C++提高笔记(六)---STL函数对象、STL常用算法(遍历、查找)
1、STL-函数对象
1.1函数对象
1.1.1函数对象概念
概念:
重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常称为函数对象
函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数
1.1.2 函数对象使用
特点:
函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象内部可以有自己的状态
函数对象可以作为参数传递
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//函数对象(仿函数)
//函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
//函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象内部可以有自己的状态
//函数对象可以作为参数传递
class MyAdd
{
public:int operator()(int v1, int v2){return v1 + v2;}
};
//1、函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
void test01()
{MyAdd myadd;cout << myadd(10, 10) << endl;
}
//2、函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象内部可以有自己的状态
class MyPrint
{
public:MyPrint(){this->count = 0;}void operator()(string text){cout << text << endl;this->count++;}int count;//内部自己状态
};
void test02()
{MyPrint myprint;myprint("hello world!");myprint("hello world!");myprint("hello world!");myprint("hello world!");cout << "MyPrint调用的次数:" << myprint.count << endl;
}
//3、函数对象可以作为参数传递
void doPrint(MyPrint& mp, string text)
{mp(text);
}
void test03()
{MyPrint myprint;doPrint(myprint, "hello C++");
}int main()
{test01();test02();test03();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
20
hello world!
hello world!
hello world!
hello world!
MyPrint调用的次数:4
hello C++
请按任意键继续. . .1.2谓词
1.2.1谓词对象
概念:
返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
如果operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
如果operator()接受二个参数,那么叫做二元谓词
1.2.2一元谓词
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//仿函数 返回值类型是bool数据类型 称为谓词
//如果operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找容器中 是否有大于5的数字//GreaterFive() 匿名函数对象vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if (it == v.end()){cout << "未找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了大于5的数字为:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
找到了大于5的数字为:6
请按任意键继续. . .1.2.3二元谓词
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//仿函数 返回值类型是bool数据类型 称为谓词
//二元谓词
class MyCompare
{
public:bool operator()(int v1,int v2){return v1 > v2;}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);sort(v.begin(), v.end());//默认升序for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;//使用函数对象,改变算法策略,变为降序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());cout << "---------------------------" << endl;for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
10 20 30 40 50
---------------------------
50 40 30 20 10
请按任意键继续. . .1.3内建函数对象
1.3.1内建函数对象意义
概念:STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
算术仿函数
关系仿函数
逻辑仿函数
用法:这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同。使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件#include<functional>
1.3.2算术仿函数
功能描述:实现四则运算。其中negate是一元运算,其他都是二元运算
仿函数原型:
template<class T>T plus<T> //加法仿函数
template<class T>T minus<T> //减法仿函数
template<class T>T multiplies<T> //乘法仿函数
template<class T>T divides<T> //除法仿函数
template<class T>T modulus<T> //取模仿函数
template<class T>T negate<T> //取反仿函数#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<functional>//内建函数对象头文件
//内建函数对象 算术仿函数
//template<class T>T plus<T> //加法仿函数
//template<class T>T minus<T> //减法仿函数
//template<class T>T multiplies<T> //乘法仿函数
//template<class T>T divides<T> //除法仿函数
//template<class T>T modulus<T> //取模仿函数
//template<class T>T negate<T> //取反仿函数//negate 一元仿函数 取反仿函数
void test01()
{negate<int>n;cout << n(50) << endl;
}
//plus 二元仿函数 加法
void test02()
{plus<int>p;//默认传入同种数据类型,不能传入不同种数据类型cout << p(10, 20) << endl;
}
int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
-50
30
请按任意键继续. . .1.3.3关系仿函数
功能描述:实现关系对比
仿函数原型:(最常用的是大于)
template<class T> bool equal_to<T> //等于
template<class T> bool not_equal _to<T> //不等于
template<class T> bool greater<T> //大于
template<class T> bool greater_equal<T> //大于等于
template<class T> bool less<T> //小于
template<class T> bool less_equal<T> //小于等于#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<functional>//内建函数对象头文件
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//内建函数对象 关系仿函数
//template<class T> bool equal_to<T> //等于
//template<class T> bool not_equal _to<T> //不等于
//template<class T> bool greater<T> //大于
//template<class T> bool greater_equal<T> //大于等于
//template<class T> bool less<T> //小于
//template<class T> bool less_equal<T> //小于等于//大于 greater
class MyCompare
{
public:bool operator()(int v1, int v2){return v1 > v2;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;//降序//sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare()); //自己重载仿函数sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());//内建函数对象(仿函数)greater,效果一致for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
10 30 40 50 20
50 40 30 20 10
请按任意键继续. . .1.3.4逻辑仿函数
功能描述:实现逻辑运算
函数原型:
template<class T> bool logical_and<T> //逻辑与
template<class T> bool 1ogical_or<T> //逻辑或
template<class T> bool logical_not<T> //逻辑非#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<functional>//内建函数对象头文件
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//内建函数对象 关系仿函数
//template<class T> bool logical_and<T> //逻辑与
//template<class T> bool 1ogical_or<T> //逻辑或
//template<class T> bool logical_not<T> //逻辑非//逻辑非 logical_not
void test01()
{vector<bool>v;v.push_back(true);v.push_back(false);v.push_back(true);v.push_back(false);for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;//利用逻辑非,将容器v搬运到容器v2中,并执行取反的操作vector<bool>v2;v2.resize(v.size());transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>());for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++){cout << *it << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
1 0 1 0
0 1 0 1
请按任意键继续. . .2、STL-常用算法
概述:
算法主要是由头文件<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成
<algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较,交换,查找,遍历操作,复制,修改等
<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数
<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象
2.1 常用遍历算法
学习目标:掌握常用的遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each //遍历容器
transform //搬运容器到另一个容器中2.1.1 for_each
功能描述:实现遍历容器
函数原型:
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
// 遍历算法 遍历容器元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _func函数或者函数对象#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 for_each
//普通函数
void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
//仿函数
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);//普通函数放函数名cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());//仿函数要放函数对象,加()cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
请按任意键继续. . .总结:for_each在实际开发中是最常用遍历方法,需要熟练掌握
2.1.2 transform
功能描述:搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
transform(iterator begl,iterator end1,iterator beg2,_func);
//beg1 源容器开始迭代器
//end1 源容器结束迭代器
//beg2 目标容器开始迭代器
//_func 函数或者函数对象#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 transform
//仿函数
class Transform
{
public:int operator()(int v){return v + 10;}
};class MyPrint
{
public:void operator()(int v){cout << v << " ";}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget;//目标容器vTarget.resize(v.size());//目标容器 需要提前开辟空间,否则搬运不成功transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());//可以在最后一个函数对搬运的数据进行运算或者改变 例如这次加10for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());//仿函数要放函数对象,加()cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
请按任意键继续. . .2.2常用查找算法
学习目标:掌握常用的查找算法
算法简介:
find //查找元素
find_if //按条件查找元素
adjacent_find //查找相邻重复元素
binary_search //二分查找法
count //统计元素个数
count_if //按条件统计元素个数2.2.1 find
功能描述:查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定校置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 find
//查找 内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if (pos == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到:" << *pos << endl;}
}class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载== 底层find知道如何对比Person数据类型bool operator==(const Person& p){if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};//查找 自定义数据类型
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);Person pp("bbb", 20);//查找有无与此人相同的人//放入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);//查找vector<Person>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);if (pos == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到此人 姓名:" << pos->m_Name << " 年龄:" << pos->m_Age << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
找到:5
找到此人 姓名:bbb 年龄:20
请按任意键继续. . .2.2.2 find_if
功能描述:按条件查找元素
函数原型:
find_if(iterator beg,iterator end,_Pred);
// 按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置选代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
//_Pred 函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 find_if
//1、查找 内置数据类型
class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator pos = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if (pos == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到大于5的数字 为:" << *pos << endl;}
}class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person& p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};//2、查找 自定义数据类型
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);Person pp("bbb", 20);//查找有无与此人相同的人//放入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);//查找年龄大于20的人vector<Person>::iterator pos = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());if (pos == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到此人 姓名:" << pos->m_Name << " 年龄:" << pos->m_Age << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
找到大于5的数字 为:6
找到此人 姓名:ccc 年龄:30
请按任意键继续. . .2.2.3 adjacent_find
功能描述:查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);
// 查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的选代器
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 adjacent_find
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);vector<int>::iterator pos = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (pos == v.end()){cout << "没有找到相邻重复元素!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *pos << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
找到相邻重复元素:3
请按任意键继续. . .2.2.4 binary_search
功能描述:查找指定元素是否存在 注意: 在无序序列中不可用
函数原型:
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 查找指定的元素,查到返回true 否则false
// 注意: 在无序序列中不可用
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素n#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 binary_search
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找容器中是否有9 元素//注意: 在无序序列中不可用//如果是无序序列,结果未知//必须要有序bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if (ret){cout << "找到了元素!" << endl;}else{cout << "未找到!" << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
找到了元素!
请按任意键继续. . .2.2.5 count
功能描述:统计元素个数
注意:统计自定义数据类型时,需要配合重载operator==
函数原型:
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 统计的元素#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 count
//1、统计内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 40);cout << "40元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}
//2、统计自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//需要加const,防止用户修改Person//否则会报错bool operator==(const Person& p){if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 40);//将人员插入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person p("诸葛亮", 35);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);cout << "与诸葛亮同岁数的人员个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
40元素个数为:3
与诸葛亮同岁数的人员个数为:3
请按任意键继续. . .2.2.6 count_if
功能描述:按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred);
// 按条件统计元素出现次数
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 count_if
//1、统计内置数据类型
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 20;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}
//2、统计自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//需要加const,防止用户修改Person//否则会报错bool operator==(const Person& p){if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class AgeGreater20
{
public:bool operator()(const Person& p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 40);Person p5("曹操", 20);//将人员插入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater20());cout << "大于20岁的人员个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test01();test02();system("pause");return 0;
}输出结果:
大于20的元素个数为:3
大于20岁的人员个数为:4
请按任意键继续. . .相关文章:
---STL函数对象、STL常用算法(遍历、查找))
C++提高笔记(六)---STL函数对象、STL常用算法(遍历、查找)
1、STL-函数对象 1.1函数对象 1.1.1函数对象概念 概念: 重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常称为函数对象 函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数 本质:函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个…...
【每日一问】手机如何开启USB调试?
一、背景 当电脑跟手机之间需要进行交互的时候,可以考虑使用usb进行连接。那么手机如何开启USB调试呢? 二、操作步骤: 思路: 步骤1:手机开启开发者模式 步骤2:在开发者模式中,开启“USB调试”…...
)
Java映射知识点(含面试大厂题含源码)
在Java中,映射(Map)是一个存储键值对的数据结构,其中每个键映射到一个值。Java提供了几种实现Map接口的类,以满足不同的需求。了解映射的知识点可以帮助你在处理需要键值关联的数据时更加高效。 核心知识点 Map接口&a…...
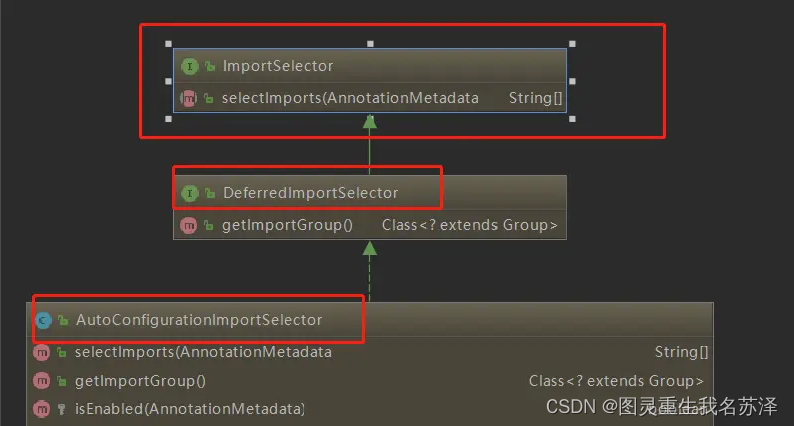
拆解Spring boot:Springboot为什么如此丝滑而简单?源码剖析解读自动装配
🎉🎉欢迎光临,终于等到你啦🎉🎉 🏅我是苏泽,一位对技术充满热情的探索者和分享者。🚀🚀 🌟持续更新的专栏《Spring 狂野之旅:从入门到入魔》 &a…...
中国银行信息系统应用架构发展历程
概述: 从 20 世纪 80 年代开始至今,我国银行业信息化历程已 有四十年历史。虽然相对于发达国家来讲,我国银行业务信 息化起步较晚,但发展速度很快, 目前我国一些大型商业银行的信息化程度已经处于全球领先水平。 “银行…...
)
掌握Go语言:探索Go语言指针,解锁高效内存操作与动态数据结构的奥秘(19)
指针是一个变量,它存储了另一个变量的地址。在Go语言中,指针提供了直接访问内存地址的能力,允许程序直接操作内存,这在某些场景下非常有用。 Go语言指针的详细使用方法 声明指针 可以使用*符号来声明指针变量,例如&…...
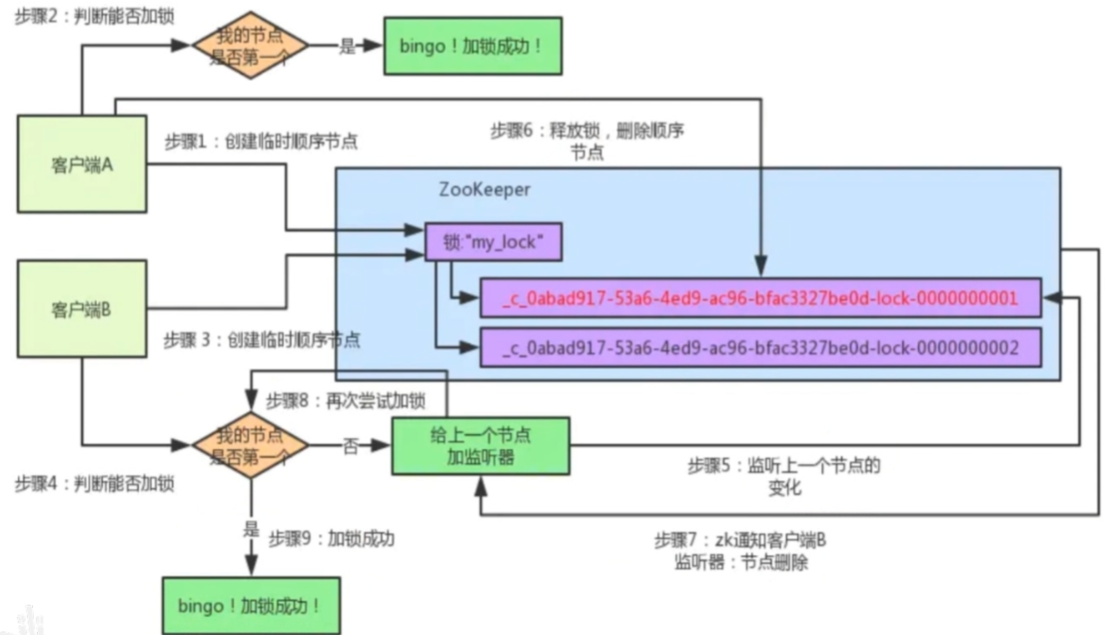
大数据面试题 —— Zookeeper
目录 ZooKeeper 的定义ZooKeeper 的特点ZooKeeper 的应用场景你觉得Zookeeper比较重要的功能ZooKeeper 的选举机制 ***zookeeper主节点故障,如何重新选举?ZooKeeper 的监听原理 ***zookeeper集群的节点数为什么建议奇数台 ***ZooKeeper 的部署方式有哪几…...

【安全类书籍-6】僵尸网络:网络程序杀手
目录 内容 用处 下载链接 内容 这本书着重探讨以下几个主题: 1. 僵尸网络基础:介绍僵尸网络的基本构成、运作机制以及在全球网络空间中的影响和威胁程度。 2. 僵尸网络技术剖析:详细分析僵尸网络的组件,如命令控制中心(C&C)、恶意软件传播途径、感染节点的招募和…...

文件的创建与删除
文件的创建 使用File类创建一个文件对象,例如:File filenew File("c:\\myletter" , "letter.txt"); public boolean createNewFile();/*如果c:\myletter目录中没 有名字为letter.txt文件,文件对象file调用createNewFil…...
图论题目集一(代码 注解)
目录 题目一: 题目二: 题目三: 题目四: 题目五: 题目六: 题目七: 题目一: #include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<cstring> using namespace st…...

解释MVC和MVVM架构模式
一、解释MVC和MVVM架构模式 MVC和MVVM都是常见的前端架构模式,用于抽象分离并解决特定问题。这两种模式在结构上具有一定的相似性,但在细节和数据处理方式上存在一些差异。 MVC,即Model-View-Controller,是一种用于应用程序分层…...

OLLAMA:如何像云端一样运行本地大语言模型
简介:揭开 OLLAMA 本地大语言模型的神秘面纱 您是否曾发现自己被云端语言模型的网络所缠绕,渴望获得更本地化、更具成本效益的解决方案?那么,您的探索到此结束。欢迎来到 OLLAMA 的世界,这个平台将彻底改变我们与大型…...

React全家桶及原理解析-lesson4-Redux
lesson4-react全家桶及原理解析.mov React全家桶及原理解析 React全家桶及原理解析 课堂⽬标资源起步Reducer 什么是reducer什么是reduceRedux 上⼿ 安装reduxredux上⼿检查点react-redux 异步代码抽取Redux拓展 redux原理 核⼼实现中间件实现redux-thunk原理react-redux原理 实…...

电商api数据接口技术开发来赞达lazada通过商品ID抓取商品详情信息item_get请求key接入演示
要获取Lazada的商品详情,你需要使用item_get请求。首先,你需要注册一个开发者账号并获取API密钥(App Key和App Secret)。然后,你可以使用以下Python代码示例来获取商品详情: # coding:utf-8 ""&…...
-音频焦点2)
零基础入门多媒体音频(2)-音频焦点2
说实话,android的代码是越来越难以阅读。业务函数里面狗皮膏药似的补丁与日俱增。继上篇简要介绍音频焦点的文章,这篇文章的主要内容是分析audiofocus的实现。看了一下午的相关代码都没找到做audiofocus策略的核心逻辑。目前能看懂的大概包含下面两个逻辑…...
Spark杂谈
文章目录 什么是Spark对比HadoopSpark应用场景Spark数据处理流程什么是RDDSpark架构相关进程入门案例:统计单词数量Spark开启historyServer 什么是Spark Spark是一个用于大规模数据处理的统一计算引擎Spark一个重要的特性就是基于内存计算,从而它的速度…...

【PyTorch】进阶学习:一文详细介绍 torch.save() 的应用场景、实战代码示例
【PyTorch】进阶学习:一文详细介绍 torch.save() 的应用场景、实战代码示例 🌈 个人主页:高斯小哥 🔥 高质量专栏:Matplotlib之旅:零基础精通数据可视化、Python基础【高质量合集】、PyTorch零基础入门教程…...

私域流量运营的关键要素和基本步骤
解锁增长的四大关键: 关键要素一:精准营销 精准营销是私域流量运营的核心所在。通过精细化运营和个性化服务,企业可以将普通用户转化为忠实粉丝,提高用户的粘性和转化率。采用数据驱动的精准营销策略,深度挖掘用户需求…...
k8s部署hadoop
(作者:陈玓玏) 配置和模板参考helm仓库:https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/apache-hadoop-helm/hadoop 先通过以下命令生成yaml文件: helm template hadoop pfisterer-hadoop/hadoop > hadoop.yaml用kube…...
卡住)
deepspeed分布式训练在pytorch 扩展(PyTorch extensions)卡住
错误展示: Using /root/.cache/torch_extensions/py310_cu121 as PyTorch extensions root... Using /root/.cache/torch_extensions/py310_cu121 as PyTorch extensions root... 错误表现: 出现在多卡训练过程的pytorch 扩展,deepspee…...

【网络】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iftop
在Linux系统中,iftop是网络管理的得力助手,能实时监控网络流量、连接情况等,帮助排查网络异常。接下来从多方面详细介绍它。 目录 【网络】每天掌握一个Linux命令 - iftop工具概述安装方式核心功能基础用法进阶操作实战案例面试题场景生产场景…...

AI Agent与Agentic AI:原理、应用、挑战与未来展望
文章目录 一、引言二、AI Agent与Agentic AI的兴起2.1 技术契机与生态成熟2.2 Agent的定义与特征2.3 Agent的发展历程 三、AI Agent的核心技术栈解密3.1 感知模块代码示例:使用Python和OpenCV进行图像识别 3.2 认知与决策模块代码示例:使用OpenAI GPT-3进…...
智慧工地云平台源码,基于微服务架构+Java+Spring Cloud +UniApp +MySql
智慧工地管理云平台系统,智慧工地全套源码,java版智慧工地源码,支持PC端、大屏端、移动端。 智慧工地聚焦建筑行业的市场需求,提供“平台网络终端”的整体解决方案,提供劳务管理、视频管理、智能监测、绿色施工、安全管…...

Qt Http Server模块功能及架构
Qt Http Server 是 Qt 6.0 中引入的一个新模块,它提供了一个轻量级的 HTTP 服务器实现,主要用于构建基于 HTTP 的应用程序和服务。 功能介绍: 主要功能 HTTP服务器功能: 支持 HTTP/1.1 协议 简单的请求/响应处理模型 支持 GET…...

回溯算法学习
一、电话号码的字母组合 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;import javax.management.loading.PrivateClassLoader;public class letterCombinations {private static final String[] KEYPAD {"", //0"", //1"abc", //2"…...
Selenium常用函数介绍
目录 一,元素定位 1.1 cssSeector 1.2 xpath 二,操作测试对象 三,窗口 3.1 案例 3.2 窗口切换 3.3 窗口大小 3.4 屏幕截图 3.5 关闭窗口 四,弹窗 五,等待 六,导航 七,文件上传 …...

【学习笔记】erase 删除顺序迭代器后迭代器失效的解决方案
目录 使用 erase 返回值继续迭代使用索引进行遍历 我们知道类似 vector 的顺序迭代器被删除后,迭代器会失效,因为顺序迭代器在内存中是连续存储的,元素删除后,后续元素会前移。 但一些场景中,我们又需要在执行删除操作…...

python爬虫——气象数据爬取
一、导入库与全局配置 python 运行 import json import datetime import time import requests from sqlalchemy import create_engine import csv import pandas as pd作用: 引入数据解析、网络请求、时间处理、数据库操作等所需库。requests:发送 …...

Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析
Qt 事件处理中 return 的深入解析 在 Qt 事件处理中,return 语句的使用是另一个关键概念,它与 event->accept()/event->ignore() 密切相关但作用不同。让我们详细分析一下它们之间的关系和工作原理。 核心区别:不同层级的事件处理 方…...

Python 训练营打卡 Day 47
注意力热力图可视化 在day 46代码的基础上,对比不同卷积层热力图可视化的结果 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torchvision import datasets, transforms from torch.utils.data import DataLoader import matplotlib.pypl…...
