分割(Paragraph Splitting)2. 按句子分割(Sentence Splitting)二、高级文本分割策略3. 重叠分割(Sliding Window)4. 递归分割(Recursive Splitting)三、生产级工具推荐5. 使用LangChain的…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...

【7色560页】职场可视化逻辑图高级数据分析PPT模版
7种色调职场工作汇报PPT,橙蓝、黑红、红蓝、蓝橙灰、浅蓝、浅绿、深蓝七种色调模版 【7色560页】职场可视化逻辑图高级数据分析PPT模版:职场可视化逻辑图分析PPT模版https://pan.quark.cn/s/78aeabbd92d1...

C#中的CLR属性、依赖属性与附加属性
CLR属性的主要特征 封装性: 隐藏字段的实现细节 提供对字段的受控访问 访问控制: 可单独设置get/set访问器的可见性 可创建只读或只写属性 计算属性: 可以在getter中执行计算逻辑 不需要直接对应一个字段 验证逻辑: 可以…...
