ThreadLocal源码
介绍
ThreadLocal是一个线程的本地变量,也就意味着这个变量是线程独有的,是不能与其他线程共享的。这样就可以避免资源竞争带来的多线程的问题。
但是,这种解决多线程安全问题的方式和加锁方式(synchronized、Lock) 是有本质的区别的,区别如下所示:
1> 关于资源的管理
当资源是多个线程共享时,访问的时候可以通过加锁的方式,逐一访问资源。
ThreadLocal是每个线程都有一个资源副本,是不需要加锁的。
2> 关于实现方式
锁是通过时间换空间的做法。
ThreadLocal是通过空间换时间的做法。
由于使用场景的不同,我们可以选择不同的技术手段,关键还是要看你的应用场景对于资源的管理是需要多线程之间共享还是单线程内部独享。
说明
- 它能让线程拥有了自己内部独享的变量
- 每一个线程可以通过get、set方法去进行操作
- 可以覆盖initialValue方法指定线程独享的值
- 通常会用来修饰类里private static final的属性,为线程设置一些状态信息,例如user ID或者Transaction ID
- 每一个线程都有一个指向threadLocal实例的弱引用,只要线程一直存活或者该threadLocal实例能被访问到,都不会被垃圾回收清理掉
常量&变量
/*** ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in* less common cases.* 对象私有常量*/private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();/*** The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at* zero.* 共享原子对象*/private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =new AtomicInteger();/*** The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.* 魔数0x61c88647,利用一定算法实现了元素的完美散列 对应十进制=1640531527。*/private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;/*** Returns the next hash code.* 获取下一个hashcode值*/private static int nextHashCode() {// 获取并增加,原子操作return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);}
构造方法
/*** Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}* method, in which case the {@code initialValue} method will not* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.** <p>This implementation simply returns {@code null}; if the* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial* value other than {@code null}, {@code ThreadLocal} must be* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an* anonymous inner class will be used.** @return the initial value for this thread-local* 返回当前线程的这个线程局部变量的“初始值” 由子类重写该方法*/protected T initialValue() {return null;}/*** Creates a thread local variable. The initial value of the variable is* determined by invoking the {@code get} method on the {@code Supplier}.** @param <S> the type of the thread local's value* @param supplier the supplier to be used to determine the initial value* @return a new thread local variable* @throws NullPointerException if the specified supplier is null* @since 1.8* 创建线程局部变量*/public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) {return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);}/*** Creates a thread local variable.* @see #withInitial(java.util.function.Supplier)*/public ThreadLocal() {}内部类
SuppliedThreadLocal
/*** An extension of ThreadLocal that obtains its initial value from* the specified {@code Supplier}.*/static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {//函数接口private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier;//在构造函数中赋值该函数接口SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) {this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);}//开接口,触发函数接口实现调用@Overrideprotected T initialValue() {return supplier.get();}}
ThreadLocalMap
数据结构仅仅是数组
通过开放地址法来解决hash冲突的问题
Entry内部类中的key是弱引用,value是强引用
/*** ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for* maintaining thread local values. No operations are exported* outside of the ThreadLocal class. The class is package private to* allow declaration of fields in class Thread. To help deal with* very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use* WeakReferences for keys. However, since reference queues are not* used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when* the table starts running out of space.*/static class ThreadLocalMap {/*** The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using* its main ref field as the key (which is always a* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.*/static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}/*** The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.*/private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;/*** The table, resized as necessary.* table.length MUST always be a power of two.*/private Entry[] table;/*** The number of entries in the table.*/private int size = 0;/*** The next size value at which to resize.*/private int threshold; // Default to 0/*** Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.* 阈值 = 容量 * 2/3 即负载因子为2/3*/private void setThreshold(int len) {threshold = len * 2 / 3;}/*** Increment i modulo len.* 从指定的下标i开始,向后获取下一个位置的下标值*/private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);}/*** Decrement i modulo len.* 从指定的下标i开始,前向获取上一个位置的下标值。*/private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);}/*** Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.* ThreadLocalMap构造函数*/ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {//table数组的默认大小 16table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];//插入数组的下标int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);//创建待插入的entry对象table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);//设置数组table中entry元素的个数为1size = 1;//设置数组table的阈值setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);}/*** Construct a new map including all Inheritable ThreadLocals* from given parent map. Called only by createInheritedMap.** @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread.*/private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;int len = parentTable.length;setThreshold(len);table = new Entry[len];for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {Entry e = parentTable[j];if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();if (key != null) {Object value = key.childValue(e.value);Entry c = new Entry(key, value);int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);while (table[h] != null)h = nextIndex(h, len);table[h] = c;size++;}}}}/*** Get the entry associated with key. This method* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part* by making this method readily inlinable.** @param key the thread local object* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {// 计算entry table索引int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);Entry e = table[i];if (e != null && e.get() == key)return e;else// 当entry的值不存在时return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);}/*** Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in* its direct hash slot.** @param key the thread local object* @param i the table index for key's hash code* @param e the entry at table[i]* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;while (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key)// 找到entryreturn e;if (k == null)// 移除过期条目expungeStaleEntry(i);else// 向下扫描i = nextIndex(i, len);e = tab[i];}return null;}/*** Set the value associated with key.** @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.//table数组Entry[] tab = table;//table数组的长度int len = tab.length;//计算数组的下标 待插入entry的下标int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);//通过哈希码和数组长度找到数组下标,从i开始往后寻找相等的ThreadLocal对象,没有就下一个indexfor (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();//如果是相同的ThreadLocal对象,则将value值覆盖更新if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}//key为null,表示ThreadLocal对象已经被GC回收 (虚引用)if (k == null) {//替换待清除的entry,并清除历史key = null 的垃圾数据replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}//没有找到 创建新的entry 插入到i的索引位置tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);//插入完entry后,最新的table数组长度int sz = ++size;//如果超过阈值,就需要rehashif (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)//对table数组和元素进行整理(扩容等操作)rehash();}/*** Remove the entry for key.*/private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {//调用entry的clear方法 这里是其父类 抽象类Reference的方法//将弱引用的对象置null,有利于GC回收内存e.clear();//清除陈旧数据expungeStaleEntry(i);return;}}}/*** Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation* with an entry for the specified key. The value passed in* the value parameter is stored in the entry, whether or not* an entry already exists for the specified key.** As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries* between two null slots.)** @param key the key* @param value the value to be associated with key* @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while* searching for key.* 替换待清除的entry*/private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;Entry e;// Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run.// We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual// incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing// up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs).//以slotToExpunge为中轴,向左遍历到的第一个空位置和向右遍历遇到的第一个空位置 之间,// 最左的第一个为旧的entry的下标int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;//从staleSlot位置向前遍历,将旧的entry空间释放//如果所有的槽位都被占满了,一直循环,直到有空的位置for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = prevIndex(i, len))//空位置if (e.get() == null)slotToExpunge = i;// Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever// occurs first//从staleSlot位置向后遍历,//遇到与key相同的entry时,执行清除操作,返回,不再继续遍历for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();// If we find key, then we need to swap it// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.//找到相同的key,替换旧的值并且和前面那个过期的对象进行位置交换if (k == key) {e.value = value;tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];tab[staleSlot] = e;// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists//向左遍历没有找到旧的entry,将staleSlot位置的entry作为旧的//向右遍历已经与旧的对象进行位置交换,待清理的位置为iif (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;//清理旧数据cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);return;}// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the// first still present in the run.//slotToExpunge == staleSlot 向左遍历找到了空位置,那么会在向右遍历过程中寻找旧的entryif (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;}// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot//将staleSlot位置的entry的value设置为GC可回收,tab[staleSlot].value = null;//在staleSlot位置创建一个新的entrytab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them//如果有过期的对象,进行清理if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);}/*** Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See* Knuth, Section 6.4** @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked* for expunging).* 清除陈旧的entry*/private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// expunge entry at staleSlot//设置下标staleSlot对应的entry可被GC回收//置空valuetab[staleSlot].value = null;//置空entrytab[staleSlot] = null;//数组元素减1size--;// Rehash until we encounter null//遍历指定删除节点的后续节点Entry e;int i;for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();//key为null,清除对应槽位的元素 size减1if (k == null) {e.value = null;tab[i] = null;size--;} else {//key不为null,后面的元素向前移动,重新获得下标int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);if (h != i) {//如果不在同一个位置,位置发生了改变,就将原来的旧位置entry = nulltab[i] = null;// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until// null because multiple entries could have been stale.while (tab[h] != null)//如果新的下标所在位置不为空,则从h开始往后遍历,直到找到空节点,插入h = nextIndex(h, len);tab[h] = e;}}}return i;}/*** Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entries.* This is invoked when either a new element is added, or* another stale one has been expunged. It performs a* logarithmic number of scans, as a balance between no* scanning (fast but retains garbage) and a number of scans* proportional to number of elements, that would find all* garbage but would cause some insertions to take O(n) time.** @param i a position known NOT to hold a stale entry. The* scan starts at the element after i.** @param n scan control: {@code log2(n)} cells are scanned,* unless a stale entry is found, in which case* {@code log2(table.length)-1} additional cells are scanned.* When called from insertions, this parameter is the number* of elements, but when from replaceStaleEntry, it is the* table length. (Note: all this could be changed to be either* more or less aggressive by weighting n instead of just* using straight log n. But this version is simple, fast, and* seems to work well.)** @return true if any stale entries have been removed.* 旧的entry是否已被清除*/private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {boolean removed = false;Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;do {i = nextIndex(i, len);Entry e = tab[i];if (e != null && e.get() == null) {n = len;removed = true;i = expungeStaleEntry(i);}//n=n/2} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);return removed;}/*** Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire* table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently* shrink the size of the table, double the table size.* 对table数组和元素进行整理*/private void rehash() {//清除表中的陈旧数据expungeStaleEntries();// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis//清理完陈旧数据,如果仍然大于阈值的3/4,就执行扩容,if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)//扩容resize();}/*** Double the capacity of the table.* 扩容 将table扩容2倍,并把老数据重新哈希散列进新的table*/private void resize() {Entry[] oldTab = table;int oldLen = oldTab.length;//扩容后的数组 2倍int newLen = oldLen * 2;Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];int count = 0;//遍历旧的entry数组for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {Entry e = oldTab[j];if (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == null) {//如果key = null,将value也置为null,有助于GC回收,防止内存泄漏e.value = null; // Help the GC} else {//key不为空//重新hash计算旧entry在新的table数组中的位置int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);//如果该位置已经被其他entry占用,向右(后)查找空位 直到找到一个没有使用的位置while (newTab[h] != null)//h递增h = nextIndex(h, newLen);//在找到的第一个空节点塞入enewTab[h] = e;//计数++ 记录保存的元素个数count++;}}}//扩容后,设置新的table数组的阈值 newLen的2/3setThreshold(newLen);//设置ThreadLocalMap的元素个数size = count;//将新table赋值给ThreadLocalMap中的entry[] tabletable = newTab;}/*** Expunge all stale entries in the table.* 清除表中的陈旧条目*/private void expungeStaleEntries() {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//遍历for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {Entry e = tab[j];//entry不为空,但是entry的key为nullif (e != null && e.get() == null)//删除该下标对应的陈旧的entryexpungeStaleEntry(j);}}}
ThreadLocal、Thread、ThreadLocalMap、Entry之间的关系
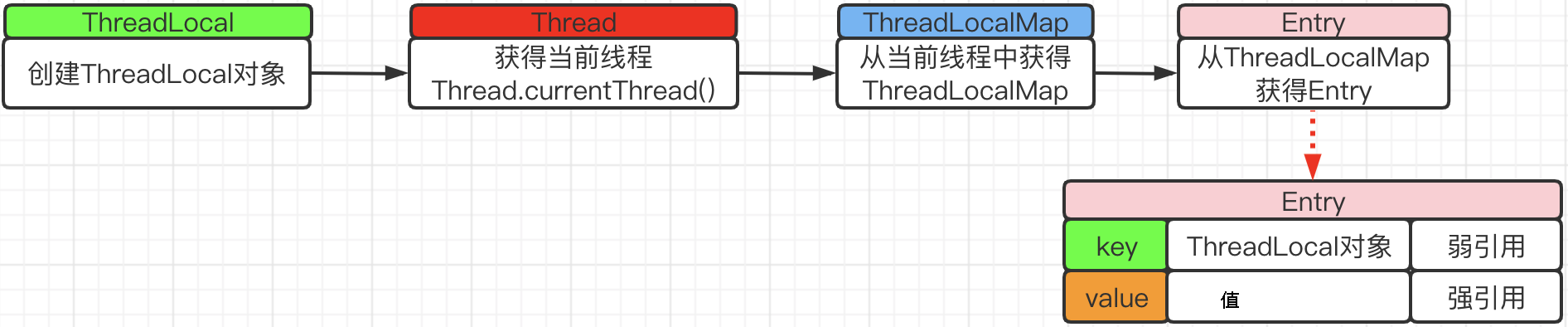
每个Thread线程都有一个ThreadLocal,
ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的一个静态内部类
ThreadLocalMap又有一个静态内部类Entry
threadLocalMap实际上有一个以threadLocal实例为key,任意缓存对象为value的Entry对象数组。
当我们为threadLocal变量赋值,实际上就是以当前threadLocal实例为key,值为value的Entry往这个threadLocalMap中存放
一个Thread最多只有一个ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap底层是一个Entry数组,
但是一个Thread可以有多个ThreadLocal,一个ThreadLocal对应一个变量数据,封装成Entry存到ThreadLocalMap中,所以就有多个Entry。
常用方法
get
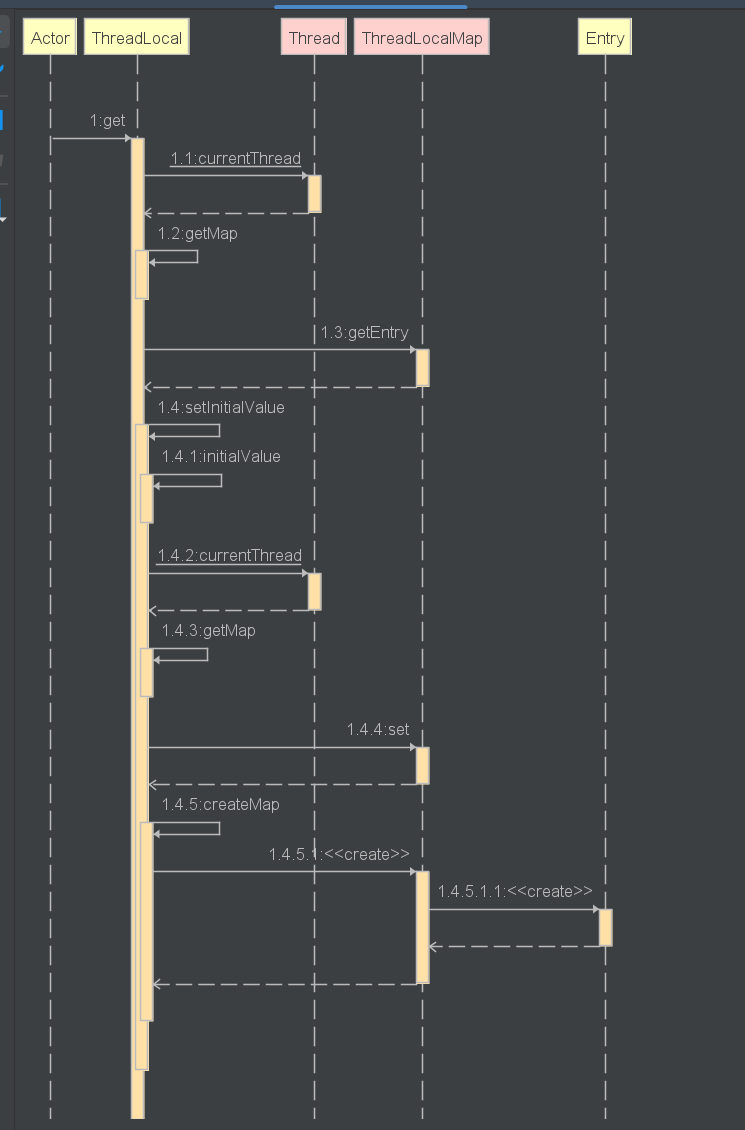
/*** Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.** @return the current thread's value of this thread-local*/public T get() {// 获得当前线程Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 从当前线程中获得ThreadLocalMap对象ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null) {// 获得对应entry对象ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")T result = (T)e.value;// 不为空,获取value正常返回return result;}}// 当ThreadLocalMap不存在时 说明还未初始化,初始化ThreadLocalMap并返回return setInitialValue();}
- 获取当前线程Thread对象,进而获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象。
- 判断当前的ThreadLocalMap是否存在,如果存在,则以当前的ThreadLocal 为 key,调用ThreadLocalMap中的getEntry方法获取对应的存储实体 e。找到对应的存储实体 e,获取存储实体 e 对应的 value值,即为我们想要的当前线程对应此ThreadLocal的值,返回结果值。
- 如果不存在,则证明此线程没有维护的ThreadLocalMap对象,调用setInitialValue方法进行初始化。返回setInitialValue初始化的值。
1.3getEntry
/*** Get the entry associated with key. This method* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part* by making this method readily inlinable.** @param key the thread local object* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {// 计算entry table索引int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);Entry e = table[i];if (e != null && e.get() == key)return e;else// 当entry的值不存在时return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);}
getEntryAfterMiss
/*** Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in* its direct hash slot.** @param key the thread local object* @param i the table index for key's hash code* @param e the entry at table[i]* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such*/private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;while (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == key)// 找到entryreturn e;if (k == null)// 移除过期条目expungeStaleEntry(i);else// 向下扫描i = nextIndex(i, len);e = tab[i];}return null;}
expungeStaleEntry
/*** Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See* Knuth, Section 6.4** @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked* for expunging).* 清除陈旧的entry*/private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;// expunge entry at staleSlot//设置下标staleSlot对应的entry可被GC回收//置空valuetab[staleSlot].value = null;//置空entrytab[staleSlot] = null;//数组元素减1size--;// Rehash until we encounter null//遍历指定删除节点的后续节点Entry e;int i;for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();//key为null,清除对应槽位的元素 size减1if (k == null) {e.value = null;tab[i] = null;size--;} else {//key不为null,后面的元素向前移动,重新获得下标int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);if (h != i) {//如果不在同一个位置,位置发生了改变,就将原来的旧位置entry = nulltab[i] = null;// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until// null because multiple entries could have been stale.while (tab[h] != null)//如果新的下标所在位置不为空,则从h开始往后遍历,直到找到空节点,插入h = nextIndex(h, len);tab[h] = e;}}}return i;}
1.4setInitialValue
/*** Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.** @return the initial value* 设置初始化值*/private T setInitialValue() {//该方法默认返回null,用户可以自定义T value = initialValue();Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null)//如果map不为null,设置初始值valuemap.set(this, value);else//如果map为null,则创建一个map,设置初始化valuecreateMap(t, value);return value;}
1.4.5createMap
/*** Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in* InheritableThreadLocal.** @param t the current thread* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map* 创建ThreadLocalMap并赋值*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}
ThreadLocalMap
/*** Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.* ThreadLocalMap构造函数*/ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {//table数组的默认大小 16table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];//插入数组的下标int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);//创建待插入的entry对象table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);//设置数组table中entry元素的个数为1size = 1;//设置数组table的阈值setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);}
setThreshold
/*** Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.* 阈值 = 容量 * 2/3 即负载因子为2/3*/private void setThreshold(int len) {threshold = len * 2 / 3;}
set
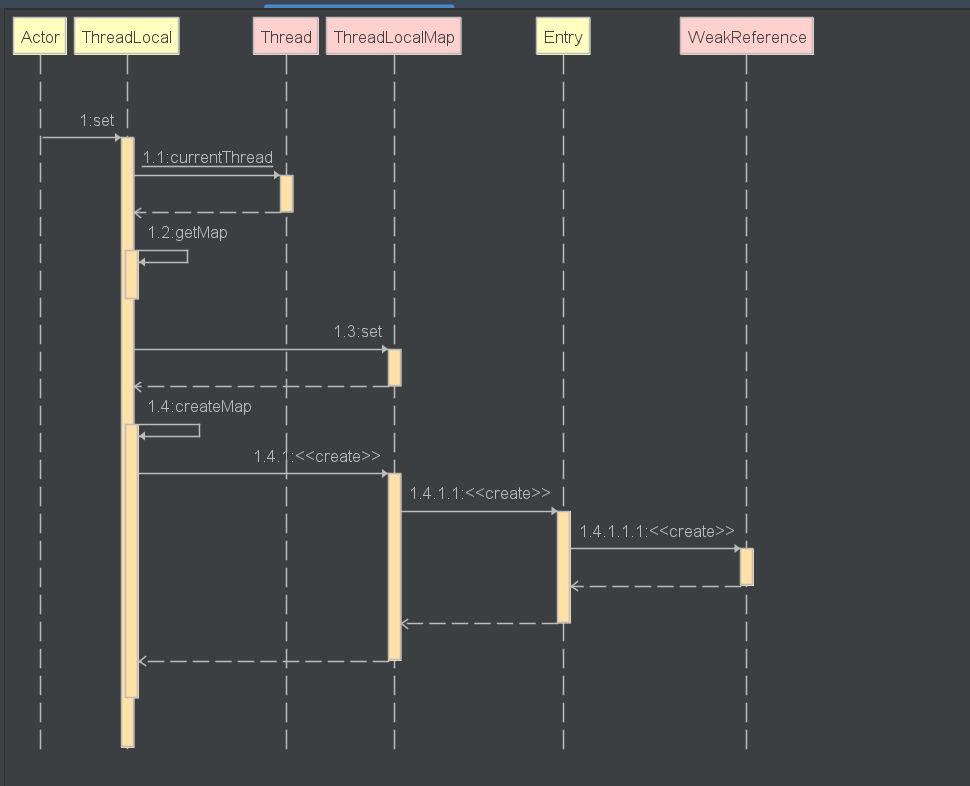
/*** Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}* method to set the values of thread-locals.** @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of* this thread-local.*/public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);if (map != null)//调用ThreadLocalMap的set方法 赋值map.set(this, value);else//map为空,创建新的ThreadLocalMapcreateMap(t, value);}
- 获取当前线程Thread对象,进而获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象。
- 判断当前的ThreadLocalMap是否存在:
- 如果存在,则调用map.set设置此实体entry。
- 如果不存在,则调用createMap进行ThreadLocalMap对象的初始化,并将此实体entry作为第一个值存放至ThreadLocalMap中。
1.3set
ThreadLocalMap.java
/*** Set the value associated with key.** @param key the thread local object* @param value the value to be set*/private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at// least as common to use set() to create new entries as// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast// path would fail more often than not.//table数组Entry[] tab = table;//table数组的长度int len = tab.length;//计算数组的下标 待插入entry的下标int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);//通过哈希码和数组长度找到数组下标,从i开始往后寻找相等的ThreadLocal对象,没有就下一个indexfor (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();//如果是相同的ThreadLocal对象,则将value值覆盖更新if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}//key为null,表示ThreadLocal对象已经被GC回收 (虚引用)if (k == null) {//替换待清除的entry,并清除历史key = null 的垃圾数据replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}//没有找到 创建新的entry 插入到i的索引位置tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);//插入完entry后,最新的table数组长度int sz = ++size;//如果超过阈值,就需要rehashif (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)//对table数组和元素进行整理(扩容等操作)rehash();}
replaceStaleEntry
/*** Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation* with an entry for the specified key. The value passed in* the value parameter is stored in the entry, whether or not* an entry already exists for the specified key.** As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries* between two null slots.)** @param key the key* @param value the value to be associated with key* @param staleSlot index of the first stale entry encountered while* searching for key.* 替换待清除的entry*/private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,int staleSlot) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;Entry e;// Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run.// We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual// incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing// up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs).//以slotToExpunge为中轴,向左遍历到的第一个空位置和向右遍历遇到的第一个空位置 之间,// 最左的第一个为旧的entry的下标int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;//从staleSlot位置向前遍历,将旧的entry空间释放//如果所有的槽位都被占满了,一直循环,直到有空的位置for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = prevIndex(i, len))//空位置if (e.get() == null)slotToExpunge = i;// Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever// occurs first//从staleSlot位置向后遍历,//遇到与key相同的entry时,执行清除操作,返回,不再继续遍历for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();// If we find key, then we need to swap it// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.//找到相同的key,替换旧的值并且和前面那个过期的对象进行位置交换if (k == key) {e.value = value;tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];tab[staleSlot] = e;// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists//向左遍历没有找到旧的entry,将staleSlot位置的entry作为旧的//向右遍历已经与旧的对象进行位置交换,待清理的位置为iif (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;//清理旧数据cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);return;}// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the// first still present in the run.//slotToExpunge == staleSlot 向左遍历找到了空位置,那么会在向右遍历过程中寻找旧的entryif (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)slotToExpunge = i;}// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot//将staleSlot位置的entry的value设置为GC可回收,tab[staleSlot].value = null;//在staleSlot位置创建一个新的entrytab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them//如果有过期的对象,进行清理if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);}
nextIndex和prevIndex
/*** Increment i modulo len.* 从指定的下标i开始,向后获取下一个位置的下标值*/private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);}/*** Decrement i modulo len.* 从指定的下标i开始,前向获取上一个位置的下标值。*/private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);}
cleanSomeSlots
/*** Heuristically scan some cells looking for stale entries.* This is invoked when either a new element is added, or* another stale one has been expunged. It performs a* logarithmic number of scans, as a balance between no* scanning (fast but retains garbage) and a number of scans* proportional to number of elements, that would find all* garbage but would cause some insertions to take O(n) time.** @param i a position known NOT to hold a stale entry. The* scan starts at the element after i.** @param n scan control: {@code log2(n)} cells are scanned,* unless a stale entry is found, in which case* {@code log2(table.length)-1} additional cells are scanned.* When called from insertions, this parameter is the number* of elements, but when from replaceStaleEntry, it is the* table length. (Note: all this could be changed to be either* more or less aggressive by weighting n instead of just* using straight log n. But this version is simple, fast, and* seems to work well.)** @return true if any stale entries have been removed.* 旧的entry是否已被清除*/private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {boolean removed = false;Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;do {i = nextIndex(i, len);Entry e = tab[i];if (e != null && e.get() == null) {n = len;removed = true;i = expungeStaleEntry(i);}//n=n/2} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);return removed;}
rehash
/*** Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire* table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently* shrink the size of the table, double the table size.* 对table数组和元素进行整理*/private void rehash() {//清除表中的陈旧数据expungeStaleEntries();// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis//清理完陈旧数据,如果仍然大于阈值的3/4,就执行扩容,if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)//扩容resize();}
expungeStaleEntries
/*** Expunge all stale entries in the table.* 清除表中的陈旧条目*/private void expungeStaleEntries() {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//遍历for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {Entry e = tab[j];//entry不为空,但是entry的key为nullif (e != null && e.get() == null)//删除该下标对应的陈旧的entryexpungeStaleEntry(j);}}
resize
/*** Double the capacity of the table.* 扩容 将table扩容2倍,并把老数据重新哈希散列进新的table*/private void resize() {Entry[] oldTab = table;int oldLen = oldTab.length;//扩容后的数组 2倍int newLen = oldLen * 2;Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];int count = 0;//遍历旧的entry数组for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {Entry e = oldTab[j];if (e != null) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();if (k == null) {//如果key = null,将value也置为null,有助于GC回收,防止内存泄漏e.value = null; // Help the GC} else {//key不为空//重新hash计算旧entry在新的table数组中的位置int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);//如果该位置已经被其他entry占用,向右(后)查找空位 直到找到一个没有使用的位置while (newTab[h] != null)//h递增h = nextIndex(h, newLen);//在找到的第一个空节点塞入enewTab[h] = e;//计数++ 记录保存的元素个数count++;}}}//扩容后,设置新的table数组的阈值 newLen的2/3setThreshold(newLen);//设置ThreadLocalMap的元素个数size = count;//将新table赋值给ThreadLocalMap中的entry[] tabletable = newTab;}
remove
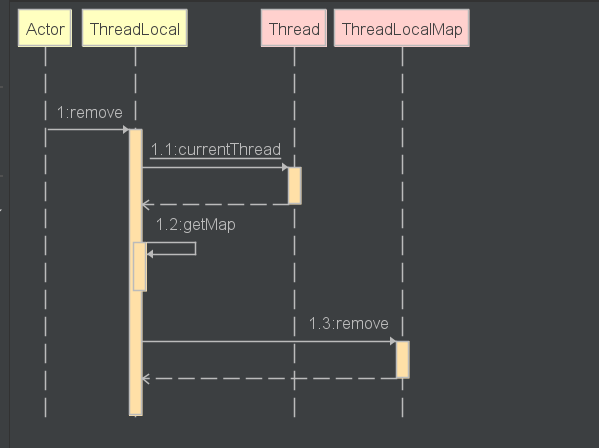
/*** Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.** @since 1.5*/public void remove() {ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());if (m != null)//调用ThreadLocalMap的remove删除m.remove(this);}
1.3remove
ThreadLocalMap.java
/*** Remove the entry for key.*/private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {//调用entry的clear方法 这里是其父类 抽象类Reference的方法//将弱引用的对象置null,有利于GC回收内存e.clear();//清除陈旧数据expungeStaleEntry(i);return;}}}
答疑
ThreadLocal内存泄漏问题
为什么会出现内存泄漏
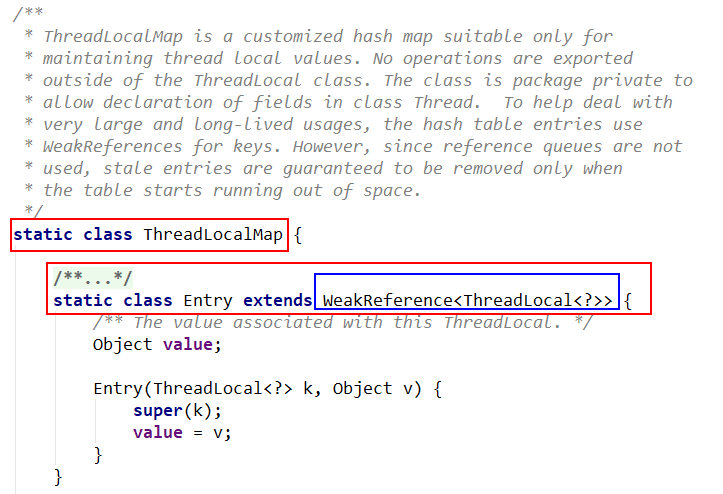
ThreadLocalMap从字面上就可以看出这是一个保存ThreadLocal对象的map(其实是以它为Key),不过是经过了两层包装的ThreadLocal对象:
(1)第一层包装是使用 WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> 将ThreadLocal对象变成一个弱引用的对象; (2)第二层包装是定义了一个专门的类 Entry 来扩展 WeakReference
每个Thread对象维护着一个ThreadLocalMap的强引用
ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的内部类,用Entry来进行存储
调用ThreadLocal的set()方法时,实际上就是往ThreadLocalMap设置值,key是ThreadLocal对象,值Value是传递进来的对象
调用ThreadLocal的get()方法时,实际上就是从ThreadLocalMap获取值,key是ThreadLocal对象
ThreadLocal本身并不存储值,它只是自己作为一个key来让线程从ThreadLocalMap获取value,正因为这个原理,所以ThreadLocal能够实现“数据隔离”,获取当前线程的局部变量值,不受其他线程影响
为什么要用弱引用?不用如何?
public void function01()
{ThreadLocal tl = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(); //line1tl.set(2021); //line2tl.get(); //line3
}line1新建了一个ThreadLocal对象,t1 是强引用指向这个对象;
line2调用set()方法后新建一个Entry,通过源码可知Entry对象里的k是弱引用指向这个对象。
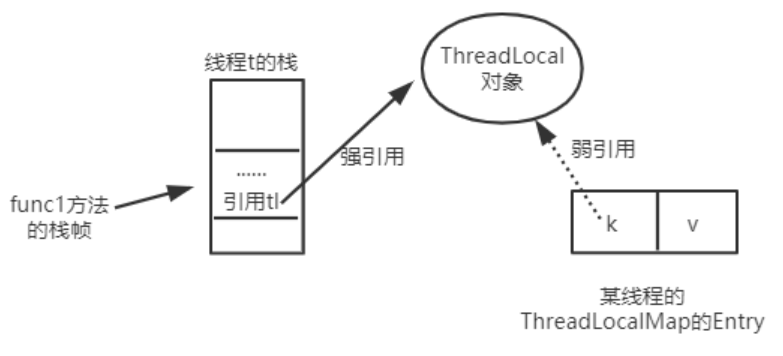
为什么源代码用弱引用?
当function01方法执行完毕后,栈帧销毁强引用 tl 也就没有了。但此时线程的ThreadLocalMap里某个entry的key引用还指向这个对象
若这个key引用是强引用,就会导致key指向的ThreadLocal对象及v指向的对象不能被gc回收,造成内存泄漏;
若这个key引用是弱引用就大概率会减少内存泄漏的问题(还有一个key为null的问题)。
使用弱引用,就可以使ThreadLocal对象在方法执行完毕后顺利被回收 ,此时Entry的key引用就指向为null。
因为map是允许存在空key的,那如何回收这些entry呢?
此后我们调用get,set或remove方法时,就会尝试删除key为null的entry,可以释放value对象所占用的内存。
总结
根据源码,我们可以发现 get,set或remove方法都可能触发清理方法expungeStaleEntry(),所以正常情况下是不会有内存泄漏的。
但是如果我们没有调用get和set的时候就会可能面临着内存泄漏。
退一步说,就算我们没有调用get和set和remove方法,线程结束的时候,也就没有强引用再指向ThreadLocal中的ThreadLocalMap了,这样ThreadLocalMap和里面的元素也会被回收掉。
但是有一种危险是,如果线程是线程池的,在线程执行完代码的时候并没有结束,只是归还给线程池,这个时候ThreadLocalMap和里面的元素是不会回收掉的,可能导致内存泄漏。
养成好习惯在使用的时候调用remove(),加快垃圾回收,避免内存泄漏。
参考: ThreadLocal源码
github:ThreadLocal源码
相关文章:

ThreadLocal源码
介绍 ThreadLocal是一个线程的本地变量,也就意味着这个变量是线程独有的,是不能与其他线程共享的。这样就可以避免资源竞争带来的多线程的问题。 但是,这种解决多线程安全问题的方式和加锁方式(synchronized、Lock) 是有本质的区…...
数据操作、查询)
Hive学习---3、DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据操作、查询
1、DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据操作 1.1 Load load语句可将文件导入到Hive表中 1、语法 load data [local] inpath filepath [overwrite] into table tablename [partition(partcol1val1,partcol2val2...)]2、关键字说明 (1&…...

chatgpt赋能python:Python去除重复元素的几种方法
Python去除重复元素的几种方法 在Python编程中,去除列表、集合、字典等数据结构中的重复元素是一个常见的操作。本文将介绍Python中去除重复元素的几种方法,并分析它们的优缺点。 方法一:使用set去重 Set是Python中的一种集合类数据结构&a…...
2年测试我迷茫了,软件测试大佬都会哪些技能?我的测试进阶之路...
目录:导读 前言一、Python编程入门到精通二、接口自动化项目实战三、Web自动化项目实战四、App自动化项目实战五、一线大厂简历六、测试开发DevOps体系七、常用自动化测试工具八、JMeter性能测试九、总结(尾部小惊喜) 前言 Python自动化测试&…...
21天学会C++:Day7----auto关键字
CSDN的uu们,大家好。这里是C入门的第七讲。 座右铭:前路坎坷,披荆斩棘,扶摇直上。 博客主页: 姬如祎 收录专栏:C专题 目录 1. 知识引入 2. auto的使用 2.1 auto与指针和引用结合起来使用 2.2 在同一…...

Vue3 + ElementPlus实战学习——模拟简单的联系人列表管理后台
文章目录 📋前言🎯demo 介绍🎯功能分析🧩数据的展示与分页功能🧩编辑功能🧩删除功能 🎯部分代码分析🎯完整代码📝最后 📋前言 这篇文章介绍一下基于 Vue3 和…...
【Go语言从入门到实战】并发篇
Go语言从入门到实战 — 并发篇 协程 Thread vs Groutine 相比之下,协程的栈大小就小很多了,创建起来也会更快,也更节省系统资源。 一个 goroutine 的栈,和操作系统线程一样,会保存其活跃或挂起的函数调用的本地变量…...
)
img标签请求 添加自定义header(二)
之前写过一篇关于img添加自定义请求头的处理方式(点击这里),那么本篇我们来看另外几种实现方法。 自定义指令 以Vue为例,我们可以定义一个全局指令,对img标签进行一些处理。 <template><img :src"src…...

Set和weakSet Map和WeakMap
Set和weakSet的用法和区别 1.Set 和weakSet 它是类似于数组,且成员值都是唯一的, 2.Set有 add has delete clear size keys values forEach entries 3.weakSet 有add has delete 4.WeakSet中只能存放对象类型,不能存放基本类型 5.WeakSet它是…...

Qt基础之三十六:异常处理
本文将介绍如何在Qt中使用try...catch和调试dump文件来处理异常。 Qt版本5.12.6 一.使用try...catch 一段简单的捕获异常的代码,新建一个控制台工程,pro文件不用修改 #include <QCoreApplication> #include <QDebug>int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {QCoreA…...

【HMS Core】【ML Kit】活体检测FAQ合集
【问题描述1】 使用示例代码集成活体检测SDK时,报错state code -7001 【解决方案】 使用示例代码前请详细阅读示例工程中的“README”文件。您需要完成以下操作后才可以运行示例代码。 在AppGallery Connect网站下载自己应用的“agconnect-services.json”文件&a…...

ChatGPT:使用OpenAI创建自己的AI网站,使用 flask web框架快速搭建网站主体
使用OpenAI创建自己的AI网站 如果你还是一个OpenAI的小白,有OpenAI的账号,但想调用OpenAI的API搞一些有意思的事,那么这一系列的教程将仔细的为你讲解如何使用OpenAI的API制作属于自己的AI网站。 使用 flask web框架快速搭建网站主体 之前…...
后端(一):Tomcat
我们之前的前端是被我们一笔带过的,那不是我们要讲的重点,而这里的后端则是重点。本章先来认识认识后端的基础。 Tomcat 是什么 我们先来聊聊什么叫做tomcat,我们熟悉的那个是汤姆猫: 这和我们Java世界中的Tomcat 不是同一只猫&…...
)
华为OD机试之最小调整顺序次数、特异性双端队列(Java源码)
最小调整顺序次数、特异性双端队列 题目描述 有一个特异性的双端队列,该队列可以从头部或尾部添加数据,但是只能从头部移出数据。 小A依次执行2n个指令往队列中添加数据和移出数据。其中n个指令是添加数据(可能从头部添加、也可能从尾部添加…...

2023年武汉住建厅七大员怎么报名?报名流程?精准题库一次过??
2023年武汉住建厅七大员怎么报名?报名流程?精准题库一次过?? 2023年武汉住建厅七大员是指施工员、质量员、资料员、材料员、机械员、标准员、劳务员,报的最多的可能就是施工员,质量员和资料员 报名流程: 1…...

Rust每日一练(Leetday0014) 组合总和II、缺失正数、接雨水
目录 40. 组合总和 II Combination Sum II 🌟🌟 41. 缺失的第一个正数 First Missing Positive 🌟🌟🌟 42. 接雨水 Trapping Rain Water 🌟🌟🌟 🌟 每日一练刷题…...
EnjoyVIID部署
1、下载 git clone https://gitee.com/tsingeye/EnjoyVIID.git 2、导入数据库 创建表enjoyviid 导入数据库(修改数据库文件里的编码) EnjoyVIID/sql/tsingeye-viid.sql 3、修改配置 vim EnjoyVIID/tsingeye-admin/src/main/resources/application-dev.yml 修改数据库连接、re…...

用Python解决爱因斯坦的数学问题
1 问题 有一条阶梯,若每步跨2阶,则剩最后一阶,若每步跨3阶,则最后剩2阶,若每步跨5阶,则最后剩4阶,若每步跨6阶,则最后剩5阶,只有每次跨7阶,最后才刚好不剩&am…...

ChatGPT提示词攻略之基本原则
下面是调用openai的completion接口的函数。但在本文中并不是重点。了解一下就好。 import openai import osfrom dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv _ load_dotenv(find_dotenv())openai.api_key os.getenv(OPENAI_API_KEY)def get_completion(prompt, model"gp…...
抖音seo源码如何开发部署?
前言:抖音seo源码,抖音矩阵系统源码搭建,抖音矩阵同步分发。抖音seo源码部署是需要对接到这些正规接口再来做开发的,目前账号矩阵程序开发的功能,围绕一键管理多个账号,做到定时投放,关键词自动…...

利用最小二乘法找圆心和半径
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #include <Eigen/Dense> // 需安装Eigen库用于矩阵运算 // 定义点结构 struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x_, double y_) : x(x_), y(y_) {} }; // 最小二乘法求圆心和半径 …...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...
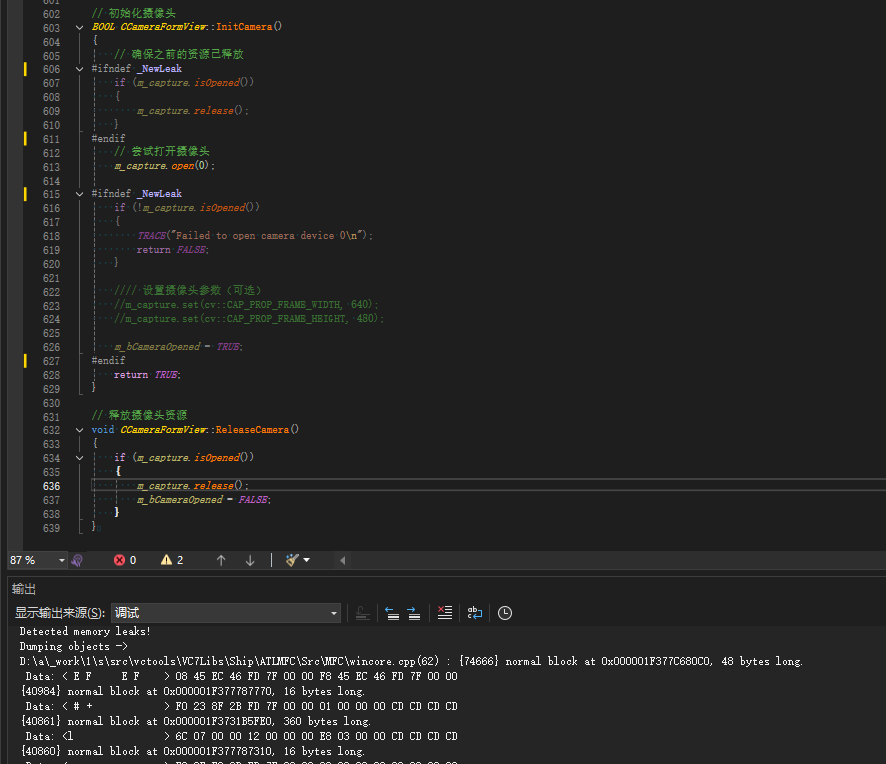
MFC内存泄露
1、泄露代码示例 void X::SetApplicationBtn() {CMFCRibbonApplicationButton* pBtn GetApplicationButton();// 获取 Ribbon Bar 指针// 创建自定义按钮CCustomRibbonAppButton* pCustomButton new CCustomRibbonAppButton();pCustomButton->SetImage(IDB_BITMAP_Jdp26)…...
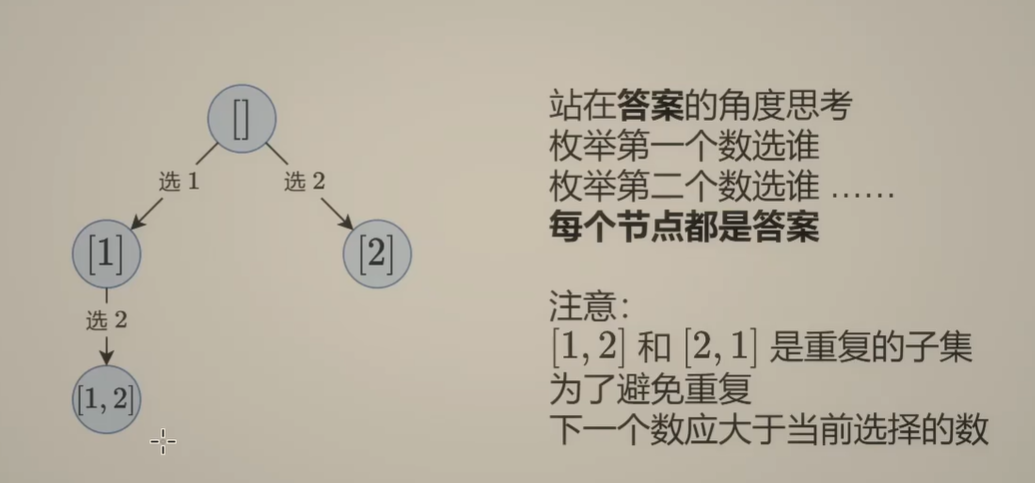
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集
Day131 | 灵神 | 回溯算法 | 子集型 子集 78.子集 78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路: 笔者写过很多次这道题了,不想写题解了,大家看灵神讲解吧 回溯算法套路①子集型回溯【基础算法精讲 14】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 完…...

java 实现excel文件转pdf | 无水印 | 无限制
文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 1.项目远程仓库配置 2.pom文件引入相关依赖 3.代码破解 二、Excel转PDF 1.代码实现 2.Aspose.License.xml 授权文件 总结 前言 java处理excel转pdf一直没找到什么好用的免费jar包工具,自己手写的难度,恐怕高级程序员花费一年的事件,也…...

电脑插入多块移动硬盘后经常出现卡顿和蓝屏
当电脑在插入多块移动硬盘后频繁出现卡顿和蓝屏问题时,可能涉及硬件资源冲突、驱动兼容性、供电不足或系统设置等多方面原因。以下是逐步排查和解决方案: 1. 检查电源供电问题 问题原因:多块移动硬盘同时运行可能导致USB接口供电不足&#x…...

vue3 字体颜色设置的多种方式
在Vue 3中设置字体颜色可以通过多种方式实现,这取决于你是想在组件内部直接设置,还是在CSS/SCSS/LESS等样式文件中定义。以下是几种常见的方法: 1. 内联样式 你可以直接在模板中使用style绑定来设置字体颜色。 <template><div :s…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...

论文浅尝 | 基于判别指令微调生成式大语言模型的知识图谱补全方法(ISWC2024)
笔记整理:刘治强,浙江大学硕士生,研究方向为知识图谱表示学习,大语言模型 论文链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2407.16127 发表会议:ISWC 2024 1. 动机 传统的知识图谱补全(KGC)模型通过…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...
