Spring 事务原理一
从本篇博客开始,我们将梳理Spring事务相关的知识点。在开始前,想先给自己定一个目标:通过此次梳理要完全理解事务的基本概念及Spring实现事务的基本原理。为实现这个目标我想按以下几个步骤进行:
- 讲解事务中的一些基本概念
- 使用Spring开发一个简单的事务案例,并作为后面代码跟踪的案例
- 跟踪Spring源码以梳理其实现事务的原理
下面就让我们按照这个步骤开始吧,本篇博客的目标有两个,一个是开发事务代码,一个是梳理事务中的基本概念。
事务中的基本概念
在日常工作中,大家都用过数据库,应该也知道在数据库层面有事务的概念。因为数据库作为一个公共资源,会被很多客户端操作,为了保证实际业务的准确性,一定要有一个方法来规避不可预料的风险。于是,数据库的设计者就提出了事务这个概念。在这个概念中一组操作组成了一个不可分割的操作单元,在这个操作单元中,所有的操作要么都成功,要么都失败,不能存在一部分成功一部分失败的情况发生,这个单元我将其称为事务单元(注意这里的事务单元我个人为了便于理解而自己起的一个名字)。就像组成元素的粒子一样,事务单元是一个无法分割的整体,其具有独立的行为模式,譬如事务A只修改A表中的一条记录,事务B会修改多张表中的多条记录。而事务具有不同行为模式的这个说法的根本原因是组成事务单元的操作序列不同。既然从操作者角度看,事务是一个独立的,且无法分割的具有不同行为模式的整体,那么为了达到这个效果,我们该如何实现呢?这是个非常复杂的问题,如果要回答是需要很多知识储备的,所以很抱歉。但我们可以这样想一下,代码本身就是在定义好的规则下运行的,那么为了实现这样一个事务单元,我们需要它具有什么样的规则呢?上面只是从宏观层面粗略的讲了一下事务单元的特点,那么从科学的角度来看事务究竟该具有一些什么特性呢?事务的特性主要有以下几点:
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务是数据库的逻辑工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么全做,要么全不做
- 一致性(Consistency):事务执行的结果必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态(一致性与原子性是密切相关的)
- 隔离性(Isolation):一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰
- 持久性(Durability):一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的
到这里,我不禁在想一个问题既然事务是一个基本的操作单元,并且这个操作单元具有上面所说的一些特性,那是不是就可以利用它为所欲为了?好像是可以的,首先我们去操作数据库的时候,有一个事务涉及到了很多表(前提:这个事务中涉及的多张表中的数据都要有变更),事务可以避免前一张表的数据变动,而后一张表数据无变化的情况发生(这里个人认为体现的是事务的原子性、一致性和持久性)。上面这个说法只是从单个事务的角度考虑的,而事实上数据库中的数据在同一时刻会被多个事务操作,这个时候这些事务又该如何执行呢?所以这里想再强调一点:事务不仅可单独运行,也可并发运行。事务是并发控制的基本单位。接下来我们先看一下多个事务并发执行时会出现一些什么问题吧:
- 脏读:所谓脏读就是事务A读取到了事务B尚未提交的数据,此时如果事务B发生错误并执行回滚操作,那么事务A读取到的数据就是脏数据。这就好比可以吃两份披萨的你,由于着急赶火车,只能拿取桌子上仅剩的一份披萨,虽然后前一个人后来又归还了一份回来,但由于你已经离开,所以无法知道这个结果。这种情况经常发生在转账和取款操作中,见下面这张图:
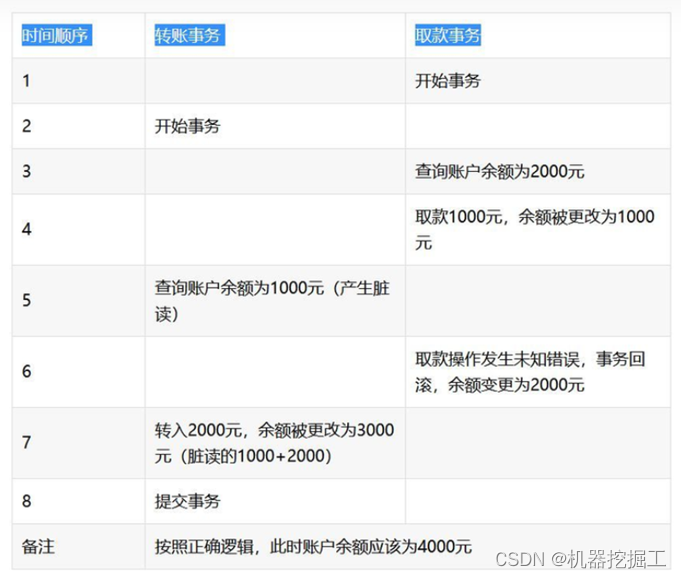
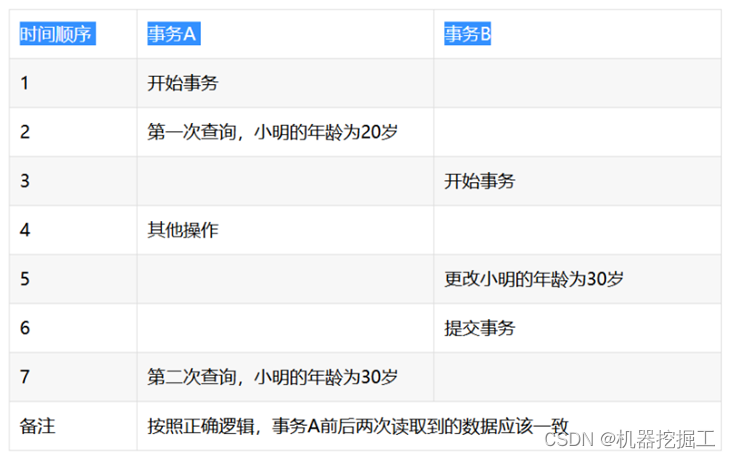
- 不可重复度:所谓不可重复读是指一个事务前后多次读取,而每次读取到的数据内容却不一致的情况。事务A在执行读取操作,由整个事务A比较大,前后读取同一条数据需要经历很长的时间。而在事务A第一次读取数据,比如此时读取了小明的年龄为20岁,事务B执行更改操作,将小明的年龄更改为30岁,此时事务A第二次读取到小明的年龄时,发现其年龄是30岁,和之前的数据不一样了,也就是数据不重复了,系统不可以读取到重复的数据,成为不可重复读。具体参见下面这幅图:
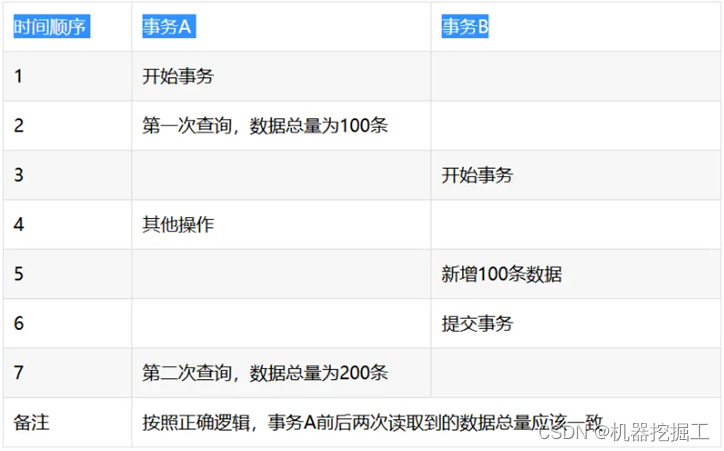
- 幻读:所谓幻读是指前后多次读取,拿到的数据总量不一致。事务A在执行读取操作,需要两次统计数据的总量,前一次查询数据总量后,此时事务B执行了新增数据的操作并提交后,这个时候事务A读取的数据总量和之前统计的不一样,就像产生了幻觉一样,平白无故的多了几条数据,成为幻读。具体详情请参见下面这幅图片:
这里想再对比一下幻读和不可重复读两个概念:不可重复读是读取了其他事务更改的数据,针对update操作。在MySQL中可以使用行级锁来解决。幻读是读取了其他事务新增的数据,针对insert和delete操作。在MySQL中可以使用表级锁来解决。
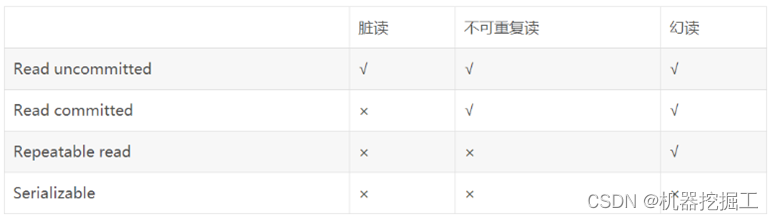
看过事务并发操作中可能出现的几个问题之后,我们再来想一下与数据库事务隔离级别有关的问题。SQL标准定义的四种隔离级别被ANSI(美国国家标准学会)和ISO/IEC(国际标准)采用,每种级别对事务的处理能力会有不同程度的影响。事务是一系列的动作,它们综合在一起才是一个完整的工作单元,这些动作必须全部完成,如果有一个失败的话,那么事务就会回滚到最开始的状态,仿佛什么都没发生过一样。数据库事务的4个隔离级别由低到高依次为Read uncommitted、Read committed、Repeatable read、Serializable,这四个级别可以逐个解决脏读、不可重复读、幻读这几类问题。具体见下面这张图:
下面我们来详细梳理一下这几个隔离级别:
- READ UNCOMMITTED(读未提交):该隔离级别表示一个事务可以读取另一个事务修改但还没有提交的数据。该级别不能防止脏读和不可重复读,因此很少使用该隔离级别
- READ_COMMITTED(读提交):该隔离级别表示一个事务只能读取另一个事务已经提交的数据。该级别可以防止脏读,这也是大多数情况下的推荐值
- REPEATABLE_READ(可重复读):该隔离级别表示一个事务在整个过程中可以多次重复执行某个查询,并且每次返回的记录都相同。即使在多次查询之间有新增的数据满足该查询,这些新增的记录也会被忽略。该级别可以防止脏读和不可重复读
- SERIALIZABLE(串行化):该隔离级别下所有的事务依次逐个执行,这样事务之间就完全不可能产生干扰,所以该级别可以防止脏读、不可重复读以及幻读。但是这将严重影响程序的性能。通常情况下也不会用到该级别。在该隔离级别下事务都是串行顺序执行的,MySQL数据库的InnoDB引擎会给读操作隐式加一把读共享锁,从而避免了脏读、不可重读复读和幻读问题
这里扩展一下——MVCC(多版本并发控制)。在MySQL中,默认的事务隔离级别是可重复读(repeatable-read),为了解决不可重复读,innodb采用了多版本并发控制来解决这一问题。MVCC是利用在每条数据后面加了隐藏的两列(创建版本号和删除版本号)来实现多版本并发控制的。每个事务在开始的时候都会有一个递增的版本号,用来和查询到的每行记录的版本号进行比较。
上面我们讲解了事务中的基本概念,接下来我们梳理一下Spring中与事务有关的几个常见问题:
Spring中的事务传播属性有几个,它们分别是什么?这个问题的答案要从Spring的事务实现组件TransactionDefinition接口中寻找,该接口的代码如下所示:
public interface TransactionDefinition {/*** Support a current transaction; create a new one if none exists.* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p>This is typically the default setting of a transaction definition* and typically defines a transaction synchronization scope.*/int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0;/*** Support a current transaction; execute non-transactionally if none exists.* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> For transaction managers with transaction synchronization,* {@code PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS} is slightly different from no transaction* at all, as it defines a transaction scope that synchronization might apply to.* As a consequence, the same resources (a JDBC {@code Connection}, a* Hibernate {@code Session}, etc) will be shared for the entire specified* scope. Note that the exact behavior depends on the actual synchronization* configuration of the transaction manager.* <p>In general, use {@code PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS} with care. In particular, do* not rely on {@code PROPAGATION_REQUIRED} or {@code PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW}* <i>within</i> a {@code PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS} scope (which may lead to* synchronization conflicts at runtime). If such nesting is unavoidable, make sure* to configure your transaction manager appropriately (typically switching to* "synchronization on actual transaction").* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#SYNCHRONIZATION_ON_ACTUAL_TRANSACTION*/int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1;/*** Support a current transaction; throw an exception if no current transaction* exists. Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p>Note that transaction synchronization within a {@code PROPAGATION_MANDATORY}* scope will always be driven by the surrounding transaction.*/int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2;/*** Create a new transaction, suspending the current transaction if one exists.* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},* which requires the {@code jakarta.transaction.TransactionManager} to be* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Jakarta EE).* <p>A {@code PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW} scope always defines its own* transaction synchronizations. Existing synchronizations will be suspended* and resumed appropriately.* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager*/int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3;/*** Do not support a current transaction; rather always execute non-transactionally.* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},* which requires the {@code jakarta.transaction.TransactionManager} to be* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Jakarta EE).* <p>Note that transaction synchronization is <i>not</i> available within a* {@code PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED} scope. Existing synchronizations* will be suspended and resumed appropriately.* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager*/int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4;/*** Do not support a current transaction; throw an exception if a current transaction* exists. Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.* <p>Note that transaction synchronization is <i>not</i> available within a* {@code PROPAGATION_NEVER} scope.*/int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5;/*** Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists,* behaving like {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED} otherwise. There is no* analogous feature in EJB.* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on* specific transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC* {@link org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager}* when working on a JDBC 3.0+ driver. Some JTA providers might support* nested transactions as well.* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager*/int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;/*** Use the default isolation level of the underlying datastore.* <p>All other levels correspond to the JDBC isolation levels.* @see java.sql.Connection*/int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;/*** Indicates that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads* can occur.* <p>This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read by another* transaction before any changes in that row have been committed (a "dirty read").* If any of the changes are rolled back, the second transaction will have* retrieved an invalid row.* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED*/int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1; // same as java.sql.Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED;/*** Indicates that dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads and* phantom reads can occur.* <p>This level only prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted* changes in it.* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED*/int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = 2; // same as java.sql.Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED;/*** Indicates that dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are prevented;* phantom reads can occur.* <p>This level prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted changes* in it, and it also prohibits the situation where one transaction reads a row,* a second transaction alters the row, and the first transaction re-reads the row,* getting different values the second time (a "non-repeatable read").* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ*/int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4; // same as java.sql.Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ;/*** Indicates that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads* are prevented.* <p>This level includes the prohibitions in {@link #ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ}* and further prohibits the situation where one transaction reads all rows that* satisfy a {@code WHERE} condition, a second transaction inserts a row* that satisfies that {@code WHERE} condition, and the first transaction* re-reads for the same condition, retrieving the additional "phantom" row* in the second read.* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE*/int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = 8; // same as java.sql.Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE;/*** Use the default timeout of the underlying transaction system,* or none if timeouts are not supported.*/int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1;/*** Return the propagation behavior.* <p>Must return one of the {@code PROPAGATION_XXX} constants* defined on {@link TransactionDefinition this interface}.* <p>The default is {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED}.* @return the propagation behavior* @see #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager#isActualTransactionActive()*/default int getPropagationBehavior() {return PROPAGATION_REQUIRED;}/*** Return the isolation level.* <p>Must return one of the {@code ISOLATION_XXX} constants defined on* {@link TransactionDefinition this interface}. Those constants are designed* to match the values of the same constants on {@link java.sql.Connection}.* <p>Exclusively designed for use with {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED} or* {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW} since it only applies to newly started* transactions. Consider switching the "validateExistingTransactions" flag to* "true" on your transaction manager if you'd like isolation level declarations* to get rejected when participating in an existing transaction with a different* isolation level.* <p>The default is {@link #ISOLATION_DEFAULT}. Note that a transaction manager* that does not support custom isolation levels will throw an exception when* given any other level than {@link #ISOLATION_DEFAULT}.* @return the isolation level* @see #ISOLATION_DEFAULT* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setValidateExistingTransaction*/default int getIsolationLevel() {return ISOLATION_DEFAULT;}/*** Return the transaction timeout.* <p>Must return a number of seconds, or {@link #TIMEOUT_DEFAULT}.* <p>Exclusively designed for use with {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED} or* {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW} since it only applies to newly started* transactions.* <p>Note that a transaction manager that does not support timeouts will throw* an exception when given any other timeout than {@link #TIMEOUT_DEFAULT}.* <p>The default is {@link #TIMEOUT_DEFAULT}.* @return the transaction timeout*/default int getTimeout() {return TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;}/*** Return whether to optimize as a read-only transaction.* <p>The read-only flag applies to any transaction context, whether backed* by an actual resource transaction ({@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRED}/* {@link #PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW}) or operating non-transactionally at* the resource level ({@link #PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS}). In the latter case,* the flag will only apply to managed resources within the application,* such as a Hibernate {@code Session}.* <p>This just serves as a hint for the actual transaction subsystem;* it will <i>not necessarily</i> cause failure of write access attempts.* A transaction manager which cannot interpret the read-only hint will* <i>not</i> throw an exception when asked for a read-only transaction.* @return {@code true} if the transaction is to be optimized as read-only* ({@code false} by default)* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronization#beforeCommit(boolean)* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager#isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()*/default boolean isReadOnly() {return false;}/*** Return the name of this transaction. Can be {@code null}.* <p>This will be used as the transaction name to be shown in a* transaction monitor, if applicable.* <p>In case of Spring's declarative transactions, the exposed name will be* the {@code fully-qualified class name + "." + method name} (by default).* @return the name of this transaction ({@code null} by default}* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager#getCurrentTransactionName()*/@Nullabledefault String getName() {return null;}// Static builder methods/*** Return an unmodifiable {@code TransactionDefinition} with defaults.* <p>For customization purposes, use the modifiable* {@link org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition}* instead.* @since 5.2*/static TransactionDefinition withDefaults() {return StaticTransactionDefinition.INSTANCE;}}
从这段代码不难看出,TransactionDefinition接口中主要定义了Spring事务的传播属性及隔离级别。其中事务传播属性有7个,事务隔离级别有5个。其中7个事务传播属性分别为:
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式继续运行
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务;如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建一个新的事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起
- PROPAGATION_NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常
- PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则创建一个事务作为当前事务的嵌套事务来运行;如果当前没有事务,则该取值等价于REQUIRED
4个事务隔离级别分别为:
- ISOLATION_DEFAULT:使用基础数据存储的默认隔离级别。所有其他级别都对应于JDBC隔离级别
- ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:读未提交
- ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:读已提交
- ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:可重复读
- ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:序列化读
Spring事务失效的场景有哪些?
@Transactional注解的作用是什么?它的常用属性有哪些?
Spring事务的底层实现是什么?如何集成其他事务管理器?
关于这几个问题,下一篇文章会给出相应的回答。
Spring事务开发案例
在Spring中开发事务代码有三种方式:基于xml配置式、编程式、声明式。其中最常用的时声明式。由于第一种开发方式相对古老,所以这里不再介绍,下面讲着重介绍后两种方式:
- 编程式:所谓编程式事务是指通过使用Spring事务组件手动开发代码来实现对事务的管理,这里的事务组件是指PlatformTransactionManager、TransactionTemplate等等,实践中更加推荐使用TransactionTemplate。在工作中有幸使用过前一种来对数据库操作进行管理
- 声明式:所谓声明式事务是指采用Spring Boot相关组件提供的事务注解来实现对事务管理,这里的事务注解是指@Transaction等等。本系列教程要讲解的就是这部分事务的原理。
关于这两种事务管理方式优缺点的一些说明:
- 编程式事务允许用户在代码中精确定义事务的边界,但是这种方式侵入了系统业务代码,对代码产生了一定的影响(简言之就是事务管理更加细致,但是对业务代码有一定的影响)
- 声明式事务有助于用户将操作与事务规则进行解耦,它基于AOP最终会交由Spring容器实现,开发人员只需关注业务逻辑实现即可(这种方式不仅仅开发简单,而且减少了代码开发量,并且代码看起来更加清爽整洁)
下面我们主要讲解声明式事务的开发案例,这种方式的入口为Application.java类,其代码如下所示:
import org.com.chinasofti.springtransaction.service.TransferService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;import java.math.BigDecimal;@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
// 注意这个注解
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringTransactionApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {// SpringApplication.run(SpringTransactionApplication.class, args);// 下面这段逻辑,可以根据需要新增TransferService transferService = (TransferService) SpringApplication.run(SpringTransactionApplication.class, args).getBean(TransferService.class);transferService.check("jack", "tom", BigDecimal.valueOf(100));}}
注意上面代码中的@EnableTransactionManagement这个注解。下面主要看一下案例的业务代码,首先看一下业务接口TransferService代码,如下所示:
import java.math.BigDecimal;public interface TransferService {void check(String from, String to, BigDecimal money);void transfer(String from, String to, BigDecimal money);}
接着再来看一下该业务接口实现类TransferServiceImpl的代码,主要关注该类上面的注解@Transactional,具体代码为:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;import java.math.BigDecimal;/*** 环绕增强开始!!* 开始增强!!* 校验开始* 校验中||...........* 校验中==...........* 校验结束* 返回之后执行* 结束增强!!* 环绕增强结束!!*/
@Service("transferService")
@Transactional
public class TransferServiceImpl implements TransferService {@Overridepublic void check(String from, String to, BigDecimal money) {System.out.println("校验开始");System.out.println("校验中||...........");try {System.out.println(1 / 0);Thread.sleep(1000 * 5);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("校验中==...........");System.out.println("校验结束");}@Overridepublic void transfer(String from, String to, BigDecimal money) {System.out.println("转账开始");System.out.println("转账中...........");System.out.println("转账结束");}}
这样事务相关的代码就开发完了。注意这里我们并没有列出操作数据表的代码。(声明文中所列内容部分源自网络,尤其《一文搞懂什么是事务 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)》这篇博文,如果想看原文,可以看点击上面的链接。在此向这篇博文作者说声谢谢!)
相关文章:

Spring 事务原理一
从本篇博客开始,我们将梳理Spring事务相关的知识点。在开始前,想先给自己定一个目标:通过此次梳理要完全理解事务的基本概念及Spring实现事务的基本原理。为实现这个目标我想按以下几个步骤进行: 讲解事务中的一些基本概念使用Sp…...

creo草绘3个实例学习笔记
creo草绘3个实例 文章目录 creo草绘3个实例草绘01草绘02草绘03 草绘01 草绘02 草绘03...

Modern C++ std::move的实现原理
前言 有一节我们分析了std::bind的实现原理,本节稍作休息分析一个比较简单的std::move 原理 std::move的原理太简单了,一句话:就是把传进来的参数强转为右值引用类型。作用为调用移动构造函数,或移动赋值函数。下面通过例子和代…...

爬虫工作量由小到大的思维转变---<第四十章 Scrapy Redis 实现IP代理池管理的最佳实践>
前言: 本篇是要结合上篇一起看的姊妹篇:爬虫工作量由小到大的思维转变---<第三十九章 Scrapy-redis 常用的那个RetryMiddleware>-CSDN博客 IP代理池的管理对于确保爬虫的稳定性和数据抓取的匿名性至关重要。围绕Scrapy-Redis框架和一个具体的IP代理池中…...

C# 实现 XOR 密码
XOR密码(异或密码)是一种简单的加密算法,它使用异或(XOR)操作来对明文和密钥进行加密和解密。 异或操作是一种位运算,它对两个二进制数的对应位进行比较,如果两个位相同(都为0或都为…...
【Web前端开发基础】CSS3之空间转换和动画
CSS3之空间转换和动画 目录 CSS3之空间转换和动画一、空间转换1.1 概述1.2 3D转换常用的属性1.3 3D转换:translate3d(位移)1.4 3D转换:perspective(视角)1.5 3D转换:rotate3d(旋转&a…...
)
Go实现一个简单的烟花秀效果(附带源码)
在 Go 语言中,要实现烟花秀效果可以使用 github.com/fogleman/gg 包进行绘图。以下是一个简单的例子: 首先,确保你已经安装了(有时候需要梯子才可以安装) github.com/fogleman/gg 包: go get -u github.c…...
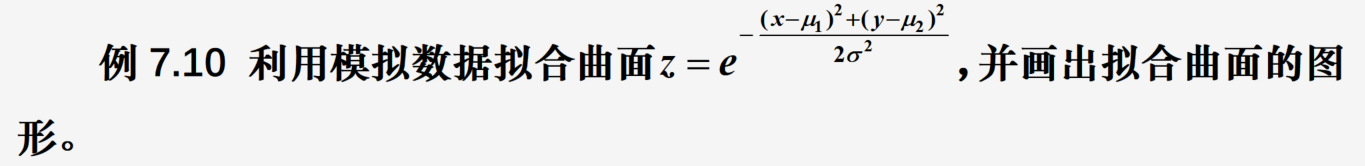
【数学建模】插值与拟合
文章目录 插值插值方法用Python解决插值问题 拟合最小二乘拟合数据拟合的Python实现 适用情况 处理由试验、测量得到的大量数据或一些过于复杂而不便于计算的函数表达式时,构造一个简单函数作为要考察数据或复杂函数的近似 定义 给定一组数据,需要确定满…...
全卷积网络:革新图像分析
一、介绍 全卷积网络(FCN)的出现标志着计算机视觉领域的一个重要里程碑,特别是在涉及图像分析的任务中。本文深入探讨了 FCN 的概念、它们的架构、它们与传统卷积神经网络 (CNN) 的区别以及它们在各个领域的应用。 就像…...

ubuntu20.04 格式化 硬盘 扩展硬盘GParted
如何在 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 上安装分区编辑器 GParted?_gparted安装-CSDN博客 sudo apt install gparted 步骤5:启动GParted 安装完成后,您可以在应用程序菜单中找到GParted。点击它以启动分区编辑器。 通过以上步骤,您可以在Ubun…...

docker的资源限制(cgroup)
前瞻 Docker 通过 Cgroup 来控制容器使用的资源配额,包括 CPU、内存、磁盘三大方面, 基本覆盖了常见的资源配额和使用量控制。 Cgroup 是 ControlGroups 的缩写,是 Linux 内核提供的一种可以限制、记录、隔离进程组所使用的物理资源(如 CPU、…...

ChatGPT与文心一言:应用示例与体验比较
ChatGPT 和文心一言哪个更好用? 为了更好地感受ChatGPT和文心一言这两款AI助手如何在实际运用中竞相辉映,我将提供一些典型的应用示例。这些示例都取自真实的用户体验,以帮助解释这两种工具如何让日常生活或工作变得更加轻松。 ChatGPT Ch…...
紫光展锐T760_芯片性能介绍_展锐T760安卓核心板定制
展锐T760核心板是一款基于国产5G芯片的智能模块,采用紫光展锐T760制程工艺为台积电6nm工艺,支持工艺具有出色的能效表现。其采用主流的44架构的八核设计,包括4颗2.2GHz A76核心和4颗A55核心设计,内存单元板载可达8GB Ram256GB ROM…...

从动力系统研究看当今数学界
6.3... Milnor’s definition of “attractors” which has been criticized above by us). The work of [KSS2] of asserting the existence of “nice open set” of Ω(p.148) would be likely not verified, for example we think the first sentence “… since f is nont…...
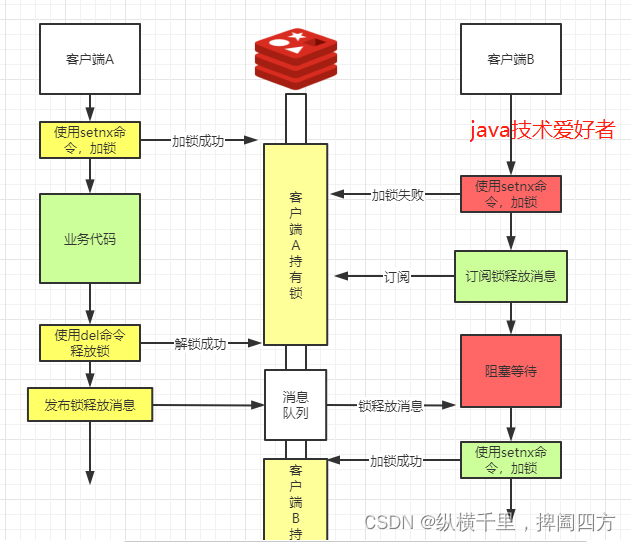
【征服redis15】分布式锁的功能与整体设计方案
目录 1. 分布式锁的概念 2.基于数据库做分布式锁 2.1 基于表主键唯一做分布式锁 2.2 基于表字段版本号做分布式锁 2.3 基于数据库排他锁做分布式锁 3.使用Redis做分布式锁 3.1 redis实现分布式锁的基本原理 3.2 问题一:增加超时机制,防止长期持有…...

MATLAB中实现机械臂逆运动学求解的方法之一是使用阻尼最小二乘法
MATLAB中实现机械臂逆运动学求解的方法之一是使用阻尼最小二乘法。阻尼最小二乘法通常用于处理数值求解问题中的不稳定性和噪声。以下是一个简单的MATLAB代码示例,演示了机械臂逆运动学的阻尼最小二乘法求解: % 机械臂参数 L1 1; % 机械臂长度 L2 1;…...
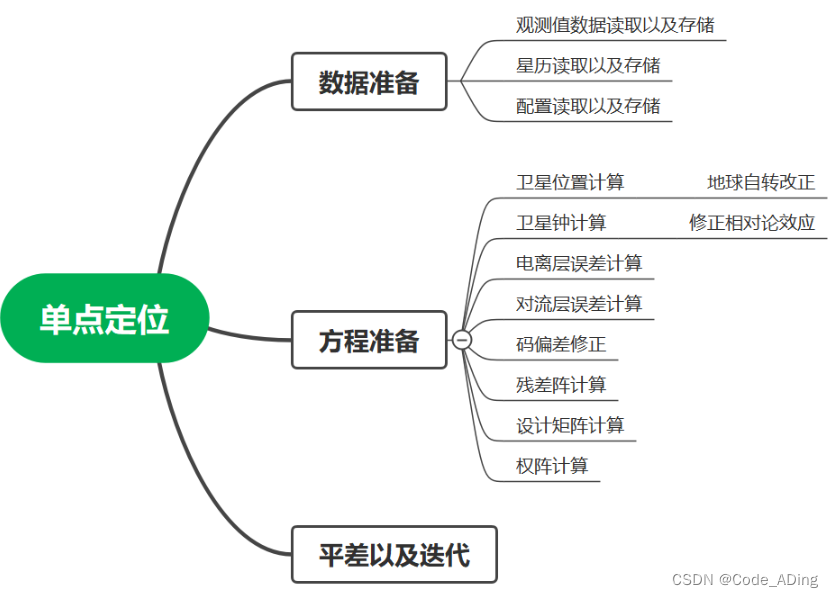
2024.1.24 GNSS 学习笔记
1.伪距观测值公式 2.载波相位观测值公式 3.单点定位技术(Single Point Positionin, SPP) 仅使用伪距观测值,不使用其他的辅助信息获得ECEF框架下绝对定位技术。 使用广播星历的轨钟进行定位,考虑到轨钟的米级精度,所以对于<1米的误差&…...
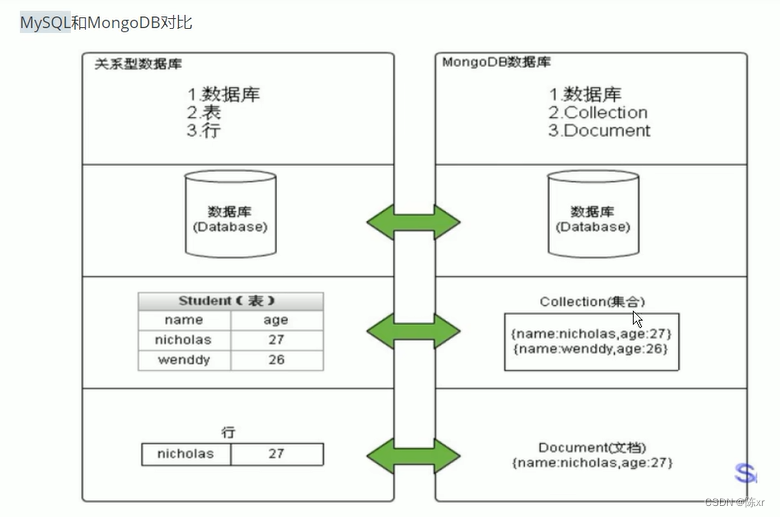
2024-01-22(MongoDB)
1.Mongodb使用的业务场景: 传统的关系型数据库/mysql在“三高”需求以及应对web2.0的网站需求面前,有点力不从心,什么是“三高”需求: a. 对数据库高并发的读写需求 b. 对海量数据的高效率存储和访问需求 c. 对数据库的高可扩…...
无人机航迹规划(六):七种元启发算法(DBO、LO、SWO、COA、LSO、KOA、GRO)求解无人机路径规划(提供MATLAB代码)
一、七种算法(DBO、LO、SWO、COA、LSO、KOA、GRO)简介 1、蜣螂优化算法DBO 蜣螂优化算法(Dung beetle optimizer,DBO)由Jiankai Xue和Bo Shen于2022年提出,该算法主要受蜣螂的滚球、跳舞、觅食、偷窃和繁…...
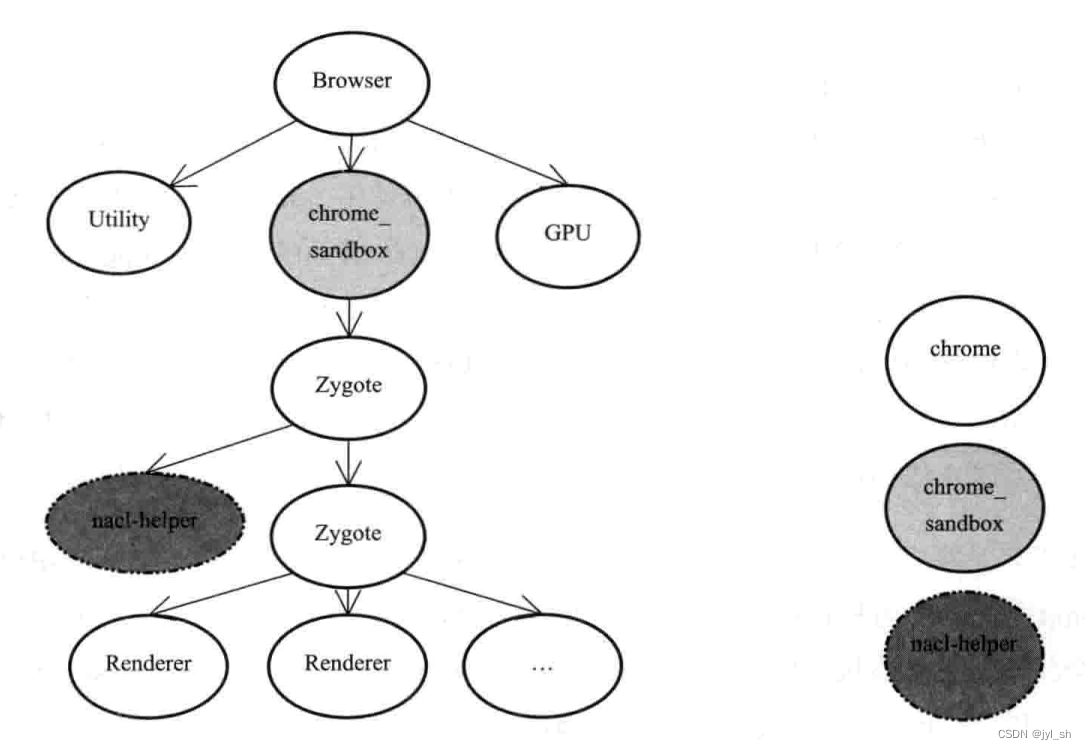
《WebKit 技术内幕》学习之十二(2):安全机制
2 沙箱模型 2.1 原理 一般而言,对于网络上的网页中的JavaScript代码和插件是不受信的(除非是经过认证的网站),特别是一些故意设计侵入浏览器运行的主机代码更是非常危险,通过一些手段或者浏览器中的漏洞,…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...
label-studio的使用教程(导入本地路径)
文章目录 1. 准备环境2. 脚本启动2.1 Windows2.2 Linux 3. 安装label-studio机器学习后端3.1 pip安装(推荐)3.2 GitHub仓库安装 4. 后端配置4.1 yolo环境4.2 引入后端模型4.3 修改脚本4.4 启动后端 5. 标注工程5.1 创建工程5.2 配置图片路径5.3 配置工程类型标签5.4 配置模型5.…...

条件运算符
C中的三目运算符(也称条件运算符,英文:ternary operator)是一种简洁的条件选择语句,语法如下: 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2• 如果“条件表达式”为true,则整个表达式的结果为“表达式1”…...
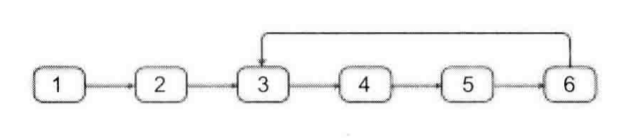
剑指offer20_链表中环的入口节点
链表中环的入口节点 给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。 若其中不包含环,则输出null。 数据范围 节点 val 值取值范围 [ 1 , 1000 ] [1,1000] [1,1000]。 节点 val 值各不相同。 链表长度 [ 0 , 500 ] [0,500] [0,500]。 …...
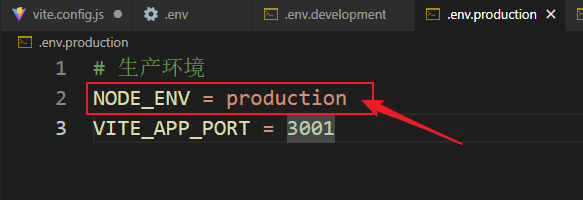
vue3+vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法
vue3vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法 .env文件作用命名规则常用的配置项示例使用方法注意事项在vite.config.js文件中读取环境变量方法 .env文件作用 .env 文件用于定义环境变量,这些变量可以在项目中通过 import.meta.env 进行访问。Vite 会自动加载这些环境变…...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...

tree 树组件大数据卡顿问题优化
问题背景 项目中有用到树组件用来做文件目录,但是由于这个树组件的节点越来越多,导致页面在滚动这个树组件的时候浏览器就很容易卡死。这种问题基本上都是因为dom节点太多,导致的浏览器卡顿,这里很明显就需要用到虚拟列表的技术&…...

laravel8+vue3.0+element-plus搭建方法
创建 laravel8 项目 composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel8 8.* 安装 laravel/ui composer require laravel/ui 修改 package.json 文件 "devDependencies": {"vue/compiler-sfc": "^3.0.7","axios": …...

力扣-35.搜索插入位置
题目描述 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。 请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。 class Solution {public int searchInsert(int[] nums, …...
让回归模型不再被异常值“带跑偏“,MSE和Cauchy损失函数在噪声数据环境下的实战对比
在机器学习的回归分析中,损失函数的选择对模型性能具有决定性影响。均方误差(MSE)作为经典的损失函数,在处理干净数据时表现优异,但在面对包含异常值的噪声数据时,其对大误差的二次惩罚机制往往导致模型参数…...
