深入理解 LinkedList 及底层源码分析
LinkedList 是基于链表结构的一种 List,在分析 LinkedList 源码前我们先对对链表结构做一个简单的了解。
一、链表的概念
链表是由一系列非连续的节点组成的存储结构,简单分下类的话,链表又分为_单向链表和双向链表,而单向 / 双向链表又可以分为循环链表和非循环链表_,下面简单就这四种链表进行图解说明:
1、单向链表
单向链表就是通过每个结点的指针指向下一个结点从而链接起来的结构,最后一个节点的 next 指向 null。

2、单向循环链表
单向循环链表和单向列表的不同是,最后一个节点的 next 不是指向null,而是指向 head 节点,形成一个“环”。

3、双向链表
从名字就可以看出,双向链表是包含两个指针的,pre 指向前一个节点,next 指向后一个节点,但是第一个节点 head 的 pre 指向 null,最后一个节点的 tail 指向 null。

4、双向循环链表
双向循环链表和双向链表的不同在于,第一个节点的 pre 指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的 next 指向第一个节点,也形成一个“环”。
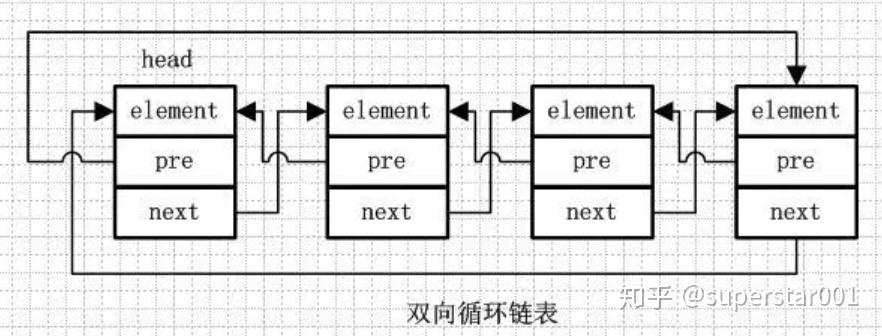
LinkedList 就是基于双向循环链表设计的。
**二、**LinkedList 介绍及其源码剖析
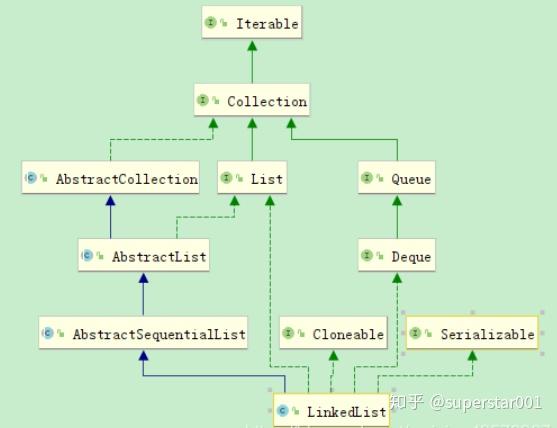
1、继承树结构:
2、LinkedList 定义
public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
LinkedList继承了 AbstractSequentialList 类,实现了 List 接口、Deque 接口、Cloneable 接口、java.io.Serializable 接口。LinkedList实现了 List 接口,即能对它进行队列操作,提供了相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。LinkedList实现了 Deque 接口,即能将 LinkedList 当作双端队列使用。LinkedList实现了 Cloneable 接口,即覆盖了函数 clone(),所以它能被克隆。LinkedList实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,这意味着 LinkedList 支持序列化,能通过序列化进行传输。
3、LinkedList 属性源码剖析
public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{// 双向链表的节点个数transient int size = 0;/*** Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */// 双向链表指向头节点的指针transient Node<E> first;/*** Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */// 双向链表指向尾节点的指针transient Node<E> last;}
从以上源码可以看出,LinkedList 的属性比较少,分别是:
- size : 双向链表的节点个数
- first: 双向链表指向头节点的指针
- last: 双向链表指向尾节点的指针
注意:first 和 last 是由引用类型 Node 连接的,这是它的一个内部类。
4、内部类 Node 源码剖析:
LinkedList 是通过双向链表实现的,而双向链表就是通过 Node 类来实现的,Node 类中通过 item 变量存储当前元素,通过 next 变量指向当前节点的下一个节点,通过 prev 变量指向当前节点的上一个节点。
private static class Node<E> {// item表示当前存储元素E item;// next表示当前节点的后置节点Node<E> next;// prev表示当前节点的前置节点Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}
}
三、构造方法及其源码剖析
1、无参构造方法
LinkedList 的无参构造就是**构造一个空的 list 集合**。
/*** Constructs an empty list. */
public LinkedList() {
}
2、有参构造方法
传入一个 Collection<? extends E> 类型参数,构造一个包含指定集合的元素的列表,按照它们由集合的迭代器返回的顺序。
/*** Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);
}
四、常用方法及其源码剖析
1、add(E e) 方法,将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */
public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;
}
其中,调用的 linkLast() 方法,设置元素 e 为最后一个元素:
/*** Links e as last element. */
void linkLast(E e) {// 获取链表的最后一个节点final Node<E> l = last;// 创建一个新节点final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);// 使新的一个节点为最后一个节点last = newNode;// 如果最后一个节点为null,则表示链表为空,则将newNode赋值给first节点if (l == null)first = newNode;else// 否则尾节点的last指向 newNodel.next = newNode;// 元素的个数加1size++;// 修改次数自增modCount++;
}
执行流程:
第一步,获取链表的最后一个节点;第二步,创建一个新节点;第三步,使新的一个节点为最后一个节点;第四步,如果最后一个节点为 null,则表示链表为空,则将 newNode 赋值给 first 节点;否则尾节点的 last 指向 newNode。
2、add(int index, E element) 方法,在指定位置插入元素
/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */
public void add(int index, E element) {// 检查索引index的位置checkPositionIndex(index);// 如果index==size,直接在链表的最后插入元素,相当于add(E e)方法if (index == size)linkLast(element);else// 否则调用node方法将index位置的节点找出,接着调用linkBefore 方法linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
执行流程:
首先检查索引 index 的位置,看下标是否越界;如果 index==size,直接在链表的最后插入元素,相当于 add(E e) 方法;否则调用 node 方法将 index 位置的节点找出,接着调用 linkBefore 方法。
其中,调用 checkPositionIndex() 方法,检查索引 index 的位置:
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {if (!isPositionIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
在增加元素的时候,调用了 linkBefore() 方法,在非 null 节点 succ 之前插入元素 e:
/*** Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. */
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;// 指定节点的前驱final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;// 创建新的节点,前驱节点为succ的前驱节点,后续节点为succ,则e元素就是插入在succ之前的final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);// 构建双向链表,succ的前驱节点为新的节点succ.prev = newNode;// 如果前驱节点为null,则把newNode赋值给firstif (pred == null)first = newNode;else// 构建双向列表pred.next = newNode;// 元素的个数加 size++;// 修改次数自增modCount++;
}
总结:
① 指定节点的前驱
② 创建新的节点,前驱节点为 succ 的前驱节点,后续节点为 succ,则 e 元素就是插入在 succ 之前的
③ 构建双向链表,succ 的前驱节点为新的节点
④ 如果前驱节点为 null,则把 newNode 赋值给 first;否则构建双向列表
3、remove() 方法删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)
/*** Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. * * @return the head of this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */
public E remove() {return removeFirst();
}
其中,调用了**removeFirst()** 方法,删除并返回第一个元素:
/*** Removes and returns the first element from this list. * * @return the first element from this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */
public E removeFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;if (f == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();return unlinkFirst(f);
}
4、remove(int index) 方法,删除指定位置的元素
/*** Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any * subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). * Returns the element that was removed from the list. * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */
public E remove(int index) {// 检查索引index的位置checkElementIndex(index);// 调用node方法获取节点,接着调用unlink(E e)方法 return unlink(node(index));
}
检查索引 index 的位置,调用 node 方法获取节点,接着调用 unlink(E e) 方法:
/*** Unlinks non-null node x. */
E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;// 获得节点的三个属性final E element = x.item;final Node<E> next = x.next;final Node<E> prev = x.prev;// 进行移除该元素之后的操作if (prev == null) {// 删除的是第一个元素first = next;} else {prev.next = next;x.prev = null;}if (next == null) {// 删除的是最后一个元素last = prev;} else {next.prev = prev;x.next = null;}// 把item置为null,让垃圾回收器回收x.item = null;// 移除一个节点,size自减size--;modCount++;return element;
}
**5、**set(int index, E element) 方法,将指定下标处的元素修改成指定值
/*** Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the * specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */
public E set(int index, E element) {checkElementIndex(index);// 通过node(int index)找到对应下标的元素Node<E> x = node(index);// 取出该节点的元素,供返回使用E oldVal = x.item;// 用新元素替换旧元素x.item = element;// 返回旧元素return oldVal;
}
执行流程:
先通过 node(int index) 找到对应下标的元素,然后修改 Node 中 item 的值。
**5、**get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) {// 检查索引index的位置checkElementIndex(index);// 调用node()方法return node(index).item;
}
在此调用了_node()_ 方法:
/*** Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */
// 这里查询使用的是先从中间分一半查找
Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);// 从前半部分进行查找if (index < (size >> 1)) {Node<E> x = first;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {// 从后半部分进行查找Node<E> x = last;for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}
}
总结:
这里查询使用的是先从中间分一半查找,根据下标是否超过链表长度的一半,来选择从前半部分开始遍历查找,还是从后半部分开始遍历查找:
① 如果 index 小于 size 的一半,就从首节点开始遍历,一直获取 x 的下一个节点
② 如果 index 大于或等于 size 的一半,就从尾节点开始遍历,一直获取 x 的上一个节点
五、双端队列操作方法的源码剖析
1、offerFirst(E e) 方法,将元素添加到首部
/*** Inserts the specified element at the front of this list. * * @param e the element to insert * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst}) * @since 1.6 */
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {addFirst(e);return true;
}
2、offerLast(E e) 方法,将元素添加到尾部
/*** Inserts the specified element at the end of this list. * * @param e the element to insert * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast}) * @since 1.6 */public boolean offerLast(E e) {addLast(e);return true;}
3、peekFirst() 方法,获取此集合列表的第一个元素值
/*** Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */public E peekFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : f.item;}
4、peekLast() 方法,获取此集合列表的最后一个元素值
/*** Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */
public E peekLast() {final Node<E> l = last;return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
5、pollFirst() 方法,删除此集合列表的第一个元素,如果为 null,则会返回 null
/*** Retrieves and removes the first element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if * this list is empty * @since 1.6 */
public E pollFirst() {final Node<E> f = first;return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
6、pollLast() 方法 ,删除此集合列表的最后一个元素,如果为 null 会返回 null
/*** Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if * this list is empty * @since 1.6 */public E pollLast() {final Node<E> l = last;return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);}
7、push(E e) 方法,将元素添加到此集合列表的首部
/*** Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other * words, inserts the element at the front of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}. * * @param e the element to push * @since 1.6 */public void push(E e) {addFirst(e);}
8、pop() 方法,删除并返回此集合列表的第一个元素,如果为null会抛出异常
/*** Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other * words, removes and returns the first element of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}. * * @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top * of the stack represented by this list) * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.6 *///删除首部,如果为null会抛出异常
public E pop() {return removeFirst();
}
9、removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)方法,删除集合中元素值等于o的第一个元素值
/*** Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element * @since 1.6 */
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {return remove(o);
}
注:removeFirstOccurrence() 和 remove 方法是一样的,它的内部调用了 remove 方法
10、removeLastOccurrence(Object o)方法,删除集合中元素值等于o的最后一个元素值
/*** Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element * @since 1.6 */
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {//因为LinkedList中的元素允许存在null值,所以需要进行null判断if (o == null) {// 从最后一个节点往前开始遍历for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {if (x.item == null) {// 调用unlink方法删除指定节点unlink(x);return true;}}} else {// 否则元素不为空,进行遍历for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;
}
六、ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别
1、二者线程都不安全,但是效率比 Vector 的高;
2、ArrayList 底层是以数组的形式保存数据,随机访问集合中的元素比 LinkedList 快(LinkedList 要移动指针);
3、LinkedList 内部以链表的形式保存集合里面数据,它随机访问集合中的元素性能比较慢,但是新增和删除时速度比 ArrayList 快(ArrayList 要移动数据)。
本文转自 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/210732993,如有侵权,请联系删除。
相关文章:

深入理解 LinkedList 及底层源码分析
LinkedList 是基于链表结构的一种 List,在分析 LinkedList 源码前我们先对对链表结构做一个简单的了解。 一、链表的概念 链表是由一系列非连续的节点组成的存储结构,简单分下类的话,链表又分为_单向链表和双向链表,而单向 / 双…...

美易官方:英伟达业绩将难以撑起股价?
美股市场似乎总是对各大公司的业绩表现抱有极大的期待,就像一个永远填不饱的“巨胃”。在这样的市场环境下,即使是业绩骄人的公司也可能难以支撑其股价。英伟达,这家在图形处理单元(GPU)领域享有盛誉的公司,…...

超实用干货!FP独立站引流攻略
在当前的市场环境下,对于希望继续从事FP和黑五类产品销售的商家来说,搭建独立站绝对是一个明智的选择。没有了第三方平台的限制,拥有自己的独立站意味着你可以完全掌控自己的商业策略和操作。 但脱离了平台,独立站推广会更加困难。…...

php之框架底层中间件模式开发实现、array_reduce的应用
众所周知php框架的中间件核心是通过array_reduce实现的 php之框架中间件模式开发实现、array_reduce的应用 1.先写个测试用例看一下函数的特性2.根据执行特性实现中间件 1.先写个测试用例看一下函数的特性 <?phpfunction kernal($a,$b){return $a . " and " .…...

fabric搭建生产网络
fabric搭建生产网络 一、生成组织结构与身份证书 解包 hyperledger-fabric-linux-amd64-2.5.0.tar.gz 1.1、crypto-config.yaml配置文件 ./bin/cryptogen showtemplate > crypto-config.yaml 将crypto-config.yaml内容修改为: # -------------------------…...

聊聊 ASP.NET Core 中间件(二):中间件和筛选器的区别
前言 有些小伙伴看到上一篇文章后,可能会发现中间件和我们之前讲的筛选器非常类似,比如它们都是通过 next 串起来的一系列的组件,并且都可以在请求处理前后执行代码,都可以通过不执行 next 来进行请求的终止。那么筛选器和中间件…...
Nginx配置Https缺少SSL模块
1、Linux下Nginx配置https nginx下载和安装此处就忽略,可自行百度 1.1、配置https 打开nginx配置文件 vim /opt/app/nginx/conf/nginx.conf相关https配置 server {listen 443 ssl; #开放端口server_name echarts.net;#域名#redirect to https#ssl on; #旧版#ssl证…...
超详细——集成学习——Adaboost实现多分类——附代码
资料参考 1.【集成学习】boosting与bagging_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 集成学习——boosting与bagging 强学习器:效果好,模型复杂 弱学习器:效果不是很好,模型简单 优点 集成学习通过将多个学习器进行结合,常可获得比单一…...
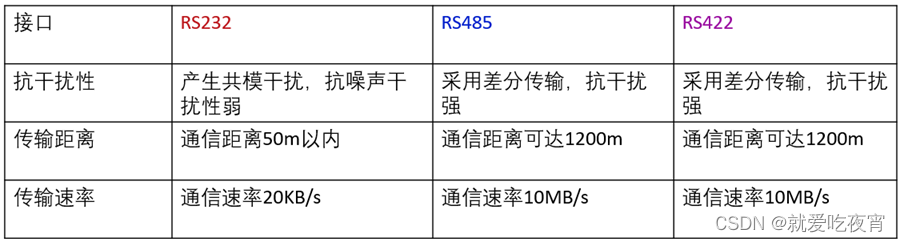
串口通信标准RS232 RS485 RS422的区别
很多工程师经常把RS-232、RS-422、RS-485称为通讯协议,其实这是不对的,它们仅仅是关于串口通讯的一个机械和电气接口标准(顶多是网络协议中的物理层),不是通讯协议,那它们又有哪些区别呢: 第一…...

jdk环境安装
jdk安装 创建软件安装的目录 mkdir -p /bigdata/{soft,server} /bigdata/soft 安装文件的存放目录 /bigdata/server 软件安装的目录 把安装的软件上传到/bigdata/soft 目录 解压到指定目录 -C :指定解压到指定目录 tar -zxvf /bigdata/soft/jdk-8u241-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /b…...
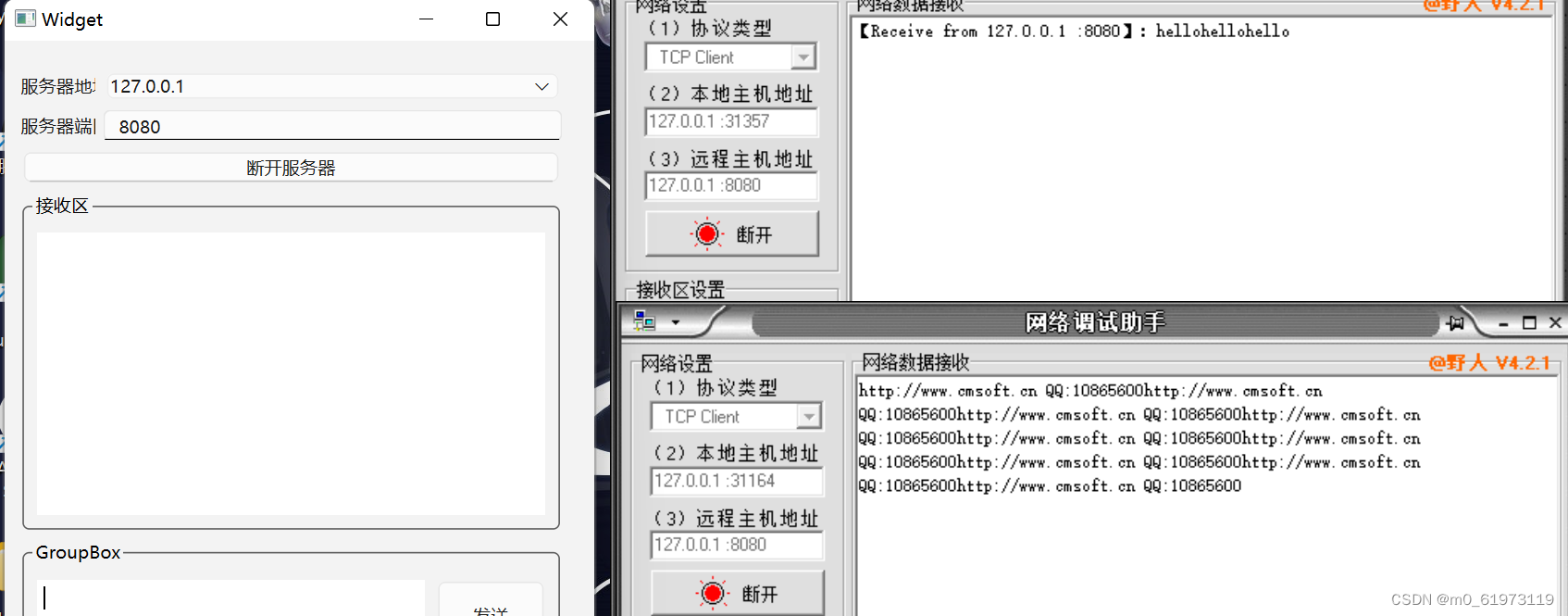
QT+网络调试助手+TCP服务器
一、UI界面设计 二、单线程 代码设计 1、 查找合法的本地地址,用于当作服务器的IP地址 #include <QThread> #include <QTcpSocket> #include <QNetworkInterface> #include <QMessageBox>QList<QHostAddress> ipAddressesList QNe…...
场景)
【unity】(1)场景
Unity的场景(Scene)是构建游戏中各种环境和级别的基础。一个场景可以包含游戏中的所有对象,如角色、道具、地形等。 创建和管理场景 创建新场景: 在Unity编辑器中,选择File > New Scene,或者使用快捷键…...

【Linux】进程间通信IPC机制
目录 一、无名管道 二、有名管道 三、共享内存 四、信号量 五、消息队列 六、套接字 一、无名管道 1.只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程之间的通信(也就是父子进程或者兄弟进程)。 2.是一个单工的通信模式,具有固定的读端和写端。 3.管道也可以看成是一种特殊的文件…...
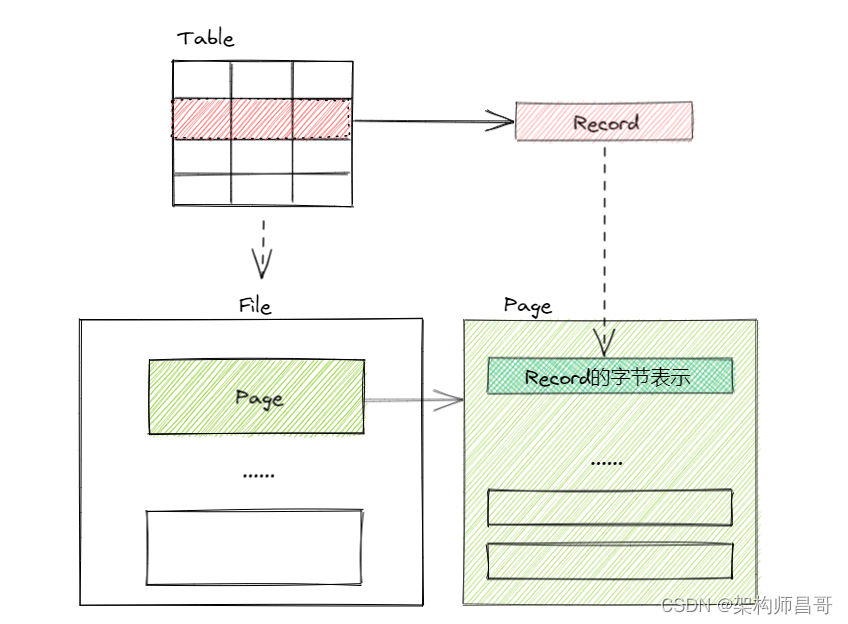
【如此简单!数据库入门系列】之效率基石 -- 磁盘空间管理
文章目录 1 前言2 磁盘空间管理3 磁盘空间管理的实现4 存储对象关系5 总结6 系列文章 1 前言 如何将表中的记录存储在物理磁盘上呢? 概念模式中,记录(Record)表示表中的一行数据,由多个列(字段或者属性&…...
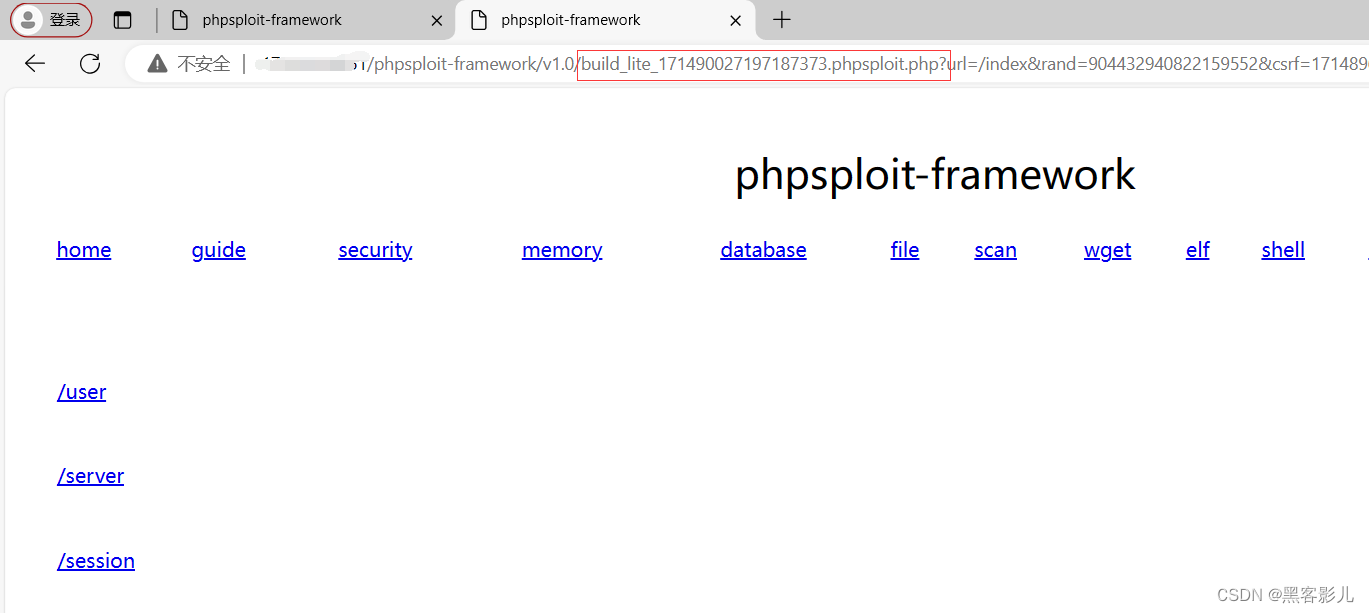
专业渗透测试 Phpsploit-Framework(PSF)框架软件小白入门教程(五)
本系列课程,将重点讲解Phpsploit-Framework框架软件的基础使用! 本文章仅提供学习,切勿将其用于不法手段! 继续接上一篇文章内容,讲述如何进行Phpsploit-Framework软件的基础使用和二次开发。 在下面的图片中&#…...
5月7日监控二叉树+斐波那契数
968.监控二叉树 给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。 节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。 计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。 示例 1: 输入:[0,0,null,0,0] 输出:1 解释ÿ…...

C++类的设计编程示例
一、银行账户类 【问题描述】 定义银行账户BankAccount类。 私有数据成员:余额balance(整型)。 公有成员方法: 无参构造方法BankAccount():将账户余额初始化为0; 带参构造方法BankAccount(int m)࿱…...
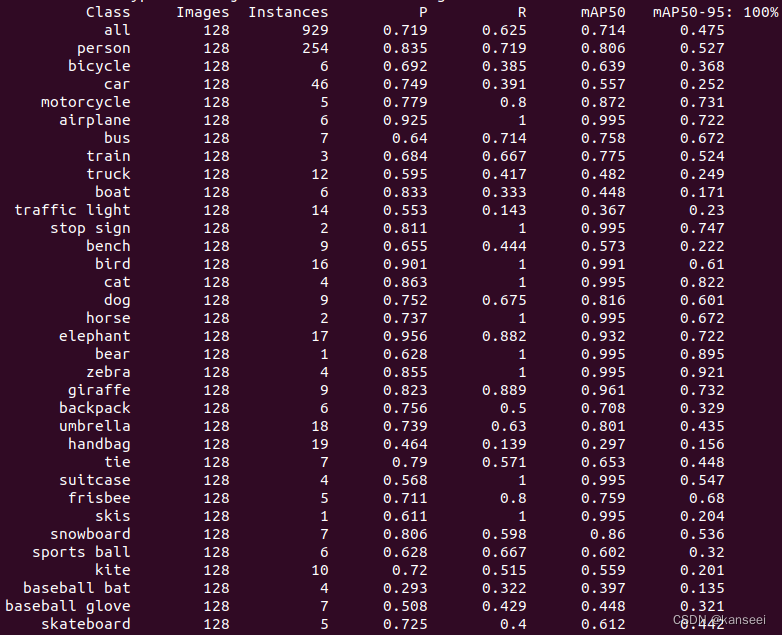
YOLOv5 V7.0 - rknn模型的验证 输出精度(P)、召回率(R)、mAP50、mAP50-95
1.简介 RKNN官方没有提供YOLOv5模型的验证工具,而YOLOv5自带的验证工具只能验证pytorch、ONNX等常见格式的模型性能,无法运行rknn格式。考虑到YOLOv5模型转换为rknn会有一定的精度损失,但是需要具体数值才能进行评估,所以需要一个…...
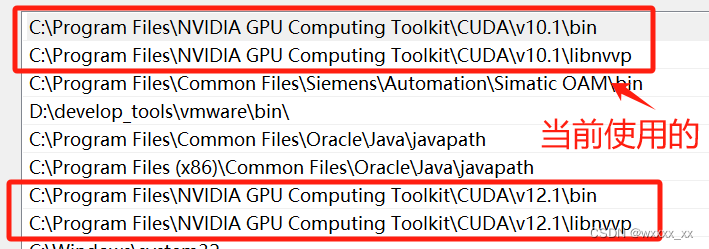
CUDA、CUDNN、Pytorch三者之间的关系
这个东西嘛,我一开始真的是一头雾水,安装起来真是麻烦死了。但是随着要复现的项目越来越多,我也不得不去学会他们是什么,以及他们之间的关系。 首先,一台电脑里面允许有多种版本的cuda存在,然后cuda分为run…...

vue-cli2,vue-cli3,vite 生产环境去掉console.log
console.log一般都是在开发环境下使用的,在生产环境下需要去除 ,如果手动删除未免也太累了,我们可以用插件对于具体环境全局处理。 vue-cli2 项目build 下面webpack.prod.config.js 文件中: plugins: [new webpack.DefinePlugin({process.en…...

AI-调查研究-01-正念冥想有用吗?对健康的影响及科学指南
点一下关注吧!!!非常感谢!!持续更新!!! 🚀 AI篇持续更新中!(长期更新) 目前2025年06月05日更新到: AI炼丹日志-28 - Aud…...
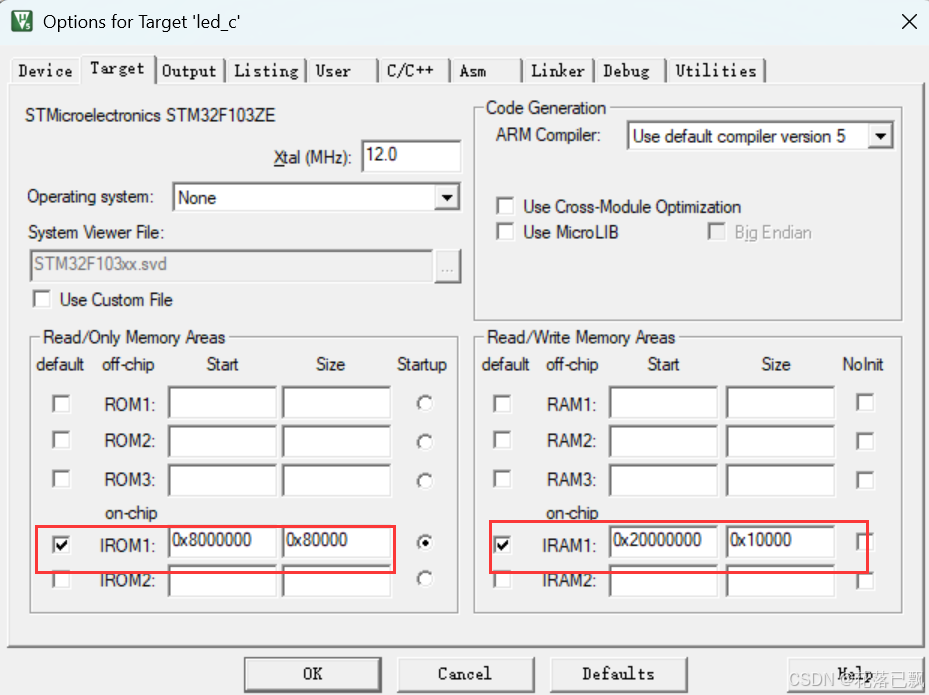
Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解
文章目录 Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解一、Flash 和 RAM 配置界面(Target 选项卡)1. IROM1(用于配置 Flash)2. IRAM1(用于配置 RAM)二、链接器设置界面(Linker 选项卡)1. 勾选“Use Memory Layout from Target Dialog”2. 查看链接器参数(如果没有勾选上面…...
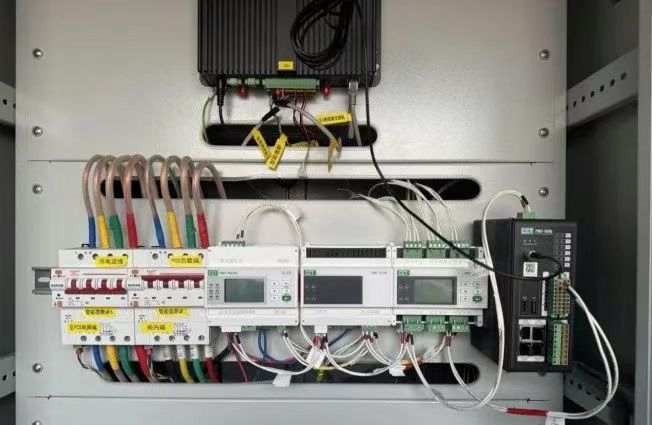
IT供电系统绝缘监测及故障定位解决方案
随着新能源的快速发展,光伏电站、储能系统及充电设备已广泛应用于现代能源网络。在光伏领域,IT供电系统凭借其持续供电性好、安全性高等优势成为光伏首选,但在长期运行中,例如老化、潮湿、隐裂、机械损伤等问题会影响光伏板绝缘层…...
SpringCloudGateway 自定义局部过滤器
场景: 将所有请求转化为同一路径请求(方便穿网配置)在请求头内标识原来路径,然后在将请求分发给不同服务 AllToOneGatewayFilterFactory import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; impor…...
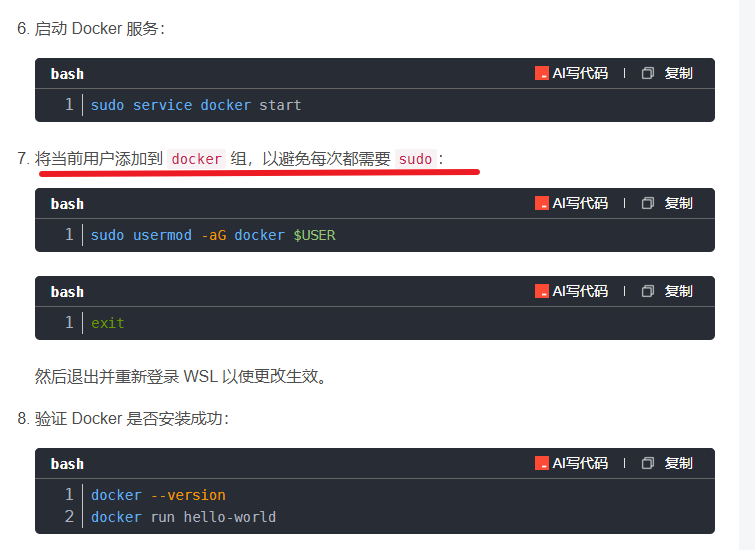
在WSL2的Ubuntu镜像中安装Docker
Docker官网链接: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/ 1、运行以下命令卸载所有冲突的软件包: for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done2、设置Docker…...

全面解析各类VPN技术:GRE、IPsec、L2TP、SSL与MPLS VPN对比
目录 引言 VPN技术概述 GRE VPN 3.1 GRE封装结构 3.2 GRE的应用场景 GRE over IPsec 4.1 GRE over IPsec封装结构 4.2 为什么使用GRE over IPsec? IPsec VPN 5.1 IPsec传输模式(Transport Mode) 5.2 IPsec隧道模式(Tunne…...

安宝特案例丨Vuzix AR智能眼镜集成专业软件,助力卢森堡医院药房转型,赢得辉瑞创新奖
在Vuzix M400 AR智能眼镜的助力下,卢森堡罗伯特舒曼医院(the Robert Schuman Hospitals, HRS)凭借在无菌制剂生产流程中引入增强现实技术(AR)创新项目,荣获了2024年6月7日由卢森堡医院药剂师协会࿰…...

TSN交换机正在重构工业网络,PROFINET和EtherCAT会被取代吗?
在工业自动化持续演进的今天,通信网络的角色正变得愈发关键。 2025年6月6日,为期三天的华南国际工业博览会在深圳国际会展中心(宝安)圆满落幕。作为国内工业通信领域的技术型企业,光路科技(Fiberroad&…...

LCTF液晶可调谐滤波器在多光谱相机捕捉无人机目标检测中的作用
中达瑞和自2005年成立以来,一直在光谱成像领域深度钻研和发展,始终致力于研发高性能、高可靠性的光谱成像相机,为科研院校提供更优的产品和服务。在《低空背景下无人机目标的光谱特征研究及目标检测应用》这篇论文中提到中达瑞和 LCTF 作为多…...
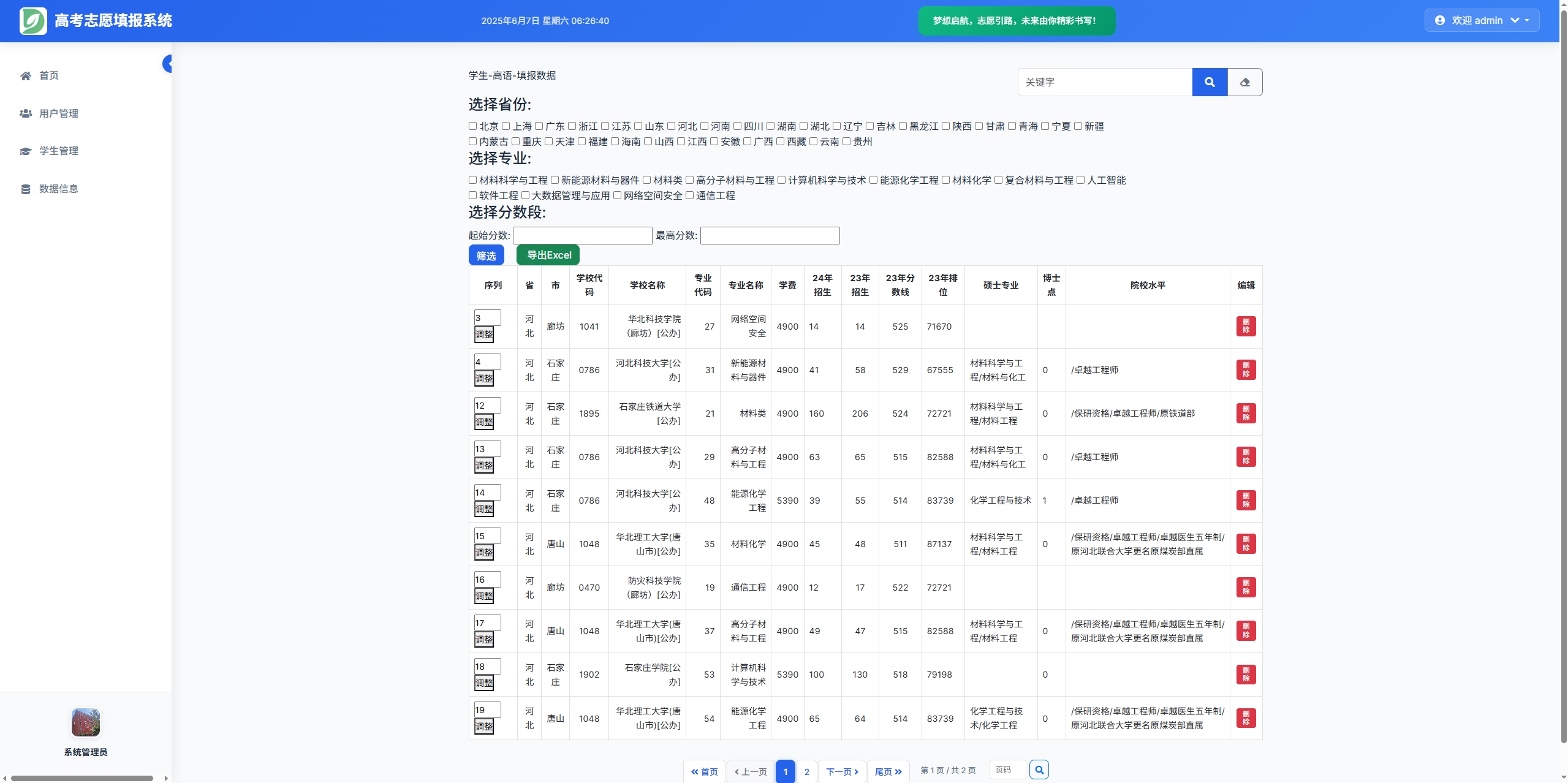
高考志愿填报管理系统---开发介绍
高考志愿填报管理系统是一款专为教育机构、学校和教师设计的学生信息管理和志愿填报辅助平台。系统基于Django框架开发,采用现代化的Web技术,为教育工作者提供高效、安全、便捷的学生管理解决方案。 ## 📋 系统概述 ### 🎯 系统定…...
