Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(十一)

题目来自 Rust Vs Go: Which Language Is Better For Developing High-Performance Applications?[1]
202. Sum of squares
Calculate the sum of squares s of data, an array of floating point values.
计算平方和
package main
import (
"math"
)
func main() {
data := []float64{0.06, 0.82, -0.01, -0.34, -0.55}
var s float64
for _, d := range data {
s += math.Pow(d, 2)
}
println(s)
}
+1.094200e+000
fn main() {
let data: Vec<f32> = vec![2.0, 3.5, 4.0];
let s = data.iter().map(|x| x.powi(2)).sum::<f32>();
println!("{}", s);
}
32.25
205. Get an environment variable
Read an environment variable with the name "FOO" and assign it to the string variable foo. If it does not exist or if the system does not support environment variables, assign a value of "none".
获取环境变量
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
foo, ok := os.LookupEnv("FOO")
if !ok {
foo = "none"
}
fmt.Println(foo)
}
none
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
foo := os.Getenv("FOO")
if foo == "" {
foo = "none"
}
fmt.Println(foo)
}
none
use std::env;
fn main() {
let foo;
match env::var("FOO") {
Ok(val) => foo = val,
Err(_e) => foo = "none".to_string(),
}
println!("{}", foo);
let user;
match env::var("USER") {
Ok(val) => user = val,
Err(_e) => user = "none".to_string(),
}
println!("{}", user);
}
none
playground
or
use std::env;
fn main() {
let foo = env::var("FOO").unwrap_or("none".to_string());
println!("{}", foo);
let user = env::var("USER").unwrap_or("none".to_string());
println!("{}", user);
}
none
playground
or
use std::env;
fn main() {
let foo = match env::var("FOO") {
Ok(val) => val,
Err(_e) => "none".to_string(),
};
println!("{}", foo);
let user = match env::var("USER") {
Ok(val) => val,
Err(_e) => "none".to_string(),
};
println!("{}", user);
}
none
playground
or
use std::env;
if let Ok(tnt_root) = env::var("TNT_ROOT") {
//
}
206. Switch statement with strings
Execute different procedures foo, bar, baz and barfl if the string str contains the name of the respective procedure. Do it in a way natural to the language.
switch语句
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
str := "baz"
switch str {
case "foo":
foo()
case "bar":
bar()
case "baz":
baz()
case "barfl":
barfl()
}
}
func foo() {
fmt.Println("Called foo")
}
func bar() {
fmt.Println("Called bar")
}
func baz() {
fmt.Println("Called baz")
}
func barfl() {
fmt.Println("Called barfl")
}
Called baz
fn main() {
fn foo() {}
fn bar() {}
fn baz() {}
fn barfl() {}
let str_ = "x";
match str_ {
"foo" => foo(),
"bar" => bar(),
"baz" => baz(),
"barfl" => barfl(),
_ => {}
}
}
207. Allocate a list that is automatically deallocated
Allocate a list a containing n elements (n assumed to be too large for a stack) that is automatically deallocated when the program exits the scope it is declared in.
分配一个自动解除分配的列表
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type T byte
func main() {
n := 10_000_000
a := make([]T, n)
fmt.Println(len(a))
}
Elements have type T. a is garbage-collected after the program exits its scope, unless we let it "escape" by taking its reference. The runtime decides if a lives in the stack on in the heap.
10000000
let a = vec![0; n];
Heap allocations are deallocated when the variable goes out of scope.
208. Formula with arrays
Given the arrays a,b,c,d of equal length and the scalar e, calculate a = e*(a+b*c+cos(d)). Store the results in a.
对数组元素进行运算
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func applyFormula(a, b, c, d []float64, e float64) {
for i, v := range a {
a[i] = e * (v + b[i] + c[i] + math.Cos(d[i]))
}
}
func main() {
a := []float64{1, 2, 3, 4}
b := []float64{5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8}
c := []float64{9, 10, 11, 12}
d := []float64{13, 14, 15, 16}
e := 42.0
fmt.Println("a is ", a)
applyFormula(a, b, c, d, e)
fmt.Println("a is now", a)
}
a is [1 2 3 4]
a is now [689.1127648209083 786.9429631647291 879.4931076599294 1001.3783018264178]
fn main() {
let mut a: [f32; 5] = [5., 2., 8., 9., 0.5]; // we want it to be mutable
let b: [f32; 5] = [7., 9., 8., 0.965, 0.98];
let c: [f32; 5] = [0., 0.8, 789456., 123456., 0.0003];
let d: [f32; 5] = [332., 0.1, 8., 9874., 0.3];
const e: f32 = 85.;
for i in 0..a.len() {
a[i] = e * (a[i] + b[i] * c[i] + d[i].cos());
}
println!("{:?}", a); //Don't have any idea about the output
}
[470.29297, 866.57544, 536830750.0, 10127158.0, 123.7286]
209. Type with automatic deep deallocation
Declare a type t which contains a string s and an integer array n with variable size, and allocate a variable v of type t. Allocate v.s and v.n and set them to the values "Hello, world!" for s and [1,4,9,16,25], respectively. Deallocate v, automatically deallocating v.s and v.n (no memory leaks).
自动深度解除分配的类型
package main
func main() {
f()
}
func f() {
type t struct {
s string
n []int
}
v := t{
s: "Hello, world!",
n: []int{1, 4, 9, 16, 25},
}
// Pretend to use v (otherwise this is a compile error)
_ = v
// When f exits, v and all its fields are garbage-collected, recursively
}
After v goes out of scope, v and all its fields will be garbage-collected, recursively
struct T {
s: String,
n: Vec<usize>,
}
fn main() {
let v = T {
s: "Hello, world!".into(),
n: vec![1,4,9,16,25]
};
}
When a variable goes out of scope, all member variables are deallocated recursively.
211. Create folder
Create the folder at path on the filesystem
创建文件夹
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
path := "foo"
_, err := os.Stat(path)
b := !os.IsNotExist(err)
fmt.Println(path, "exists:", b)
err = os.Mkdir(path, os.ModeDir)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
info, err2 := os.Stat(path)
b = !os.IsNotExist(err2)
fmt.Println(path, "exists:", b)
fmt.Println(path, "is a directory:", info.IsDir())
}
foo exists: false
foo exists: true
foo is a directory: true
or
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
path := "foo/bar"
_, err := os.Stat(path)
b := !os.IsNotExist(err)
fmt.Println(path, "exists:", b)
err = os.Mkdir(path, os.ModeDir)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Could not create", path, "with os.Mkdir")
}
info, err2 := os.Stat(path)
b = !os.IsNotExist(err2)
fmt.Println(path, "exists:", b)
err = os.MkdirAll(path, os.ModeDir)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Could not create", path, "with os.MkdirAll")
}
info, err2 = os.Stat(path)
b = !os.IsNotExist(err2)
fmt.Println(path, "exists:", b)
fmt.Println(path, "is a directory:", info.IsDir())
}
foo/bar exists: false
Could not create foo/bar with os.Mkdir
foo/bar exists: false
foo/bar exists: true
foo/bar is a directory: true
use std::fs;
use std::path::Path;
fn main() {
let path = "/tmp/goofy";
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{} exists: {}", path, b);
let r = fs::create_dir(path);
match r {
Err(e) => {
println!("error creating {}: {}", path, e);
std::process::exit(1);
}
Ok(_) => println!("created {}: OK", path),
}
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{} exists: {}", path, b);
}
/tmp/goofy exists: false
created /tmp/goofy: OK
/tmp/goofy exists: true
or
use std::fs;
use std::path::Path;
fn main() {
let path = "/tmp/friends/goofy";
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{} exists: {}", path, b);
// fs::create_dir can't create parent folders
let r = fs::create_dir(path);
match r {
Err(e) => println!("error creating {}: {}", path, e),
Ok(_) => println!("created {}: OK", path),
}
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{} exists: {}", path, b);
// fs::create_dir_all does create parent folders
let r = fs::create_dir_all(path);
match r {
Err(e) => println!("error creating {}: {}", path, e),
Ok(_) => println!("created {}: OK", path),
}
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{} exists: {}", path, b);
}
/tmp/friends/goofy exists: false
error creating /tmp/friends/goofy: No such file or directory (os error 2)
/tmp/friends/goofy exists: false
created /tmp/friends/goofy: OK
/tmp/friends/goofy exists: true
212. Check if folder exists
Set boolean b to true if path exists on the filesystem and is a directory; false otherwise.
检查文件夹是否存在
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
path := "foo"
info, err := os.Stat(path)
b := !os.IsNotExist(err) && info.IsDir()
fmt.Println(path, "is a directory:", b)
err = os.Mkdir(path, os.ModeDir)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
info, err = os.Stat(path)
b = !os.IsNotExist(err) && info.IsDir()
fmt.Println(path, "is a directory:", b)
}
foo is a directory: false
foo is a directory: true
use std::path::Path;
fn main() {
let path = "/etc";
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{}: {}", path, b);
let path = "/goofy";
let b: bool = Path::new(path).is_dir();
println!("{}: {}", path, b);
}
/etc: true
/goofy: false
215. Pad string on the left
Prepend extra character c at the beginning of string s to make sure its length is at least m. The length is the number of characters, not the number of bytes.
左侧补齐字符串
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"unicode/utf8"
)
func main() {
m := 3
c := "-"
for _, s := range []string{
"",
"a",
"ab",
"abc",
"abcd",
"é",
} {
if n := utf8.RuneCountInString(s); n < m {
s = strings.Repeat(c, m-n) + s
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
}
---
--a
-ab
abc
abcd
--é
use unicode_width::{UnicodeWidthChar, UnicodeWidthStr};
if let Some(columns_short) = m.checked_sub(s.width()) {
let padding_width = c
.width()
.filter(|n| *n > 0)
.expect("padding character should be visible");
// Saturate the columns_short
let padding_needed = columns_short + padding_width - 1 / padding_width;
let mut t = String::with_capacity(s.len() + padding_needed);
t.extend((0..padding_needed).map(|_| c)
t.push_str(&s);
s = t;
}
*This uses the Unicode display width to determine the padding needed. This will be appropriate for most uses of monospaced text.
It assumes that m won't combine with other characters to form a grapheme.*
217. Create a Zip archive
Create a zip-file with filename name and add the files listed in list to that zip-file.
创建压缩文件
package main
import (
"archive/zip"
"bytes"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
list := []string{
"readme.txt",
"gopher.txt",
"todo.txt",
}
name := "archive.zip"
err := makeZip(list, name)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
func makeZip(list []string, name string) error {
// Create a buffer to write our archive to.
buf := new(bytes.Buffer)
// Create a new zip archive.
w := zip.NewWriter(buf)
// Add some files to the archive.
for _, filename := range list {
// Open file for reading
input, err := os.Open(filename)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Create ZIP entry for writing
output, err := w.Create(filename)
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = io.Copy(output, input)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
// Make sure to check the error on Close.
err := w.Close()
if err != nil {
return err
}
N := buf.Len()
err = ioutil.WriteFile(name, buf.Bytes(), 0777)
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Println("Written a ZIP file of", N, "bytes")
return nil
}
func init() {
// Create some files in the filesystem.
var files = []struct {
Name, Body string
}{
{"readme.txt", "This archive contains some text files."},
{"gopher.txt", "Gopher names:\nGeorge\nGeoffrey\nGonzo"},
{"todo.txt", "Get animal handling licence.\nWrite more examples."},
}
for _, file := range files {
err := ioutil.WriteFile(file.Name, []byte(file.Body), 0777)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
}
list contains filenames of files existing in the filesystem. In this example, the zip data is buffered in memory before writing to the filesystem.
2009/11/10 23:00:00 Written a ZIP file of 492 bytes
use zip::write::FileOptions;
let path = std::path::Path::new(_name);
let file = std::fs::File::create(&path).unwrap();
let mut zip = zip::ZipWriter::new(file); zip.start_file("readme.txt", FileOptions::default())?;
zip.write_all(b"Hello, World!\n")?;
zip.finish()?;
or
use zip::write::FileOptions;
fn zip(_name: &str, _list: Vec<&str>) -> zip::result::ZipResult<()>
{
let path = std::path::Path::new(_name);
let file = std::fs::File::create(&path).unwrap();
let mut zip = zip::ZipWriter::new(file);
for i in _list.iter() {
zip.start_file(i as &str, FileOptions::default())?;
}
zip.finish()?;
Ok(())
}
218. List intersection
Create list c containing all unique elements that are contained in both lists a and b. c should not contain any duplicates, even if a and b do. The order of c doesn't matter.
列表的交集
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type T int
func main() {
a := []T{4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
b := []T{1, 3, 9, 5, 7, 9, 7, 7}
// Convert to sets
seta := make(map[T]bool, len(a))
for _, x := range a {
seta[x] = true
}
setb := make(map[T]bool, len(a))
for _, y := range b {
setb[y] = true
}
// Iterate in one pass
var c []T
for x := range seta {
if setb[x] {
c = append(c, x)
}
}
fmt.Println(c)
}
[5 7 9]
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main() {
let a = vec![1, 2, 3, 4];
let b = vec![2, 4, 6, 8, 2, 2];
let unique_a = a.iter().collect::<HashSet<_>>();
let unique_b = b.iter().collect::<HashSet<_>>();
let c = unique_a.intersection(&unique_b).collect::<Vec<_>>();
println!("c: {:?}", c);
}
c: [2, 4]
or
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main() {
let a = vec![1, 2, 3, 4];
let b = vec![2, 4, 6, 8, 2, 2];
let set_a: HashSet<_> = a.into_iter().collect();
let set_b: HashSet<_> = b.into_iter().collect();
let c = set_a.intersection(&set_b);
println!("c: {:?}", c);
}
c: [2, 4]
219. Replace multiple spaces with single space
Create string t from the value of string s with each sequence of spaces replaced by a single space.
Explain if only the space characters will be replaced, or the other whitespaces as well: tabs, newlines.
用单个空格替换多个空格
package main
import (
"fmt"
"regexp"
)
// regexp created only once, and then reused
var whitespaces = regexp.MustCompile(`\s+`)
func main() {
s := `
one two
three
`
t := whitespaces.ReplaceAllString(s, " ")
fmt.Printf("t=%q", t)
}
t=" one two three "
use regex::Regex;
fn main() {
let s = "
one two
three
";
let re = Regex::new(r"\s+").unwrap();
let t = re.replace_all(s, " ");
println!("{}", t);
}
one two three
220. Create a tuple value
Create t consisting of 3 values having different types.
Explain if the elements of t are strongly typed or not.
创建元组值a
t := []interface{}{
2.5,
"hello",
make(chan int),
}
A slice of empty interface may hold any values (not strongly typed).
fn main() {
let mut t = (2.5, "hello", -1);
t.2 -= 4;
println!("{:?}", t);
}
(2.5, "hello", -5)
参考资料
Rust Vs Go: Which Language Is Better For Developing High-Performance Applications?: https://analyticsindiamag.com/rust-vs-go-which-language-is-better-for-developing-high-performance-applications/
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布
相关文章:

Rust vs Go:常用语法对比(十一)
题目来自 Rust Vs Go: Which Language Is Better For Developing High-Performance Applications?[1] 202. Sum of squares Calculate the sum of squares s of data, an array of floating point values. 计算平方和 package mainimport ( "math")func main() { da…...
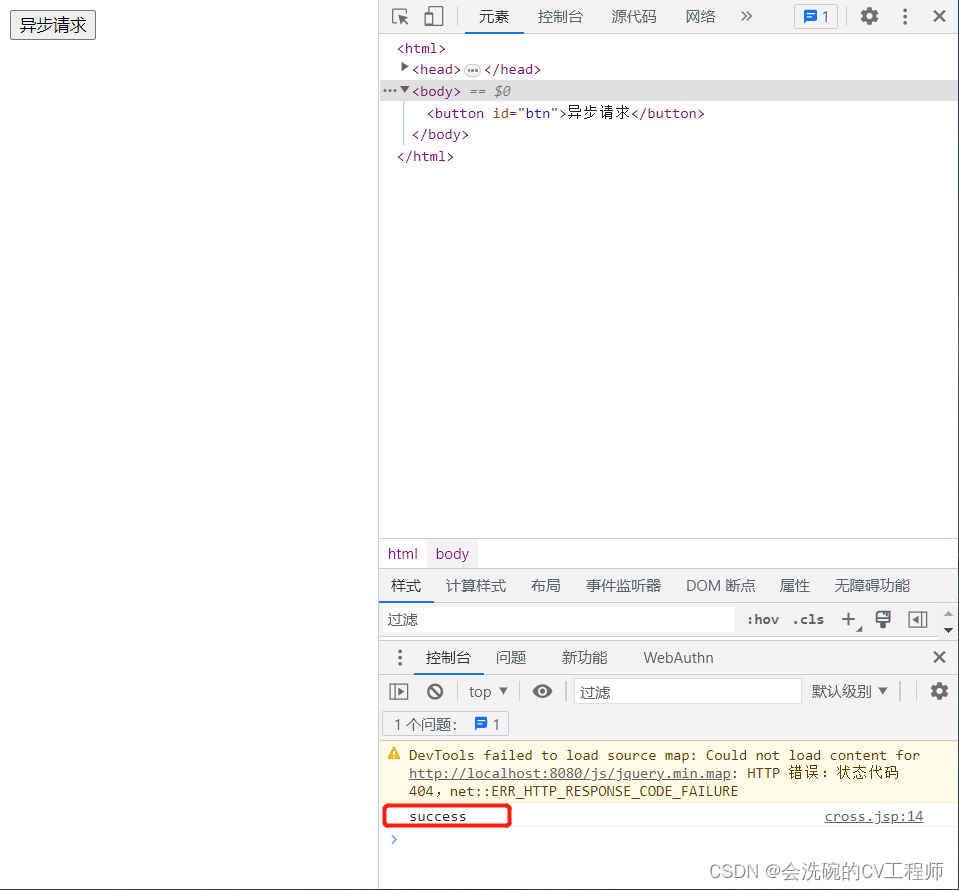
Spring MVC拦截器和跨域请求
一、拦截器简介 SpringMVC的拦截器(Interceptor)也是AOP思想的一种实现方式。它与Servlet的过滤器(Filter)功能类似,主要用于拦截用户的请求并做相应的处理,通常应用在权限验证、记录请求信息的日志、判断用…...

C++初阶--C++入门
目录 前言C关键字命名空间命名空间的定义命名空间的使用加命名空间名称及作用域限定符使用using namespace 命名空间名称引入使用using将命名空间中的成员引入 C的输入与输出缺省参数全缺省半缺省参数 函数重载参数类型不同参数个数不同参数类型顺序不同 引用引用特性 常引用使…...
)
Matlab实现PID控制仿真(附上30个完整仿真源码+数据)
本文介绍了如何使用Matlab实现PID控制器的仿真。首先,我们将简要介绍PID控制器的原理和控制算法。然后,我们将使用Matlab编写一个简单的PID控制器,并使用仿真环境来验证其性能。最后,我们将通过调整PID控制器的参数来优化控制系统…...

微信小程序:文件下载
目录 第一步 请求资源 第二步 获取资源后写入到微信本地 获取资源 写入资源(wx.getFileSystemManager)writeFile 的api 第三步 读取资源(openDocument与saveImageToPhotosAlbum) 第一步 请求资源 下面是请求接口中的脚本内容 export let baseUrl http://192.168.78.112…...
QString和QByteArray的区别
QString和QByteArray的区别 本质格式转换QString字符串格式化打印长度 本质 QString是对QByteArray的再次封装 QString可以通过char*来构造,也可以通过QByteArray来构造 QByteArray就是char* QString是编码后的char* QString也是封装了字符串, 但是内部的编码为utf…...
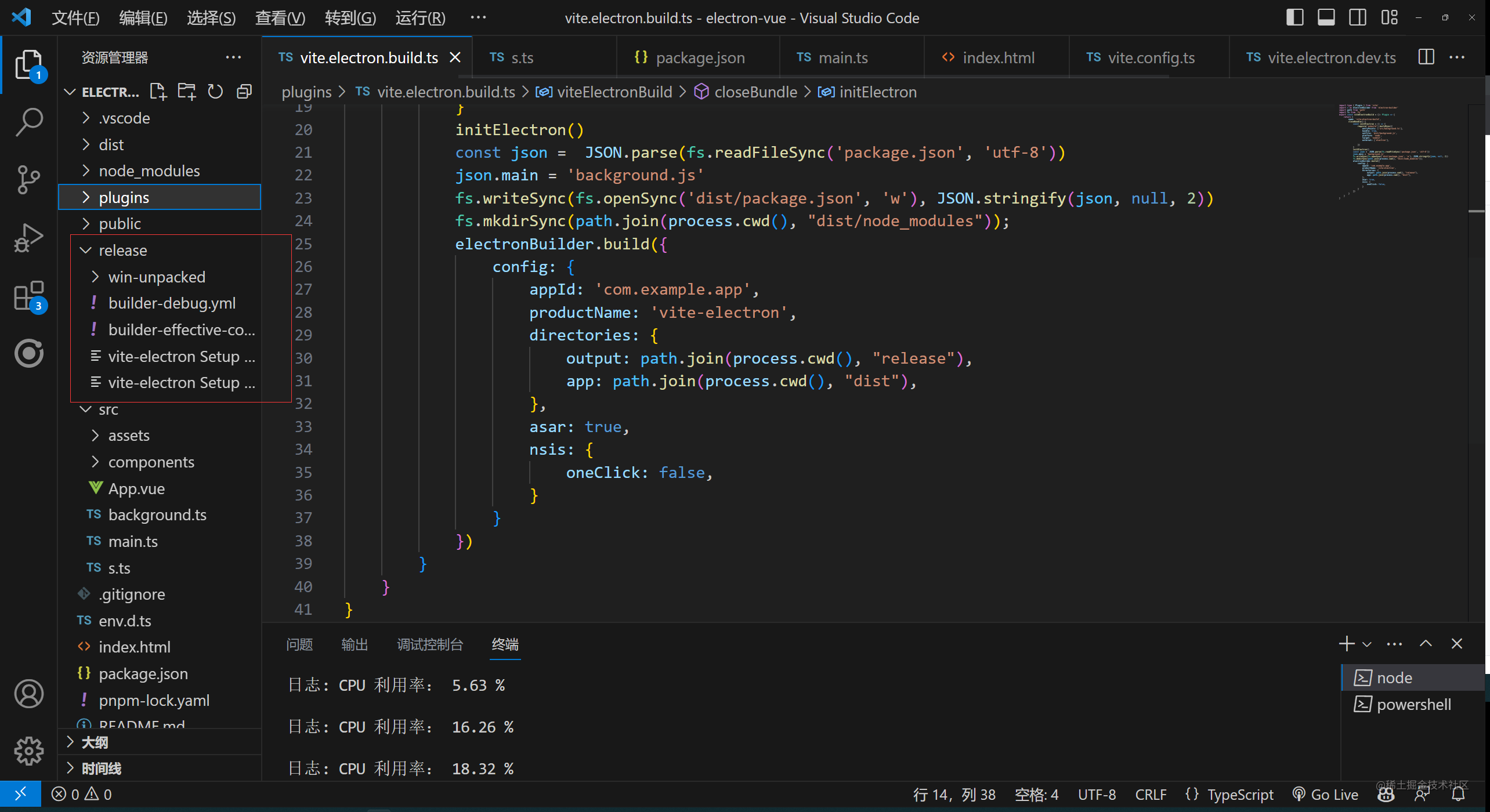
Vue3 Vite electron 开发桌面程序
Electron是一个跨平台的桌面应用程序开发框架,它允许开发人员使用Web技术(如HTML、CSS和JavaScript)构建桌面应用程序,这些应用程序可以在Windows、macOS和Linux等操作系统上运行。 Electron的核心是Chromium浏览器内核和Node.js…...

【Nodejs】Express模板使用
1.Express脚手架的安装 安装Express脚手架有两种方式: 使用express-generator安装 使用命令行进入项目目录,依次执行: cnpm i -g express-generator可通过express -h查看命令行的指令含义 express -hUsage: express [options] [dir] Optio…...
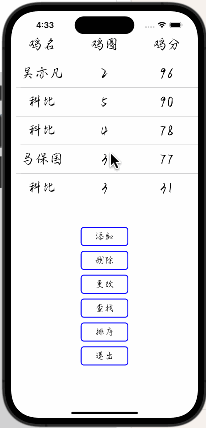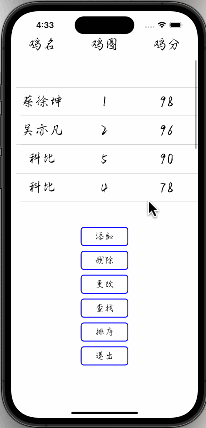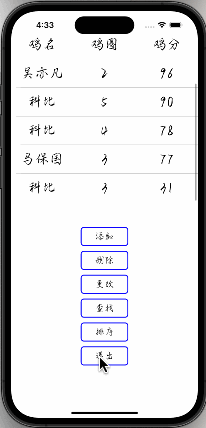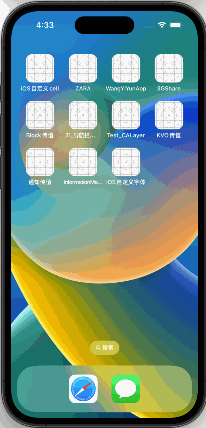
【iOS】App仿写--管理系统
文章目录 前言一、账号界面二、功能界面三、添加功能四、删除功能五、更改功能六、查找功能七、排序功能八、退出功能总结 前言 在日常生活中,如果用文字来记述与管理我们数据会十分麻烦,并且人工成本较高,这里笔者给出一种管理系统的模版&a…...

JS实现队列的数据结构
创建queue.ts /*** 队列*/ export default class Queue<T> {private items: object;private count: number;private header: number;constructor() {this.items {};this.count this.header 0;}/*** 入队列* param element* returns 当前队列的数量*/enqueue(element:…...
:通过代理使用外部工具)
title: 用 LangChain 构建基于资料库的问答机器人(四):通过代理使用外部工具
上一篇教程我们介绍了 ReAct 系统,这是一个非常强大的行为模式,但它需要编写大量的示例来告诉 LLM 如何思考、行动,并且为了遵循这个模式,还需要编写代码来分析生成文字、调用函数、拼接 prompt 等,这些工作都是十分繁…...
使用 CSS 自定义属性
我们常见的网站日夜间模式的变化,其实用到了 css 自定义属性。 CSS 自定义属性(也称为 CSS 变量)是一种在 CSS 中预定义和使用的变量。它们提供了一种简洁和灵活的方式来通过多个 CSS 规则共享相同的值,使得样式更易于维护和修改。…...

Unity 性能优化一:性能标准、常用工具
性能标准 推荐耗时: 性能提现到玩家直观感受,就是帧率,为了达到要求的帧率,就要控制CPU的耗时,不同类型的游戏,对帧率要求不一样。下面是推荐耗时: 推荐内存: 避免游戏闪退的重点…...

【http长连接+池化】
参考: https://it.cha138.com/ios/show-49862.html http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-16480950-id-103597.html https://www.cnblogs.com/kevin-yuan/p/13731552.html https://www.jianshu.com/p/17e9aacca438 一、http长连接和短连接 HTTP协议是无状态的协议&#…...
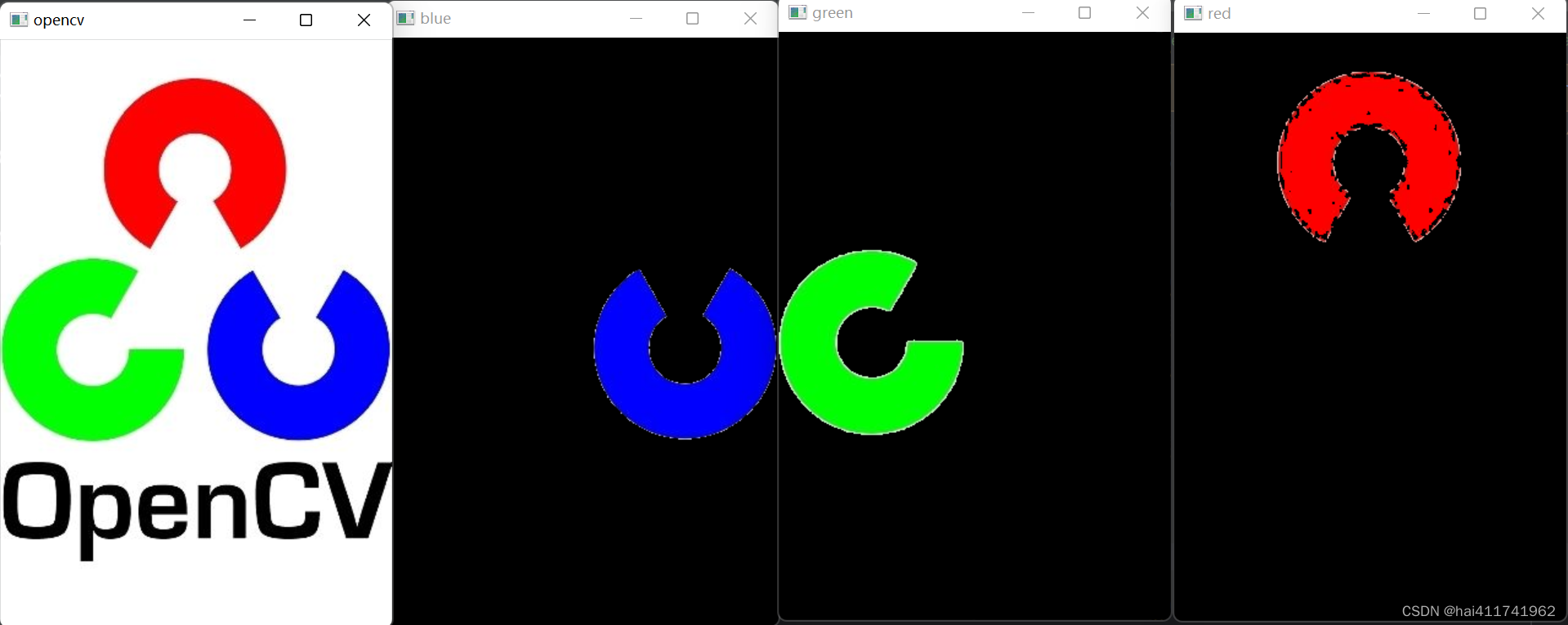
opencv-20 深入理解HSV 色彩空间(通过指定,标记颜色等来拓展ROI区域)
RGB 色彩空间是一种被广泛接受的色彩空间,但是该色彩空间过于抽象,我们不能够直接通过其值感知具体的色彩。 我们更习惯使用直观的方式来感知颜色,HSV 色彩空间提供了这样 的方式。 通过 HSV色彩空间,我们能够更加方便地通过色调、…...

python调用arcgis功能一例
python调用arcgis功能一例 执行方法: D:\data\python>python test_Select.pywindow11下环境变量设置 此电脑/属性/系统/高级系统设置/高级/环境变量/path path中添加全局目录:C:\Python27\ArcGIS10.4 test_Select.py脚本内容 # Name: Select_Examp…...
Spring MVC 是什么?
一、什么是 Spring MVC? 官方对于 Spring MVC 的描述是这样的: Spring Web MVC is the original web framework built on the Servlet API and has been included in the Spring Framework from the very beginning. The formal name, “Spring Web …...
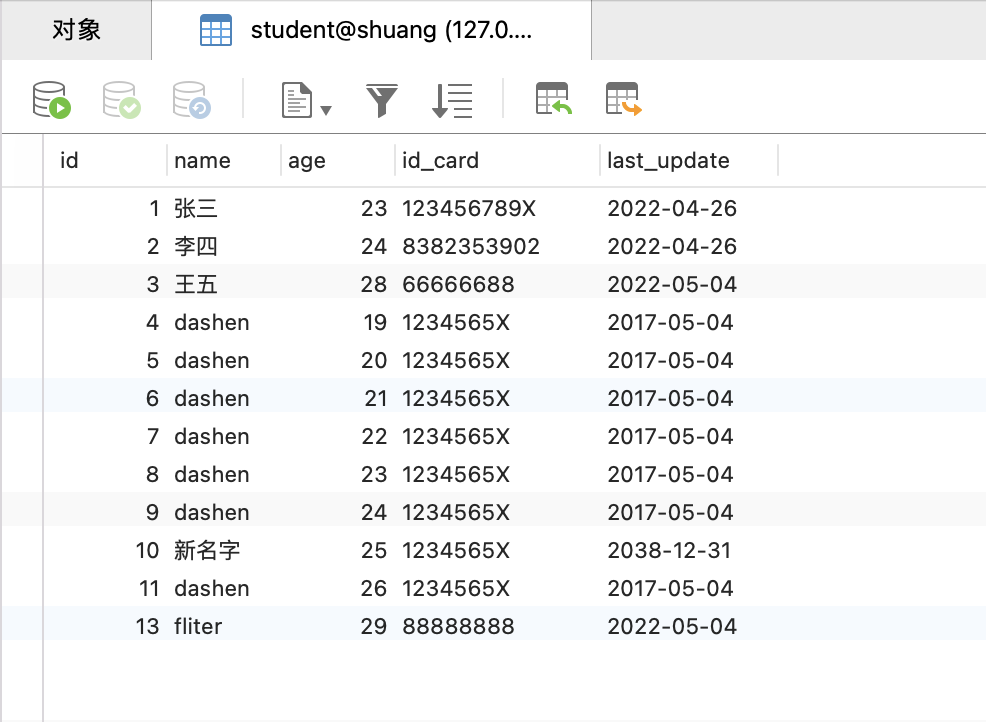
Rust操作MySQL
查询 本部分是对 「Rust入门系列」Rust 中使用 MySQL[1]的学习与记录 经常使用的时间处理库: chrono 流式查询使用: query_iter 输出到Vec使用: query 映射到结构体使用: query_map 获取单条数据使用: query_first 命名…...

JAVA面试总结-Redis篇章(二)——缓存击穿
JAVA面试总结-Redis篇章(二) 缓存击穿解决方案一:互斥锁解决方案二:逻辑过期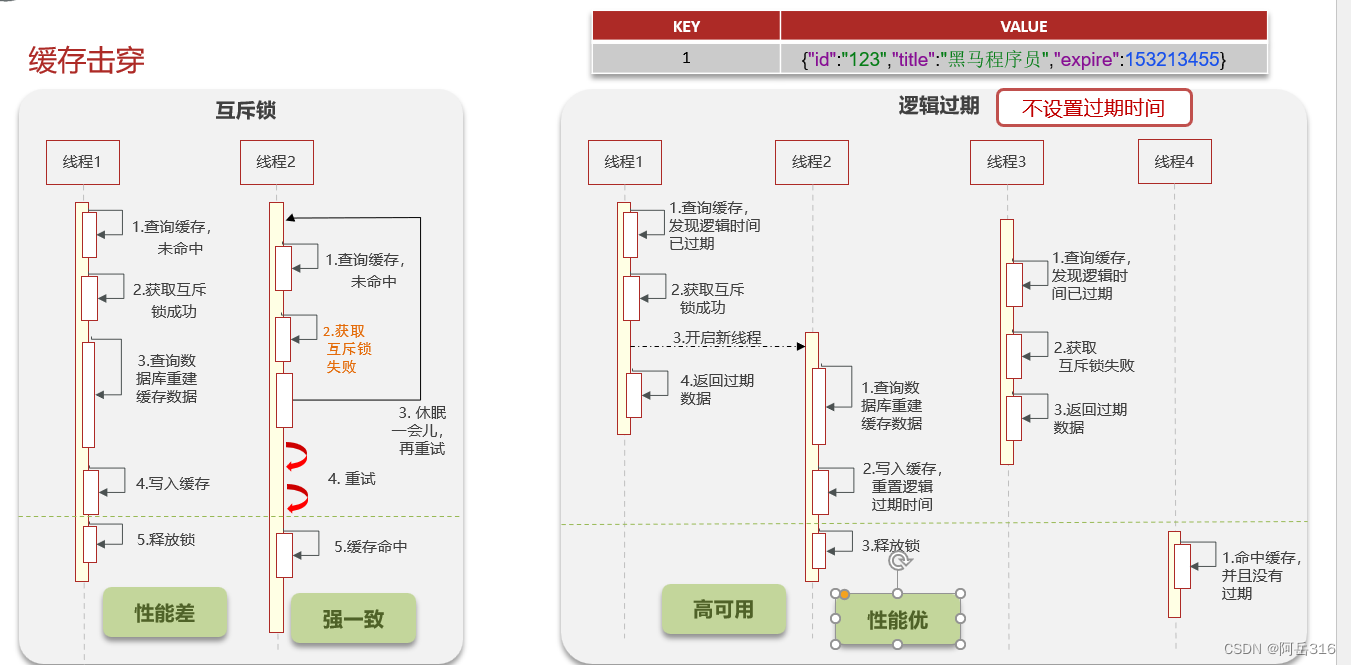 缓存击穿 解决方案一:互斥锁 解决方案二&…...

Spring相关知识点
概述 分层的轻量级的全栈开源框架 展示层SprigMVC 持久层 Spring JDBCTemplate 业务层事务管理 注: 轻量级:API简单 全栈:各层都有相应解决方案 在Spring的体系结构中,由上而下,逐层依赖 Spring相当于是一个粘合剂&…...

深入剖析AI大模型:大模型时代的 Prompt 工程全解析
今天聊的内容,我认为是AI开发里面非常重要的内容。它在AI开发里无处不在,当你对 AI 助手说 "用李白的风格写一首关于人工智能的诗",或者让翻译模型 "将这段合同翻译成商务日语" 时,输入的这句话就是 Prompt。…...
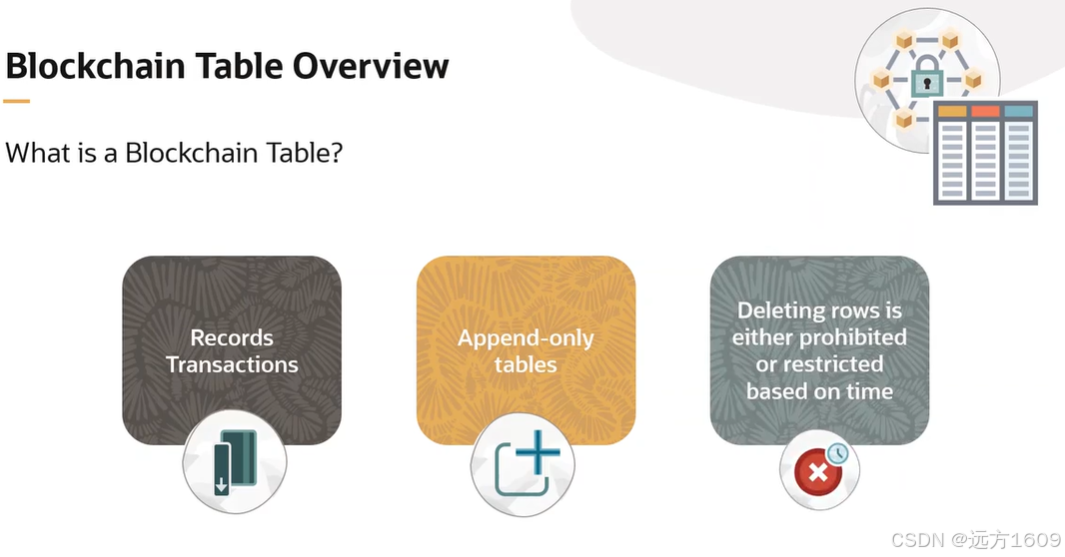
23-Oracle 23 ai 区块链表(Blockchain Table)
小伙伴有没有在金融强合规的领域中遇见,必须要保持数据不可变,管理员都无法修改和留痕的要求。比如医疗的电子病历中,影像检查检验结果不可篡改行的,药品追溯过程中数据只可插入无法删除的特性需求;登录日志、修改日志…...
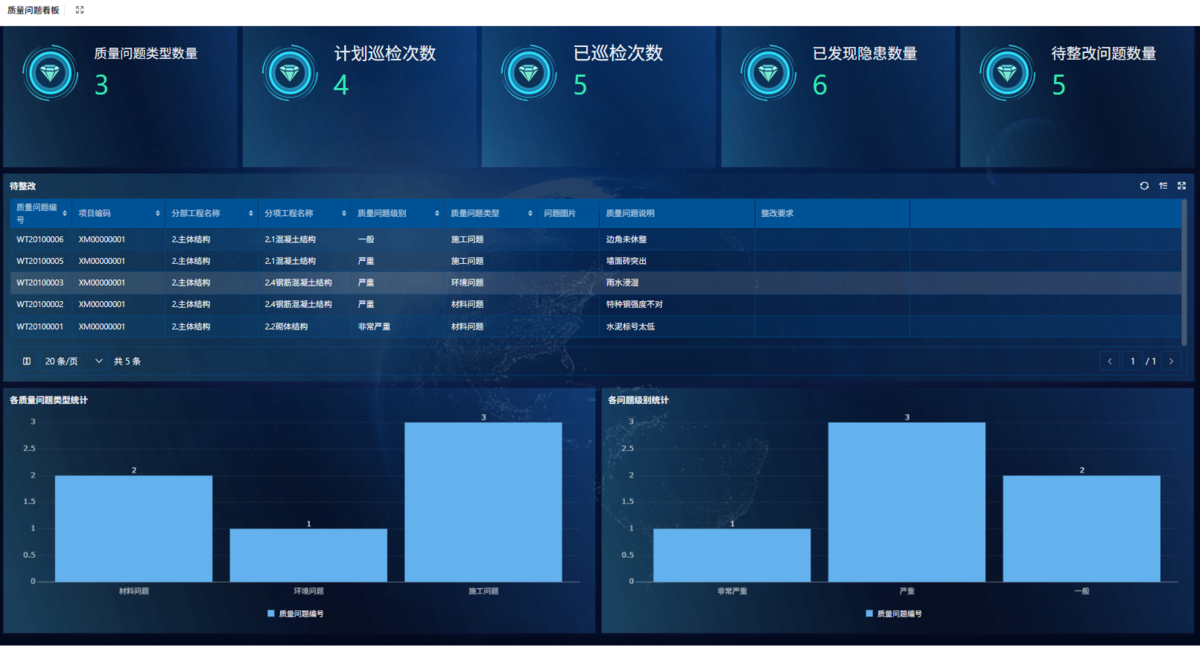
为什么需要建设工程项目管理?工程项目管理有哪些亮点功能?
在建筑行业,项目管理的重要性不言而喻。随着工程规模的扩大、技术复杂度的提升,传统的管理模式已经难以满足现代工程的需求。过去,许多企业依赖手工记录、口头沟通和分散的信息管理,导致效率低下、成本失控、风险频发。例如&#…...
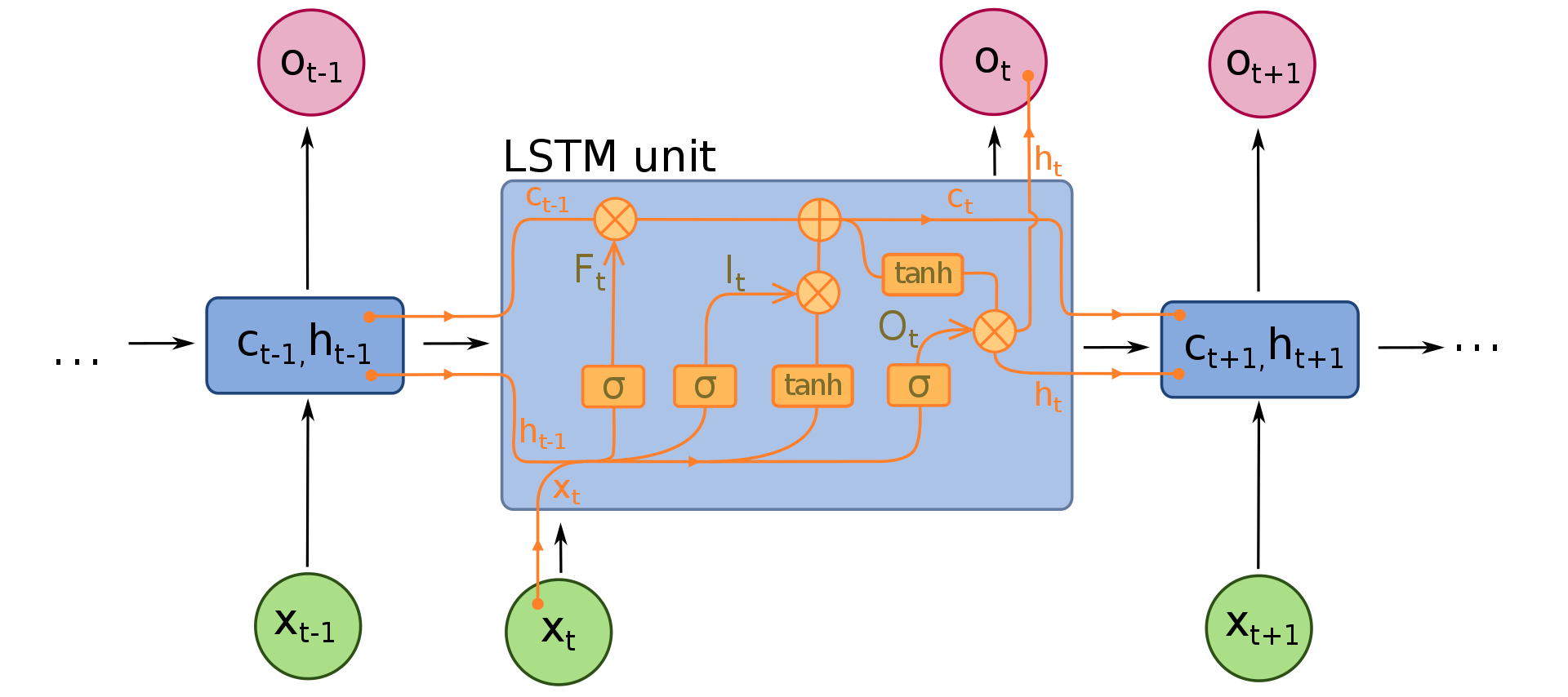
NLP学习路线图(二十三):长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,我们时刻面临着处理序列数据的核心挑战。无论是理解句子的结构、分析文本的情感,还是实现语言的翻译,都需要模型能够捕捉词语之间依时序产生的复杂依赖关系。传统的神经网络结构在处理这种序列依赖时显得力不从心,而循环神经网络(RNN) 曾被视为…...

Spring AI与Spring Modulith核心技术解析
Spring AI核心架构解析 Spring AI(https://spring.io/projects/spring-ai)作为Spring生态中的AI集成框架,其核心设计理念是通过模块化架构降低AI应用的开发复杂度。与Python生态中的LangChain/LlamaIndex等工具类似,但特别为多语…...

MySQL账号权限管理指南:安全创建账户与精细授权技巧
在MySQL数据库管理中,合理创建用户账号并分配精确权限是保障数据安全的核心环节。直接使用root账号进行所有操作不仅危险且难以审计操作行为。今天我们来全面解析MySQL账号创建与权限分配的专业方法。 一、为何需要创建独立账号? 最小权限原则…...
Reasoning over Uncertain Text by Generative Large Language Models
https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829 1. 概述 文本中的不确定性在许多语境中传达,从日常对话到特定领域的文档(例如医学文档)(Heritage 2013;Landmark、Gulbrandsen 和 Svenevei…...
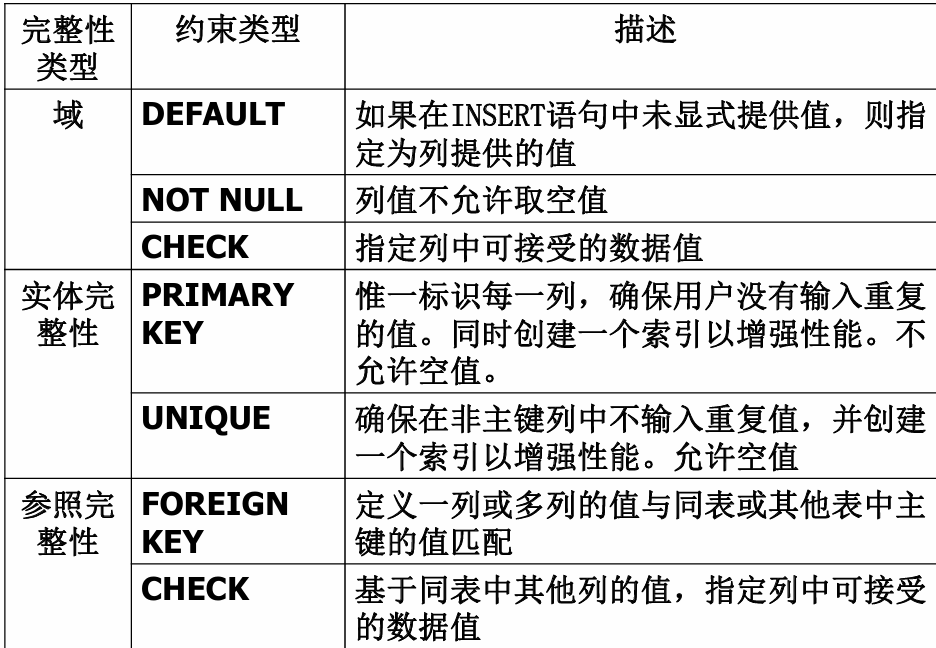
七、数据库的完整性
七、数据库的完整性 主要内容 7.1 数据库的完整性概述 7.2 实体完整性 7.3 参照完整性 7.4 用户定义的完整性 7.5 触发器 7.6 SQL Server中数据库完整性的实现 7.7 小结 7.1 数据库的完整性概述 数据库完整性的含义 正确性 指数据的合法性 有效性 指数据是否属于所定…...
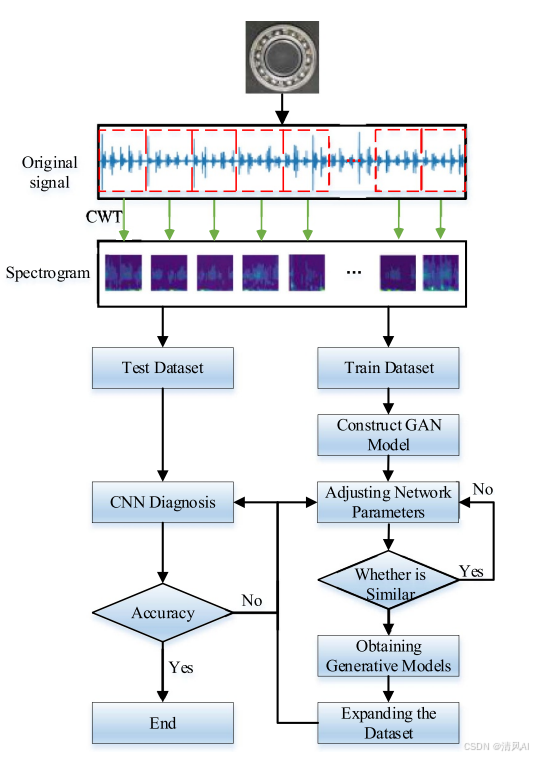
基于IDIG-GAN的小样本电机轴承故障诊断
目录 🔍 核心问题 一、IDIG-GAN模型原理 1. 整体架构 2. 核心创新点 (1) 梯度归一化(Gradient Normalization) (2) 判别器梯度间隙正则化(Discriminator Gradient Gap Regularization) (3) 自注意力机制(Self-Attention) 3. 完整损失函数 二…...

【Android】Android 开发 ADB 常用指令
查看当前连接的设备 adb devices 连接设备 adb connect 设备IP 断开已连接的设备 adb disconnect 设备IP 安装应用 adb install 安装包的路径 卸载应用 adb uninstall 应用包名 查看已安装的应用包名 adb shell pm list packages 查看已安装的第三方应用包名 adb shell pm list…...
