Linux驱动开发——高级I/O操作(一)
一个设备除了能通过读写操作来收发数据或返回、保存数据,还应该有很多其他的操作。比如一个串口设备还应该具备波特率获取和设置、帧格式获取和设置的操作;一个LED设备甚至不应该有读写操作,而应该具备点灯和灭灯的操作。硬件设备是如此众多,各种操作也纷繁复杂,所以内核将读写之外的其他I/O操作都委派给了另外一个函数接口:ioctl。而且,文件I/O还具备多种模型,比如非阻塞、阻塞、I/O多路复用,异步I/O和异步通知。接下来要学习如何在驱动中实现这些高级I/O操作,还简要介绍了 proc接口操作的实现。
ioctl设备操作
为了处理设备非数据的操作(这些可以通过read、write 接口来实现),内核将对设备的控制操作委派给了ioctl 接口,ioctl 也是一个系统调用,其函数原型如下。
int ioctl(int d, int request, ...);
d是要操作文件的文件描述符,request是代表不同操作的数字值,比如驱动可以规定0x12345678 表示点灯,而0x12345679表示灭灯等。但是这个操作码,更确切地说是命令,应该具有一定的编码规则,这个我们在后面会介绍。…是C语言中实参个数可变的函数原型声明形式,但在这里表示的是第三个参数可有可无。比如对于刚才的 LED例子,第三个参数可以用于指定将哪个LED点亮或熄灭,0表示LEDO,1表示LED1等。因为第三个形参是unsigned long类型的,所以除了可以传递数字值,还可以传递一个指针,这样就可以和内核空间交互任意多个字节的数据。
查看前面的file_operations结构的定义,和ioctl系统调用对应的驱动接口函数是 unlocked_ioctl和compat_ioctl,compat ioctl是为了处理32位程序和64位内核兼容的一个函数接口,和体系结构相关。unlocked ioctl的函数原型如下。
long (*unlocked ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
第一个参数表示打开的文件的file 结构指针,第二个参数和系统调用的第二个参数 request对应,第三个参数对应系统调用函数的第三个参数。
还要说明的是,在之前的内核版本中,同ioctl系统调用的驱动接口也是ioctl,但是最近的内核废除了该接口。因为之前的ioctl接口在调用之前要获得大内核锁(BLK,一种全局的粗粒度锁),如果ioctl的执行时间过长,则会导致内核其他也需要大内核锁的代码需要延迟很长时间,严重降低了效率(关于锁的机制,后面会仔细学习)。
之前说到用于ioctl的命令需要遵从一种编码规则,那么这个编码规则是怎样的呢?在当前的内核源码版本中,命令按照以下方式组成。
比特位 含义
31-30 00-命令不带参数
10-命令需要从驱动中获取数据,读方向01-命令需要把数据写入驱动,写方向
11-命令既要写入数据又要获取数据,读写双向
29-16 如果命令带参数,则指定参数所占用的内存空间大小
15-8 每个驱动全局唯一的幻数(魔数)
7-0 命令码
上述内容摘自内核文档“Documentation/ioctl/ioctl-decoding.ixt”。也就是说,一个白令由四部分组成,每部分有规定的意义和位宽限制。之所以这样定义命令,而不是简地用0,1,2,…来定义命令,是为了避免命令定义的重复,从而导致应用程序误操作。把一个命令发送给本不应该执行它的驱动程序,而驱动程序又错误地执行了这个命令采用这种机制,使得驱动有机会来检查这个命令是否属于驱动,从一定程度上避免了这种问题的发生。理想的要求是比特义幻数在一种体系结构下是全局唯一的,但很显然,这很难做到。尽管如此,我们还是应该遵从内核所规定的这种命令定义形式。
内核提供了一组宏来定义、提取命令中的字段信息,代码如下。
#define __IOC(dir,type,nr,size)\
(((dir) << __IOC_DIRSHIFT) | \
((type) << __IOC_TYPESHIfT) | \
((nr) << __IOC_NRSHIFT) | \
((size) << __IOC_SIZESHIFT))
#ifndef __KERNEL__
#define _IOC_TYPECHECK(t) (sizeof(t))
#endif
#define _IO(type,nr) IOC( IOC NONE,(type),(nr),0)
#define _IOR(type,nr,size) IOC(_I0C_READ, (type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOW(type,nr,size) IOC(_IOC_WRITE, (type),(nr),(_IOC_TYpEcHECK(size)))
#define _IOWR(type,nr,size) IOC(_IOC_READI_IOC_WRITE, (type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))#define _Ioc DIR(nr) (((nr)>> _IOC_DIRSHIFT) & _IOC_DIRMASK)
#define _IOC_TYPE(nr) (((nr) >>_IOC_TYPESHIFT) & _IOC_TYPEMASK)
#define _IOC_NR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_NRSHIFT) & _IOC_NRMASK)
#define _IOC_SIZE(nr) (((nr)>> _IOC_SIZESHIFT)& _IOC_SIZEMASK) 定义命令所使用的最底层的宏是_IOC,它将4个部分通过移位合并在一起。假如要定义一个设置串口帧格式的命令,那么按照前面的规则,这个命令要带参数,并且是将数据写入到驱动,则最高两个比特是01。如果要写入的参数是一个struct option的结构,而结构占 12个字节,那么比特29到比特 16的10进制值应该是12。如果定义幻数为字母s,命令码为2,最终就应使用_IOC(1,'s',0,12)来定义该命令。不过内核还提供了更方便的宏,刚才那个命令可以通过_IOW('s’,2,struct option)来定义。另外还有4个宏_IOC_DIR、_IOC_TYPE、_IOC_NR和_IOC_SIZE来分别提取命令中的4个部分。
在实现unlocked_ioctl 接口函数之前,我们还要来看看ioctl系统调用的过程。相关代码如下。
/** linux/fs/ioctl.c** Copyright (C) 1991, 1992 Linus Torvalds*/#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/security.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/writeback.h>
#include <linux/buffer_head.h>
#include <linux/falloc.h>#include <asm/ioctls.h>/* So that the fiemap access checks can't overflow on 32 bit machines. */
#define FIEMAP_MAX_EXTENTS (UINT_MAX / sizeof(struct fiemap_extent))/*** vfs_ioctl - call filesystem specific ioctl methods* @filp: open file to invoke ioctl method on* @cmd: ioctl command to execute* @arg: command-specific argument for ioctl** Invokes filesystem specific ->unlocked_ioctl, if one exists; otherwise* returns -ENOTTY.** Returns 0 on success, -errno on error.*/
static long vfs_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{int error = -ENOTTY;if (!filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl)goto out;error = filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);if (error == -ENOIOCTLCMD)error = -ENOTTY;out:return error;
}static int ioctl_fibmap(struct file *filp, int __user *p)
{struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;int res, block;/* do we support this mess? */if (!mapping->a_ops->bmap)return -EINVAL;if (!capable(CAP_SYS_RAWIO))return -EPERM;res = get_user(block, p);if (res)return res;res = mapping->a_ops->bmap(mapping, block);return put_user(res, p);
}/*** fiemap_fill_next_extent - Fiemap helper function* @fieinfo: Fiemap context passed into ->fiemap* @logical: Extent logical start offset, in bytes* @phys: Extent physical start offset, in bytes* @len: Extent length, in bytes* @flags: FIEMAP_EXTENT flags that describe this extent** Called from file system ->fiemap callback. Will populate extent* info as passed in via arguments and copy to user memory. On* success, extent count on fieinfo is incremented.** Returns 0 on success, -errno on error, 1 if this was the last* extent that will fit in user array.*/
#define SET_UNKNOWN_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DELALLOC)
#define SET_NO_UNMOUNTED_IO_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_ENCRYPTED)
#define SET_NOT_ALIGNED_FLAGS (FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_TAIL|FIEMAP_EXTENT_DATA_INLINE)
int fiemap_fill_next_extent(struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u64 logical,u64 phys, u64 len, u32 flags)
{struct fiemap_extent extent;struct fiemap_extent __user *dest = fieinfo->fi_extents_start;/* only count the extents */if (fieinfo->fi_extents_max == 0) {fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped++;return (flags & FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST) ? 1 : 0;}if (fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped >= fieinfo->fi_extents_max)return 1;if (flags & SET_UNKNOWN_FLAGS)flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_UNKNOWN;if (flags & SET_NO_UNMOUNTED_IO_FLAGS)flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_ENCODED;if (flags & SET_NOT_ALIGNED_FLAGS)flags |= FIEMAP_EXTENT_NOT_ALIGNED;memset(&extent, 0, sizeof(extent));extent.fe_logical = logical;extent.fe_physical = phys;extent.fe_length = len;extent.fe_flags = flags;dest += fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped;if (copy_to_user(dest, &extent, sizeof(extent)))return -EFAULT;fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped++;if (fieinfo->fi_extents_mapped == fieinfo->fi_extents_max)return 1;return (flags & FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST) ? 1 : 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(fiemap_fill_next_extent);/*** fiemap_check_flags - check validity of requested flags for fiemap* @fieinfo: Fiemap context passed into ->fiemap* @fs_flags: Set of fiemap flags that the file system understands** Called from file system ->fiemap callback. This will compute the* intersection of valid fiemap flags and those that the fs supports. That* value is then compared against the user supplied flags. In case of bad user* flags, the invalid values will be written into the fieinfo structure, and* -EBADR is returned, which tells ioctl_fiemap() to return those values to* userspace. For this reason, a return code of -EBADR should be preserved.** Returns 0 on success, -EBADR on bad flags.*/
int fiemap_check_flags(struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u32 fs_flags)
{u32 incompat_flags;incompat_flags = fieinfo->fi_flags & ~(FIEMAP_FLAGS_COMPAT & fs_flags);if (incompat_flags) {fieinfo->fi_flags = incompat_flags;return -EBADR;}return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(fiemap_check_flags);static int fiemap_check_ranges(struct super_block *sb,u64 start, u64 len, u64 *new_len)
{u64 maxbytes = (u64) sb->s_maxbytes;*new_len = len;if (len == 0)return -EINVAL;if (start > maxbytes)return -EFBIG;/** Shrink request scope to what the fs can actually handle.*/if (len > maxbytes || (maxbytes - len) < start)*new_len = maxbytes - start;return 0;
}static int ioctl_fiemap(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{struct fiemap fiemap;struct fiemap __user *ufiemap = (struct fiemap __user *) arg;struct fiemap_extent_info fieinfo = { 0, };struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);struct super_block *sb = inode->i_sb;u64 len;int error;if (!inode->i_op->fiemap)return -EOPNOTSUPP;if (copy_from_user(&fiemap, ufiemap, sizeof(fiemap)))return -EFAULT;if (fiemap.fm_extent_count > FIEMAP_MAX_EXTENTS)return -EINVAL;error = fiemap_check_ranges(sb, fiemap.fm_start, fiemap.fm_length,&len);if (error)return error;fieinfo.fi_flags = fiemap.fm_flags;fieinfo.fi_extents_max = fiemap.fm_extent_count;fieinfo.fi_extents_start = ufiemap->fm_extents;if (fiemap.fm_extent_count != 0 &&!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, fieinfo.fi_extents_start,fieinfo.fi_extents_max * sizeof(struct fiemap_extent)))return -EFAULT;if (fieinfo.fi_flags & FIEMAP_FLAG_SYNC)filemap_write_and_wait(inode->i_mapping);error = inode->i_op->fiemap(inode, &fieinfo, fiemap.fm_start, len);fiemap.fm_flags = fieinfo.fi_flags;fiemap.fm_mapped_extents = fieinfo.fi_extents_mapped;if (copy_to_user(ufiemap, &fiemap, sizeof(fiemap)))error = -EFAULT;return error;
}#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCKstatic inline sector_t logical_to_blk(struct inode *inode, loff_t offset)
{return (offset >> inode->i_blkbits);
}static inline loff_t blk_to_logical(struct inode *inode, sector_t blk)
{return (blk << inode->i_blkbits);
}/*** __generic_block_fiemap - FIEMAP for block based inodes (no locking)* @inode: the inode to map* @fieinfo: the fiemap info struct that will be passed back to userspace* @start: where to start mapping in the inode* @len: how much space to map* @get_block: the fs's get_block function** This does FIEMAP for block based inodes. Basically it will just loop* through get_block until we hit the number of extents we want to map, or we* go past the end of the file and hit a hole.** If it is possible to have data blocks beyond a hole past @inode->i_size, then* please do not use this function, it will stop at the first unmapped block* beyond i_size.** If you use this function directly, you need to do your own locking. Use* generic_block_fiemap if you want the locking done for you.*/int __generic_block_fiemap(struct inode *inode,struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, loff_t start,loff_t len, get_block_t *get_block)
{struct buffer_head map_bh;sector_t start_blk, last_blk;loff_t isize = i_size_read(inode);u64 logical = 0, phys = 0, size = 0;u32 flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED;bool past_eof = false, whole_file = false;int ret = 0;ret = fiemap_check_flags(fieinfo, FIEMAP_FLAG_SYNC);if (ret)return ret;/** Either the i_mutex or other appropriate locking needs to be held* since we expect isize to not change at all through the duration of* this call.*/if (len >= isize) {whole_file = true;len = isize;}/** Some filesystems can't deal with being asked to map less than* blocksize, so make sure our len is at least block length.*/if (logical_to_blk(inode, len) == 0)len = blk_to_logical(inode, 1);start_blk = logical_to_blk(inode, start);last_blk = logical_to_blk(inode, start + len - 1);do {/** we set b_size to the total size we want so it will map as* many contiguous blocks as possible at once*/memset(&map_bh, 0, sizeof(struct buffer_head));map_bh.b_size = len;ret = get_block(inode, start_blk, &map_bh, 0);if (ret)break;/* HOLE */if (!buffer_mapped(&map_bh)) {start_blk++;/** We want to handle the case where there is an* allocated block at the front of the file, and then* nothing but holes up to the end of the file properly,* to make sure that extent at the front gets properly* marked with FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST*/if (!past_eof &&blk_to_logical(inode, start_blk) >= isize)past_eof = 1;/** First hole after going past the EOF, this is our* last extent*/if (past_eof && size) {flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED|FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST;ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,phys, size,flags);} else if (size) {ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,phys, size, flags);size = 0;}/* if we have holes up to/past EOF then we're done */if (start_blk > last_blk || past_eof || ret)break;} else {/** We have gone over the length of what we wanted to* map, and it wasn't the entire file, so add the extent* we got last time and exit.** This is for the case where say we want to map all the* way up to the second to the last block in a file, but* the last block is a hole, making the second to last* block FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST. In this case we want to* see if there is a hole after the second to last block* so we can mark it properly. If we found data after* we exceeded the length we were requesting, then we* are good to go, just add the extent to the fieinfo* and break*/if (start_blk > last_blk && !whole_file) {ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,phys, size,flags);break;}/** if size != 0 then we know we already have an extent* to add, so add it.*/if (size) {ret = fiemap_fill_next_extent(fieinfo, logical,phys, size,flags);if (ret)break;}logical = blk_to_logical(inode, start_blk);phys = blk_to_logical(inode, map_bh.b_blocknr);size = map_bh.b_size;flags = FIEMAP_EXTENT_MERGED;start_blk += logical_to_blk(inode, size);/** If we are past the EOF, then we need to make sure as* soon as we find a hole that the last extent we found* is marked with FIEMAP_EXTENT_LAST*/if (!past_eof && logical + size >= isize)past_eof = true;}cond_resched();} while (1);/* If ret is 1 then we just hit the end of the extent array */if (ret == 1)ret = 0;return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__generic_block_fiemap);/*** generic_block_fiemap - FIEMAP for block based inodes* @inode: The inode to map* @fieinfo: The mapping information* @start: The initial block to map* @len: The length of the extect to attempt to map* @get_block: The block mapping function for the fs** Calls __generic_block_fiemap to map the inode, after taking* the inode's mutex lock.*/int generic_block_fiemap(struct inode *inode,struct fiemap_extent_info *fieinfo, u64 start,u64 len, get_block_t *get_block)
{int ret;mutex_lock(&inode->i_mutex);ret = __generic_block_fiemap(inode, fieinfo, start, len, get_block);mutex_unlock(&inode->i_mutex);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(generic_block_fiemap);#endif /* CONFIG_BLOCK *//** This provides compatibility with legacy XFS pre-allocation ioctls* which predate the fallocate syscall.** Only the l_start, l_len and l_whence fields of the 'struct space_resv'* are used here, rest are ignored.*/
int ioctl_preallocate(struct file *filp, void __user *argp)
{struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);struct space_resv sr;if (copy_from_user(&sr, argp, sizeof(sr)))return -EFAULT;switch (sr.l_whence) {case SEEK_SET:break;case SEEK_CUR:sr.l_start += filp->f_pos;break;case SEEK_END:sr.l_start += i_size_read(inode);break;default:return -EINVAL;}return do_fallocate(filp, FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE, sr.l_start, sr.l_len);
}static int file_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);int __user *p = (int __user *)arg;switch (cmd) {case FIBMAP:return ioctl_fibmap(filp, p);case FIONREAD:return put_user(i_size_read(inode) - filp->f_pos, p);case FS_IOC_RESVSP:case FS_IOC_RESVSP64:return ioctl_preallocate(filp, p);}return vfs_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
}static int ioctl_fionbio(struct file *filp, int __user *argp)
{unsigned int flag;int on, error;error = get_user(on, argp);if (error)return error;flag = O_NONBLOCK;
#ifdef __sparc__/* SunOS compatibility item. */if (O_NONBLOCK != O_NDELAY)flag |= O_NDELAY;
#endifspin_lock(&filp->f_lock);if (on)filp->f_flags |= flag;elsefilp->f_flags &= ~flag;spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);return error;
}static int ioctl_fioasync(unsigned int fd, struct file *filp,int __user *argp)
{unsigned int flag;int on, error;error = get_user(on, argp);if (error)return error;flag = on ? FASYNC : 0;/* Did FASYNC state change ? */if ((flag ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) {if (filp->f_op->fasync)/* fasync() adjusts filp->f_flags */error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, on);elseerror = -ENOTTY;}return error < 0 ? error : 0;
}static int ioctl_fsfreeze(struct file *filp)
{struct super_block *sb = file_inode(filp)->i_sb;if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))return -EPERM;/* If filesystem doesn't support freeze feature, return. */if (sb->s_op->freeze_fs == NULL)return -EOPNOTSUPP;/* Freeze */return freeze_super(sb);
}static int ioctl_fsthaw(struct file *filp)
{struct super_block *sb = file_inode(filp)->i_sb;if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))return -EPERM;/* Thaw */return thaw_super(sb);
}/** When you add any new common ioctls to the switches above and below* please update compat_sys_ioctl() too.** do_vfs_ioctl() is not for drivers and not intended to be EXPORT_SYMBOL()'d.* It's just a simple helper for sys_ioctl and compat_sys_ioctl.*/
int do_vfs_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int fd, unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg)
{int error = 0;int __user *argp = (int __user *)arg;struct inode *inode = file_inode(filp);switch (cmd) {case FIOCLEX:set_close_on_exec(fd, 1);break;case FIONCLEX:set_close_on_exec(fd, 0);break;case FIONBIO:error = ioctl_fionbio(filp, argp);break;case FIOASYNC:error = ioctl_fioasync(fd, filp, argp);break;case FIOQSIZE:if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode) || S_ISREG(inode->i_mode) ||S_ISLNK(inode->i_mode)) {loff_t res = inode_get_bytes(inode);error = copy_to_user(argp, &res, sizeof(res)) ?-EFAULT : 0;} elseerror = -ENOTTY;break;case FIFREEZE:error = ioctl_fsfreeze(filp);break;case FITHAW:error = ioctl_fsthaw(filp);break;case FS_IOC_FIEMAP:return ioctl_fiemap(filp, arg);case FIGETBSZ:return put_user(inode->i_sb->s_blocksize, argp);default:if (S_ISREG(inode->i_mode))error = file_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);elseerror = vfs_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);break;}return error;
}SYSCALL_DEFINE3(ioctl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
{int error;struct fd f = fdget(fd);if (!f.file)return -EBADF;error = security_file_ioctl(f.file, cmd, arg);if (!error)error = do_vfs_ioctl(f.file, fd, cmd, arg);fdput(f);return error;
}
sys_ioctl 函数首先调用了 security_file_ioctl,然后调用了 do_vfs_ioctl,在 do_vfs_ioctl中先对一些特殊的命令进行了处理,再调用vfs_ioctl,在vfs_ioctl中最后调用了驱动的 unlocked_ioctl。之所以要来看这个系统调用的过程,是为了让大家明白,在我们的驱动解析这些命令之前已经有内核的代码来处理这些命令了,如果我们的命令定义和这些命令一样,那么我们驱动中的unlocked_ioctl就永远不会得到调用了。这些命令(如FIOCLEX等)的定义,请大家参阅内核源码,在此不详细列出了。
经过前面的介绍,我们可能已经知道 unlocked_ioctl 接口函数的实现形式就是一个大的switch语句,如同do_vfsioctl一样。下面就是将前面的虚拟串口驱动添加unlocked_ioctl接口后的完整代码.
#ifndef _VSER_H
#define _VSER_Hstruct option {unsigned int datab;unsigned int parity;unsigned int stopb;
};#define VS_MAGIC 's'#define VS_SET_BAUD _IOW(VS_MAGIC, 0, unsigned int)
#define VS_GET_BAUD _IOW(VS_MAGIC, 1, unsigned int)
#define VS_SET_FFMT _IOW(VS_MAGIC, 2, struct option)
#define VS_GET_FFMT _IOW(VS_MAGIC, 3, struct option)#endif
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/kfifo.h>#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>#include "vser.h"#define VSER_MAJOR 256
#define VSER_MINOR 0
#define VSER_DEV_CNT 1
#define VSER_DEV_NAME "vser"struct vser_dev {unsigned int baud;struct option opt;struct cdev cdev;
};DEFINE_KFIFO(vsfifo, char, 32);
static struct vser_dev vsdev;static int vser_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{ return 0;
}static int vser_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{return 0;
}static ssize_t vser_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,loff_t *pos)
{int ret;unsigned int copied = 0;ret = kfifo_to_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}static ssize_t vser_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{int ret;unsigned int copied = 0;ret = kfifo_from_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}static long vser_ioctl(struct file *flip, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{if(_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != VS_MAGIC)return -ENOTTY;switch (cmd) {case VS_SET_BAUD:vsdev.baud = arg;break;case VS_GET_BAUD:arg = vsdev.baud;break;case VS_SET_FFMT:if(copy_from_user(&vsdev.opt, (struct option __user *)arg, sizeof(struct option)))return -EFAULT;break;case VS_GET_FFMT:if(copy_to_user((struct option __user *)arg, &vsdev.opt, sizeof(struct option)))return -EFAULT;break;default:return -ENOTTY;}return 0;
}static struct file_operations vser_ops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = vser_open,.release = vser_release,.read = vser_read,.write = vser_write,.unlocked_ioctl = vser_ioctl,
};static int __init vser_init(void)
{int ret;dev_t dev;dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR,VSER_MINOR);ret = register_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT, VSER_DEV_NAME);if(ret)goto reg_err;cdev_init(&vsdev.cdev, &vser_ops);vsdev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;vsdev.baud = 115200;vsdev.opt.datab = 8;vsdev.opt.parity = 0;vsdev.opt.stopb = 1;ret = cdev_add(&vsdev.cdev, dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);if (ret)goto add_err;return 0;add_err:unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);reg_err:return ret;
}static void __exit vser_exit(void)
{dev_t dev;dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR,VSER_MINOR);cdev_del(&vsdev.cdev);unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
}module_init(vser_init);
module_exit(vser_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("name <E-mail>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple module");
MODULE_ALIAS("virtual-serial");
在vser.h头文件中,先定义了一个结构类型struct option,其中包含了波特率、奇偶校验、停止位成员。然后定义了 4个命令,分别是设置波特率、获取波特率、设置帧格式、获取帧格式。
在vser.c 文件中,代码第19行至第23 行,定义了一个vser_dev结构,将波特率、帧格式信息同 cdev包含在了一起。相应的,在代码第 106 行至第109行初始化了这些成员。代码第 91 行添加了 unlocked_ioctl接口,实现的函数是 vser_ioctl。vser_ioctl 和我们预期的是一致的,首先通过_IOC_TYPE 宏提取出命令中的幻数字段,然后和预定义的幻数进行比较,如果不匹配则返回-ENOTTY,表示参数不对(用-ENOTTY表示这一错误,是历史原因造成的);如果匹配则根据命令进行相应的操作。在这里特意演示了第三个参数的两种使用方法,第一种方法是直接传数据,如波特率。第二种方法是传指针,如帧格式。
在帧格式的设置和获取上使用了 copy_to_user 和copy_from_user 两个函数,它们的函数原型如下。
unsigned long_must_check copy_to_user(void __user *to, const void *from, unsigned long n);
unsigned long_must_check copy_from_user(void *to, const void __user *from, unsigned long n);
__must_check 要求必须检查函数返回值,to 是目的内存地址,from 是源内存地址,是期望复制的字节数。这两个函数都返回未复制成功的字节数,也就是说,如果全部复制成功,则函数返回0。之所以用这两个函数,而没有用 memcpy函数,是因为该函数调用了 access_ok 来验证用户空间的内存是否真实可读写,避免了在内核中的缺页故障带来的一些问题。还要说明的是,这两个函数可能会使进程休眠。如果只是复制简单的数据类型(如char、short、int等),那么还有两个使用方便的宏,分别是 get_user 和 put_user,它们的原型及使用示例如下。这两个宏的性质和前面两个函数的性质类似.
get user(x,p)
put user(x,p)
int ret=0x12345678;
int val;
put user(ret,(int __user *)arg);
get user(val, (int __user *)arg);测试一下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>#include "vser.h"int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd;int ret;unsigned int baud;struct option opt = {8,1,1};fd = open("/dev/vser0", O_RDWR);if(fd == -1)goto fail;baud = 9600;ret = ioctl(fd, VS_SET_BAUD, baud);if (ret == -1)goto fail;ret = ioctl(fd, VS_GET_BAUD, baud);if (ret == -1)goto fail;ret = ioctl(fd, VS_SET_FFMT, &opt);if (ret == -1)goto fail;ret = ioctl(fd, VS_GET_FFMT, &opt);if (ret == -1)goto fail;printf("baud rate: %d\n", baud);printf("frame format: %d%c%d\n", opt.datab, opt.parity == 0 ? 'N' : opt.parity == 1 ? 'O' : 'E',opt.stopb);close(fd);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);fail:perror("ioctl test");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);return 0;
}
相关文章:

Linux驱动开发——高级I/O操作(一)
一个设备除了能通过读写操作来收发数据或返回、保存数据,还应该有很多其他的操作。比如一个串口设备还应该具备波特率获取和设置、帧格式获取和设置的操作;一个LED设备甚至不应该有读写操作,而应该具备点灯和灭灯的操作。硬件设备是如此众多,…...

适配器模式:C++设计模式中的瑞士军刀
适配器模式揭秘:C设计模式中的瑞士军刀引言设计模式的重要性适配器模式简介与应用场景适配器模式在现代软件设计中的地位与价值适配器模式基本概念适配器模式的定义与核心思想类适配器与对象适配器的比较设计原则与适配器模式的关系类适配器实现类适配器模式的UML图…...
【三十天精通Vue 3】 第三天 Vue 3的组件详解
✅创作者:陈书予 🎉个人主页:陈书予的个人主页 🍁陈书予的个人社区,欢迎你的加入: 陈书予的社区 🌟专栏地址: 三十天精通 Vue 3 文章目录引言一、Vue 3 组件的概述1. Vue 3 的组件系统2. Vue 3 组件的特点…...

SqlServer实用系统视图,你了解多少?
SqlServer实用系统视图,你了解多少?前言master..spt_valuessysdatabasessysprocesses一套组合拳sysobjectssys.all_objectssyscolumnssystypessyscommentssysindexes结束语前言 在使用任何数据库软件的时候,该软件都会提供一些可能不是那么公…...

NodeJS Cluster模块基础教程
Cluster简介 默认情况下,Node.js不会利用所有的CPU,即使机器有多个CPU。一旦这个进程崩掉,那么整个 web 服务就崩掉了。 应用部署到多核服务器时,为了充分利用多核 CPU 资源一般启动多个 NodeJS 进程提供服务,这时就…...
[C++笔记]vector
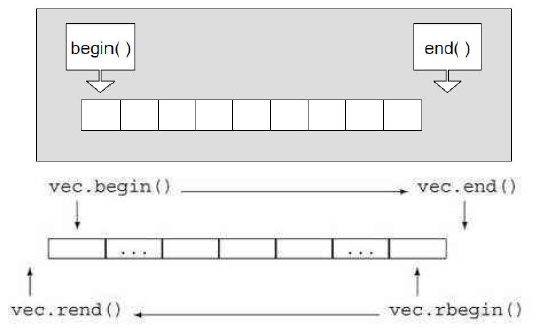
vector vector的说明文档 vector是表示可变大小数组的序列容器(动态顺序表)。就像数组一样,vector也采用连续的存储空间来储存元素。这就意味着可以用下标对vector的元素进行访问,和数组一样高效。与数组不同的是,它的大小可以动态改变——…...

Python 迁移学习实用指南:1~5
原文:Hands-On Transfer Learning with Python 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 译者:飞龙 本文来自【ApacheCN 深度学习 译文集】,采用译后编辑(MTPE)流程来尽可能提升效率。 不要担心自己的形象,只关心如…...
【CSS重点知识】属性计算的过程
✍️ 作者简介: 前端新手学习中。 💂 作者主页: 作者主页查看更多前端教学 🎓 专栏分享:css重难点教学 Node.js教学 从头开始学习 ajax学习 标题什么是计算机属性确定声明值层叠冲突继承使用默认值总结什么是计算机属性 CSS属性值的计算…...
Java避免死锁的几个常见方法(有测试代码和分析过程)
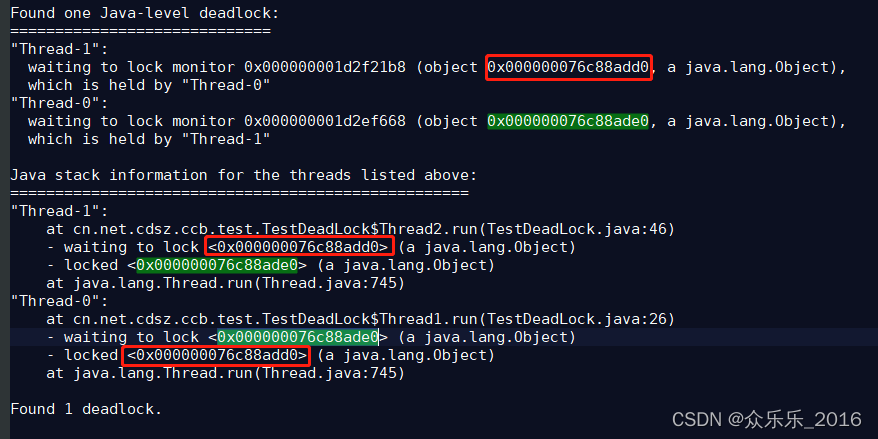
目录 Java避免死锁的几个常见方法 死锁产生的条件 上死锁代码 然后 :jstack 14320 >> jstack.text Java避免死锁的几个常见方法 Java避免死锁的几个常见方法 避免一个线程同时获取多个锁。避免一个线程在锁内同时占用多个资源,尽量保证每个锁…...
go binary包
binary包使用与详解 最近在看一个第三方包的库源码,bigcache,发现其中用到了binary 里面的函数,所以准备研究一下。 可以看到binary 包位于encoding/binary,也就是表示这个包的作用是编辑码作用的,看到文档给出的解释…...
CompletableFuture使用详解(IT枫斗者)
CompletableFuture使用详解 简介 概述 CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力…...
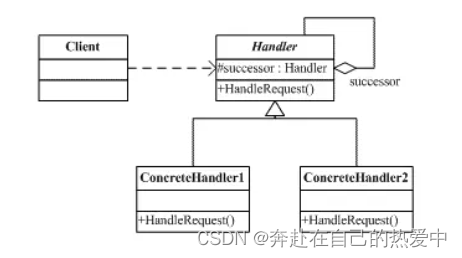
4.15--设计模式之创建型之责任链模式(总复习版本)---脚踏实地,一步一个脚印
一、什么是责任链模式: 责任链模式属于行为型模式,是为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链,将链中每一个节点看作是一个对象,每个节点处理的请求均不同,且内部自动维护一个下一节点对象。 当一个请求从链式的首端发出时&a…...
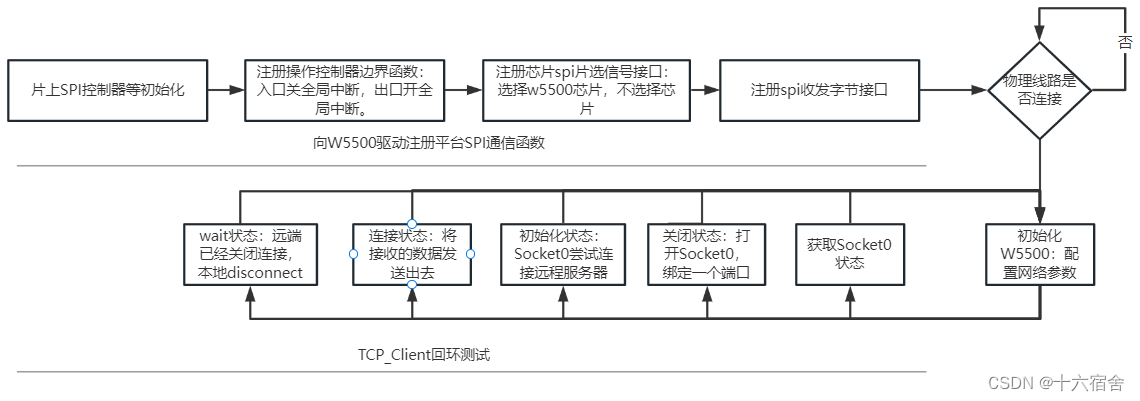
STM32+W5500实现以太网通信
STM32系列32位微控制器基于Arm Cortex-M处理器,旨在为MCU用户提供新的开发自由度。它包括一系列产品,集高性能、实时功能、数字信号处理、低功耗/低电压操作、连接性等特性于一身,同时还保持了集成度高和易于开发的特点。本例采用STM32作为MC…...
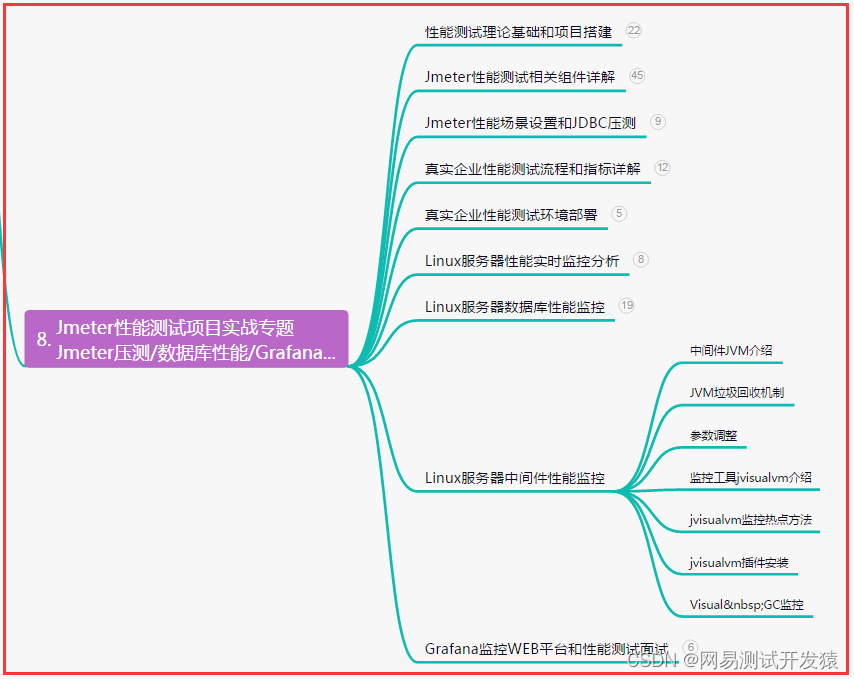
全网最详细,Jmeter性能测试-性能基础详解,终成测试卷王(一)
目录:导读前言一、Python编程入门到精通二、接口自动化项目实战三、Web自动化项目实战四、App自动化项目实战五、一线大厂简历六、测试开发DevOps体系七、常用自动化测试工具八、JMeter性能测试九、总结(尾部小惊喜)前言 发起请求 发起HTTP…...

人工智能概述
一、人工智能发展必备三要素 算法 数据 算力 CPU、GPU、TPU 计算力之CPU、GPU对比: CPU主要适合I\O密集型任务GPU主要适合计算密集型任务 什么样的程序适合在GPU上运行? 计算密集型的程序 所谓计算密集型(Compute-intensive)的程序,就是…...

API接口安全—webservice、Swagger、WEBpack
API接口安全—webservice、Swagger、WEBpack1. API接口介绍1.1. 常用的API接口类1.1.1. API接口分类1.1.1.1. 类库型API1.1.1.2. 操作系统型API1.1.1.3. 远程应用型API1.1.1.4. WEB应用型API1.1.1.5. 总结1.1.2. API接口类型1.1.2.1. HTTP类接口1.1.2.2. RPC类接口1.1.2.3. web…...

从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+]
目录 从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+] 程序设计 程序分析 从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+] 输出从前M个字母中取N个的无重复字母排列 Input 输入M N 1<=M=10, N<=M Output 按字典序输出排列 Sample Input 4 2 Sample Output A B A C A D B A B C B …...

ES forceMerge 强制段合并为什么会提升检索性能?
根据以前的测试,forceMerge段合并,将段的个数合并成一个。带来了将近一倍的性能提升,测试过程文档(请参考我的另外一篇文章):ES优化实战- forceMerge搜索提升测试报告_es forcemerge_水的精神的博客-CSDN博…...

macOS Ventura 13.3.1 (22E261) Boot ISO 原版可引导镜像
本站下载的 macOS 软件包,既可以拖拽到 Applications(应用程序)下直接安装,也可以制作启动 U 盘安装,或者在虚拟机中启动安装。另外也支持在 Windows 和 Linux 中创建可引导介质。 macOS Ventura 13.3.1 为 Mac 提供下…...
html+css+JavaScript+json+servlet的社区系统(手把手教学)
目录 课前导读: 一、系统前期准备 二、前端代码的编写 三、登陆页面简介 四、注册页面 五、社区列表页 六、社区详情页 七、社区发帖页 八、注销 九、访问链接 登陆页面http://175.178.20.77:8080/java106_blog_system/login.html 总结: 课前…...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(二)
HoST框架核心实现方法详解 - 论文深度解读(第二部分) 《Learning Humanoid Standing-up Control across Diverse Postures》 系列文章: 论文深度解读 + 算法与代码分析(二) 作者机构: 上海AI Lab, 上海交通大学, 香港大学, 浙江大学, 香港中文大学 论文主题: 人形机器人…...
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...
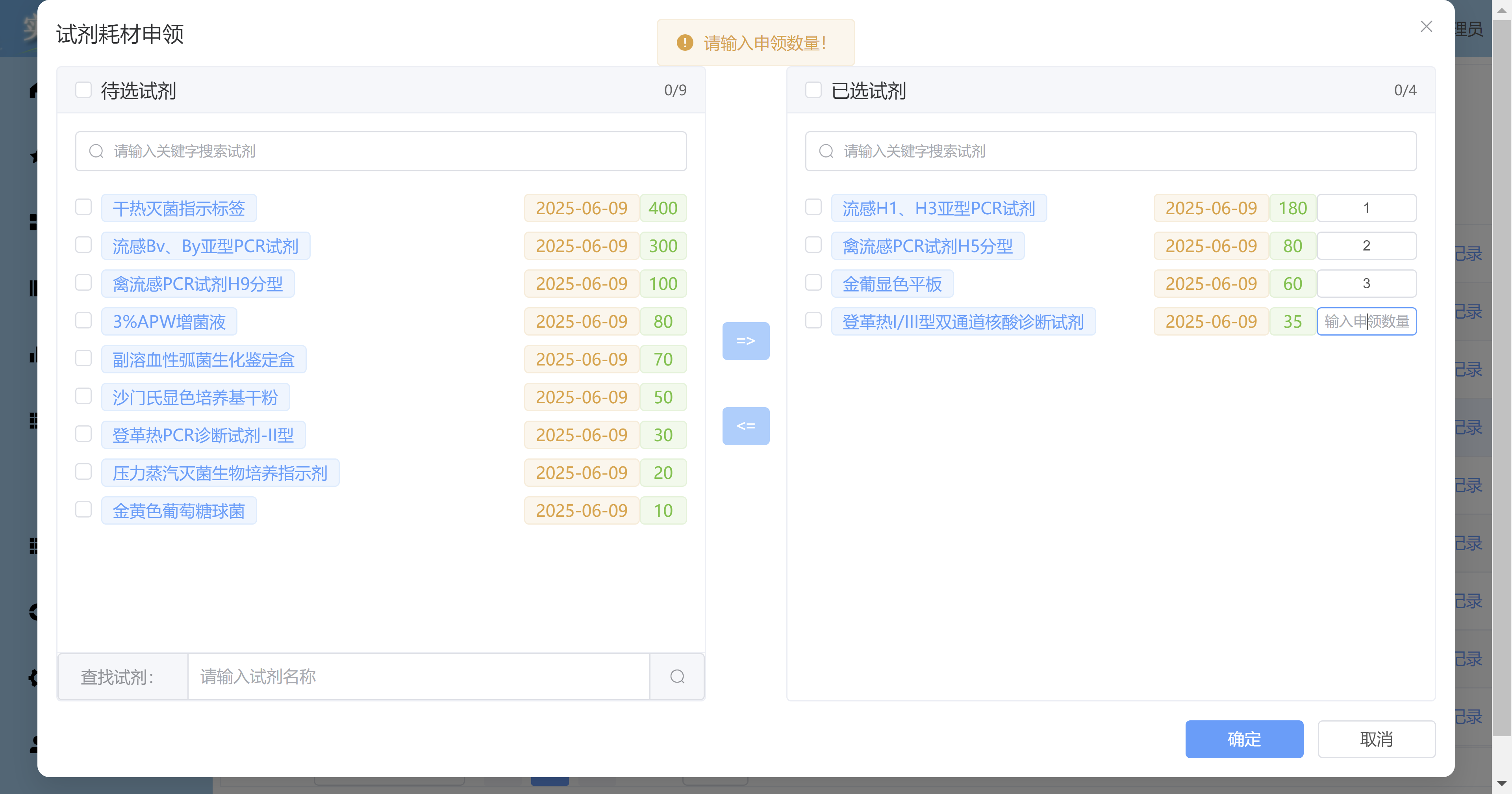
Vue3 + Element Plus + TypeScript中el-transfer穿梭框组件使用详解及示例
使用详解 Element Plus 的 el-transfer 组件是一个强大的穿梭框组件,常用于在两个集合之间进行数据转移,如权限分配、数据选择等场景。下面我将详细介绍其用法并提供一个完整示例。 核心特性与用法 基本属性 v-model:绑定右侧列表的值&…...

java调用dll出现unsatisfiedLinkError以及JNA和JNI的区别
UnsatisfiedLinkError 在对接硬件设备中,我们会遇到使用 java 调用 dll文件 的情况,此时大概率出现UnsatisfiedLinkError链接错误,原因可能有如下几种 类名错误包名错误方法名参数错误使用 JNI 协议调用,结果 dll 未实现 JNI 协…...

Android Bitmap治理全解析:从加载优化到泄漏防控的全生命周期管理
引言 Bitmap(位图)是Android应用内存占用的“头号杀手”。一张1080P(1920x1080)的图片以ARGB_8888格式加载时,内存占用高达8MB(192010804字节)。据统计,超过60%的应用OOM崩溃与Bitm…...
)
Angular微前端架构:Module Federation + ngx-build-plus (Webpack)
以下是一个完整的 Angular 微前端示例,其中使用的是 Module Federation 和 npx-build-plus 实现了主应用(Shell)与子应用(Remote)的集成。 🛠️ 项目结构 angular-mf/ ├── shell-app/ # 主应用&…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...

iview框架主题色的应用
1.下载 less要使用3.0.0以下的版本 npm install less2.7.3 npm install less-loader4.0.52./src/config/theme.js文件 module.exports {yellow: {theme-color: #FDCE04},blue: {theme-color: #547CE7} }在sass中使用theme配置的颜色主题,无需引入,直接可…...
C++_哈希表
本篇文章是对C学习的哈希表部分的学习分享 相信一定会对你有所帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、基础概念 1. 哈希核心思想: 哈希函数的作用:通过此函数建立一个Key与存储位置之间的映射关系。理想目标:实现…...
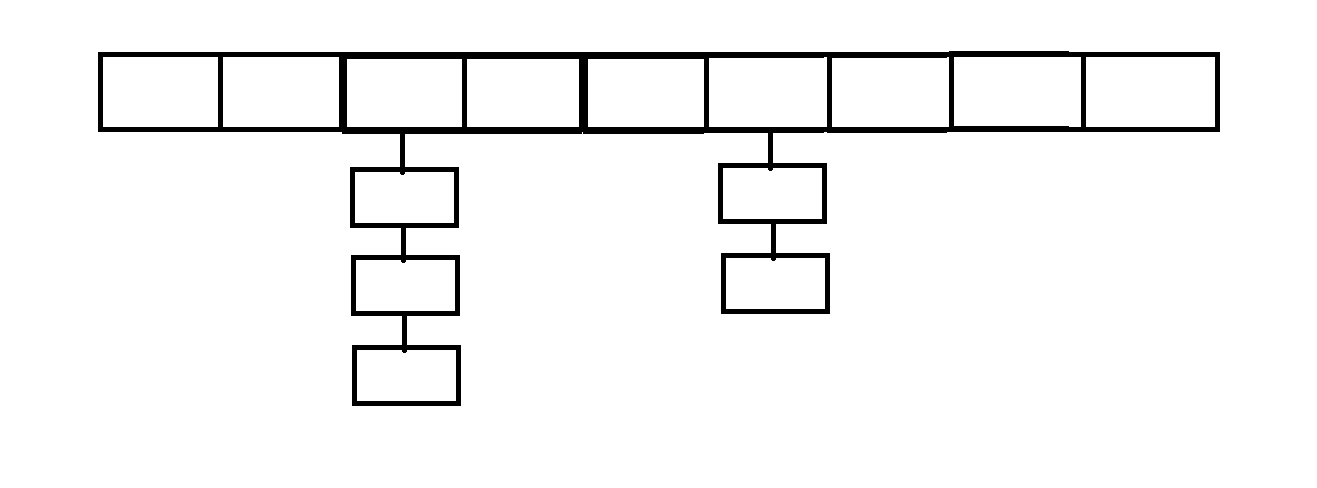
之(六) ——通用对象池总结(核心))
怎么开发一个网络协议模块(C语言框架)之(六) ——通用对象池总结(核心)
+---------------------------+ | operEntryTbl[] | ← 操作对象池 (对象数组) +---------------------------+ | 0 | 1 | 2 | ... | N-1 | +---------------------------+↓ 初始化时全部加入 +------------------------+ +-------------------------+ | …...
