CompletableFuture详解-初遇者-很细
目录
一、创建异步任务
1. supplyAsync
2. runAsync
3.获取任务结果的方法
二、异步回调处理
1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync
2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
2.thenRun和thenRunAsync
3.whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
4.handle和handleAsync
三、多任务组合处理
1.thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
2.applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
3.allOf / anyOf
CompletableFuture是jdk8的新特性。CompletableFuture实现了CompletionStage接口和Future接口,前者是对后者的一个扩展,增加了异步会点、流式处理、多个Future组合处理的能力,使Java在处理多任务的协同工作时更加顺畅便利。
代码涉及到lambda表达式() -> {} 用法,不熟悉的可先看下Lambda表达式详解
一、创建异步任务
1. supplyAsync
supplyAsync是创建带有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法。子线程是异步执行的,主线程休眠等待子线程执行完成,子线程执行完成后唤醒主线程,主线程获取任务执行结果后退出。
// 带返回值异步请求,默认线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
// 带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
测试代码:
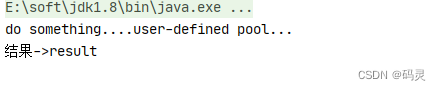
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");return "result";});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 自定义线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....user-defined pool...");return "result";}, executorService);//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}测试结果:

2. runAsync
runAsync是创建没有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
// 不带返回值的异步请求,默认线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
// 不带返回值的异步请求,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 自定义线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");}, executorService);//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());
}测试结果:


3.获取任务结果的方法
// 如果完成则返回结果,否则就抛出具体的异常
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
// 最大时间等待返回结果,否则就抛出具体异常
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
// 完成时返回结果值,否则抛出unchecked异常。为了更好地符合通用函数形式的使用,如果完成此 CompletableFuture所涉及的计算引发异常,则此方法将引发unchecked异常并将底层异常作为其原因
public T join()
// 如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。测试调用直接值valueIfAbsent
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
// 如果任务没有完成,返回的值设置为给定值;测试直接结束任务,不会执行
public boolean complete(T value)
// 如果任务没有完成,就抛出给定异常;测试直接结束任务,不会执行。
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something....");return "result";});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.complete("hello"));}测试结果

二、异步回调处理
1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,带有返回值。
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;return result;});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApply((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;return result;});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}测试结果:
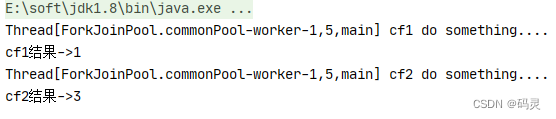

从上面代码和测试结果我们发现thenApply和thenApplyAsync区别在于,使用thenApply方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenApplyAsync在子任务中是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenApplyAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
thenAccep表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,无返回值。
测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "main thread ");CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}测试结果:


从上面代码和测试结果我们发现thenAccep和thenAccepAsync区别在于,使用thenAccep方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenAccepAsync在子任务中是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenAccepAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
2.thenRun和thenRunAsync
thenRun表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,无入参,无返回值。
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRun(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "main thread ");CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRunAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}测试结果:
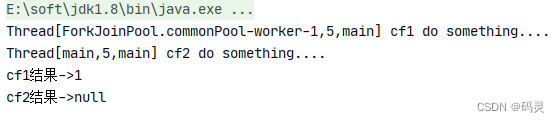

从上面代码和测试结果我们发现thenRun和thenRunAsync区别在于,使用thenRun方法时子任务与父任务使用的是同一个线程,而thenRunAsync在子任务中是另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenRunAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
3.whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
whenComplete是当某个任务执行完成后执行的回调方法,会将执行结果或者执行期间抛出的异常传递给回调方法,如果是正常执行则异常为null,回调方法对应的CompletableFuture的result和该任务一致,如果该任务正常执行,则get方法返回执行结果,如果是执行异常,则get方法抛出异常。
测试代码:
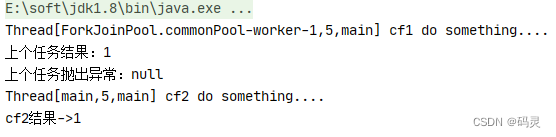
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");//int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "main thread ");CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");//int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenCompleteAsync((result, e) -> {System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}测试结果
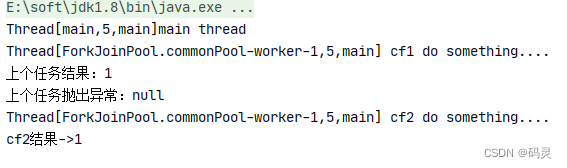
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}测试结果:

whenCompleteAsync和whenComplete区别也是whenCompleteAsync另起一个线程执行任务,并且thenRunAsync可以自定义线程池,默认的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()线程池。
4.handle和handleAsync
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值。
测试代码:
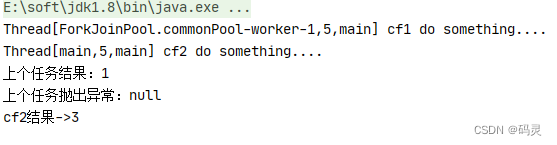
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");// int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.handle((result, e) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);return result+2;});//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}测试结果 :
三、多任务组合处理
1.thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,只有两个任务都正常完成时,才进行下阶段任务。
区别:thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为所提供函数的参数,且该方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。
测试代码:
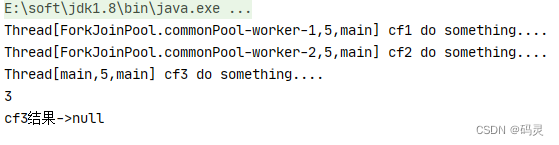
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");return a + b;});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
} public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println(a + b);});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");return 2;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2, () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}测试结果:


2.applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
这三个方法和上面一样也是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,当有一个任务正常完成时,就会进行下阶段任务。
区别:applyToEither会将已经完成任务的执行结果作为所提供函数的参数,且该方法有返回值;acceptEither同样将已经完成任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterEither没有入参,也没有返回值。
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf1 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf2 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = cf1.applyToEither(cf2, (result) -> {System.out.println("接收到" + result);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");return "cf3 任务完成";});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf1 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf2 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.acceptEither(cf2, (result) -> {System.out.println("接收到" + result);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");return "cf1 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");return "cf2 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterEither(cf2, () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());
}测试结果:
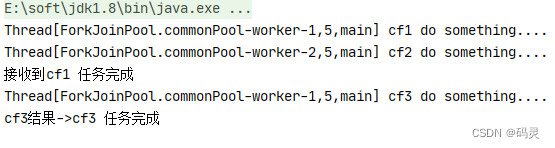
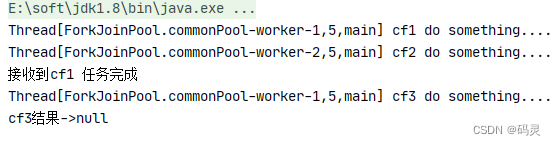
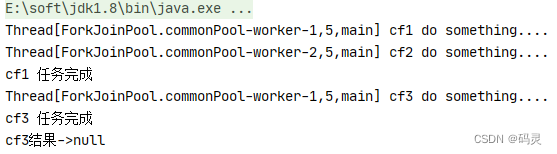
从上面可以看出cf1任务完成需要2秒,cf2任务完成需要5秒,使用applyToEither组合两个任务时,只要有其中一个任务完成时,就会执行cf3任务,显然cf1任务先完成了并且将自己任务的结果传值给了cf3任务,cf3任务中打印了接收到cf1任务完成,接着完成自己的任务,并返回cf3任务完成;acceptEither和runAfterEither类似,acceptEither会将cf1任务的结果作为cf3任务的入参,但cf3任务完成时并无返回值;runAfterEither不会将cf1任务的结果作为cf3任务的入参,它是没有任务入参,执行完自己的任务后也并无返回值。
3.allOf / anyOf
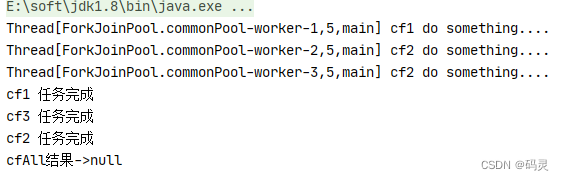
allOf:CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
anyOf :CompletableFuture是多个任务只要有一个任务执行完成,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回执行完成任务的结果。
测试代码:
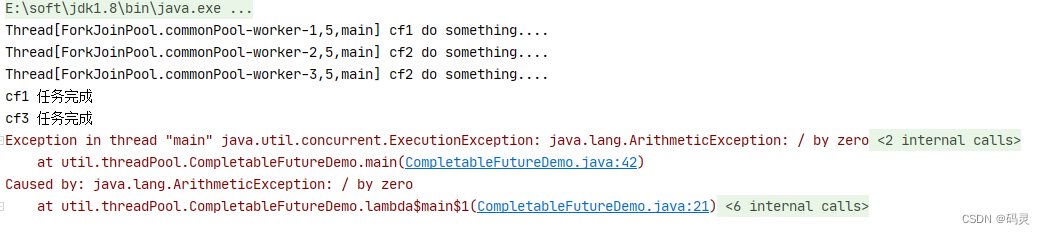
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");return "cf1 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");//int a = 1/0;Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");return "cf2 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");return "cf3 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");return "cf1 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");return "cf2 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");return "cf3 任务完成";});CompletableFuture<Object> cfAll = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}测试结果:
//int a = 1/0; 异常行去掉注释后结果

相关文章:

CompletableFuture详解-初遇者-很细
目录 一、创建异步任务 1. supplyAsync 2. runAsync 3.获取任务结果的方法 二、异步回调处理 1.thenApply和thenApplyAsync 2.thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync 2.thenRun和thenRunAsync 3.whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync 4.handle和handleAsync 三、多任务组合处理 1…...
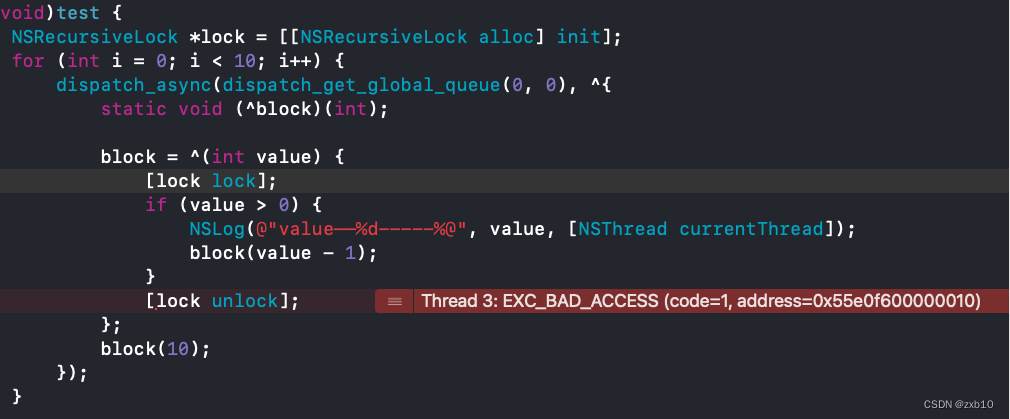
【iOS】—— iOS中的相关锁
文章目录 自旋锁1.OSSpinLock2.os_unfair_lock3.atomic 互斥锁pthread_mutexsynchronizedobjc_sync_enterobjc_sync_exit注意事项 NSLockNSRecursiveLock信号量条件锁NSConditionNSConditionLock 读写锁总结 锁作为一种非强制的机制,被用来保证线程安全。每一个线程…...

表单重复提交:
1. 表单重复提交原因 当用户提交完请求,浏览器会记录最后一次请求的全部信息。用户按下功能键F5,就会发起浏览器记录的最后一次请求。如果最后一次请求为添加操作,那么此时刷新按钮就会再次提交数据,造成表单重复提交。 2. 表单…...
之创建共享内存分配机制(Shared Memory Allocation)(2 - 2))
【0197】共享内存管理结构(shmem)之创建共享内存分配机制(Shared Memory Allocation)(2 - 2)
文章目录 1. 概述2. 初始化事务管理器 ShmemVariableCache2.1 从共享内存分配 VariableCacheData 大小内存空间2.1.1 分配对齐块2.2 内存空间清零相关文章: 【0195】共享内存管理结构(shmem)之概念篇(1) 【0196】共享内存管理结构(shmem)之创建共享内存分配机制(Shared…...
ChatGPT国内免费使用方法有哪些?
目录 ChatGPT介绍:一、ChatGPT是什么?二、ChatGPT发展:三、ChatGPT 优点:四、国内使用ChatGPT方法五、结语: ChatGPT介绍: 一、ChatGPT是什么? ChatGPT 是一个基于语言模型 GPT-3.5 的聊天机器人,ChatGPT模型是Instruct GPT的姊妹模型(siblingmodel&a…...

【CloudCompare教程】012:基于点云数据的测量功能
本文讲解CloudCompare基于点云数据的测量功能,主要有:点云索引、坐标、距离、角度、面积、标签等。 文章目录 一、加载地形点云数据二、基于点云数据的测量功能1. 选择单点并显示信息2. 选择两点并显示分割信息3. 选择三点并显示相关三角形信息4. 定义矩形2D标签5. 保存当前标…...
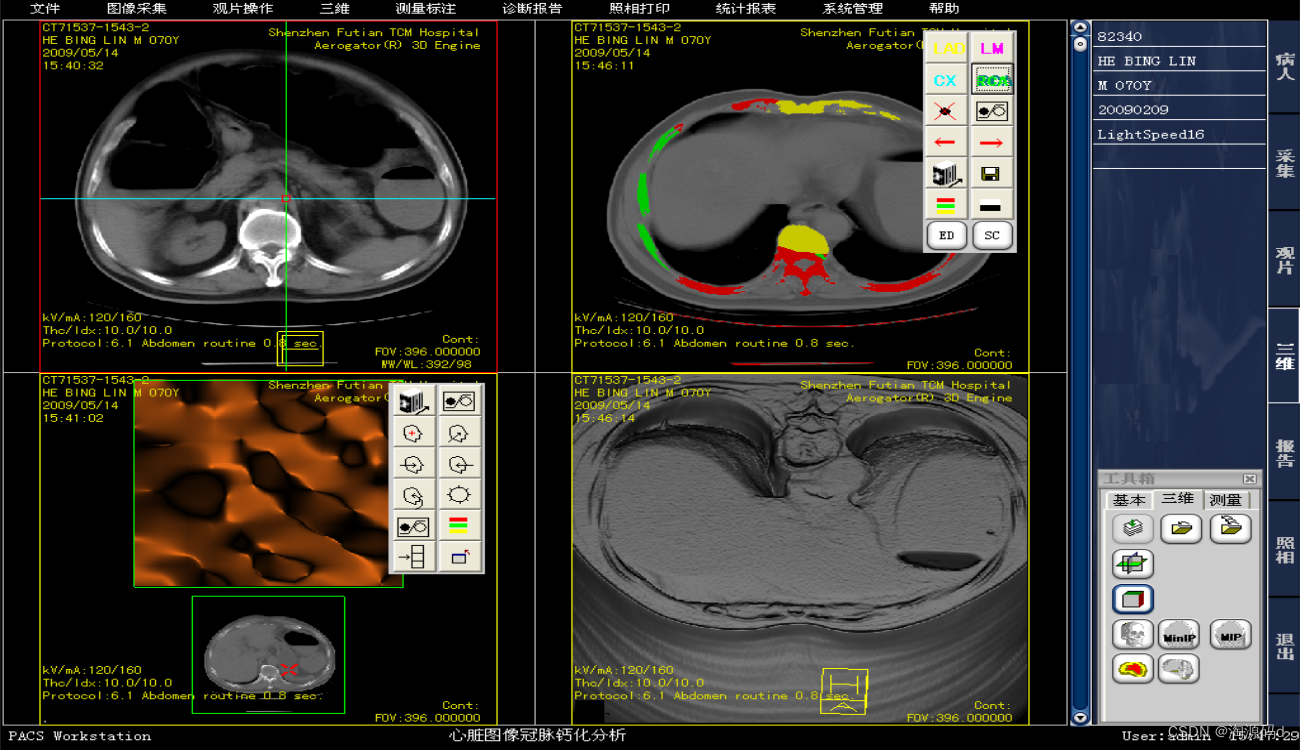
一体化医学影像平台PACS源码,影像存档与传输系统源码
PACS影像存档与传输系统源码 PACS即影像存档与传输系统,是医学影像、数字化图像技术、计算机技术和网络通讯技术相结合的产物,是处理各种医学影像信息的采集、存储、报告、输出、管理、查询的计算机应用程序。 是基于DICOM标准的医学影像管理系统&…...

一篇文章打好SQL基础,熟悉数据库的基础操作和方法,以及安装MySQL软件包和Python操作MySQL基础使用
1.SQL的概述 SQL的全称:Structured Query Language,结构化查询语言,用于访问和处理数据库的标准计算机语言。 SQL语言1974年有Boyce和Chamberlin提出的,并且首先在IBM公司研制的关系数据库系统SystemR上实现。 经过多年发展&am…...
C4D R26 渲染学习笔记 建模篇(3):生成器
文章目录 前文回顾介绍篇建模篇 生成器介绍生成器变形器搭配举例 生成器详细介绍细分曲面布料曲面 未完待续 前文回顾 介绍篇 C4D R26 渲染学习笔记(1):C4D版本选择和初始UI框介绍 C4D R26 渲染学习笔记(2)ÿ…...

智慧梁场3D建模
智慧梁场3D建模:数字化革命下的新起点 随着科技的迅猛发展,数字化已经成为了现代工业生产的必然趋势。作为传统工业的核心产业,建筑行业也在不断地探索数字化变革的新路径。而“智慧梁场3D建模”便是其中的一项杰出实践。 梁场是建筑…...

《程序员面试金典(第6版)》面试题 02.08. 环路检测(哈希法,双指针,检测链表是否有环)
题目描述 给定一个链表,如果它是有环链表,实现一个算法返回环路的开头节点。若环不存在,请返回 null。 题目传送门:面试题 02.08. 环路检测 如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链…...

软考A计划-试题模拟含答案解析-卷六
点击跳转专栏>Unity3D特效百例点击跳转专栏>案例项目实战源码点击跳转专栏>游戏脚本-辅助自动化点击跳转专栏>Android控件全解手册点击跳转专栏>Scratch编程案例 👉关于作者 专注于Android/Unity和各种游戏开发技巧,以及各种资源分享&am…...
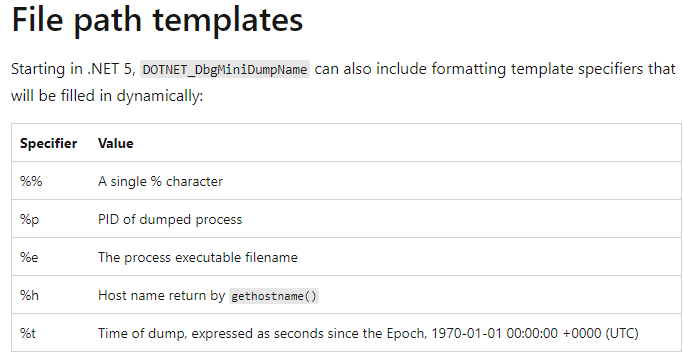
Linux 上的 .NET 崩溃了怎么抓 Dump
一:背景 1. 讲故事 训练营中有朋友问在 Linux 上如何抓 crash dump,在我的系列文章中演示的大多是在 Windows 平台上,这也没办法要跟着市场走,谁让 .NET 的主战场在工控 和 医疗 呢,上一张在 合肥 分享时的一个统计图…...

QT桌面项目(状态栏和导航栏设置)
文章目录 前言一、状态栏二、导航栏三、同时添加状态栏和导航栏总结 前言 为了和我们这个项目做的更加真实,这里为我们的项目添加上状态栏和导航栏让他变成更加接近手机的桌面效果。 一、状态栏 这个状态栏就是显示时间和wifi状态,电池电量的…...

数据链路层:点对点协议PPP
数据链路层:点对点协议PPP 笔记来源: 湖科大教书匠:点对点协议PPP 声明:该学习笔记来自湖科大教书匠,笔记仅做学习参考 数据链路层只负责直接相连的两个结点之间的通信 PPP是点对点数据链路层协议 用户通过ISP接入因特…...

C/C++读取txt文件中的float数据并用指针存储
C语言中读取txt文件中的数据 以下是一个简单的示例代码,演示如何在C语言中读取txt文件中的数据: #include <stdio.h>int main() {FILE *fp;char buffer[100];// 打开文件fp fopen("example.txt", "r");// 如果文件打开失败…...
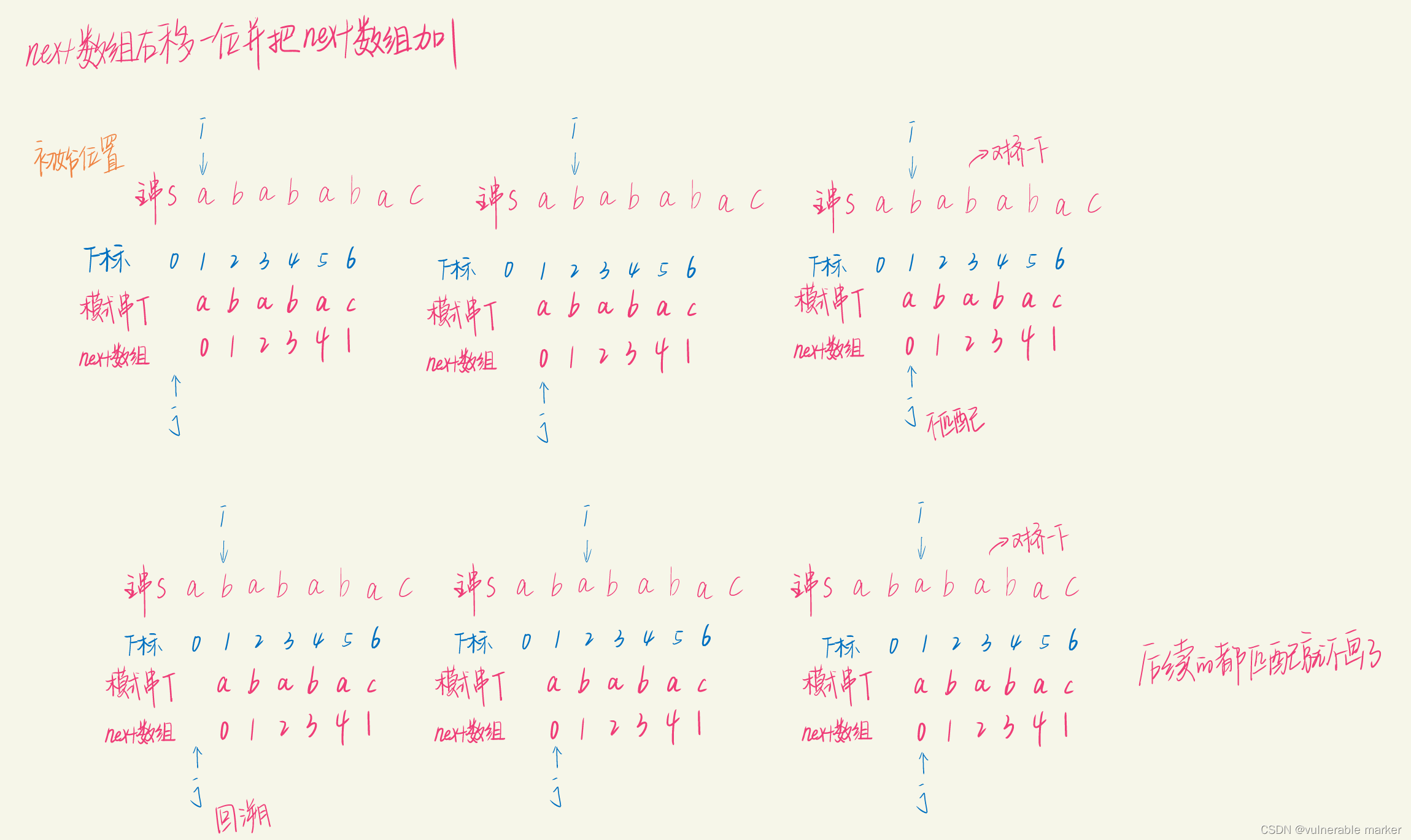
对KMP算法的一点碎碎念——上篇
对KMP算法的一点碎碎念——上篇 文章目录 对KMP算法的一点碎碎念——上篇1. KMP 算法 Next数组 求解问题1.1 前置知识-最长公共前后缀LCP1.1.1 前缀与后缀1.1.2 最长公共前后缀LCP 1.2 手算法求解 Next数组值(3种常见情况)1.2.1 情况1: next数组 正常存放匹配字符的长度情况1的…...

算法---边界着色
题目 给你一个大小为 m x n 的整数矩阵 grid ,表示一个网格。另给你三个整数 row、col 和 color 。网格中的每个值表示该位置处的网格块的颜色。 两个网格块属于同一 连通分量 需满足下述全部条件: 两个网格块颜色相同 在上、下、左、右任意一个方向上…...

二叉排序树的查找、插入、删除
目录 二叉排序树的定义 二叉排序树的查找 二叉排序树的插入 二叉排序树的定义 二叉排序树的定义 二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree, BST),也称二叉查找树。 二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是一棵具有下列特性的非空二叉…...
《Opencv3编程入门》学习笔记—第三章
《Opencv3编程入门》学习笔记 记录一下在学习《Opencv3编程入门》这本书时遇到的问题或重要的知识点。 第三章 HighGUI图形用户界面初步 一、图像的载入、显示和输出到文件 (一)OpenCV的命名空间 简单的OpenCV程序标配: #include <o…...
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器的上位机配置操作说明
LBE-LEX系列工业语音播放器|预警播报器|喇叭蜂鸣器专为工业环境精心打造,完美适配AGV和无人叉车。同时,集成以太网与语音合成技术,为各类高级系统(如MES、调度系统、库位管理、立库等)提供高效便捷的语音交互体验。 L…...

【大模型RAG】拍照搜题技术架构速览:三层管道、两级检索、兜底大模型
摘要 拍照搜题系统采用“三层管道(多模态 OCR → 语义检索 → 答案渲染)、两级检索(倒排 BM25 向量 HNSW)并以大语言模型兜底”的整体框架: 多模态 OCR 层 将题目图片经过超分、去噪、倾斜校正后,分别用…...
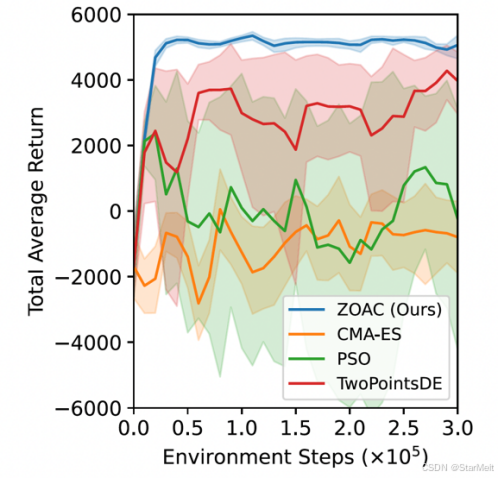
突破不可导策略的训练难题:零阶优化与强化学习的深度嵌合
强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)是工业领域智能控制的重要方法。它的基本原理是将最优控制问题建模为马尔可夫决策过程,然后使用强化学习的Actor-Critic机制(中文译作“知行互动”机制),逐步迭代求解…...

Cesium1.95中高性能加载1500个点
一、基本方式: 图标使用.png比.svg性能要好 <template><div id"cesiumContainer"></div><div class"toolbar"><button id"resetButton">重新生成点</button><span id"countDisplay&qu…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility 1. 实验室环境1.1 实验室环境1.2 小测试 2. The Endor System2.1 部署应用2.2 检查现有策略 3. Cilium 策略实体3.1 创建 allow-all 网络策略3.2 在 Hubble CLI 中验证网络策略源3.3 …...

MODBUS TCP转CANopen 技术赋能高效协同作业
在现代工业自动化领域,MODBUS TCP和CANopen两种通讯协议因其稳定性和高效性被广泛应用于各种设备和系统中。而随着科技的不断进步,这两种通讯协议也正在被逐步融合,形成了一种新型的通讯方式——开疆智能MODBUS TCP转CANopen网关KJ-TCPC-CANP…...
ServerTrust 并非唯一
NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust 只是 authenticationMethod 的冰山一角 要理解 NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust, 首先要明白它只是 authenticationMethod 的选项之一, 并非唯一 1 先厘清概念 点说明authenticationMethodURLAuthenticationChallenge.protectionS…...

图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享
图标图表系列PPT模版,柱状图PPT模版,线状图PPT模版,折线图PPT模版,饼状图PPT模版,雷达图PPT模版,树状图PPT模版 图表类系列各种样式PPT模版分享:图表系列PPT模板https://pan.quark.cn/s/20d40aa…...

站群服务器的应用场景都有哪些?
站群服务器主要是为了多个网站的托管和管理所设计的,可以通过集中管理和高效资源的分配,来支持多个独立的网站同时运行,让每一个网站都可以分配到独立的IP地址,避免出现IP关联的风险,用户还可以通过控制面板进行管理功…...
Python 实现 Web 静态服务器(HTTP 协议)
目录 一、在本地启动 HTTP 服务器1. Windows 下安装 node.js1)下载安装包2)配置环境变量3)安装镜像4)node.js 的常用命令 2. 安装 http-server 服务3. 使用 http-server 开启服务1)使用 http-server2)详解 …...
