高性能JSON框架之FastJson的简单使用
高性能JSON框架之FastJson的简单使用、
1.前言
1.1.FastJson的介绍:
JSON协议使用方便,越来越流行,JSON的处理器有很多,这里我介绍一下FastJson,FastJson是阿里的开源框架,被不少企业使用,是一个极其优秀的Json框架,Github地址: FastJson
1.2.FastJson的特点:
1.FastJson数度快,无论序列化和反序列化,都是当之无愧的fast
2.功能强大(支持普通JDK类包括任意Java Bean Class、Collection、Map、Date或enum)
3.零依赖(没有依赖其它任何类库)
1.3.FastJson的简单说明:
FastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了下面三个类:
1.JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换
2.JSONObject:fastJson提供的json对象
3.JSONArray:fastJson提供json数组对象
2.FastJson的用法
首先定义三个json格式的字符串
//json字符串-简单对象型
private static final String JSON_OBJ_STR = "{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12}";//json字符串-数组类型
private static final String JSON_ARRAY_STR = "[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]";//复杂格式json字符串
private static final String COMPLEX_JSON_STR = "{\"teacherName\":\"crystall\",\"teacherAge\":27,\"course\":{\"courseName\":\"english\",\"code\":1270},\"students\":[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]}";
2.1.JSON格式字符串与JSON对象之间的转换
2.1.1.json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换
/*** json字符串-简单对象型到JSONObject的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONStrToJSONObject() {JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));}/*** JSONObject到json字符串-简单对象型的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONObjectToJSONStr() {//已知JSONObject,目标要转换为json字符串JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);// 第一种方式String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(jsonObject);// 第二种方式//String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();System.out.println(jsonString);
}
2.1.2.json字符串(数组类型)与JSONArray之间的转换
/*** json字符串-数组类型到JSONArray的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONStrToJSONArray() {JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//遍历方式1int size = jsonArray.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));}//遍历方式2for (Object obj : jsonArray) {JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj;System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));}
}/*** JSONArray到json字符串-数组类型的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONArrayToJSONStr() {//已知JSONArray,目标要转换为json字符串JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//第一种方式String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(jsonArray);// 第二种方式//String jsonString = jsonArray.toJSONString(jsonArray);System.out.println(jsonString);
}
2.1.3.复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换
/*** 复杂json格式字符串到JSONObject的转换*/
@Test
public void testComplexJSONStrToJSONObject() {JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);String teacherName = jsonObject.getString("teacherName");Integer teacherAge = jsonObject.getInteger("teacherAge");System.out.println("teacherName: " + teacherName + " teacherAge: " + teacherAge);JSONObject jsonObjectcourse = jsonObject.getJSONObject("course");//获取JSONObject中的数据String courseName = jsonObjectcourse.getString("courseName");Integer code = jsonObjectcourse.getInteger("code");System.out.println("courseName: " + courseName + " code: " + code);JSONArray jsonArraystudents = jsonObject.getJSONArray("students");//遍历JSONArrayfor (Object object : jsonArraystudents) {JSONObject jsonObjectone = (JSONObject) object;String studentName = jsonObjectone.getString("studentName");Integer studentAge = jsonObjectone.getInteger("studentAge");System.out.println("studentName: " + studentName + " studentAge: " + studentAge);}
}/*** 复杂JSONObject到json格式字符串的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONObjectToComplexJSONStr() {//复杂JSONObject,目标要转换为json字符串JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);//第一种方式//String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(jsonObject);//第二种方式String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();System.out.println(jsonString);}
2.2.JSON格式字符串与javaBean之间的转换
2.2.1.json字符串-简单对象型与javaBean之间的转换
/*** json字符串-简单对象到JavaBean之间的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONStrToJavaBeanObj() {//第一种方式JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);String studentName = jsonObject.getString("studentName");Integer studentAge = jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge");//Student student = new Student(studentName, studentAge);//第二种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类//Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {});//第三种方式,使用Gson的思想Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, Student.class);System.out.println(student);
}/*** JavaBean到json字符串-简单对象的转换*/
@Test
public void testJavaBeanObjToJSONStr() {Student student = new Student("lily", 12);String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(student);System.out.println(jsonString);
}
2.2.2.json字符串-数组类型与javaBean之间的转换
/*** json字符串-数组类型到JavaBean_List的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONStrToJavaBeanList() {//第一种方式JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//遍历JSONArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();Student student = null;for (Object object : jsonArray) {JSONObject jsonObjectone = (JSONObject) object;String studentName = jsonObjectone.getString("studentName");Integer studentAge = jsonObjectone.getInteger("studentAge");student = new Student(studentName,studentAge);students.add(student);}System.out.println("students: " + students);//第二种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类List<Student> studentList = JSONArray.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});System.out.println("studentList: " + studentList);//第三种方式,使用Gson的思想List<Student> studentList1 = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR, Student.class);System.out.println("studentList1: " + studentList1);}/*** JavaBean_List到json字符串-数组类型的转换*/
@Test
public void testJavaBeanListToJSONStr() {Student student = new Student("lily", 12);Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();students.add(student);students.add(studenttwo);String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(students);System.out.println(jsonString);}
2.2.3.复杂json格式字符串与与javaBean之间的转换
/*** 复杂json格式字符串到JavaBean_obj的转换*/
@Test
public void testComplexJSONStrToJavaBean(){//第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类Teacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});System.out.println(teacher);//第二种方式,使用Gson思想Teacher teacher1 = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, Teacher.class);System.out.println(teacher1);
}/*** 复杂JavaBean_obj到json格式字符串的转换*/
@Test
public void testJavaBeanToComplexJSONStr(){//已知复杂JavaBean_objTeacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(teacher);System.out.println(jsonString);
}
2.3.javaBean与json对象间的之间的转换
2.3.1.简单javaBean与json对象之间的转换
/*** 简单JavaBean_obj到json对象的转换*/
@Test
public void testJavaBeanToJSONObject(){//已知简单JavaBean_objStudent student = new Student("lily", 12);//方式一String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(student);JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);System.out.println(jsonObject);//方式二JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSONObject.toJSON(student);System.out.println(jsonObject1);
}/*** 简单json对象到JavaBean_obj的转换*/
@Test
public void testJSONObjectToJavaBean(){//已知简单json对象JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);//第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<Student>() {});System.out.println(student);//第二种方式,使用Gson的思想Student student1 = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), Student.class);System.out.println(student1);
}
2.3.2.JavaList与JsonArray之间的转换
/*** JavaList到JsonArray的转换*/
@Test
public void testJavaListToJsonArray() {//已知JavaListStudent student = new Student("lily", 12);Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();students.add(student);students.add(studenttwo);//方式一String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(students);JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonString);System.out.println(jsonArray);//方式二JSONArray jsonArray1 = (JSONArray) JSONArray.toJSON(students);System.out.println(jsonArray1);
}/*** JsonArray到JavaList的转换*/
@Test
public void testJsonArrayToJavaList() {//已知JsonArrayJSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类ArrayList<Student> students = JSONArray.parseObject(jsonArray.toJSONString(),new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});System.out.println(students);//第二种方式,使用Gson的思想List<Student> students1 = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonArray.toJSONString(), Student.class);System.out.println(students1);
}
2.3.3.复杂JavaBean_obj与json对象之间的转换
/*** 复杂JavaBean_obj到json对象的转换*/
@Test
public void testComplexJavaBeanToJSONObject() {//已知复杂JavaBean_objStudent student = new Student("lily", 12);Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();students.add(student);students.add(studenttwo);Course course = new Course("english", 1270);Teacher teacher = new Teacher("crystall", 27, course, students);//方式一String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(teacher);JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);System.out.println(jsonObject);//方式二JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSONObject.toJSON(teacher);System.out.println(jsonObject1);}/*** 复杂json对象到JavaBean_obj的转换*/
@Test
public void testComplexJSONObjectToJavaBean() {//已知复杂json对象JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);//第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类Teacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});System.out.println(teacher);//第二种方式,使用Gson的思想Teacher teacher1 = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), Teacher.class);System.out.println(teacher1);
}
相关文章:

高性能JSON框架之FastJson的简单使用
高性能JSON框架之FastJson的简单使用、 1.前言 1.1.FastJson的介绍: JSON协议使用方便,越来越流行,JSON的处理器有很多,这里我介绍一下FastJson,FastJson是阿里的开源框架,被不少企业使用,是一个极其优秀的Json框架,Github地址: FastJson 1.2.FastJson的特点: 1.F…...
)
★判断素数的几种方法(由易到难,由慢到快)
素数的定义: 素数,又称为质数,指的是“大于1的整数中,只能被1和这个数本身整除的数”。换句话说,素数是只有两个正约数(1和本身)的自然数。素数在数论中有着重要的地位,且素数的个数…...

vue svelte solid 虚拟滚动性能对比
前言 由于svelte solid 两大无虚拟DOM框架,由于其性能好,在前端越来越有影响力。 因此本次想要验证,这三个框架关于实现表格虚拟滚动的性能。 比较版本 vue3.4.21svelte4.2.12solid-js1.8.15 比较代码 这里使用了我的 stk-table-vue(np…...
IDEA中新增文件,弹出框提示是否添加到Git点错了,怎么重新设置?
打开一个配置了Git的项目,新增一个文件,会弹出下面这个框。提示是否将新增的文件交给Git管理。 一般来说,会选择ADD,并勾选Dont ask agin,添加并不再询问。如果不小心点错了,可在IDEA中重新设置(…...

LV15 day5 字符设备驱动读写操作实现
一、读操作实现 ssize_t xxx_read(struct file *filp, char __user *pbuf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos); 完成功能:读取设备产生的数据 参数: filp:指向open产生的struct file类型的对象,表示本次read对应的那次open pbuf&#…...
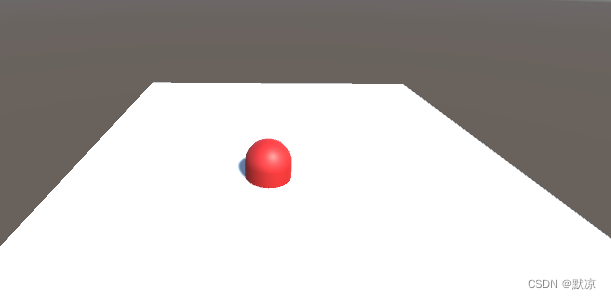
Uninty 鼠标点击(摄像机发出射线-检测位置)
平面来触发碰撞,胶囊用红色材质方便观察。 脚本挂载到胶囊上方便操作。 目前实现的功能,鼠标左键点击,胶囊就移动到那个位置上。 using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine;public class c6 : MonoBe…...

描述下Vue自定义指令
描述下Vue自定义指令 (1)自定义指令基本内容(2)使用场景(3)使用案例 在 Vue2.0 中,代码复用和抽象的主要形式是组件。然而,有的情况下,你仍然需要对普通 DOM 元素进行底层…...

2024.3.7
作业: 1、OSI的七层网络模型有哪些,每一层有什么作用? (1)应用层 负责处理不同应用程序之间的通信,需要满足提供的协议,确保数据发送方和接收方的正确 (2)表示层…...

this.$watch 侦听器 和 停止侦听器
使用组件实例的$watch()方法来命令式地创建一个侦听器; 它还允许你提前停止该侦听器 语法:this.$watch(data, method, object) 1. data:侦听的数据源,类型为String 2. method:回调函数&#x…...

P1030 [NOIP2001 普及组] 求先序排列题解
题目 给出一棵二叉树的中序与后序排列。求出它的先序排列。(约定树结点用不同的大写字母表示,且二叉树的节点个数≤8)。 输入输出格式 输入格式 共两行,均为大写字母组成的字符串,表示一棵二叉树的中序与后序排列。…...

【分布式】NCCL Split Tree kernel内实现情况 - 06
相关系列 【分布式】NCCL部署与测试 - 01 【分布式】入门级NCCL多机并行实践 - 02 【分布式】小白看Ring算法 - 03 【分布式】大模型分布式训练入门与实践 - 04 目录 相关系列概述1.1 Tree1.2 double binary tree初始化和拓扑2.1 Tree的初始化与差异2.2 ncclGetBtreeKernel内部…...
)
C语言深入学习 --- 4.自定义类型(结构体+枚举+联合)
第四章 自定义类型:结构体,枚举,联合 结构体 结构体类型的声明 结构的自引用 结构体变量的定义和初始化 结构体的内存对齐 结构体实现位段(位段的填充 和 可移植性) 枚举 枚举类型的定义 枚举的优点 枚举的使…...

AI自然语言中默认上下文长度4K 几K是什么意思?
环境: 4K 问题描述: AI自然语言中默认上下文长度4K 几K是什么意思? 解决方案: 在自然语言处理中,“k” 表示 “千”,是一种简写方式。当我们说 “4k” 时,实际上指的是 “4,000”。在上下文…...

vSphere 8考试认证题库 2024最新(VCP 8.0版本)
VMware VCP-DCV(2V0-21.23)认证考试题库,已全部更新,答案已经完成校对,完整题库请扫描上方二维码访问。正常考可以考到450分以上(满分500分,300分通过) An administrator is tasked …...

系统学习Python——装饰器:“私有“和“公有“属性案例-[装饰器参数、状态保持和外层作用域]
分类目录:《系统学习Python》总目录 文章《系统学习Python——装饰器:“私有“和“公有“属性案例-[实现私有属性]》中使用的类装饰器接受任意多个参数来命名私有属性。然而真正发生的情况是,参数传递给了Private函数,然后Private…...

星辰天合参与编制 国内首个可兼顾 AI 大模型训练的高性能计算存储标准正式发布
近日,在中国电子工业标准化技术协会高标委的支持和指导下,XSKY星辰天合作为核心成员参与编制的《高性能计算分布式存储系统技术要求》团体标准,在中国电子工业标准化技术协会网站正式发布。 该团体标准强调了分布式存储系统对包括传统高性能计…...

算法训练day38动态规划基础Leetcode509斐波纳切数70爬楼梯746使用最小花费爬楼梯
什么是动态规划 对于动态规划问题,我将拆解为如下五步曲,这五步都搞清楚了,才能说把动态规划真的掌握了! 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义确定递推公式dp数组如何初始化确定遍历顺序举例推导dp数组&a…...
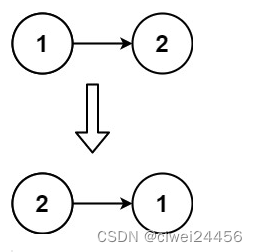
Leetcode 206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。 示例 1: 输入:head [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1] 示例 2: 输入:head [1,2] 输出:[2,1] 示例 3: 输…...

电子科技大学课程《计算机网络系统》(持续更新)
前言 本校的课程课时有所缩减,因此可能出现与你学习的课程有所减少的情况,因此对其他学校的同学更多的作为参考作用。本文章适合学生的期中期末考试,以及想要考研电子科技大学的同学,电子科技大学同学请先看附言。 第一章 计算…...

HBase介绍、特点、应用场景、生态圈
目录: 一、HBase简介 二、NoSQL和关系型数据库对比 三、HBase特点 四、应用场景 五、HBase生态圈技术 一、HBase简介 HBase是一个领先的NoSQL数据库 是一个面向列存储的NoSQL数据库 是一个分布式Hash Map,底层数据是Key-Value格式 基于Coogle Big Table论文 使用HD…...

Chapter03-Authentication vulnerabilities
文章目录 1. 身份验证简介1.1 What is authentication1.2 difference between authentication and authorization1.3 身份验证机制失效的原因1.4 身份验证机制失效的影响 2. 基于登录功能的漏洞2.1 密码爆破2.2 用户名枚举2.3 有缺陷的暴力破解防护2.3.1 如果用户登录尝试失败次…...

SCAU期末笔记 - 数据分析与数据挖掘题库解析
这门怎么题库答案不全啊日 来简单学一下子来 一、选择题(可多选) 将原始数据进行集成、变换、维度规约、数值规约是在以下哪个步骤的任务?(C) A. 频繁模式挖掘 B.分类和预测 C.数据预处理 D.数据流挖掘 A. 频繁模式挖掘:专注于发现数据中…...
【Java_EE】Spring MVC
目录 Spring Web MVC 编辑注解 RestController RequestMapping RequestParam RequestParam RequestBody PathVariable RequestPart 参数传递 注意事项 编辑参数重命名 RequestParam 编辑编辑传递集合 RequestParam 传递JSON数据 编辑RequestBody …...
Reasoning over Uncertain Text by Generative Large Language Models
https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829 1. 概述 文本中的不确定性在许多语境中传达,从日常对话到特定领域的文档(例如医学文档)(Heritage 2013;Landmark、Gulbrandsen 和 Svenevei…...

2025季度云服务器排行榜
在全球云服务器市场,各厂商的排名和地位并非一成不变,而是由其独特的优势、战略布局和市场适应性共同决定的。以下是根据2025年市场趋势,对主要云服务器厂商在排行榜中占据重要位置的原因和优势进行深度分析: 一、全球“三巨头”…...

AI+无人机如何守护濒危物种?YOLOv8实现95%精准识别
【导读】 野生动物监测在理解和保护生态系统中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,传统的野生动物观察方法往往耗时耗力、成本高昂且范围有限。无人机的出现为野生动物监测提供了有前景的替代方案,能够实现大范围覆盖并远程采集数据。尽管具备这些优势…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...

提升移动端网页调试效率:WebDebugX 与常见工具组合实践
在日常移动端开发中,网页调试始终是一个高频但又极具挑战的环节。尤其在面对 iOS 与 Android 的混合技术栈、各种设备差异化行为时,开发者迫切需要一套高效、可靠且跨平台的调试方案。过去,我们或多或少使用过 Chrome DevTools、Remote Debug…...
)
uniapp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息(地理位置/文件)
UniApp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息全攻略(地理位置/文件) 一、功能实现原理 腾讯云 IM 通过 消息扩展机制 支持富媒体类型,核心实现方式: 标准消息类型:直接使用 SDK 内置类型(文件、图片等)自…...
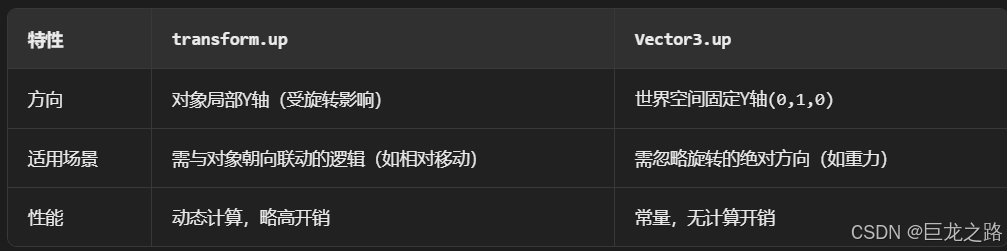
Unity中的transform.up
2025年6月8日,周日下午 在Unity中,transform.up是Transform组件的一个属性,表示游戏对象在世界空间中的“上”方向(Y轴正方向),且会随对象旋转动态变化。以下是关键点解析: 基本定义 transfor…...
