Springboot如何使用面向切面编程AOP?
Springboot如何使用面向切面编程AOP?
在 Spring Boot 中使用面向切面编程(AOP)非常简单,Spring Boot 提供了对 AOP 的自动配置支持。以下是详细的步骤和示例,帮助你快速上手 Spring Boot 中的 AOP。
1. 添加依赖
首先,在 pom.xml(Maven)或 build.gradle.kts(Gradle)中添加 Spring Boot Starter AOP 依赖:
Maven
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
Gradle-Kotlin build.gradle.kts
dependencies {implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop")
}
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop")
Gradle-Groovy build.gradle
dependencies {implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'
}
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'
2. 编写切面类
切面类是一个普通的 Spring Bean,使用 @Aspect 注解标记。切面类中定义了切点(Pointcut)和通知(Advice)。
示例:记录方法执行日志的切面
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect // 标记为切面类
@Component // 标记为 Spring Bean
public class LoggingAspect {// 定义切点:拦截 com.example.service 包下的所有方法@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")public void serviceMethods() {}// 前置通知:在目标方法执行前执行@Before("serviceMethods()")public void logBeforeMethod() {System.out.println("方法即将执行...");}
}
3. 定义目标服务类
编写一个普通的 Spring 服务类,作为 AOP 的目标对象。
示例:用户服务类
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {public void createUser(String name) {System.out.println("创建用户: " + name);}public void deleteUser(String name) {System.out.println("删除用户: " + name);}
}
4. 启用 AOP 支持
Spring Boot 默认会自动启用 AOP 支持,无需额外配置。如果需要手动启用,可以在主应用类上添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用 AOP 支持
public class MyApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);}
}
5. 运行并验证
启动 Spring Boot 应用,调用 UserService 的方法,观察切面是否生效。
示例:调用服务方法
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class AppRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {userService.createUser("Alice");userService.deleteUser("Bob");}
}
输出结果
方法即将执行...
创建用户: Alice
方法即将执行...
删除用户: Bob
6. 常用 AOP 注解
Spring AOP 提供了多种通知类型,以下是常用的注解:
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
@Before | 在目标方法执行前执行。 |
@After | 在目标方法执行后执行(无论是否抛出异常)。 |
@AfterReturning | 在目标方法成功返回后执行。 |
@AfterThrowing | 在目标方法抛出异常后执行。 |
@Around | 环绕通知,可以控制目标方法的执行(如修改参数、返回值或捕获异常)。 |
示例:环绕通知
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class TimingAspect {@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")public Object measureExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("方法执行时间: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");return result;}
}
7. 切点表达式
切点表达式用于定义拦截的目标方法。以下是常见的表达式示例:
| 表达式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..)) | 拦截 com.example.service 包下的所有方法。 |
execution(* com.example.service.UserService.*(..)) | 拦截 UserService 类中的所有方法。 |
execution(* com.example.service.*.create*(..)) | 拦截 com.example.service 包下以 create 开头的方法。 |
@annotation(com.example.LogExecutionTime) | 拦截带有 @LogExecutionTime 注解的方法。 |
自定义注解示例
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogExecutionTime {}
在方法上使用注解:
@Service
public class UserService {@LogExecutionTimepublic void createUser(String name) {System.out.println("创建用户: " + name);}
}
在切面中拦截注解:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogExecutionTimeAspect {@Around("@annotation(com.example.LogExecutionTime)")public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Object result = joinPoint.proceed();long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("方法执行时间: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");return result;}
}
8. 总结
- Spring Boot 通过
spring-boot-starter-aop提供了对 AOP 的自动支持。 - 使用
@Aspect定义切面类,结合@Before、@After、@Around等注解实现通知。 - 切点表达式(
execution)用于定义拦截的目标方法。 - 可以通过自定义注解实现更灵活的切面逻辑。
通过以上步骤,你可以在 Spring Boot 中轻松实现面向切面编程(AOP),增强代码的可维护性和可扩展性。
在Spring Boot中使用面向切面编程(AOP)通常涉及以下几个步骤:
1. 引入依赖
虽然Spring Boot的spring-boot-starter已经包含了AOP的依赖,但为了确保AOP功能被正确启用,你可以在pom.xml中显式添加spring-boot-starter-aop依赖(尽管这通常是可选的,因为spring-boot-starter-web等常用starter已经包含了它)。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 启用AOP
在Spring Boot中,你通常不需要显式启用AOP,因为@SpringBootApplication注解已经包含了@EnableAspectJAutoProxy,后者负责启用AOP代理。但是,如果你想要自定义AOP代理的行为(例如,使用CGLIB而不是JDK动态代理),你可以通过添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解并设置其属性来实现。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) // 使用CGLIB代理
public class MySpringBootApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApplication.class, args);}
}
然而,在大多数情况下,默认设置就足够了。
3. 定义切面类
切面类是一个用@Aspect注解标记的类,它包含了切点(pointcut)和通知(advice)。
- 切点:定义了哪些方法将被拦截。
- 通知:定义了拦截到方法时要执行的操作。
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {// 定义一个切点,匹配所有com.example.service包下的所有方法@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service..*(..))")public void myPointcut() {// 这是一个空方法,仅用于定义切点表达式}// 在方法执行之前执行@Before("myPointcut()")public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("Before method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());}// 在方法执行之后执行(无论是否抛出异常)@After("myPointcut()")public void afterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("After method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());}// 在方法执行之后执行(仅当方法正常返回时)@AfterReturning(pointcut = "myPointcut()", returning = "result")public void afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {System.out.println("After returning method: " + joinPoint.getSignature() + " with result: " + result);}// 在方法抛出异常时执行@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "myPointcut()", throwing = "exception")public void afterThrowingAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable exception) {System.out.println("After throwing method: " + joinPoint.getSignature() + " with exception: " + exception);}// 环绕通知,可以在方法执行前后自定义逻辑@Around("myPointcut()")public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {System.out.println("Before proceeding method: " + joinPoint.getSignature());Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法System.out.println("After proceeding method: " + joinPoint.getSignature() + " with result: " + result);return result;}
}
4. 应用切面
一旦你定义了切面类并将其作为Spring组件(通过@Component注解)注册到Spring容器中,Spring AOP将自动应用这些切面到匹配的bean上。
注意事项
- 切面类本身必须是一个Spring管理的bean,因此通常会在切面类上使用
@Component或其他相关的Spring注解。 - 切点表达式定义了哪些方法将被拦截。你可以使用AspectJ的切点表达式语言(Pointcut Expression Language, PEL)来编写复杂的切点表达式。
- 通知方法可以有参数,这些参数可以是
JoinPoint、ProceedingJoinPoint(对于环绕通知)或任何由切点表达式捕获的参数(通过@Args注解)。 - 环绕通知必须处理目标方法的调用(通过
ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed()),并且可以返回结果或抛出异常。
通过以上步骤,你就可以在Spring Boot项目中成功使用AOP来实现横切关注点(如日志记录、事务管理、权限校验等)的分离。
在 Spring Boot 中使用面向切面编程(AOP)可以帮助你分离横切关注点,如日志记录、事务管理等,从主要业务逻辑中分离出来。Spring AOP 是基于代理的实现,默认情况下支持方法级别的拦截。下面是如何在 Spring Boot 应用中配置和使用 AOP 的步骤:
1. 添加依赖
首先,确保你的 build.gradle 或 pom.xml 文件中包含了 spring-boot-starter-aop 依赖。
对于 Gradle,添加如下依赖到你的 build.gradle 文件:
dependencies {implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'
}
对于 Maven,在你的 pom.xml 文件中添加:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 启用 AOP 支持
Spring Boot 自动配置了 AOP 支持,所以通常不需要额外的手动配置。但是,如果你的应用有多个配置类,确保它们被正确扫描到。一般情况下,只需保证主应用程序类或配置类上包含 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解(尽管大多数情况下自动配置已经足够)。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AopConfig {
}
不过,如果你只是简单地使用 Spring Boot,并且没有特别复杂的配置需求,这个注解通常是不必要的,因为 Spring Boot 已经为你自动启用了 AOP 支持。
3. 创建一个切面
创建一个类并使用 @Aspect 注解标记它。然后,定义切入点(Pointcut)和通知(Advice),例如前置通知(@Before)、后置通知(@After)、返回通知(@AfterReturning)、异常通知(@AfterThrowing)和环绕通知(@Around)。
示例代码:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {@Before("execution(* com.example.demo.service.*.*(..))")public void beforeMethodExecution() {System.out.println("A method in the service layer is about to be called.");}
}
4. 定义切入点表达式
上述例子中的 "execution(* com.example.demo.service.*.*(..))" 是一个切入点表达式,表示匹配 com.example.demo.service 包下的所有类的所有方法。你可以根据需要调整此表达式来精确控制哪些方法会被拦截。
5. 测试你的切面
最后,编写一些测试用例或者运行你的应用来验证 AOP 切面是否按预期工作。确保目标方法被调用时,相应的通知也会被执行。
通过以上步骤,你应该能够在 Spring Boot 应用中成功配置并使用 AOP。这种方式不仅能够帮助你清晰地分离关注点,还能使代码更加简洁和易于维护。
在 Spring Boot 中使用面向切面编程(AOP)可以高效地实现日志记录、事务管理、权限校验等横切关注点。以下是 详细步骤和实际应用场景 的总结:
1. 添加依赖
Spring Boot 默认通过 spring-boot-starter-aop 提供对 AOP 的自动配置支持:
Maven
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
Gradle
dependencies {implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop")
}
2. 编写切面类
切面类需用 @Aspect 和 @Component 注解标记,定义切点和通知。
示例:日志记录切面
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {// 定义切点:拦截 service 包下的所有方法@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")public void serviceMethods() {}// 前置通知:方法执行前记录日志@Before("serviceMethods()")public void logMethodStart() {System.out.println("方法开始执行...");}// 后置通知:方法执行后记录日志(无论是否异常)@After("serviceMethods()")public void logMethodEnd() {System.out.println("方法执行结束。");}// 环绕通知:计算方法执行时间@Around("serviceMethods()")public Object measureTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("方法执行耗时: " + (end - start) + "ms");return result;}
}
3. 定义目标服务
编写一个普通的 Spring Bean 作为切面拦截的目标。
示例:用户服务
@Service
public class UserService {public void createUser(String name) {System.out.println("创建用户: " + name);}
}
4. 验证效果
调用 UserService 的方法时,切面逻辑自动生效:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);userService.createUser("Alice");}
}
输出结果
方法开始执行...
创建用户: Alice
方法执行结束。
方法执行耗时: 2ms
5. 核心注解详解
(1) 切点表达式(Pointcut)
- 语法:
execution(修饰符 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型)) - 常用示例:
execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..)):拦截service包下所有类的所有方法。execution(* com.example.service.UserService.create*(..)):拦截UserService中以create开头的方法。@annotation(com.example.LogTrack):拦截带有@LogTrack注解的方法。
(2) 通知类型(Advice)
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
@Before | 目标方法执行前触发。 |
@After | 目标方法执行后触发(无论是否抛出异常)。 |
@AfterReturning | 目标方法成功返回后触发(可获取返回值)。 |
@AfterThrowing | 目标方法抛出异常后触发(可捕获异常对象)。 |
@Around | 包裹目标方法,可控制方法执行、修改参数或返回值。 |
示例:获取方法参数和返回值
@Aspect
@Component
public class DataAspect {@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",returning = "result")public void logResult(Object result) {System.out.println("方法返回值: " + result);}@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..)) && args(name)")public void logArgument(String name) {System.out.println("方法参数: " + name);}
}
6. 高级用法
(1) 自定义注解实现切面
定义注解标记需要拦截的方法,提高代码可读性。
步骤1:定义注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogTrack {}
步骤2:在方法上使用注解
@Service
public class OrderService {@LogTrackpublic void placeOrder(String orderId) {System.out.println("下单成功: " + orderId);}
}
步骤3:切面拦截注解
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogTrackAspect {@Around("@annotation(com.example.LogTrack)")public Object trackMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {System.out.println("开始追踪方法...");Object result = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("追踪结束。");return result;}
}
(2) 处理异常
在 @AfterThrowing 中捕获并处理异常。
@Aspect
@Component
public class ExceptionAspect {@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",throwing = "ex")public void handleException(Exception ex) {System.out.println("捕获异常: " + ex.getMessage());// 发送报警邮件或记录日志}
}
7. 常见问题与解决
问题1:切面未生效
- 原因:
- 切面类未被 Spring 管理(缺少
@Component)。 - 切点表达式未匹配到目标方法。
- 目标方法未被 Spring 代理(如直接通过
new创建对象)。
- 切面类未被 Spring 管理(缺少
- 解决:
- 确保切面类添加了
@Component。 - 使用
@Autowired获取 Bean,而非直接实例化。
- 确保切面类添加了
问题2:环绕通知未调用 proceed()
- 现象:目标方法未执行。
- 解决:在
@Around方法中必须调用joinPoint.proceed()。
8. 实际应用场景
- 日志记录:自动记录方法入参、返回值、执行时间。
- 事务管理:结合
@Transactional实现声明式事务。 - 权限校验:在方法执行前检查用户权限。
- 性能监控:统计接口耗时,优化慢查询。
- 缓存管理:在方法执行前后操作缓存(如 Redis)。
总结
Spring Boot 通过简化配置和自动代理机制,使得 AOP 的实现非常便捷。核心步骤:
- 添加
spring-boot-starter-aop依赖。 - 使用
@Aspect和@Component定义切面类。 - 通过切点表达式精准定位目标方法。
- 选择合适的通知类型(
@Before、@Around等)实现横切逻辑。
掌握 AOP 后,可以大幅减少重复代码,提升系统的可维护性和扩展性。
相关文章:

Springboot如何使用面向切面编程AOP?
Springboot如何使用面向切面编程AOP? 在 Spring Boot 中使用面向切面编程(AOP)非常简单,Spring Boot 提供了对 AOP 的自动配置支持。以下是详细的步骤和示例,帮助你快速上手 Spring Boot 中的 AOP。 1. 添加依赖 首先ÿ…...
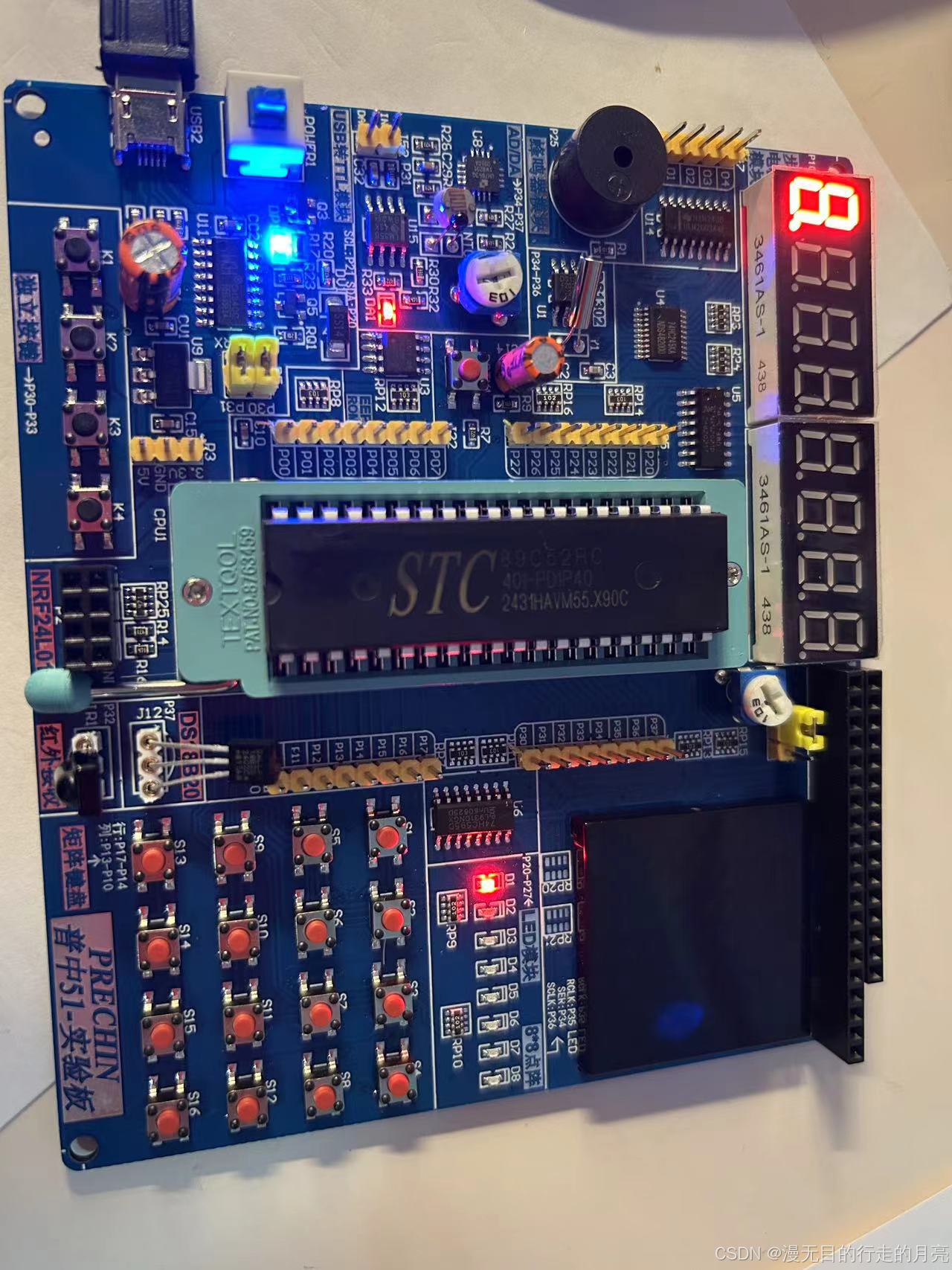
51单片机(STC89C52)开发:点亮一个小灯
软件安装: 安装开发板CH340驱动。 安装KEILC51开发软件:C51V901.exe。 下载软件:PZ-ISP.exe 创建项目: 新建main.c 将main.c加入至项目中: main.c:点亮一个小灯 #include "reg52.h"sbit LED1P2^0; //P2的…...
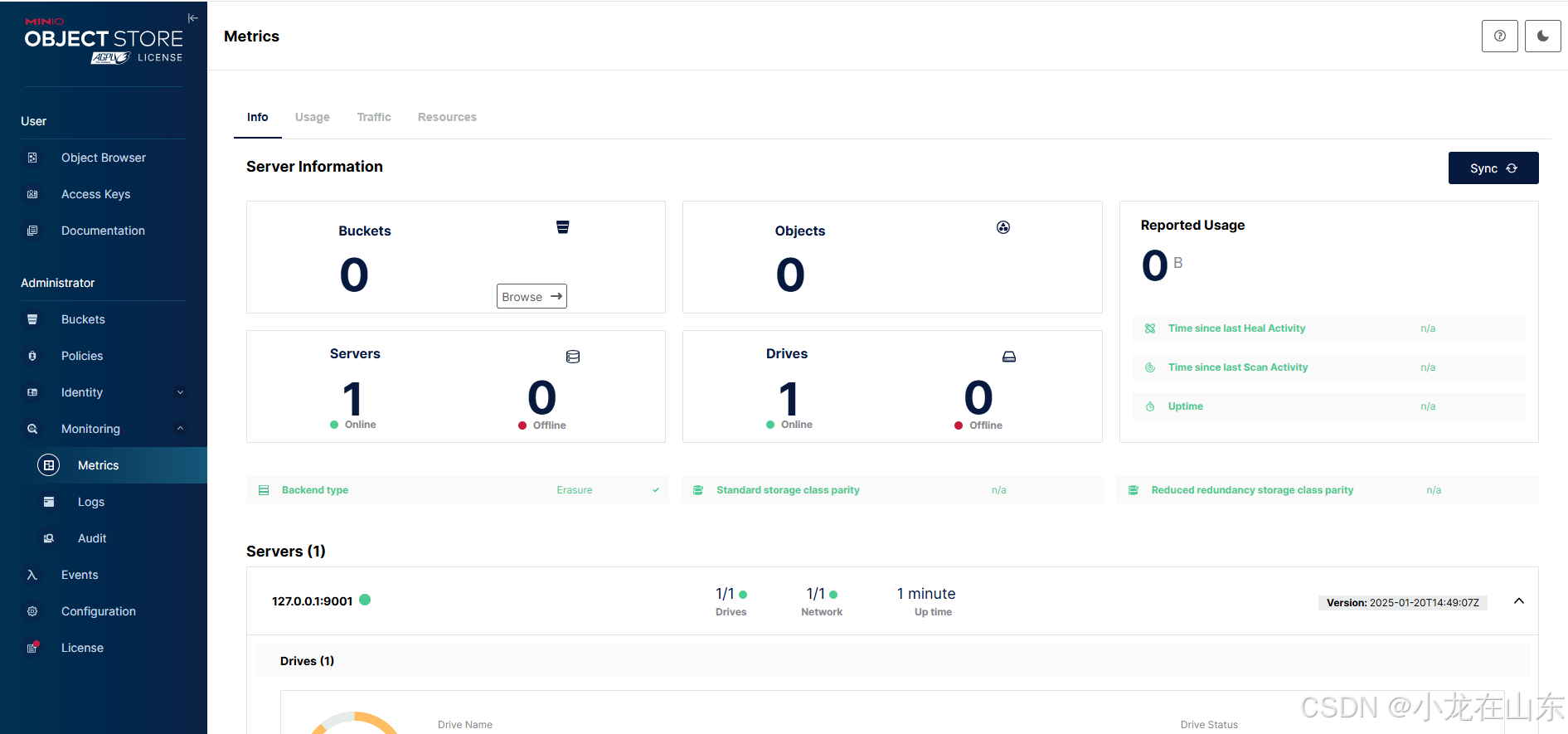
基于MinIO的对象存储增删改查
MinIO是一个高性能的分布式对象存储服务。Python的minio库可操作MinIO,包括创建/列出存储桶、上传/下载/删除文件及列出文件。 查看帮助信息 minio.exe --help minio.exe server --help …...
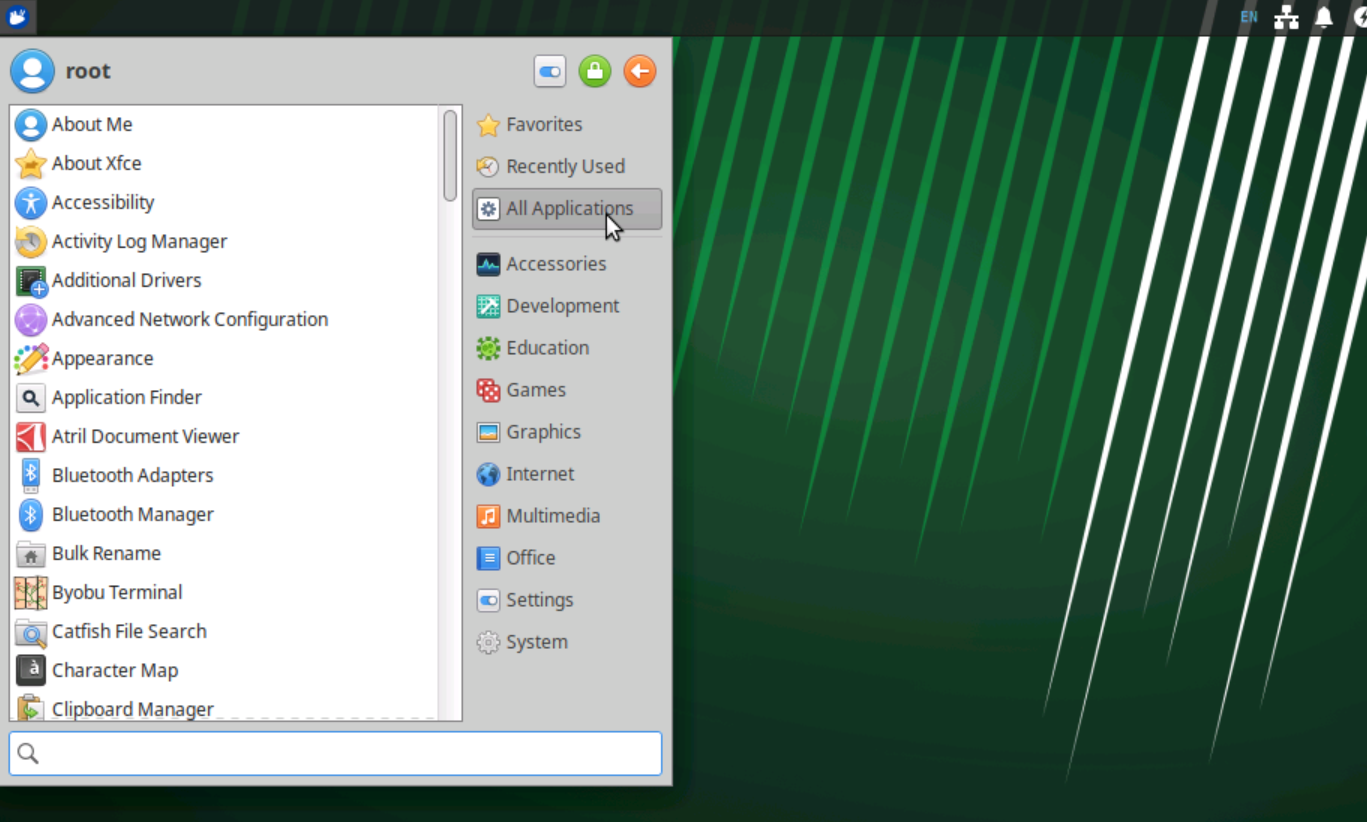
Ubuntu Server 安装 XFCE4桌面
Ubuntu Server没有桌面环境,一些软件有桌面环境使用起来才更加方便,所以我尝试安装桌面环境。常用的桌面环境有:GNOME、KDE Plasma、XFCE4等。这里我选择安装XFCE4桌面环境,主要因为它是一个极轻量级的桌面环境,适合内…...

MySQL 存储函数:数据库的自定义函数
在数据库开发中,存储函数(Stored Function)是一种非常有用的工具。它允许我们创建自定义的函数,这些函数可以在 SQL 查询中像内置函数一样使用,用于实现特定的逻辑和计算。本文将深入探讨 MySQL 存储函数的概念、与存储…...
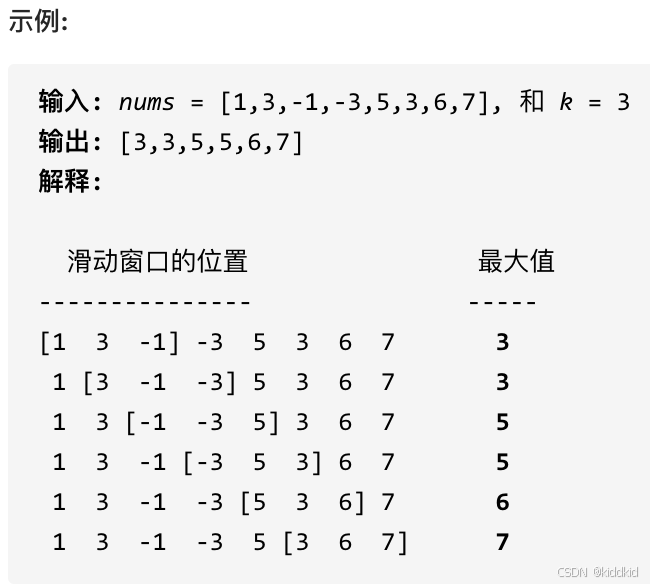
代码随想录_栈与队列
栈与队列 232.用栈实现队列 232. 用栈实现队列 使用栈实现队列的下列操作: push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。 pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。 peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。 empty() – 返回队列是否为空。 思路: 定义两个栈: 入队栈, 出队栈, 控制出入…...

【微服务与分布式实践】探索 Sentinel
参数设置 熔断时长 、最小请求数、最大RT ms、比例阈值、异常数 熔断策略 慢调⽤⽐例 当单位统计时⻓内请求数⽬⼤于设置的最⼩请求数⽬,并且慢调⽤的⽐例⼤于阈值,则接下来的熔断时⻓内请求会⾃动被熔断 异常⽐例 当单位统计时⻓内请求数⽬⼤于设置…...
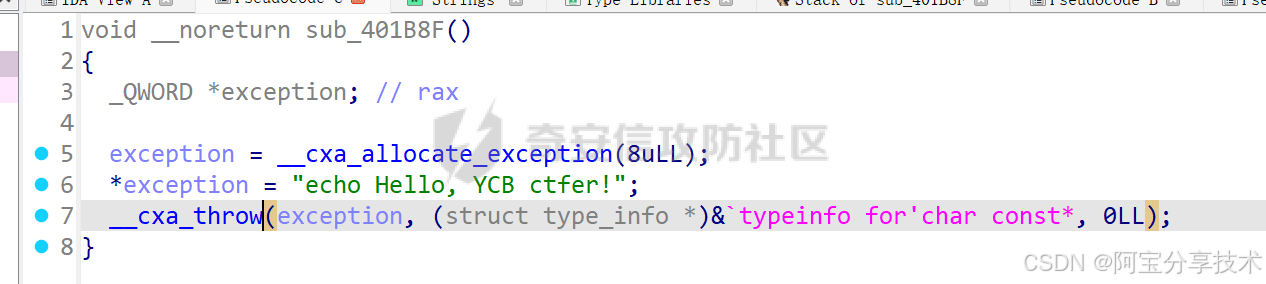
深入研究异常处理机制
一、原理探究 C异常处理 本节内容针对 Linux 下的 C 异常处理机制,重点在于研究如何在异常处理流程中利用溢出漏洞,所以不对异常处理及 unwind 的过程做详细分析,只做简单介绍 异常机制中主要的三个关键字:throw 抛出异常&#x…...

【memgpt】letta 课程4:基于latta框架构建MemGpt代理并与之交互
Lab 3: Building Agents with memory 基于latta框架构建MemGpt代理并与之交互理解代理状态,例如作为系统提示符、工具和agent的内存查看和编辑代理存档内存MemGPT 代理是有状态的 agents的设计思路 每个步骤都要定义代理行为 Letta agents persist information over time and…...
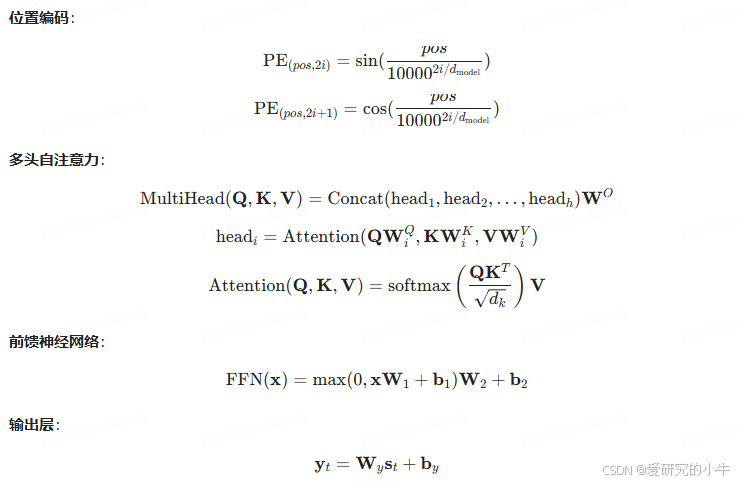
讯飞智作 AI 配音技术浅析(二):深度学习与神经网络
讯飞智作 AI 配音技术依赖于深度学习与神经网络,特别是 Tacotron、WaveNet 和 Transformer-TTS 模型。这些模型通过复杂的神经网络架构和数学公式,实现了从文本到自然语音的高效转换。 一、Tacotron 模型 Tacotron 是一种端到端的语音合成模型ÿ…...
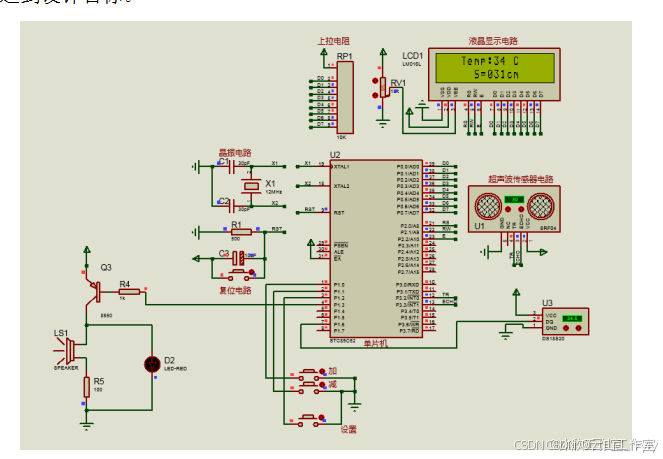
基于单片机的超声波液位检测系统(论文+源码)
1总体设计 本课题为基于单片机的超声波液位检测系统的设计,系统的结构框图如图2.1所示。其中包括了按键模块,温度检测模块,超声波液位检测模块,显示模块,蜂鸣器等器件设备。其中,采用STC89C52单片机作为主控…...

Autogen_core: test_code_executor.py
目录 代码代码解释 代码 import textwrapimport pytest from autogen_core.code_executor import (Alias,FunctionWithRequirements,FunctionWithRequirementsStr,ImportFromModule, ) from autogen_core.code_executor._func_with_reqs import build_python_functions_file f…...

从0开始使用面对对象C语言搭建一个基于OLED的图形显示框架
目录 前言 环境介绍 代码与动机 架构设计,优缺点 博客系列指引 前言 笔者前段时间花费了一周,整理了一下自从TM1637开始打算的,使用OLED来搭建一个通用的显示库的一个工程。笔者的OLED库已经开源到Github上了,地址在…...
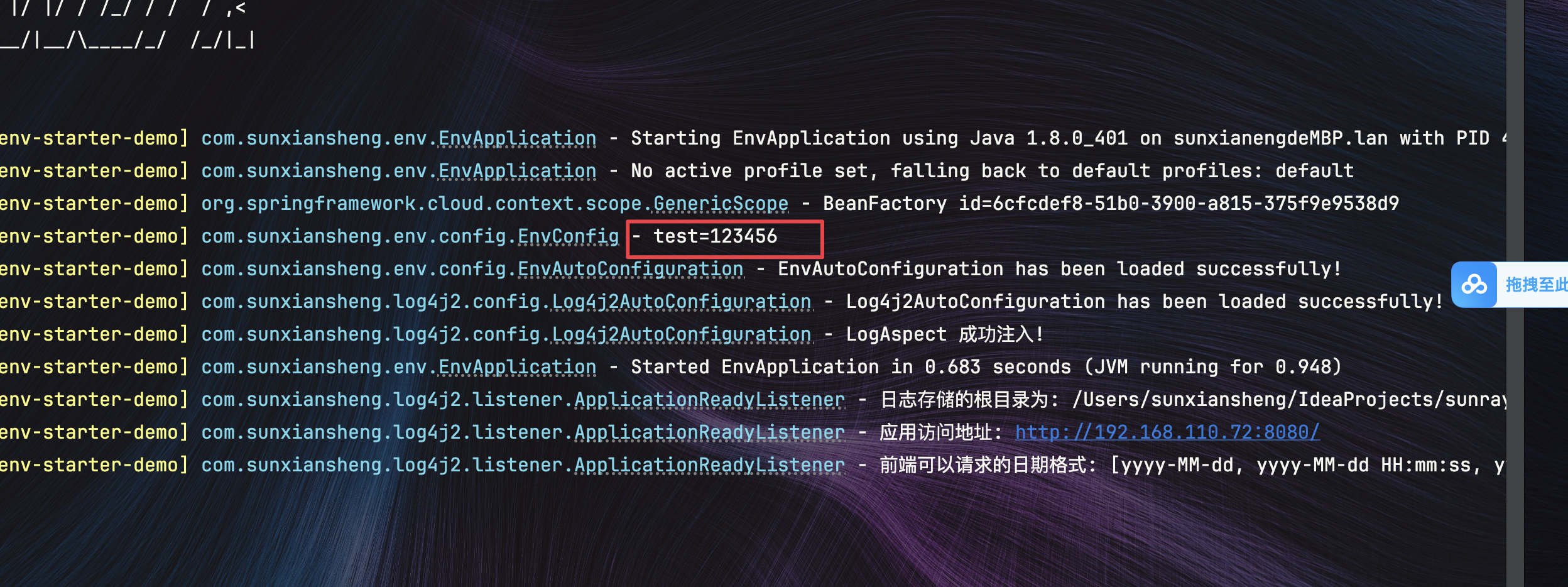
Java实现.env文件读取敏感数据
文章目录 1.common-env-starter模块1.目录结构2.DotenvEnvironmentPostProcessor.java 在${xxx}解析之前执行,提前读取配置3.EnvProperties.java 这里的path只是为了代码提示4.EnvAutoConfiguration.java Env模块自动配置类5.spring.factories 自动配置和注册Enviro…...

Go反射指南
概念: 官方对此有个非常简明的介绍,两句话耐人寻味: 反射提供一种让程序检查自身结构的能力反射是困惑的源泉 第1条,再精确点的描述是“反射是一种检查interface变量的底层类型和值的机制”。 第2条,很有喜感的自嘲…...
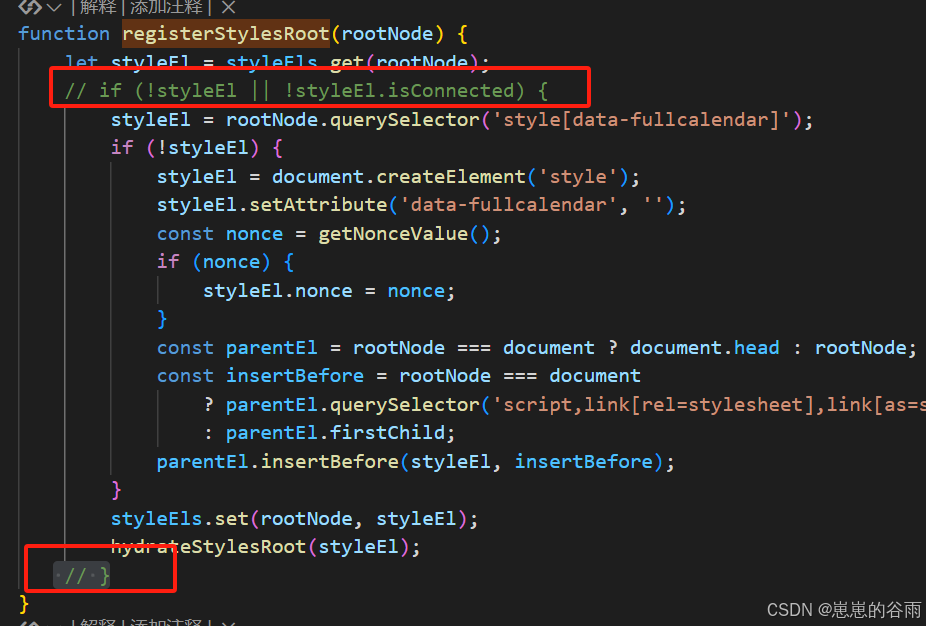
Fullcalendar @fullcalendar/react 样式错乱丢失问题和导致页面卡顿崩溃问题
问题描述: 我使用 fullcalendar的react版本时,出现了一个诡异的问题,当我切换到 一个iframe页面时(整个页面是一个iframe嵌入的),再切换回来日历的样式丢失了!不仅丢失了样式还导致页面崩溃了&…...
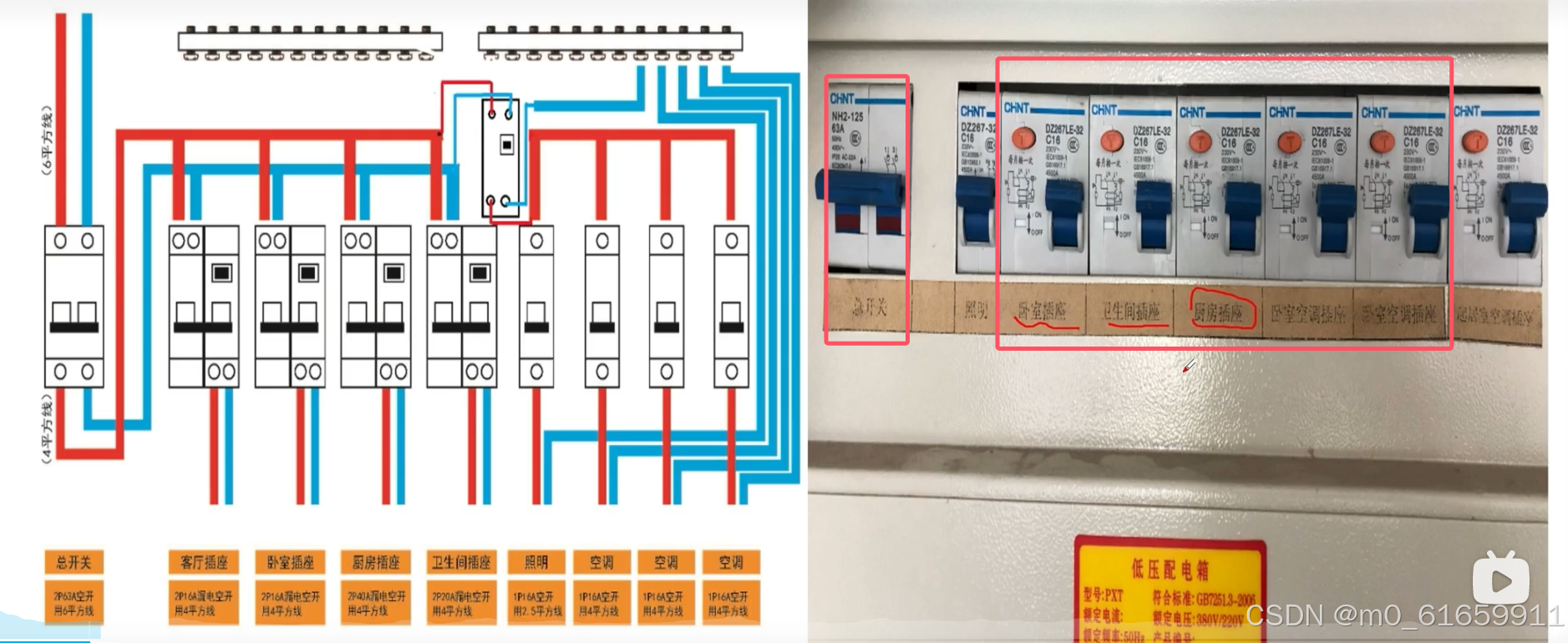
【电工基础】4.低压电器元件,漏电保护器,熔断器,中间继电器
一。漏电保护器 1.使用区域 我们在家用总开关上使用空气开关(断路器),其余的厨房卧室为漏电保护器。 2.漏电保护器的简介 1.漏电:就是流入的电流和流出的电流不等,意味着电路回路中还有其它分支,可能是电流通过人体进…...
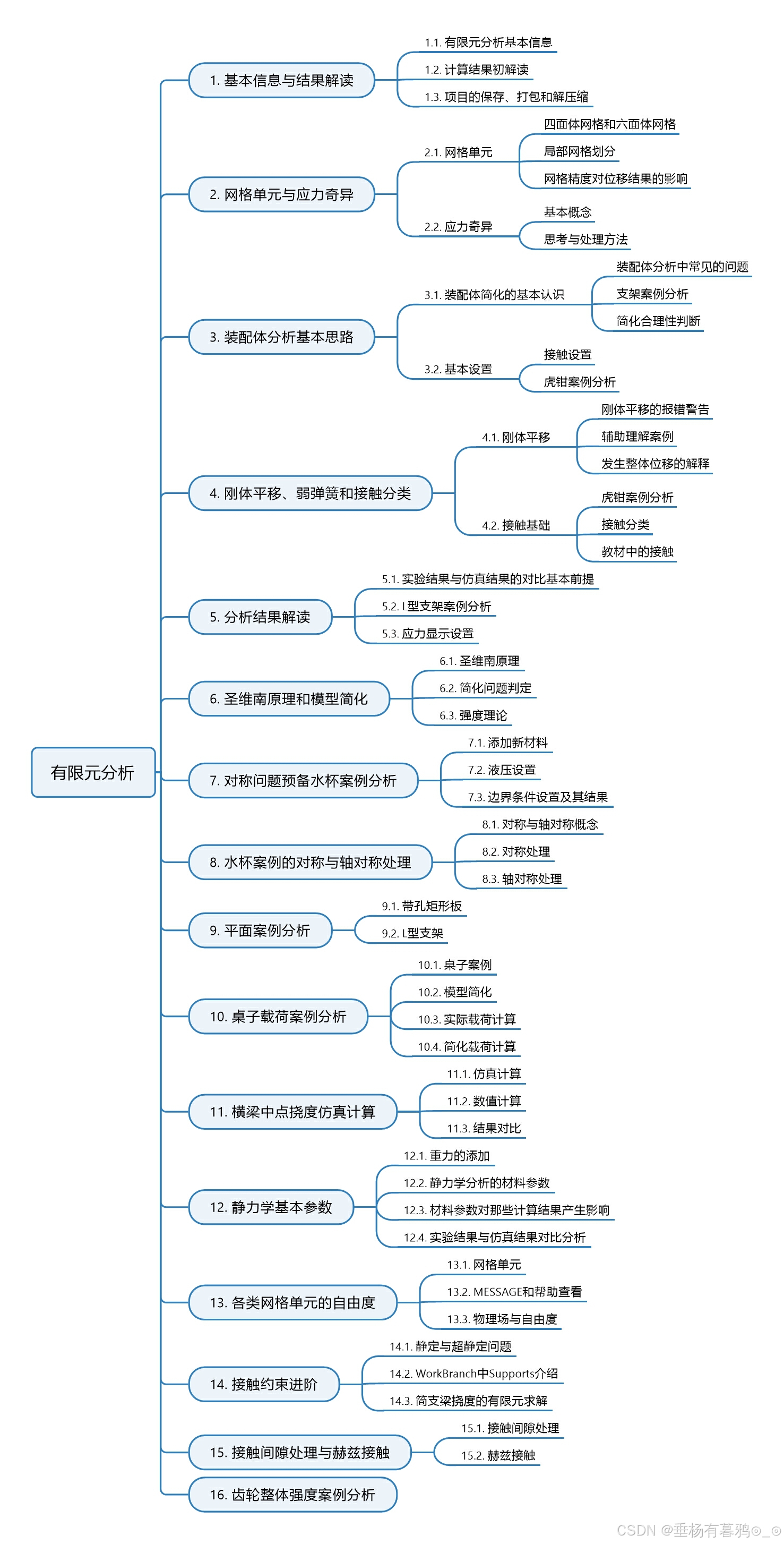
有限元分析学习——Anasys Workbanch第一阶段笔记梳理
第一阶段笔记主要源自于哔哩哔哩《ANSYS-workbench 有限元分析应用基础教程》 张晔 主要内容导图: 笔记导航如下: Anasys Workbanch第一阶段笔记(1)基本信息与结果解读_有限元分析变形比例-CSDN博客 Anasys Workbanch第一阶段笔记(2)网格单元与应力奇…...
C++中常用的十大排序方法之1——冒泡排序
成长路上不孤单😊😊😊😊😊😊 【😊///计算机爱好者😊///持续分享所学😊///如有需要欢迎收藏转发///😊】 今日分享关于C中常用的排序方法之——冒泡排序的相关…...
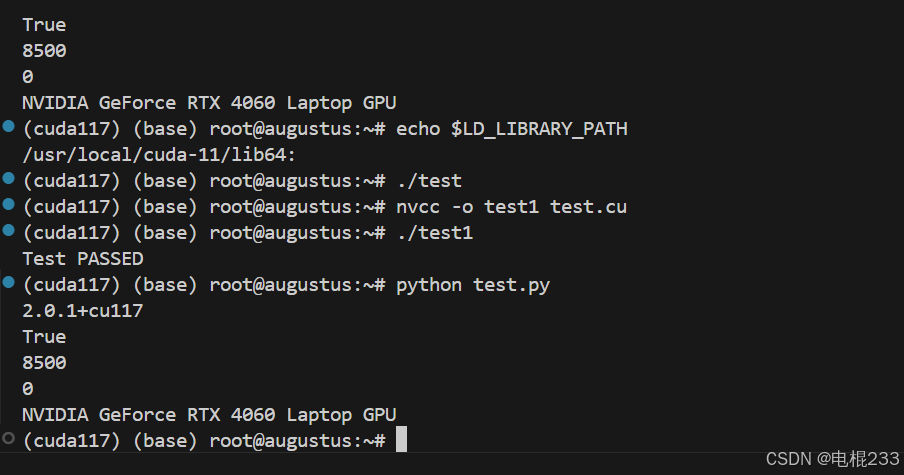
vscode+WSL2(ubuntu22.04)+pytorch+conda+cuda+cudnn安装系列
最近在家过年闲的没事,于是研究起深度学习开发工具链的配置和安装,之前欲与天公试比高,尝试在win上用vscodecuda11.6vs2019的cl编译器搭建cuda c编程环境,最后惨败,沦为笑柄,痛定思痛,这次直接和…...

wan2.1-vae中小企业AI基建:以wan2.1-vae为起点构建企业级AIGC能力中台
wan2.1-vae中小企业AI基建:以wan2.1-vae为起点构建企业级AIGC能力中台 1. 平台介绍与核心价值 wan2.1-vae是基于Qwen-Image-2512模型的AI图像生成平台,专为企业级AIGC应用设计。这个平台最突出的特点是能够通过简单的文字描述,快速生成高质…...

PostgreSQL新手必看:从零开始配置远程连接与pgAdmin图形化管理
PostgreSQL远程连接与pgAdmin图形化管理实战指南 1. 为什么需要远程连接PostgreSQL? PostgreSQL默认配置仅允许本地连接,这在实际开发和生产环境中显然不够用。想象一下,你的数据库服务器部署在云端或内网,而开发团队分布在各地…...

成为MWC26焦点,华为Atlas超节点凭什么重塑智算产业格局?
2026年,Agentic AI(AI智能体)正从技术探索加速迈向规模化落地。来自分析机构IDC的报告显示,未来五年,全球AI智能体生态将经历一场指数级的扩张,到2030年,超过22亿个AI智能体将作为“新数字劳动力…...

使用实时云渲染LarkXR顺利搭建云VR方案
Paraverse平行云自研的实时云渲染产品LarkXR,是行业内应用最广泛的企业级云渲染PaaS服务平台,具备的“云-网-端-PaaS平台“属性,支持私有化/公有云部署,支持全终端覆盖。 平行云秉持开发者友好的理念,多年来持续运营开…...

百考通AI文献综述:让研究起点更清晰
在学术研究的起步阶段,文献综述始终是奠定研究基础、厘清研究脉络的核心环节。它不仅需要广泛检索国内外文献,更要系统梳理研究进展、提炼核心观点、指出研究空白,对文献积累不足、时间精力有限的学子而言,常常陷入“文献难找、梳…...

Claude code学习记录
Claude代码学习过程记录技术文章大纲 参考文献:Claude Code首次使用指南:十分钟创建完整项目 | 果叔AI世界 学习准备阶段 下载git bush,提供类似linux的命令行环境,git安装路径:Git - Install 1.安装Node.js 访问官…...
最终版)
sql函数总结(成绩在于平时,成功在于积累)最终版
1、有时间了总结一下,下面每个函数的应用,每个函数的应用可以举一反三。 1.1、datediff(只支持天)与timestampdiff(支持任何单位) 1.2、curdate,curtime,date(提取年月日…...

微积分不再可怕:用动画打开数学新世界
微积分不再可怕:用动画打开数学新世界 【免费下载链接】videos 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/GitHub_Trending/vi/videos 微积分作为高等数学的核心内容,常常让初学者望而生畏。但通过GitHub推荐项目精选中的vi/videos项目,你将发现…...

Nano-Banana软萌拆拆屋效果展示:旗袍盘扣/滚边/开衩部位精细化呈现
Nano-Banana软萌拆拆屋效果展示:旗袍盘扣/滚边/开衩部位精细化呈现 1. 引言:当AI遇见传统美学 想象一下,一件精美的旗袍,它的盘扣、滚边、开衩,这些凝聚了匠心的细节,如果能像乐高积木一样被“拆开”&…...

Cogito 3B真实输出:从模糊业务需求到数据库ER图+SQL Schema+API设计
Cogito 3B真实输出:从模糊业务需求到数据库ER图SQL SchemaAPI设计 1. 快速了解Cogito 3B模型 Cogito v1预览版是Deep Cogito推出的混合推理模型,这个3B参数的模型在大多数标准测试中都表现出色,超越了同等规模的其他开源模型。简单来说&…...
