Ribbon 源码分析【Ribbon 负载均衡】
前言
在 Spring Cloud 2020 版本以后,移除了对 Netflix 的依赖,也就移除了负载均衡器 Ribbon,Spring Cloud 官方推荐使用 Loadbalancer 替换 Ribbon,而在 LoadBalancer 之前 Spring Cloud 一直使用的是 Ribbon 来做负载[均衡器的,而且 Ribbon 的负载均衡策略也比 Loadbalancer 更为丰富,本篇分享一些关于 Ribbon 相关的源码。
Ribbon 的自动配置
老规矩我们在分析 Ribbon 的源码之前还是去看一下 spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon 的 META-INF 包下的 spring.factories 文件中的内容,内容如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonAutoConfiguration
Ribbon 的 META-INF 包下的 spring.factories 文件中的内容非常简单,只有一个 RibbonAutoConfiguration 类,我们来看下这个类都有什么逻辑。
RibbonAutoConfiguration 类源码分析
RibbonAutoConfiguration 是 Ribbon 的全局配置,主要是加载 Ribbon 客户端工厂、负载均衡客户端、配置类工厂、重试机制工厂等,RibbonAutoConfiguration 类在启动的时候就会被加载,。
//标记为配置类
@Configuration
//注入的条件
@Conditional({RibbonAutoConfiguration.RibbonClassesConditions.class})
//为所有 RibbonClients 提供默认客户端配置
@RibbonClients
//加载配置类后加载 EurekaClientAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {"org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration"}
)
//加载配置类之前加载 LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigureBefore({LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class, AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class})
//使用 RibbonEagerLoadProperties ServerIntrospectorProperties
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class, ServerIntrospectorProperties.class})
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {//注入 configurations@Autowired(required = false)private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList();//Ribbon 的饥饿加载模式配置类 Ribbon 在进行客户端负载均衡的时候并不是在服务启动时候就初始化好的 而是在调用的时候才会去创建相应的 client 开启饥饿模式可以提前加载 client@Autowiredprivate RibbonEagerLoadProperties ribbonEagerLoadProperties;public RibbonAutoConfiguration() {}@Beanpublic HasFeatures ribbonFeature() {return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Ribbon", Ribbon.class);}//创建 Ribbon 客户端负载均衡器的工厂@Beanpublic SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);return factory;}//Ribbon 负载均衡器客户端 可以查询所有服务实例@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean({LoadBalancerClient.class})public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(this.springClientFactory());}//Ribbon 重试工厂@Bean@ConditionalOnClass(name = {"org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate"})@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryPolicyFactory(final SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {return new RibbonLoadBalancedRetryFactory(clientFactory);}//获取配置的@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory() {return new PropertiesFactory();}//如果配置了饥饿加载 就初始化 RibbonApplicationContextInitializer@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty({"ribbon.eager-load.enabled"})public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer ribbonApplicationContextInitializer() {return new RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(this.springClientFactory(), this.ribbonEagerLoadProperties.getClients());}static class RibbonClassesConditions extends AllNestedConditions {RibbonClassesConditions() {super(ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);}@ConditionalOnClass({Ribbon.class})static class RibbonPresent {RibbonPresent() {}}@ConditionalOnClass({AsyncRestTemplate.class})static class AsyncRestTemplatePresent {AsyncRestTemplatePresent() {}}@ConditionalOnClass({RestTemplate.class})static class RestTemplatePresent {RestTemplatePresent() {}}@ConditionalOnClass({IClient.class})static class IClientPresent {IClientPresent() {}}}private static class OnRibbonRestClientCondition extends AnyNestedCondition {OnRibbonRestClientCondition() {super(ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);}@ConditionalOnProperty({"ribbon.restclient.enabled"})static class RibbonProperty {RibbonProperty() {}}/** @deprecated */@Deprecated@ConditionalOnProperty({"ribbon.http.client.enabled"})static class ZuulProperty {ZuulProperty() {}}}@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documented@Conditional({RibbonAutoConfiguration.OnRibbonRestClientCondition.class})@interface ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient {}@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)@ConditionalOnClass({HttpRequest.class})@RibbonAutoConfiguration.ConditionalOnRibbonRestClientprotected static class RibbonClientHttpRequestFactoryConfiguration {@Autowiredprivate SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;protected RibbonClientHttpRequestFactoryConfiguration() {}@Beanpublic RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(final RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory) {return (restTemplate) -> {restTemplate.setRequestFactory(ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory);};}@Beanpublic RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory() {return new RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory(this.springClientFactory);}}
}RibbonClientConfiguration 类源码分析
RibbonClientConfiguration 类在加载机制是在第一次执行 Feign 请求时候才会被加载,RibbonClientConfiguration 加载时候会注入 Ribbon 客户端配置类、负载均衡算法、服务列表、负载均衡器、服务列表过滤器、负载均衡器上下文、重试处理器、服务拦截器、预处理器等。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@Import({HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class, RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class})
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {//默认连接超时时间 1 秒public static final int DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 1000;//默认读取超时时间 1 秒public static final int DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT = 1000;//默认的 GZIP 负载public static final boolean DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD = true;//Ribbon 客户端名称@RibbonClientNameprivate String name = "client";//Ribbon 配置工厂@Autowiredprivate PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory;public RibbonClientConfiguration() {}//Ribbon 客户端配置@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {//默认的配置类DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();//加载配置config.loadProperties(this.name);//设置超时时间config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, 1000);//设置读取超时时间config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, 1000);//Gzip 负载config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.GZipPayload, true);return config;}//负载均衡算法@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, this.name)) {return (IRule)this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, this.name);} else {//默认负载均衡算法(先过滤再轮训的负载均衡算法)ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);return rule;}}//检测服务健康状态@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {return (IPing)(this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, this.name) ? (IPing)this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, this.name) : new DummyPing());}//服务列表@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, this.name)) {return (ServerList)this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, this.name);} else {ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);return serverList;}}//服务更新列表@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);}//负载均衡器 @Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter, IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {return (ILoadBalancer)(this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, this.name) ? (ILoadBalancer)this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, this.name) : new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(config, rule, ping, serverList, serverListFilter, serverListUpdater));}//Ribbon 服务列表过滤器@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ServerListFilter<Server> ribbonServerListFilter(IClientConfig config) {if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerListFilter.class, this.name)) {return (ServerListFilter)this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerListFilter.class, config, this.name);} else {ZonePreferenceServerListFilter filter = new ZonePreferenceServerListFilter();filter.initWithNiwsConfig(config);return filter;}}//Ribbon 负载均衡器上下文@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic RibbonLoadBalancerContext ribbonLoadBalancerContext(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, IClientConfig config, RetryHandler retryHandler) {return new RibbonLoadBalancerContext(loadBalancer, config, retryHandler);}//重试处理器@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic RetryHandler retryHandler(IClientConfig config) {return new DefaultLoadBalancerRetryHandler(config);}//服务拦截器@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector() {return new DefaultServerIntrospector();}//预处理器@PostConstructpublic void preprocess() {RibbonUtils.setRibbonProperty(this.name, CommonClientConfigKey.DeploymentContextBasedVipAddresses.key(), this.name);}static class OverrideRestClient extends RestClient {private IClientConfig config;private ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector;protected OverrideRestClient(IClientConfig config, ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector) {this.config = config;this.serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector;this.initWithNiwsConfig(this.config);}public URI reconstructURIWithServer(Server server, URI original) {URI uri = RibbonUtils.updateToSecureConnectionIfNeeded(original, this.config, this.serverIntrospector, server);return super.reconstructURIWithServer(server, uri);}protected Client apacheHttpClientSpecificInitialization() {ApacheHttpClient4 apache = (ApacheHttpClient4)super.apacheHttpClientSpecificInitialization();apache.getClientHandler().getHttpClient().getParams().setParameter("http.protocol.cookie-policy", "ignoreCookies");return apache;}}
}Ribbion 负载均衡算法分析
Ribbon 作为一个负载均衡器,其具备丰富的负载均衡策略,这也是其相比 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 的优势,LoadBalancer 只提供了随机和轮训两种负载均衡算法,下面我们来分析一下 Ribbon 复杂均衡算法,IRule 是 Ribbon 负载均衡算法的接口。
IRule 接口源码分析
IRule 是 Ribbon 负载均衡算法的接口,接口定义了三个方法,如下:
- choose(Object var1):根据指定的算法中从服务列表中选取一个要访问的可用服务。
- setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer var1):设置负载均衡器。
- getLoadBalancer():获取负载均衡器。
package com.netflix.loadbalancer;public interface IRule {//根据指定的算法中从服务列表中选取一个要访问的可用服务Server choose(Object var1);//设置负载均衡器void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer var1);//获取负载均衡器ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}IRule 的实现类如下:
- RandomRule:随机算法,统计服务个数,使用服务个数,生成一个随机数下标,通过生成的随机数,返回一个可用的服务。
- RoundRobinRule:轮训算法,依次执行。
- WeightedResponseTimeRule:响应时间权重轮询算法,继承自RoundRobinRule,是对轮询算法进行的扩展,加入了权重计算。
- RetryRule:重试算法,实际调用的也是轮询算法,只是在没有获取到服务时,会进行循环重试操作,超过设置的时间限制,则会退出,默认为 500ms。
- BestAvailableRule:最小并发算法,会遍历所有的服务提供者,选择并发量最小的那个服务。
- AvailabilityFilteringRule:可用性断言过滤器算法。
- ZoneAvoidanceRule :先过滤后轮训的算法,也是默认的负载均衡算法。
RandomRule 随机算法源码分析
RandomRule#choose 是 Ribbom 负载均衡随机算法的实现,主要逻辑如下:
- ILoadBalancer 为空判断,如果 ILoadBalancer 为空,则直接返回服务为 null。
- ILoadBalancer 不为空,且 Server 也不为空,则直接返回 Server 。
- ILoadBalancer 不为空,且 Server 为空,获取所有服务列表,使用服务列表数量获取一个随机数,使用这个随机数在可用服务列表中获取服务。
- 如果上一步获取的服务为空,则当前线程让出 CPU 资源,再次重新循环获取,出现这种情况可能是服务出现瞬时状态,如果获取的服务不为空,则判断服务是否还存活着,服务存活,直接返回服务,负责则会让出 CPU 资源,再次重新循环获取服务。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule#choose(com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer, java.lang.Object)
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {//负载均衡器为空判断if (lb == null) {//负载均衡器为空 则直接返回空return null;} else {//服务Server server = null;//开启while 循环while(server == null) {//判断当前线程是否被中断if (Thread.interrupted()) {//如果当前线程被中断 直接返回 nullreturn null;}//获取所有可以访问的服务实例列表List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();//获取所有的服务实例列表List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();int serverCount = allList.size();//判断所有服务列表的个数是否为0if (serverCount == 0) {//所有服务列表的个数为 0 返回 nullreturn null;}//使用所有服务列表来获取一个随机数int index = this.chooseRandomInt(serverCount);//在可用服务列表中 获取随机数下标的服务server = (Server)upList.get(index);//判断服务服务是否为 nulif (server == null) {//如果服务为空 则当前线程让出 CPU 资源 再次重新循环获取 出现这种情况可能是服务出现瞬时状态Thread.yield();} else {//判断服务是否还存活着if (server.isAlive()) {//服务存活 直接返回服务return server;}//有服务 服务又没有存活 则会让出 CPU 资源 再继续循环获取server = null;Thread.yield();}}//server 不为空 直接返回return server;}
}RoundRobinRule 轮训算法源码分析
RoundRobinRule#choose 方法是 Ribbon 负载均衡轮训算法的实现,具体逻辑如下:
- ILoadBalancer 为空判断,如果 ILoadBalancer 为空,则直接返回服务为 null。
- ILoadBalancer 不为空,执行 while 循环获取 Server。
- 判断 Server 是否为空且 count++ 是否小于10,满足条件,则判断所有服务数量和所有可用服务数量是否都不等于0,如果都不等于0,则使用轮训算法获取服务,对服务为空及可用性判断后返回,否则直接返回 null。
- 轮训算法的核心就是 next = (current + 1) % modulo;,也就是当前服务的请求总数+1,然后和服务总数取模,得到下标,也就是需要返回的服务对象。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule#choose(com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer, java.lang.Object)
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {//判断负载均衡器if (lb == null) {log.warn("no load balancer");//负载均衡器为空 返回 nullreturn null;} else {//负载均衡器不为空Server server = null;//计数int count = 0;//while 循环while(true) {//服务是否为空 count++是否小于10if (server == null && count++ < 10) {//满足条件 获取所有的可用服务列表List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();//获取所有的服务列表List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();//可用服务列表数量int upCount = reachableServers.size();//所有服务列表数量int serverCount = allServers.size();//可用服务列表和所有服务列表是否都不等于0if (upCount != 0 && serverCount != 0) {//获取服务索引 每次都会 ++int nextServerIndex = this.incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);//从所用服务列表中根据索引获取服务server = (Server)allServers.get(nextServerIndex);//服务为空判断if (server == null) {//服务为空 然后 cpu 资源 等待下一次循环Thread.yield();} else {//服务不为空 进行服务存活判断 和服务是否准备就绪if (server.isAlive() && server.isReadyToServe()) {//满足条件 返回服务return server;}//否则给服务复制为 nullserver = null;}//跳出循环continue;}log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);return null;}//跳出while 循环的条件if (count >= 10) {log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb);}return server;}}
}//com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule#incrementAndGetModulo
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {//当前Server请求总数int current;//下一席int next;do {current = this.nextServerCyclicCounter.get();//modulo 服务总数next = (current + 1) % modulo;} while(!this.nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next));return next;
}WeightedResponseTimeRule 类源码分析
WeightedResponseTimeRule 是 Ribbon 负载均衡响应时间权重的实现,该类继承了 RoundRobinRule,对轮询算法进行了扩展,加入了权重计算,可以为每个服务分配动态权重,然后然后加权循环,权重高的则会优先执行,我们先来看看该来的构造方法。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.ResponseTimeWeightedRule#ResponseTimeWeightedRule()
public ResponseTimeWeightedRule() {
}//com.netflix.loadbalancer.ResponseTimeWeightedRule#ResponseTimeWeightedRule()
public ResponseTimeWeightedRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {//调用了父类的构造方法 也就是 RoundRobinRule#RoundRobinRulesuper(lb);
}WeightedResponseTimeRule 提供了一个无参构造方法和一个有参构造方法,负载均衡需要使用 ILoadBalancer,无参构造方法我们就不深究了,我们重点看一下有参构造方法,有参构造方法中调用了 super(lb),也就是调用了父类 RoundRobinRule 的构造方法,我们来看一下 RoundRobinRule 的构造方法。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule#RoundRobinRule(com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer)
public RoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {this();//调用了 WeightedResponseTimeRule#setLoadBalancer 方法this.setLoadBalancer(lb);
}RoundRobinRule#RoundRobinRule 方法中又调用了 this.setLoadBalancer(lb) 方法,也就是调用了 WeightedResponseTimeRule#setLoadBalancer 方法,我们接着往下看。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule#setLoadBalancer
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb) {//还是先调用了父类的 setLoadBalancer 方法 com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule#setLoadBalancersuper.setLoadBalancer(lb);//判断 负载均衡器的类型 是否是 BaseLoadBalancerif (lb instanceof BaseLoadBalancer) {//是 获取负载均衡器的 namethis.name = ((BaseLoadBalancer)lb).getName();}//调用 ResponseTimeWeightedRule#initialize 方法this.initialize(lb);
}WeightedResponseTimeRule#setLoadBalancer 方法中先调用了 父类的 AbstractLoadBalancerRule#setLoadBalancer 方法(RoundRobinRule 类继承了 AbstractLoadBalancerRule),接着判断了 ILoadBalancer 的类型,最后调用了 ResponseTimeWeightedRule#initialize 方法,我们接着看。
ResponseTimeWeightedRule#initialize 方法源码分析
ResponseTimeWeightedRule#initialize 方法首先会判断服务权重计时器是否为空,不为空则清除服务权重计时器,然后创建服务权重计时器,并立刻开启定时任务执行权重计算(默认每30秒执行一次),开启任务后也会先执行一次权重计算,最后会在 JVM 关闭时候把权重计算清除。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.ResponseTimeWeightedRule#initialize
void initialize(ILoadBalancer lb) {//判断服务权重计时器是否为空if (this.serverWeightTimer != null) {//服务权重计数器不为空 则清除服务权重计时器this.serverWeightTimer.cancel();}//创建服务权重计时器this.serverWeightTimer = new Timer("NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" + this.name, true);//执行定时任务 0秒后执行任务 定时执行 间隔时间默认30秒 private int serverWeightTaskTimerInterval = 30000;this.serverWeightTimer.schedule(new ResponseTimeWeightedRule.DynamicServerWeightTask(), 0L, (long)this.serverWeightTaskTimerInterval);//创建服务权重ResponseTimeWeightedRule.ServerWeight sw = new ResponseTimeWeightedRule.ServerWeight();//计算权重sw.maintainWeights();//jvm关闭时 通知定时任务 权重清空Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(new Runnable() {public void run() {ResponseTimeWeightedRule.logger.info("Stopping NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-{}", ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.name);ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.serverWeightTimer.cancel();}}));
}DynamicServerWeightTask 源码分析
DynamicServerWeightTask 是执行服务权重分配的任务类,该类的主要逻辑在于调用了 ServerWeight#maintainWeights 方法,我们重点关注该方法即可。
class DynamicServerWeightTask extends TimerTask {DynamicServerWeightTask() {}//定时任务的 run 方法public void run() {//创建一个服务权重ResponseTimeWeightedRule.ServerWeight serverWeight = ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.new ServerWeight();try {//调用权重计算方法 ServerWeight#maintainWeightsserverWeight.maintainWeights();} catch (Exception var3) {ResponseTimeWeightedRule.logger.error("Error running DynamicServerWeightTask for {}", ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.name, var3);}}
}ServerWeight#maintainWeights 方法源码分析
ServerWeight#maintainWeights 方法主要是用来维持服务权重的,主要逻辑如下:
- 获取负载均衡器,负载均衡器为空判断,如果负载均衡器为空,不予处理。
- 使用 CAS 设置当前服务是否正在进行权重分配中,设置成功继续执行业务逻辑,否则不予处理。
- 对负载均衡器统计数据为空判断,不为空继续执行业务逻辑,为空则不予处理。
- 循环遍历所有服务,得到总响应时间,总响应时间等于每个服务的平均响应时间求和。
- 循环服务列表,设置服务的权重,服务权重=总响应时间-服务的平均响应时间,这样服务的响应时间越长,其服务权重则越低。
public void maintainWeights() {//获取负载均衡器ILoadBalancer lb = ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.getLoadBalancer();//负载均衡器为空判断if (lb != null) {//负载均衡器不为空//使用 CAS 设置当前服务正在进行权重分配中if (ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {try {ResponseTimeWeightedRule.logger.info("Weight adjusting job started");//强转之后获取负载均衡器的统计数据AbstractLoadBalancer nlb = (AbstractLoadBalancer)lb;LoadBalancerStats stats = nlb.getLoadBalancerStats();//负载均衡器的统计数据为空判断if (stats != null) {//不为空 初始化响应时间double totalResponseTime = 0.0D;//服务统计数据ServerStats ss;//迭代遍历所有服务 总响应时间 totalResponseTime 等于每个服务的平均响应时间求和 totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg()for(Iterator var6 = nlb.getAllServers().iterator(); var6.hasNext(); totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg()) {//得到服务Server server = (Server)var6.next();//获取单个服务统计信息ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server);}//当前权重Double weightSoFar = 0.0D;//权重列表List<Double> finalWeights = new ArrayList();//获取所有服务Iterator var20 = nlb.getAllServers().iterator();//迭代遍历所有服务while(var20.hasNext()) {//获取服务Server serverx = (Server)var20.next();//获取服务的统计信息ServerStats ssx = stats.getSingleServerStat(serverx);//服务权重=总响应时间-服务的平均响应时间 这样服务的响应时间越长 其服务权重则越低double weight = totalResponseTime - ssx.getResponseTimeAvg();weightSoFar = weightSoFar + weight;//设置权重finalWeights.add(weightSoFar);}//设置权重列表ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.setWeights(finalWeights);return;}} catch (Exception var16) {ResponseTimeWeightedRule.logger.error("Error calculating server weights", var16);return;} finally {ResponseTimeWeightedRule.this.serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(false);}}}
}WeightedResponseTimeRule#choose 方法源码分析
WeightedResponseTimeRule#choose 方法是响应时间权重轮训负载均衡规则的实现,具体逻辑如下:
- ILoadBalancer 为空判断,如果 ILoadBalancer 为空,则直接返回服务为 null。
- ILoadBalancer 不为空,执行 while 循环获取 Server。
- 判断当前线程是否被中断,如果被中断,则直接返回 null。
- 获取所有的服务列表,如果服务为空,则直接返回 null。
- 找出最大的权重。
- 判断是否有进行权重初始化,如果没有进行权重初始化,则调用父类 RoundRobinRule 的随机算法得到 server,如果进行了权重初始化,则使用最大权重生成一个大于或等于 0.0 且小于 1.0 的随机浮点数,也就是权重,然后遍历权重列表,从权重列表中找到大于计算出来的权重的索引,根据得到的索引去服务列表中获取服务。
WeightedResponseTimeRule 响应时间权重轮训规则的实现方式就是使用定时任务去计算权重,定时任务中会判断服务的平均响应时间,平均响应时间越大,权重越小,在进行负载均衡时,会使用权重成一个随机数,然后循环服务列表,找到权重大于这个随机数服务。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule#choose
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {//负载均衡器为空判断if (lb == null) {//负载均衡器为空 直接返回 nullreturn null;} else {//定义 ServeriServer server = null;//while 循环while(server == null) {//获取服务权重集合List<Double> currentWeights = this.accumulatedWeights;//当前线程是否被中断if (Thread.interrupted()) {//当前线程被中断 直接返回 nullreturn null;}//获取所有服务列表List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();//服务列表的 size 也就是服务的个数int serverCount = allList.size();//服务个数为0 判断if (serverCount == 0) {//服务个数为0 直接返回 nullreturn null;}//服务索引int serverIndex = 0;//找出最大的权重double maxTotalWeight = currentWeights.size() == 0 ? 0.0D : (Double)currentWeights.get(currentWeights.size() - 1);//最大权重小于 0.001 且 服务数等于权重数 if (!(maxTotalWeight < 0.001D) && serverCount == currentWeights.size()) {//最大权重小于 0.001 且 服务数等于权重数 取非 表示采用权重轮训算法//返回一个大于或等于 0.0 且小于 1.0 的随机浮点数 也就是权重double randomWeight = this.random.nextDouble() * maxTotalWeight;int n = 0;//迭代遍历权重列表for(Iterator var13 = currentWeights.iterator(); var13.hasNext(); ++n) {Double d = (Double)var13.next();//权重列表中的权重大于计算出来的权重 也就找到了 server 索引下标if (d >= randomWeight) {serverIndex = n;break;}}//根据索引去服务列表中获取服务server = (Server)allList.get(serverIndex);} else {//表示没有初始化权重 使用父类 RoundRobinRule 的随机算法 得到serverserver = super.choose(this.getLoadBalancer(), key);//server 为空判断if (server == null) {//不为空直接返回serverreturn server;}}//server 为空判断if (server == null) {//server 为空 线程休眠Thread.yield();} else {//服务是否是活跃的if (server.isAlive()) {//是返回 server return server;}//否则给server 赋值为 nullserver = null;}}//server 不为空 直接返回serverreturn server;}
}RetryRule#choose 方法源码分析
RetryRule#choose 方法是重试负载均衡规则的实现,具体逻辑如下:
- 获取当前请求时间,计算出限制时间(允许请求的最大时间)。
- 使用轮训负载负载均衡规则获取一个服务。
- 如果获取到的服务不为空 || 服务不是活跃的 && 当前时间小于限制时间,则创建一个中断线程的任务,中断时间为 deadline - System.currentTimeMillis()。
- 开启 while 循环使用轮训的负载均衡规则获取服务,如果服务不为空是活跃的或者当前时间大于限制时间,则结束循环,返回 Server。
可以看出 RetryRule 实际调用的是轮询算法,在没有获取到服务时,会进行循环重试操作,超过设置的时间限制(默认为500 毫秒),则会退出。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.RetryRule#choose(com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer, java.lang.Object)
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {//获取当前请求时间long requestTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//限制时间(允许请求的最大时间)=当前时间+500毫秒 long maxRetryMillis = 500L;long deadline = requestTime + this.maxRetryMillis;//应答的 serverServer answer = null;//IRule subRule = new RoundRobinRule();//使用轮询算法获取一个服务answer = this.subRule.choose(key);if ((answer == null || !answer.isAlive()) && System.currentTimeMillis() < deadline) {//服务不为空//服务不是活跃的//当前时间小于限制时间//创建一个中断线程的任务 deadline - System.currentTimeMillis() 后打断线程InterruptTask task = new InterruptTask(deadline - System.currentTimeMillis());//开启 while 循环 只要当前线程没有被中断 就一直循环执行while(!Thread.interrupted()) {//使用轮询算法获取一个服务answer = this.subRule.choose(key);if (answer != null && answer.isAlive() || System.currentTimeMillis() >= deadline) {//服务不为空 && 服务是活跃的 || 当前时间已经大于限制时间 则退出 while 循环break;}//线程让出 cpu 资源Thread.yield();}//while 循环结束 清除任务task.cancel();}//返回服务return answer != null && answer.isAlive() ? answer : null;
}BestAvailableRule#choose 方法源码分析
BestAvailableRule 继承了ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule,主要逻辑如下:
- 判断负载均衡器统计信息是否为空,如果为空则调用父类的负载均衡算法,也就是轮询算法规则(ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule#choose)。
- 负载均衡器统计信息不为空,获取所有服务,判断当前时间服务断路器是否打开,短路打开不做处理,断路器如果没有打开,则判断并发连接数是否小于最小并发连接数,小于则完成赋值,返回 Server。
- 会遍历所有的服务提供者,选择并发量最小的那个服务,这个算法,可以将请求转发到压力最小的服务器,但是如果副本数太多,每次都要循环计算出最小并发,还是比较好资源的。
- 最后会再次对 Server 为空进行判断,如果 Server 为空则调用父类的负载均衡算法,也就是轮询算法规则(ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule#choose)。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.BestAvailableRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {//负载均衡器统计信息为空判断if (this.loadBalancerStats == null) {//如果统计信息为空 调用父类的负载均衡规则 也就是轮询算法规则 ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule#choosereturn super.choose(key);} else {//不为空 获取所有的 serverList<Server> serverList = this.getLoadBalancer().getAllServers();//最小并发连接数int minimalConcurrentConnections = 2147483647;//当前时间long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Server chosen = null;//迭代遍历 服务列表Iterator var7 = serverList.iterator();while(var7.hasNext()) {Server server = (Server)var7.next();//获取服务统计信息ServerStats serverStats = this.loadBalancerStats.getSingleServerStat(server);//服务断路器是否打开if (!serverStats.isCircuitBreakerTripped(currentTime)) {//服务断路器没有打开//获取并发连接数int concurrentConnections = serverStats.getActiveRequestsCount(currentTime);//判断并发连接数是否小于最小并发连接数if (concurrentConnections < minimalConcurrentConnections) {//小于 则把当前并发连接数赋值给 最小并发连接数minimalConcurrentConnections = concurrentConnections;//赋值 serverchosen = server;}}}//server 为 null 判断if (chosen == null) {//调用父类的负载均衡算法 其实就是轮询的算法 ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule#choosereturn super.choose(key);} else {return chosen;}}
}//com.netflix.loadbalancer.ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {//轮训规则为空判断if (this.roundRobinRule != null) {//轮训规则不为空 执行轮训规则算法return this.roundRobinRule.choose(key);} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("This class has not been initialized with the RoundRobinRule class");}
}
AvailabilityFilteringRule#choose 方法源码分析
可用性过滤规则 AvailabilityFilteringRule 继承自 PredicateBasedRule,它和其他规则不一样,它将服务委托给 AbstractServerPredicate 过滤掉一些连接失败且高并发的 Server。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.AvailabilityFilteringRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {int count = 0;//RoundRobinRule roundRobinRule = new RoundRobinRule();//循环使用轮训算法获取服务 最大循环10次for(Server server = this.roundRobinRule.choose(key); count++ <= 10; server = this.roundRobinRule.choose(key)) {//断言规则判断 sever 是否符合规则 符合规则返回 不符合规则重新选择if (this.predicate.apply(new PredicateKey(server))) {return server;}}//如果循环了10次还没有找到 server 就调用父类的方法 PredicateBasedRule#choosereturn super.choose(key);
}//com.netflix.loadbalancer.PredicateBasedRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {//获取负载均衡器ILoadBalancer lb = this.getLoadBalancer();//从断言中循环过滤后返回 serverOptional<Server> server = this.getPredicate().chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(lb.getAllServers(), key);//返回 serverreturn server.isPresent() ? (Server)server.get() : null;
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule 源码分析
ZoneAvoidanceRule 继承了 PredicateBasedRule 类,ZoneAvoidanceRule 的构造方法中传入了 ZoneAvoidancePredicate 和 AvailabilityPredicate,ZoneAvoidancePredicate 判断一个 Zone 的运行性能是否可用,剔除不可用的 Zone Server,AvailabilityPredicate 用于过滤掉连接数过多的 Server,该规则会先过滤,然后使用轮询算法,选出可用的服务,Ribbon 默认使用的也是这个负载均衡策略。
//com.netflix.loadbalancer.ZoneAvoidanceRule#ZoneAvoidanceRule
public ZoneAvoidanceRule() {//区域断言ZoneAvoidancePredicate zonePredicate = new ZoneAvoidancePredicate(this);//可用性断言AvailabilityPredicate availabilityPredicate = new AvailabilityPredicate(this);this.compositePredicate = this.createCompositePredicate(zonePredicate, availabilityPredicate);
}//com.netflix.loadbalancer.PredicateBasedRule#choose
public Server choose(Object key) {//获取负载均衡器ILoadBalancer lb = this.getLoadBalancer();//从断言中循环过滤后返回 serverOptional<Server> server = this.getPredicate().chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(lb.getAllServers(), key);//返回 serverreturn server.isPresent() ? (Server)server.get() : null;
}
如有不正确的地方请各位指出纠正。
相关文章:

Ribbon 源码分析【Ribbon 负载均衡】
前言 在 Spring Cloud 2020 版本以后,移除了对 Netflix 的依赖,也就移除了负载均衡器 Ribbon,Spring Cloud 官方推荐使用 Loadbalancer 替换 Ribbon,而在 LoadBalancer 之前 Spring Cloud 一直使用的是 Ribbon 来做负载[均衡器的…...

Python | Leetcode Python题解之第385题迷你语法分析器
题目: 题解: class Solution:def deserialize(self, s: str) -> NestedInteger:if s[0] ! [:return NestedInteger(int(s))stack, num, negative [], 0, Falsefor i, c in enumerate(s):if c -:negative Trueelif c.isdigit():num num * 10 int…...

进程间通信-进程池
目录 理解 完整代码 完善代码 回收子进程: 不回收子进程: 子进程使用重定向优化 理解 #include <iostream> #include <unistd.h> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <sys/types.h>void work(int rfd) {…...

【PYTHON 基础系列-request 模块介绍】
一、requests库简介 使用requests库能快速构建 HTTP 请求,而无需深入了解底层网络协议细节。其API设计直观,使得发送请求就像调用函数一样简单,同时提供了丰富的选项以满足复杂网络交互的需求。这种设计使得无论是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者…...

springboot 实现策略模式通过id进入不同的服务类service
在Spring Boot中实现策略模式,通常是将不同的算法封装在单独的类中,并使它们可以相互替换。这些类通常都实现同一个接口。在Spring Boot应用中,你可以通过Spring的依赖注入(DI)来管理这些策略类的实例,并通…...

AUC真的什么情形下都适合吗
AUC(Area Under the ROC Curve)是一个广泛使用的性能评价指标,它衡量了分类模型在不同阈值下区分正类和负类的能力。然而,在某些情况下,AUC可能不是最准确的评价指标,以下是几种可能的情况: 数据极度不均衡:在数据极度不均衡的情况下,即使模型只预测多数类,AUC也可能…...

Flutter基本组件Text使用
Text是一个文本显示控件,用于在应用程序界面中显示单行或多行文本内容。 Text简单Demo import package:flutter/material.dart;class MyTextDemo extends StatelessWidget {const MyTextDemo({super.key});overrideWidget build(BuildContext context) {return Sca…...

DDS基本原理--FPGA学习笔记
DDS信号发生器原理: timescale 1ns / 1ps // // Company: // Engineer: // // Create Date: 2024/09/04 15:20:30 // Design Name: hilary // Module Name: DDS_Module //module DDS_Module(Clk,Reset_n,Fword,Pword,Data);input Clk;input Reset_n;input [31:0]…...

有temp表包含A,B两列,使用SQL,对B列进行处理,形成C列,按A列顺序,B列值不变,则C列累计技术,B列值变化,则C列重新开始计数
有temp表,使用SQL,对B列进行处理,形成C列,按A列顺序,B列值不变,则C列累计技术,B列值变化,则C列重新开始计数 建表语句如下 CREATE TABLE temp(A STRING ,B STRING );INSERT INTO …...
【H2O2|全栈】关于HTML(6)HTML基础(五 · 完结篇)
HTML基础知识 目录 HTML基础知识 前言 准备工作 标签的具体分类(五) 本文中的标签在什么位置中使用? 表单(二) 下拉选择菜单 文本域 案例 拓展标签 iframe框架 案例 预告和回顾 后话 前言 本系列博客介…...

2024第三届大学生算法大赛 真题训练一 解题报告 | 珂学家
前言 题解 这是第三届大学生算法大赛(第二届为清华社杯)的赛前练习赛一. 这是上界比赛的体验报告: 2023第二届“清华社杯”大学生算法大赛 解题报告(流水账版) | 珂学家,个人还是非常推荐这个比赛。 难度分布:4 easy/4 mid-hard/2 hard 赛前练习赛一…...

IIS网站允许3D模型类型的文件
参与threejs项目的研发,本地开发完成后,发布后使用时发现模型文件不能正常获取资源,原因是IIS站点默认不支持模型类型。 一开始是通过直接在IIS网站管理中的类型添加来实现网站对类型的支持。 后来发现一段对于后端来说可以直接实现代码上添加…...

Linux 性能调优之CPU上下文切换
写在前面 博文内容为 Linux 性能指标 CPU 上下文切换认知内容涉及: 上下文认知,发生上下文切换的场景有哪些上下文指标信息查看,内核上下文切换事件跟踪,系统上下文切换统计上下文异常场景分析,CPU亲和性配置优化上下文…...

【无标题】符文价值的退化页
我们利用现有的符文体系建立了一个健全的符文扩展空间,可假若符文让我们感到十分困惑,我们不介意毁灭它们,让一切回到没有字迹的蛮荒纪。 如此,眼睛也失去了作用。我们的成GUO也会给后来者提供又是一DUI 令人眼花缭乱的无用符咒。…...

DFS 算法:洛谷B3625迷宫寻路
我的个人主页 {\large \mathsf{{\color{Red} 我的个人主页} } } 我的个人主页 往 {\color{Red} {\Huge 往} } 往 期 {\color{Green} {\Huge 期} } 期 文 {\color{Blue} {\Huge 文} } 文 章 {\color{Orange} {\Huge 章}} 章 DFS 算法:记忆化搜索DFS 算法…...

结构开发笔记(七):solidworks软件(六):装配摄像头、摄像头座以及螺丝,完成摄像头结构示意图
若该文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处 本文章博客地址:https://hpzwl.blog.csdn.net/article/details/141931518 长沙红胖子Qt(长沙创微智科)博文大全:开发技术集合(包含Qt实用技术、树莓派、三维、OpenCV…...

Android 15 新特性快速解读指南
核心要点 16K 页面大小支持目前作为开发人员选项提供,并非强制要求。 引入多项提升开发体验、多语言支持、多媒体功能、交互体验和隐私安全的更新。 重点关注前台服务限制、Window Insets 行为变化、AndroidManifest 文件限制等适配要求。 开发体验 ApplicationS…...
】机器人工具箱Link类函数参数说明)
【机器人工具箱Robotics Toolbox开发笔记(十九)】机器人工具箱Link类函数参数说明
机器人工具箱中的Link对象保存于机器人连杆相关的所有信息,如运动学参数、刚体惯性参数、电机和传动参数等。 与Link对象有关参数如表1所示。 表1 Link对象参数 参 数 意 义 参 数 意 义 A 连杆变换矩阵 islimit 测试关节是否超过软限制 RP RP关节类型 isrevo…...

排查SQL Server中的内存不足及其他疑难问题
文章目录 引言I DMV 资源信号灯资源信号灯 DMV sys.dm_exec_query_resource_semaphores( 确定查询执行内存的等待)查询性能计数器什么是内存授予?II DBCC MEMORYSTATUS 查询内存对象III DBCC 命令释放多个 SQL Server 内存缓存 - 临时度量值IV 等待资源池 %ls (%ld)中的内存…...
输送线相机拍照信号触发(博途PLC高速计数器中断立即输出应用)
博途PLC相关中断应用请参考下面文章链接: T法测速功能块 T法测速功能块(博途PLC上升沿中断应用)-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读165次。本文介绍了博途PLC中T法测速的原理和应用,包括如何开启上升沿中断、配置中断以及T法测速功能块的使用。重点讲述了在中断事件发生后执行的功能块处…...
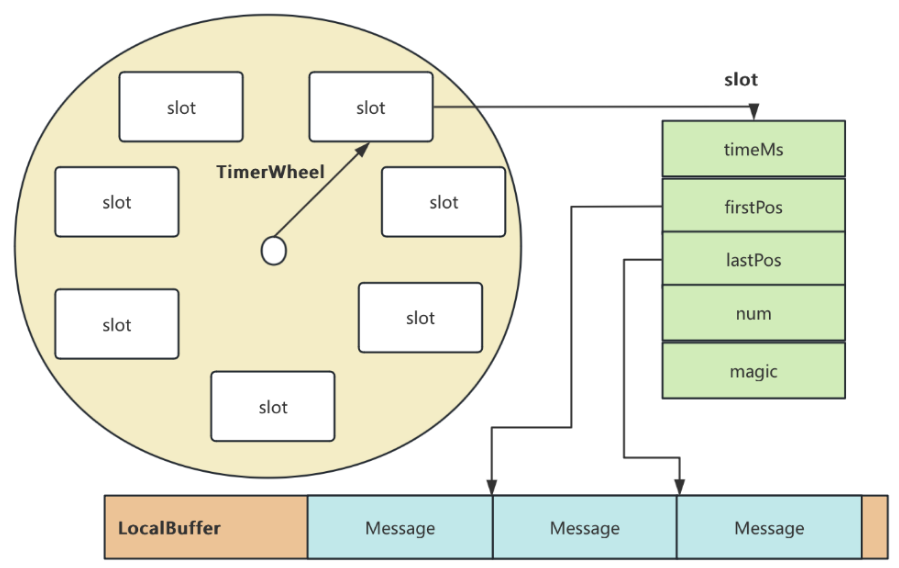
RocketMQ延迟消息机制
两种延迟消息 RocketMQ中提供了两种延迟消息机制 指定固定的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个MessageDelayLevel参数,对应18个预设的延迟级别指定时间点的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个DeliverTimeMS指定一个Long类型表示的具体时间点。到了时间点后…...

FastAPI 教程:从入门到实践
FastAPI 是一个现代、快速(高性能)的 Web 框架,用于构建 API,支持 Python 3.6。它基于标准 Python 类型提示,易于学习且功能强大。以下是一个完整的 FastAPI 入门教程,涵盖从环境搭建到创建并运行一个简单的…...

蓝桥杯 2024 15届国赛 A组 儿童节快乐
P10576 [蓝桥杯 2024 国 A] 儿童节快乐 题目描述 五彩斑斓的气球在蓝天下悠然飘荡,轻快的音乐在耳边持续回荡,小朋友们手牵着手一同畅快欢笑。在这样一片安乐祥和的氛围下,六一来了。 今天是六一儿童节,小蓝老师为了让大家在节…...

使用van-uploader 的UI组件,结合vue2如何实现图片上传组件的封装
以下是基于 vant-ui(适配 Vue2 版本 )实现截图中照片上传预览、删除功能,并封装成可复用组件的完整代码,包含样式和逻辑实现,可直接在 Vue2 项目中使用: 1. 封装的图片上传组件 ImageUploader.vue <te…...
新能源汽车智慧充电桩管理方案:新能源充电桩散热问题及消防安全监管方案
随着新能源汽车的快速普及,充电桩作为核心配套设施,其安全性与可靠性备受关注。然而,在高温、高负荷运行环境下,充电桩的散热问题与消防安全隐患日益凸显,成为制约行业发展的关键瓶颈。 如何通过智慧化管理手段优化散…...
项目部署到Linux上时遇到的错误(Redis,MySQL,无法正确连接,地址占用问题)
Redis无法正确连接 在运行jar包时出现了这样的错误 查询得知问题核心在于Redis连接失败,具体原因是客户端发送了密码认证请求,但Redis服务器未设置密码 1.为Redis设置密码(匹配客户端配置) 步骤: 1).修…...

稳定币的深度剖析与展望
一、引言 在当今数字化浪潮席卷全球的时代,加密货币作为一种新兴的金融现象,正以前所未有的速度改变着我们对传统货币和金融体系的认知。然而,加密货币市场的高度波动性却成为了其广泛应用和普及的一大障碍。在这样的背景下,稳定…...
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...

Fabric V2.5 通用溯源系统——增加图片上传与下载功能
fabric-trace项目在发布一年后,部署量已突破1000次,为支持更多场景,现新增支持图片信息上链,本文对图片上传、下载功能代码进行梳理,包含智能合约、后端、前端部分。 一、智能合约修改 为了增加图片信息上链溯源,需要对底层数据结构进行修改,在此对智能合约中的农产品数…...
