Android车载——VehicleHal初始化(Android 11)
1 概述
VehicleHal是AOSP中车辆服务相关的hal层服务。它主要定义了与汽车硬件交互的标准化接口和属性管理,是一个独立的进程。
2 进程启动
VehicleHal相关代码在源码树中的hardware/interfaces/automotive目录下
首先看下Android.bp文件:
cc_binary {name: "android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service",defaults: ["vhal_v2_0_target_defaults"],vintf_fragments: ["android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service.xml",],init_rc: ["android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service.rc"],vendor: true,relative_install_path: "hw",srcs: ["VehicleService.cpp"],shared_libs: ["libbase","libjsoncpp","libprotobuf-cpp-lite",],static_libs: ["android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-manager-lib","android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-default-impl-lib","android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-libproto-native","libqemu_pipe",],
}
标准的hal服务层定义,入口在VehicleService.cpp,其他依赖文件在static_libs中定义。服务的可执行文件编译完成之后的名称是android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service。
进程是hal服务进程,由init通过解析rc文件进行拉起
service vendor.vehicle-hal-2.0 /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-serviceclass haluser vehicle_networkgroup system inet
进程名vendor.vehicle-hal-2.0,执行的就是/vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service这个可执行文件,class为hal,用户是vehicle_network,用户组是system和inet。
在init中class_start hal的时候启动该hal进程。
3 VHAL初始化
VHAL进程的入口在VehicleService.cpp中的main函数
hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/VehicleService.cpp
// xy:VHAL的入口函数,由init进程启动
int main(int /* argc */, char* /* argv */ []) {// xy:缓存属性值的地方auto store = std::make_unique<VehiclePropertyStore>();// xy:模拟与真实车辆的连接auto connector = std::make_unique<impl::EmulatedVehicleConnector>();// xy:模拟Hal,Hal的具体实现auto hal = std::make_unique<impl::EmulatedVehicleHal>(store.get(), connector.get());// xy:汽车模拟类,模拟车辆信号auto emulator = std::make_unique<impl::VehicleEmulator>(hal.get());// xy:VHAL的服务实现入口auto service = std::make_unique<VehicleHalManager>(hal.get());// xy:设置存储属性值的池子,便于重复使用connector->setValuePool(hal->getValuePool());// xy:设置binder线程数量configureRpcThreadpool(4, false /* callerWillJoin */);ALOGI("Registering as service...");// xy:将当前服务注册到HwServiceManager中status_t status = service->registerAsService();if (status != OK) {ALOGE("Unable to register vehicle service (%d)", status);return 1;}// Setup a binder thread pool to be a car watchdog client.// xy:watchDog设置ABinderProcess_setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(1);ABinderProcess_startThreadPool();sp<Looper> looper(Looper::prepare(0 /* opts */));std::shared_ptr<WatchdogClient> watchdogClient =ndk::SharedRefBase::make<WatchdogClient>(looper, service.get());// The current health check is done in the main thread, so it falls short of capturing the real// situation. Checking through HAL binder thread should be considered.if (!watchdogClient->initialize()) {ALOGE("Failed to initialize car watchdog client");return 1;}ALOGI("Ready");while (true) {looper->pollAll(-1 /* timeoutMillis */);}return 1;
}
接下来逐步解析各个模块的初始化
3.1 VehiclePropertyStore初始化
VehiclePropertyStore类的主要职责是缓存车辆数据,采用默认构造函数,构造函数中没有初始化逻辑。
using PropertyMap = std::map<RecordId, VehiclePropValue>;
std::unordered_map<int32_t /* VehicleProperty */, RecordConfig> mConfigs;
PropertyMap mPropertyValues; // Sorted map of RecordId : VehiclePropValue.
主要初始化了这两个数据对象,其中mConfigs用于存储属性配置,mPropertyValues用于存储属性值。
3.2 EmulatedVehicleConnector初始化
也是采用无参构造,初始化了一个对象
EmulatedUserHal mEmulatedUserHal;
3.3 EmulatedVehicleHal初始化
EmulatedVehicleHal(VehiclePropertyStore* propStore, VehicleHalClient* client,EmulatedUserHal* emulatedUserHal = nullptr);
这个类只有一个三个参数的构造函数,第三个参数有默认值,其实现如下:
EmulatedVehicleHal::EmulatedVehicleHal(VehiclePropertyStore* propStore, VehicleHalClient* client,EmulatedUserHal* emulatedUserHal): mPropStore(propStore),mHvacPowerProps(std::begin(kHvacPowerProperties), std::end(kHvacPowerProperties)),mRecurrentTimer(std::bind(&EmulatedVehicleHal::onContinuousPropertyTimer, this,std::placeholders::_1)),mVehicleClient(client),mEmulatedUserHal(emulatedUserHal) {initStaticConfig();for (size_t i = 0; i < arraysize(kVehicleProperties); i++) {mPropStore->registerProperty(kVehicleProperties[i].config);}mVehicleClient->registerPropertyValueCallback(std::bind(&EmulatedVehicleHal::onPropertyValue,this, std::placeholders::_1,std::placeholders::_2));
}
这个构造函数初始化的时候传入的两个参数是在main函数中创建的VehiclePropertyStore对象和EmulatedVehicleConnector对象,而这个构造函数的第二个参数却是VehicleHalClient,这是怎么回事呢?
class EmulatedVehicleConnector : public IPassThroughConnector<VehicleHalClient, VehicleHalServer>template <typename VehicleClientType, typename VehicleServerType>
class IPassThroughConnector : public VehicleClientType, public VehicleServerType
从上面可以看出,EmulatedVehicleConnector继承自IPassThroughConnector,而IPassThroughConnector定义了两个模板,IPassThroughConnector继承这两个模板类。所以EmulatedVehicleConnector继承VehicleHalClient和VehicleHalServer。所以EmulatedVehicleConnector是VehicleHalClient的子类。
接着分析EmulatedVehicleHal的构造函数,这里用传入的VehiclePropertyStore对象初始化mPropStore。
std::unordered_set<int32_t> mHvacPowerProps;const int32_t kHvacPowerProperties[] = {toInt(VehicleProperty::HVAC_FAN_SPEED),toInt(VehicleProperty::HVAC_FAN_DIRECTION),
};mHvacPowerProps(std::begin(kHvacPowerProperties), std::end(kHvacPowerProperties))
然后初始化这个成员变量,将数组中的两个空调相关的property的propId添加到mHvacPowerProps这个vector中。
RecurrentTimer mRecurrentTimer;mRecurrentTimer(std::bind(&EmulatedVehicleHal::onContinuousPropertyTimer, this,std::placeholders::_1)),RecurrentTimer(const Action& action) : mAction(action) {mTimerThread = std::thread(&RecurrentTimer::loop, this, action);}
这个是一个执行定时任务相关的类,初始化成员变量mRecurrentTimer为一个RecurrentTimer对象,这个对象在初始化的时候会创建一个线程,这个线程中会定时执行传入的函数。具体的分析见3.7小结。
mVehicleClient(client)
然后初始化mVehicleClient为main函数中创建的EmulatedVehicleConnector对象。
mEmulatedUserHal(emulatedUserHal)
这个使用默认参数,空指针。
void EmulatedVehicleHal::initStaticConfig() {for (auto&& it = std::begin(kVehicleProperties); it != std::end(kVehicleProperties); ++it) {const auto& cfg = it->config;VehiclePropertyStore::TokenFunction tokenFunction = nullptr;switch (cfg.prop) {case OBD2_FREEZE_FRAME: {tokenFunction = [](const VehiclePropValue& propValue) {return propValue.timestamp;};break;}default:break;}mPropStore->registerProperty(cfg, tokenFunction);}
}
然后初始化属性配置,kVehicleProperties是一个定义了车辆属性配置的结构体数组,以下是其中的一个元素,表示车辆的空调温度设置的属性配置:
{.config = {.prop = toInt(VehicleProperty::HVAC_TEMPERATURE_SET),.access = VehiclePropertyAccess::READ_WRITE,.changeMode = VehiclePropertyChangeMode::ON_CHANGE,.areaConfigs = {VehicleAreaConfig{.areaId = HVAC_LEFT,.minFloatValue = 16,.maxFloatValue = 32,},VehicleAreaConfig{.areaId = HVAC_RIGHT,.minFloatValue = 16,.maxFloatValue = 32,}}},.initialAreaValues = {{HVAC_LEFT, {.floatValues = {16}}},{HVAC_RIGHT, {.floatValues = {20}}}}},
OBD2_FREEZE_FRAME表示冻结帧,跟诊断相关,暂时不清楚,暂不看这块的处理。然后会将所有的属性配置注册到VehiclePropertyStore中。
这些属性配置就是vhal中支持的属性,如果没有在这个结构体数组中定义,则该功能不支持,供应商提供的新的需要在这个结构体中新增。
后面的for循环和initStaticConfig中的逻辑一样,跳过,这块应该没什么意义的。
mVehicleClient->registerPropertyValueCallback(std::bind(&EmulatedVehicleHal::onPropertyValue,this, std::placeholders::_1,std::placeholders::_2));
最后注册callback函数到EmulatedVehicleConnector对象中,回调函数是EmulatedVehicleHal::onPropertyValue。
至此,就初始化完成了,主要做的就是创建EmulatedVehicleHal对象,并且注册一些回调函数,然后比较重要的一点是加载了所有的属性配置到VehiclePropertyStore中。
3.4 VehicleEmulator初始化
VehicleEmulator::VehicleEmulator(EmulatedVehicleHalIface* hal) : mHal{hal} {mHal->registerEmulator(this);ALOGI("Starting SocketComm");mSocketComm = std::make_unique<SocketComm>(this);mSocketComm->start();if (android::base::GetBoolProperty("ro.kernel.qemu", false)) {ALOGI("Starting PipeComm");mPipeComm = std::make_unique<PipeComm>(this);mPipeComm->start();}
}
持有EmulatedVehicleHal对象,创建SocketComm或者PipeComm,并启动,这是模拟的与VHAL连接的客户端的通信类。
3.5 VehicleHalManager初始化
VehicleHalManager(VehicleHal* vehicleHal): mHal(vehicleHal),mSubscriptionManager(std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onAllClientsUnsubscribed,this, std::placeholders::_1)) {init();}
先将EmulatedVehicleHal保存至mHal变量中,然后会初始化一个订阅相关的类SubscriptionManager,最后调用init函数。
SubscriptionManager初始化见3.6小节,接下来分析init函数
hidl_vec<VehiclePropValue> mHidlVecOfVehiclePropValuePool;
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void VehicleHalManager::init() {ALOGI("VehicleHalManager::init");//初始化mHidlVecOfVehiclePropValuePool为20,用于存储VehiclePropValuemHidlVecOfVehiclePropValuePool.resize(kMaxHidlVecOfVehiclPropValuePoolSize);//批处理相关的初始化mBatchingConsumer.run(&mEventQueue,kHalEventBatchingTimeWindow,std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onBatchHalEvent,this, _1));//事件处理相关初始化mHal->init(&mValueObjectPool,std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onHalEvent, this, _1),std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onHalPropertySetError, this,_1, _2, _3));// Initialize index with vehicle configurations received from VehicleHal.auto supportedPropConfigs = mHal->listProperties();mConfigIndex.reset(new VehiclePropConfigIndex(supportedPropConfigs));std::vector<int32_t> supportedProperties(supportedPropConfigs.size());//for (const auto& config : supportedPropConfigs) {supportedProperties.push_back(config.prop);}
}
VehiclePropConfigIndex初始化见3.7小节
3.5.1 批处理初始化
ConcurrentQueue<VehiclePropValuePtr> mEventQueue;
constexpr std::chrono::milliseconds kHalEventBatchingTimeWindow(10);
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
mBatchingConsumer.run(&mEventQueue,kHalEventBatchingTimeWindow,std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onBatchHalEvent,this, _1));
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void run(ConcurrentQueue<T>* queue,std::chrono::nanoseconds batchInterval,const OnBatchReceivedFunc& func) {mQueue = queue;mBatchInterval = batchInterval;mWorkerThread = std::thread(&BatchingConsumer<T>::runInternal, this, func);
}
先看这部分代码,mQueue=mEventQueue,用于添加事件,是VehiclePropValuePtr类型事件。mBatchInterval=kHalEventBatchingTimeWindow=10,然后创建了一个线程,执行的函数是BatchingConsumer::runInternal,传入的参数是VehicleHalManager::onBatchHalEvent。
void runInternal(const OnBatchReceivedFunc& onBatchReceived) {if (mState.exchange(State::RUNNING) == State::INIT) {while (State::RUNNING == mState) {mQueue->waitForItems();if (State::STOP_REQUESTED == mState) break;std::this_thread::sleep_for(mBatchInterval);if (State::STOP_REQUESTED == mState) break;std::vector<T> items = mQueue->flush();if (items.size() > 0) {onBatchReceived(items);}}}mState = State::STOPPED;}
批处理这个类的主要作用就是循环执行mQueue中的事件,如果有事件到来就执行,没有就休眠。mQueue事件什么时候添加后续分析。
3.5.2 初始化现有属性值
VehiclePropValuePool mValueObjectPool;VehiclePropValuePool(size_t maxRecyclableVectorSize = 4) :mMaxRecyclableVectorSize(maxRecyclableVectorSize) {};
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
mHal->init(&mValueObjectPool,std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onHalEvent, this, _1),std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onHalPropertySetError, this,_1, _2, _3));
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void init(VehiclePropValuePool* valueObjectPool,const HalEventFunction& onHalEvent,const HalErrorFunction& onHalError) {mValuePool = valueObjectPool;mOnHalEvent = onHalEvent;mOnHalPropertySetError = onHalError;onCreate();
}
mValuePool存储的是VehiclePropValuePool对象,是用于VehiclePropValue解析的池子,方便循环利用。mOnHalEvent是onHalEvent函数,mOnHalPropertySetError是onHalPropertySetError函数,然后调用onCreate函数。onCreate是一个虚函数,由实际的VehicleHal类实现,即EmulatedVehicleHal中的实现:
// Parse supported properties list and generate vector of property values to hold current values.
void EmulatedVehicleHal::onCreate() {static constexpr bool shouldUpdateStatus = true;//遍历所有的属性配置for (auto& it : kVehicleProperties) {VehiclePropConfig cfg = it.config;int32_t numAreas = cfg.areaConfigs.size();if (isDiagnosticProperty(cfg)) {// do not write an initial empty value for the diagnostic properties// as we will initialize those separately.continue;}// A global property will have only a single areaif (isGlobalProp(cfg.prop)) {numAreas = 1;}//对于分区属性的处理for (int i = 0; i < numAreas; i++) {int32_t curArea;if (isGlobalProp(cfg.prop)) {curArea = 0;} else {curArea = cfg.areaConfigs[i].areaId;}// Create a separate instance for each individual zone//初始化VehiclePropValueVehiclePropValue prop = {.areaId = curArea,.prop = cfg.prop,};//设置初始属性值if (it.initialAreaValues.size() > 0) {auto valueForAreaIt = it.initialAreaValues.find(curArea);if (valueForAreaIt != it.initialAreaValues.end()) {prop.value = valueForAreaIt->second;} else {ALOGW("%s failed to get default value for prop 0x%x area 0x%x",__func__, cfg.prop, curArea);}} else {prop.value = it.initialValue;}//属性值写入VehiclePropertyStoremPropStore->writeValue(prop, shouldUpdateStatus);}}initObd2LiveFrame(*mPropStore->getConfigOrDie(OBD2_LIVE_FRAME));initObd2FreezeFrame(*mPropStore->getConfigOrDie(OBD2_FREEZE_FRAME));
}
这块主要就是将根据默认配置里面的属性配置,将初始化的属性值写入到VehiclePropertyStore中进行缓存。
3.6 SubscriptionManager初始化
SubscriptionManager是在VehicleHalManager中创建并持有的。
mSubscriptionManager(std::bind(&VehicleHalManager::onAllClientsUnsubscribed,this, std::placeholders::_1))
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SubscriptionManager(const OnPropertyUnsubscribed& onPropertyUnsubscribed): mOnPropertyUnsubscribed(onPropertyUnsubscribed),mCallbackDeathRecipient(new DeathRecipient(std::bind(&SubscriptionManager::onCallbackDead, this, std::placeholders::_1)))
{}
传入的参数是一个函数,保存在mOnPropertyUnsubscribed中,并初始化mCallbackDeathRecipient为一个DeathRecipient对象,这个对象构造时的参数为onCallbackDead函数。
DeathRecipient(const OnClientDead& onClientDead): mOnClientDead(onClientDead) {}
onCallbackDead保存在mOnClientDead中。
VehicleHalManager中创建SubscriptionManager对象,并对其进行管理。
3.7 RecurrentTimer初始化
RecurrentTimer由EmulatedVehicleHal的构造函数初始化,并适时回调EmulatedVehicleHal中的回调函数。
RecurrentTimer mRecurrentTimer;mRecurrentTimer(std::bind(&EmulatedVehicleHal::onContinuousPropertyTimer, this,std::placeholders::_1)),RecurrentTimer(const Action& action) : mAction(action) {mTimerThread = std::thread(&RecurrentTimer::loop, this, action);}using Action = std::function<void(const std::vector<int32_t>& cookies)>;
接着3.3节中分析,RecurrentTimer对象创建后,赋值给mRecurrentTimer。RecurrentTimer创建时,传入的参数是一个function类型数据,包含的是一个函数。EmulatedVehicleHal::onContinuousPropertyTimer,bind函数的第二个参数传入this,因为是一个成员函数,然后是一个参数占位符,因为该函数需要传入一个参数。
然后RecurrentTimer的构造函数中,创建了一个线程,执行的函数是RecurrentTimer::loop,传入的参数是Action对象,即onContinuousPropertyTimer
void loop(const Action& action) {static constexpr auto kInvalidTime = TimePoint(Nanos::max());std::vector<int32_t> cookies;while (!mStopRequested) {auto now = Clock::now();auto nextEventTime = kInvalidTime;cookies.clear();{std::unique_lock<std::mutex> g(mLock);for (auto&& it : mCookieToEventsMap) {//获取定时上报事件RecurrentEvent& event = it.second;if (event.absoluteTime <= now) {event.updateNextEventTime(now);cookies.push_back(event.cookie);}if (nextEventTime > event.absoluteTime) {nextEventTime = event.absoluteTime;}}}if (cookies.size() != 0) {action(cookies);}std::unique_lock<std::mutex> g(mLock);mCond.wait_until(g, nextEventTime); // nextEventTime can be nanoseconds::max()}
}
mStopRequested没有其他地方赋值,有默认值为false,所以会进入while循环。
这里主要是定时事件上报的处理逻辑,如果到时间了,就会加入到cookies这个变量中,并调用action这个回到函数,即onContinuousPropertyTimer这个回调函数去处理所有到时间的定时事件。
4 初始化流程图
plantuml代码:
@startumlparticipant init
box
participant VehicleService
participant VehicleHalManager
participant VehicleEmulator
participant EmulatedVehicleHal
participant EmulatedVehicleConnector
participant VehiclePropertyStore
participant SocketComm
participant SubscriptionManager
participant DeathRecipient
participant BatchingConsumer
endboxinit -> VehicleService: 拉起服务
VehicleService -> VehiclePropertyStore: new VehiclePropertyStore()
VehicleService -> EmulatedVehicleConnector: new EmulatedVehicleConnector()
VehicleService -> EmulatedVehicleHal: new EmulatedVehicleHal(VehiclePropertyStore* propStore, \n\tVehicleHalClient* client, EmulatedUserHal* emulatedUserHal = nullptr);
EmulatedVehicleHal -> EmulatedVehicleHal: initStaticConfig()
EmulatedVehicleHal -> VehiclePropertyStore: registerProperty(const VehiclePropConfig& config, \n\tVehiclePropertyStore::TokenFunction tokenFunc)
EmulatedVehicleHal -> EmulatedVehicleConnector: registerPropertyValueCallback(PropertyCallBackType&& callback)
VehicleService -> VehicleEmulator: new VehicleEmulator(EmulatedVehicleHalIface* hal)
VehicleEmulator -> EmulatedVehicleHal: registerEmulator(this)
VehicleEmulator -> SocketComm: start()
VehicleService -> VehicleHalManager: new VehicleHalManager(VehicleHal* vehicleHal)
VehicleHalManager -> SubscriptionManager: new (const OnPropertyUnsubscribed& onPropertyUnsubscribed\n\t: mOnPropertyUnsubscribed(onPropertyUnsubscribed),\n\tmCallbackDeathRecipient(new DeathRecipient(\n\tstd::bind(&SubscriptionManager::onCallbackDead, this, std::placeholders::_1)))
SubscriptionManager -> DeathRecipient: new DeathRecipient(const OnClientDead& onClientDead)
VehicleHalManager -> VehicleHalManager: init()
VehicleHalManager -> BatchingConsumer: run()
loopBatchingConsumer -> BatchingConsumer: runInternal(const OnBatchReceivedFunc& onBatchReceived)
end loop
VehicleHalManager -> EmulatedVehicleHal: init( \n\tVehiclePropValuePool* valueObjectPool, \n\tconst HalEventFunction& onHalEvent, \n\tconst HalErrorFunction& onHalError)
EmulatedVehicleHal -> EmulatedVehicleHal: onCreate()
EmulatedVehicleHal -> VehiclePropertyStore: writeValue(const VehiclePropValue& propValue, bool updateStatus)
VehicleService -> EmulatedVehicleConnector: setValuePool(VehiclePropValuePool* valuePool)
VehicleService -> VehicleHalManager: registerAsService()
@enduml流程图

相关文章:

Android车载——VehicleHal初始化(Android 11)
1 概述 VehicleHal是AOSP中车辆服务相关的hal层服务。它主要定义了与汽车硬件交互的标准化接口和属性管理,是一个独立的进程。 2 进程启动 VehicleHal相关代码在源码树中的hardware/interfaces/automotive目录下 首先看下Android.bp文件: cc_binary …...

CTFshow 命令执行 web37-web40
目录 web37 方法一:php://input 方法二:data协议 web38 web39 web40 方法一:构造文件读取 方法二:构造数组rce web37 error_reporting(0); if(isset($_GET[c])){$c $_GET[c];if(!preg_match("/flag/i", $c)){incl…...
码 进制))
数据结构与算法篇((原/反/补)码 进制)
目录 讲解一:原/反/补)码 一、原码 二、反码 三、补码 四、有符号位整型 五、无符号位整型 六、Java中的整型 七、整数在底层存储形式 讲解二:进制 一、简介 二、常用的进制 十进制 二进制 八进制 十六进制 知识补充 三、进制转换 1. 二…...

Python画笔案例-077 绘制 颜色饱和度测试
1、绘制 颜色饱和度测试 通过 python 的turtle 库绘制 颜色饱和度测试,如下图: 2、实现代码 绘制 颜色饱和度测试,以下为实现代码: """饱和度渐变示例,本程序需要coloradd模块支持,请在cmd窗口,即命令提示符下输入pip install coloradd进行安装。本程序演…...

简历投递经验01
嵌入式简历制作指南与秋招求职建议 技术要求概览 在嵌入式领域求职时,技术能力是HR和面试官最关注的点之一。以下是一些关键技术点,以及它们在简历中的体现方式。 1. 编程语言与开发环境 掌握C/C语言。熟悉至少一种单片机或微处理器的开发环境。 2.…...

数据和算力共享
数据和算力共享 针对数字化应用实践中需要在不同的物理域和信息域中进行数据的访问交换以及共享计算等需求,本文分析了在数据平台、数据集成系统以及信息交换系统中存在的问题。 在基于联邦学习的基础上,提出一种跨域数据计算共享系统,能够同时共享数据和计算资源,并支持在线…...

SpringBoot 集成 Ehcache 实现本地缓存
目录 1、Ehcache 简介2、Ehcache 集群方式3、工作原理3.1、缓存写入3.2、缓存查找3.3、缓存过期和驱逐3.4、缓存持久化 4、入门案例 —— Ehcache 2.x 版本4.1、单独使用 Ehcache4.1.1、引入依赖4.1.2、配置 Ehcache4.1.2.1、XML 配置方式4.1.2.1.1、新建 ehcache.xml4.1.2.1.2…...

CSP-J 复赛真题 P9749 [CSP-J 2023] 公路
文章目录 前言[CSP-J 2023] 公路题目描述输入格式输出格式样例 #1样例输入 #1样例输出 #1 提示 示例代码代码解析思考过程总结 总结 前言 在CSP-J 2023的复赛中,出现了一道引人注目的题目——“公路”。这道题目不仅考察了选手们对算法的理解和运用能力,…...

MeterSphere压测配置说明
在MeterSphere中,执行性能测试时的配置参数对测试结果有重要影响。以下是对MeterSphere压测配置中几个关键参数的解释: 执行方式:决定了测试的执行模式,例如可以按照持续时间或迭代次数来执行测试。 按持续时间:在这种…...

数据库软题6.1-关系模式-关系模式的各种键
关系模式的各种键 题1-由关系模式求候选键 1. 候选键唯一不冗余 对选项进行闭包运算,如果得到全部属性U,则为候选码 A:AC-ABC-ABCD B:AB-ABC-ABCD C:AE-ABE-ABCE -ABCDE-ABCDEH D:DE2. R的候选码可以从A1,A2,A3,A1A2,A1A3,A2A3,A1A2A3中选择ÿ…...

ulimit:资源限制
一、命令简介 ulimit 是一个用于资源管理的工具,对于确保系统资源的合理分配和安全使用至关重要。 使用场景: 系统管理:限制用户进程使用的资源,防止资源滥用,保证系统稳定。调试:调整核心文件大…...

解决Python使用Selenium 时遇到网页 <body> 划不动的问题
如果在使用 Selenium 时遇到网页的 <body> 划不动的问题,这通常是因为页面的滚动机制(例如,可能使用了一个具有固定高度的容器或自定义的滚动条)导致无法通过简单的 JavaScript 实现滚动。可以通过以下方法来解决该问题。 …...

pytorch版本和cuda版本不匹配问题
文章目录 🌕问题:Python11.8安装pytorch11.3失败🌕CUDA版本和pytorch版本的关系🌕安装Pytorch2.0.0🌙pip方法🌙cuda方法 🌕问题:Python11.8安装pytorch11.3失败 🌕CUDA版…...

Vue/组件的生命周期
这篇文章借鉴了coderwhy大佬的Vue生命周期 在Vue实例化或者创建组件的过程中 内部涉及到一系列复杂的阶段 每一个阶段的前后时机都可能对应一个钩子函数 以下是我根据coderwhy大佬文章对于每一个阶段的一些看法 1.过程一 首先实例化Vue或者组件 在实例化之前 会对应一个钩子函…...

【Nacos架构 原理】内核设计之Nacos寻址机制
文章目录 前提设计内部实现单机寻址文件寻址地址服务器寻址 前提 对于集群模式,集群内的每个Nacos成员都需要相互通信。因此这就带来一个问题,该以何种方式去管理集群内部的Nacos成员节点信息,即Nacos内部的寻址机制。 设计 要能够感知到节…...
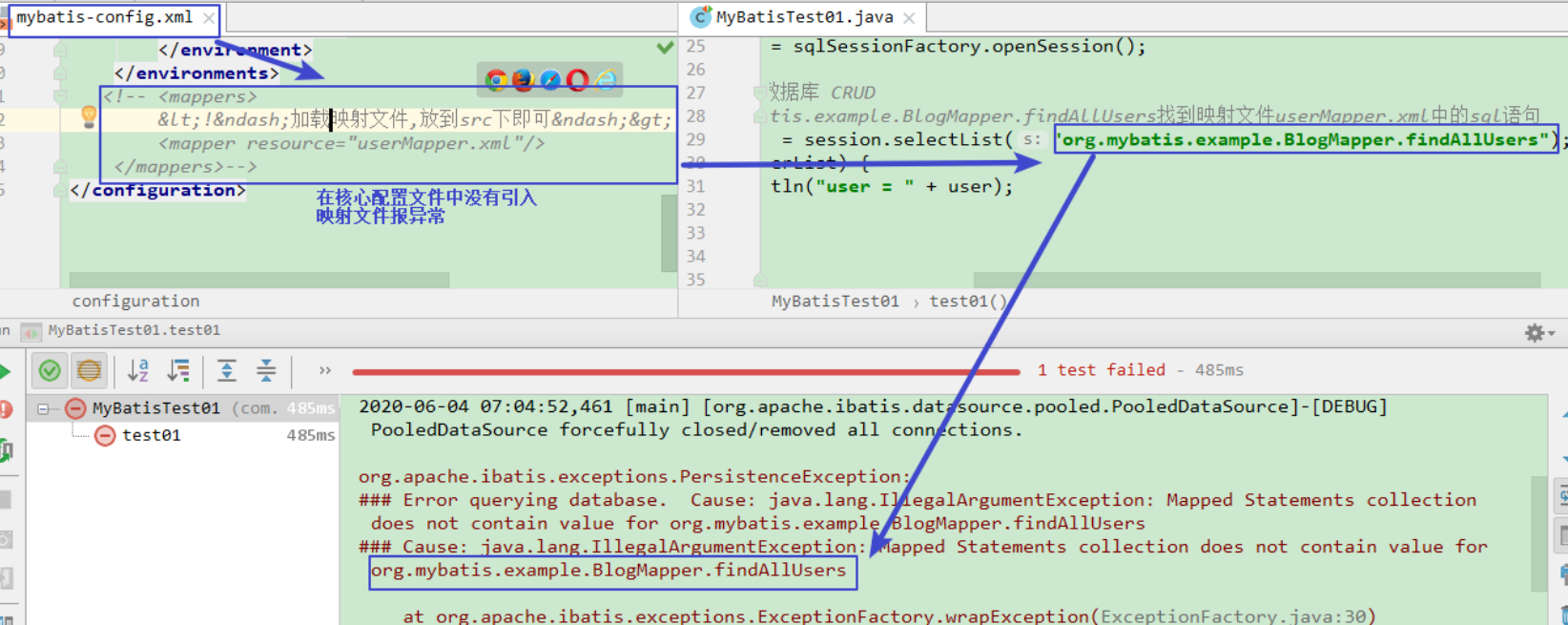
入门案例:mybatis流程,核心,常见错误
入门案例:mybatis执行流程分析 说明: 1.第一步:是从核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml中构建SqlSessionFactory对象,由于核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml中关联了映射文件UserMapper.xml,所以在SqlSessionFactory中也存在映射文件的…...

C++ | Leetcode C++题解之第456题132模式
题目: 题解: class Solution { public:bool find132pattern(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();vector<int> candidate_i {nums[0]};vector<int> candidate_j {nums[0]};for (int k 1; k < n; k) {auto it_i upper_…...

自然语言处理问答系统
✅作者简介:2022年博客新星 第八。热爱国学的Java后端开发者,修心和技术同步精进。 🍎个人主页:Java Fans的博客 🍊个人信条:不迁怒,不贰过。小知识,大智慧。 💞当前专栏…...

Python的几个高级特性
引言 Python是一种功能强大的编程语言,它简洁的语法和强大的库支持使其成为数据科学和机器学习领域的热门选择。在Python的高级特性中,生成器、迭代器、闭包、装饰器和内置高阶函数是实现高效、优雅代码的关键。本文将逐一介绍这些特性,并提…...

【颜色平衡树 / E】
题目 思路 DFS暴力 60分 代码 #include <bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; const int N 5010; const int M 5010; int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; int c[N], f; int ans; void add(int a, int b) // 添加一条边a->b {e[idx] b, ne[idx] h[a], h[a] idx ; } …...

web vue 项目 Docker化部署
Web 项目 Docker 化部署详细教程 目录 Web 项目 Docker 化部署概述Dockerfile 详解 构建阶段生产阶段 构建和运行 Docker 镜像 1. Web 项目 Docker 化部署概述 Docker 化部署的主要步骤分为以下几个阶段: 构建阶段(Build Stage):…...
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频)
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(62)使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频UDPTCPRTSPlibavGStreamerRTPlibcamerasrc GStreamer 元素 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频 本节介绍来自 rpica…...
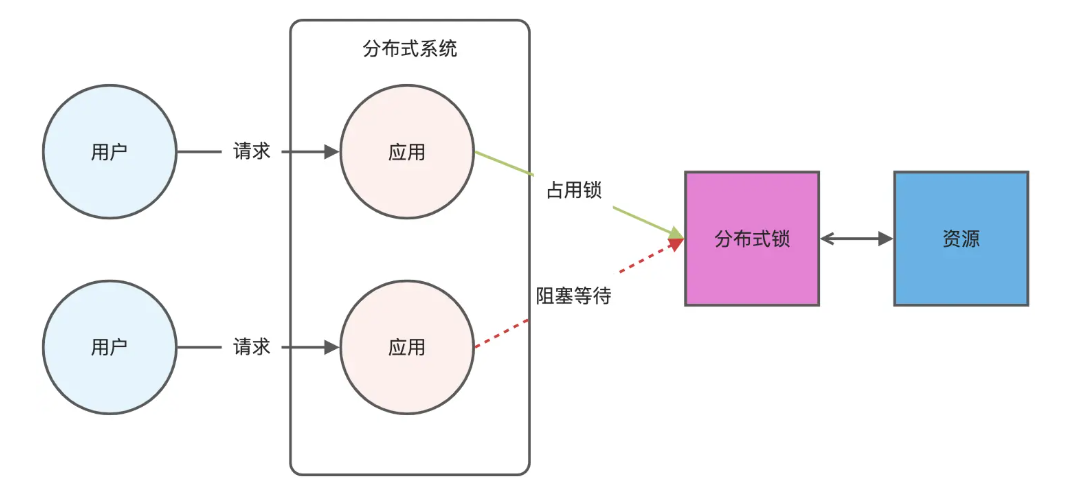
Redis相关知识总结(缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿,Redis实现分布式锁,如何保持数据库和缓存一致)
文章目录 1.什么是Redis?2.为什么要使用redis作为mysql的缓存?3.什么是缓存雪崩、缓存穿透、缓存击穿?3.1缓存雪崩3.1.1 大量缓存同时过期3.1.2 Redis宕机 3.2 缓存击穿3.3 缓存穿透3.4 总结 4. 数据库和缓存如何保持一致性5. Redis实现分布式…...
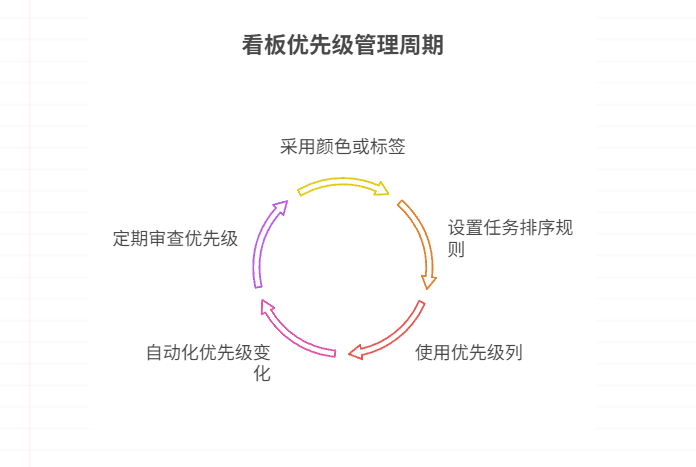
如何在看板中体现优先级变化
在看板中有效体现优先级变化的关键措施包括:采用颜色或标签标识优先级、设置任务排序规则、使用独立的优先级列或泳道、结合自动化规则同步优先级变化、建立定期的优先级审查流程。其中,设置任务排序规则尤其重要,因为它让看板视觉上直观地体…...

AI编程--插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他
AI编程插件对比分析:CodeRider、GitHub Copilot及其他 随着人工智能技术的快速发展,AI编程插件已成为提升开发者生产力的重要工具。CodeRider和GitHub Copilot作为市场上的领先者,分别以其独特的特性和生态系统吸引了大量开发者。本文将从功…...

JDK 17 新特性
#JDK 17 新特性 /**************** 文本块 *****************/ python/scala中早就支持,不稀奇 String json “”" { “name”: “Java”, “version”: 17 } “”"; /**************** Switch 语句 -> 表达式 *****************/ 挺好的ÿ…...

数据库分批入库
今天在工作中,遇到一个问题,就是分批查询的时候,由于批次过大导致出现了一些问题,一下是问题描述和解决方案: 示例: // 假设已有数据列表 dataList 和 PreparedStatement pstmt int batchSize 1000; // …...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...

【JavaSE】绘图与事件入门学习笔记
-Java绘图坐标体系 坐标体系-介绍 坐标原点位于左上角,以像素为单位。 在Java坐标系中,第一个是x坐标,表示当前位置为水平方向,距离坐标原点x个像素;第二个是y坐标,表示当前位置为垂直方向,距离坐标原点y个像素。 坐标体系-像素 …...
可以参考以下方法:)
根据万维钢·精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法:
根据万维钢精英日课6的内容,使用AI(2025)可以参考以下方法: 四个洞见 模型已经比人聪明:以ChatGPT o3为代表的AI非常强大,能运用高级理论解释道理、引用最新学术论文,生成对顶尖科学家都有用的…...
